While carrying a long-awaited baby, unfortunately, not all expectant mothers can calmly enjoy their situation. In some conditions, a woman has to frequently visit her gynecologist, undergo various examinations, and constantly undergo tests. For example, if CPRF is diagnosed during pregnancy, then constant medical supervision is necessary, since such a pathology is fraught with oxygen starvation for the baby.
But this pathology does not occur in the same way in all pregnant women. Manifestations and consequences depend on the duration and severity of the condition. Fetoplacental insufficiency is a whole complex of disorders of the placenta and fetus as a result of complications during pregnancy or gynecological pathologies.
The concept of the OSA
The term OAGA (complicated obstetric and gynecological history) refers to the totality of information about a woman’s gynecological health - unfavorable factors that can negatively affect the current pregnancy and childbirth.
In other words, OGA during pregnancy can be diagnosed to an expectant mother who has problems associated with childbearing function.
An obstetric and gynecological history is carried out individually for each woman during a real pregnancy.
What is it in gynecology of the OAG
The term OAGA (complicated obstetric and gynecological history) refers to the totality of information about a woman’s gynecological health - unfavorable factors that can negatively affect the current pregnancy and childbirth.
In other words, OGA during pregnancy can be diagnosed to an expectant mother who has problems associated with childbearing function.
An obstetric and gynecological history is carried out individually for each woman during a real pregnancy.
Oga diagnosis in gynecology
Responsibility for the life of an unborn child falls on a woman’s shoulders long before she becomes pregnant. Nine months of gestation test the strength of not only her body, but also her character. Often, as in the famous prayer, she has to come to terms with the fact that it is impossible to change, and show her will in those matters that depend only on her.
Familiarity with perinatal terms is the first step towards effective interaction with doctors.
What are OAA and OGA?
The abbreviations OAA, OGA, and OAGA may appear in the patient's medical record after the first visit to the doctor or after diagnostic procedures. They reflect the features of the anamnesis - the background of pregnancy.
Letter indices in a compressed form reflect the risks that may arise during pregnancy; the obstetrician addresses them to his colleagues and doctors so that they can navigate during diagnostic and therapeutic actions.
The medical history can be characterized by the following terms: Aggravated obstetric history (OA), Aggravated gynecological history (PAA), Aggravated obstetric-gynecological history (OAGA), or the same abbreviations with the addition of the letter K at the beginning, which means “extremely” and enhances the meaning of the term . Linguistic decoding gives only a hint of the meaning; it is important to understand why such a classification was introduced and what functional load the anamnesis itself bears in the complex of medical measures that accompany gestation and the stage of labor.
Medical care during pregnancy consists not only of eliminating emerging problems, but also of professional prognosis, which cannot be carried out without a clear and detailed picture of the patient’s past. Routine examinations ascertain the current state of health of the fetus and mother. Without information about potential risks, they will have to be carried out blindly, which can lead to omissions and errors.
What do these terms include?
A burdened obstetric history (OAH) is based on the presence in the patient's history of:
- spontaneous miscarriage;
- artificial termination of pregnancy;
- premature birth;
- abnormalities of the placenta;
- fetal death, stillbirth;
- childbirth with complications: bleeding, early rupture of amniotic fluid, fetal hypoxia, weakness of labor or rapid labor, rupture, etc.;
- measures to maintain pregnancy;
- surgical intervention during pregnancy and childbirth;
- congenital defects in children.
A burdened gynecological history (GHA) is based on the presence of:
- menstrual dysfunction;
- infectious, inflammatory and tumor lesions of the vagina, uterus, cervix, tubes and ovaries;
- pathologies in the structure of the reproductive organs.
If problems are identified in both groups, the condition of the pregnant woman can be characterized by a mixed index - OAGA. Another category is Compounded Somatic History (OSA). This is a general characteristic to designate chronic diseases and pathologies of the cardiovascular, digestive, endocrine and nervous systems of the body.
What tests does a woman with this diagnosis need to undergo?
A correctly formulated anamnesis is a guide to action, research, preventive and therapeutic, which minimize pregnancy complications.
A burdened medical history requires increased attention to mandatory routine examinations, the appointment of targeted diagnostic procedures and preventive measures, as well as therapy, including medications, which are prescribed after assessing the risks to the fetus and maternal health.
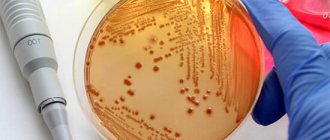
Targeted laboratory and instrumental tests are carried out to identify infections and inflammatory processes, taking into account the fact that they can occur without pronounced symptoms. It is possible to prescribe detailed hormonal tests and subsequent correction of hormonal levels.
In the presence of chronic pathologies, such as thyroid diseases, diabetes mellitus, heart defects, in collaboration with highly specialized doctors, a method of supportive and therapeutic measures is determined that will contribute to the normal course of pregnancy.
What measures need to be taken?
The presence of problems in the past creates the need to plan pregnancy - to go through the stage of diagnosis and treatment before conception occurs. Women who struggle with infertility go through this stage automatically, and in many cases find themselves in a better position than those who risked becoming pregnant without first visiting a doctor's office.
You can understand why women would want to erase the tragic complications of past pregnancies and find solace in the next attempt, but fertility is not limited to conception.
The influence of OAA and AGA factors on subsequent pregnancies should not be underestimated, nor should they be given too much importance.
Source: https://g-women.ru/yaichniki/oaga-v-ginekologii-chto-eto.html
Components of the OAS
A pregnant woman may have a burdened obstetric-gynecological history if the following factors have been present in the past:
- Abortion. Artificial termination of pregnancy negatively affects women's health - a hormonal imbalance occurs, leading the body to stress, and the risks of inflammatory and infectious diseases of the reproductive system increase.
- Miscarriage. This includes miscarriages (before 28 weeks of gestation) and preterm birth (28 to 37 weeks). If spontaneous abortion occurs 2 or more times in a row, then the woman is diagnosed with recurrent miscarriage, in which each subsequent pregnancy is in danger of being terminated.
- Early placental abruption. Premature placental abruption can occur at any stage of pregnancy and can be partial or complete. In any case, this is a serious pathology that requires treatment and careful monitoring of the pregnancy.
- Complications during childbirth. Trauma to the birth canal, ruptures, abnormal labor, large blood loss - all this and much more can lead to problems in subsequent births.
- Pathologies in previously born children. In this case, doctors carefully monitor the pregnant woman and find out the causes of the pathologies of the previously born child in order to exclude the same problem.
Thus, OAGA accompanies pregnancy when one or more points are identified. In this case, indications for establishing a complicated medical history can also be the stillbirth of a baby or his death in the first 4 weeks, Rh conflict of parents, pathologies of the woman’s genital organs, hormonal imbalance and menstrual irregularities, etc.
Placental abruption is one of the reasons for the diagnosis of OGA in the future
Like most pregnant women, my medical record for pregnancy management included the inscription “OAGA”. The diagnosis was made due to previous two failed pregnancies - spontaneous miscarriages in the early stages. In this regard, from the 4th week of gestation, the doctor prescribed Duphaston as a maintenance hormonal drug and additional ultrasound examinations in the first and second trimesters. Otherwise, the management of my pregnancy differed little from other uncomplicated ones - a scheduled visit to the gynecologist, regular urine and blood tests, ultrasound in each trimester. The pregnancy ended successfully, delivery occurred on time.
Oga diagnosis in gynecology
Responsibility for the life of an unborn child falls on a woman’s shoulders long before she becomes pregnant. Nine months of gestation test the strength of not only her body, but also her character.
Often, as in the famous prayer, she has to come to terms with the fact that it is impossible to change, and show her will in those matters that depend only on her.
Familiarity with perinatal terms is the first step towards effective interaction with doctors.
What are OAA and OGA?
The abbreviations OAA, OGA, and OAGA may appear in the patient's medical record after the first visit to the doctor or after diagnostic procedures. They reflect the features of the anamnesis - the background of pregnancy.
Letter indices in a compressed form reflect the risks that may arise during pregnancy; the obstetrician addresses them to his colleagues and doctors so that they can navigate during diagnostic and therapeutic actions.
The medical history can be characterized by the following terms: Aggravated obstetric history (OA), Aggravated gynecological history (PAA), Aggravated obstetric-gynecological history (OAGA), or the same abbreviations with the addition of the letter K at the beginning, which means “extremely” and enhances the meaning of the term . Linguistic decoding gives only a hint of the meaning; it is important to understand why such a classification was introduced and what functional load the anamnesis itself bears in the complex of medical measures that accompany gestation and the stage of labor.
Medical care during pregnancy consists not only of eliminating emerging problems, but also of professional prognosis, which cannot be carried out without a clear and detailed picture of the patient’s past. Routine examinations ascertain the current state of health of the fetus and mother. Without information about potential risks, they will have to be carried out blindly, which can lead to omissions and errors.
What do these terms include?
A burdened obstetric history (OAH) is based on the presence in the patient's history of:
- spontaneous miscarriage;
- artificial termination of pregnancy;
- premature birth;
- abnormalities of the placenta;
- fetal death, stillbirth;
- childbirth with complications: bleeding, early rupture of amniotic fluid, fetal hypoxia, weakness of labor or rapid labor, rupture, etc.;
- measures to maintain pregnancy;
- surgical intervention during pregnancy and childbirth;
- congenital defects in children.
A burdened gynecological history (GHA) is based on the presence of:
- menstrual dysfunction;
- infectious, inflammatory and tumor lesions of the vagina, uterus, cervix, tubes and ovaries;
- pathologies in the structure of the reproductive organs.
If problems are identified in both groups, the condition of the pregnant woman can be characterized by a mixed index - OAGA. Another category is Compounded Somatic History (OSA). This is a general characteristic to designate chronic diseases and pathologies of the cardiovascular, digestive, endocrine and nervous systems of the body.
What tests does a woman with this diagnosis need to undergo?
A correctly formulated anamnesis is a guide to action, research, preventive and therapeutic, which minimize pregnancy complications.
A burdened medical history requires increased attention to mandatory routine examinations, the appointment of targeted diagnostic procedures and preventive measures, as well as therapy, including medications, which are prescribed after assessing the risks to the fetus and maternal health.
Targeted laboratory and instrumental tests are carried out to identify infections and inflammatory processes, taking into account the fact that they can occur without pronounced symptoms. It is possible to prescribe detailed hormonal tests and subsequent correction of hormonal levels.
In the presence of chronic pathologies, such as thyroid diseases, diabetes mellitus, heart defects, in collaboration with highly specialized doctors, a method of supportive and therapeutic measures is determined that will contribute to the normal course of pregnancy.
What measures need to be taken?
The presence of problems in the past creates the need to plan pregnancy - to go through the stage of diagnosis and treatment before conception occurs. Women who struggle with infertility go through this stage automatically, and in many cases find themselves in a better position than those who risked becoming pregnant without first visiting a doctor's office.
You can understand why women would want to erase the tragic complications of past pregnancies and find solace in the next attempt, but fertility is not limited to conception.
The influence of OAA and AGA factors on subsequent pregnancies should not be underestimated, nor should they be given too much importance.
Contacting doctors in advance can, figuratively speaking, clear the medical history and create the most favorable starting conditions for the future baby.
The risk factors listed in the descriptions of complicated pregnancies suggest early registration.
Sometimes superstitious horror and indifference leads to irresponsibility: when answering the obstetrician’s questions, women hide negative information or present it with distortions. This attitude is fraught with medical errors.
If for some reason the patient provided inaccurate information, she always has the opportunity to supplement or reasonably change the anamnesis data.
Regular medical examination or observation by the same trusted gynecologist who keeps detailed documentation is not always possible.
Universal advice to all women who want to experience the happiness of motherhood: create a home archive, collecting all documents about the state of your health, starting with data on heredity and the results of examinations during puberty.
This will help restore the chronology and provide specialized information to the doctor on whom the child’s health depends.
If a diagnosis of a complicated pregnancy has already been made, and this happens in 80% of pregnancies in the Russian Federation, then you need to actively cooperate with doctors, following their instructions, and taking advantage of the freedom to receive an alternative opinion from specialists on any of the problems that arise. A term with a scary name is a life-saving signal that will help you carry and give birth to a healthy baby.
Female pregnancy is a natural physiological process, during which there should be no complications or obstacles to the birth of healthy offspring. However, in practice, the period of bearing a baby is often accompanied by pathologies that can be prevented or eliminated by having a complete medical history of the expectant mother.
The concept of the OSA
The term OAGA (complicated obstetric and gynecological history) refers to the totality of information about a woman’s gynecological health - unfavorable factors that can negatively affect the current pregnancy and childbirth.
In other words, OGA during pregnancy can be diagnosed to an expectant mother who has problems associated with childbearing function.
An obstetric and gynecological history is carried out individually for each woman during a real pregnancy.
Components of the OAS
A pregnant woman may have a burdened obstetric-gynecological history if the following factors have been present in the past:
- Abortion. Artificial termination of pregnancy negatively affects women's health - a hormonal imbalance occurs, leading the body to stress, and the risks of inflammatory and infectious diseases of the reproductive system increase.
- Miscarriage. This includes miscarriages (before 28 weeks of gestation) and preterm birth (28 to 37 weeks). If spontaneous abortion occurs 2 or more times in a row, then the woman is diagnosed with recurrent miscarriage, in which each subsequent pregnancy is in danger of being terminated.
- Early placental abruption. Premature placental abruption can occur at any stage of pregnancy and can be partial or complete. In any case, this is a serious pathology that requires treatment and careful monitoring of the pregnancy.
- Complications during childbirth. Trauma to the birth canal, ruptures, abnormal labor, large blood loss - all this and much more can lead to problems in subsequent births.
- Pathologies in previously born children. In this case, doctors carefully monitor the pregnant woman and find out the causes of the pathologies of the previously born child in order to exclude the same problem.
Source: https://gemoglobin.top/diagnoz-oga-v-ginekologii/
Statistics for Russia
According to statistics in Russia, the number of pregnant women diagnosed with OHA is increasing every year. Currently, a complicated medical history accompanies about 80% of pregnancies, i.e. 8 out of 10 expectant mothers have certain risk factors during the period of bearing a child.
In 50% of pregnancies with a complicated obstetric-gynecological history, patients require inpatient hospitalization, where close monitoring and timely treatment are provided.
Factors leading to aggravated medical history during pregnancy
Among the reasons why a woman may be diagnosed with OHA are:
- Socio-biological disadvantage. The absence or insufficient amount of funds to purchase the necessary medicines, vitamins, quality food, clothing and much more often leads the expectant mother to stress, which negatively affects the pregnancy. This group includes women without education and without work (or with low-paid work), leading an immoral lifestyle, as well as pregnant women who are forced to earn money through hard physical labor. In this case, pregnancy most often occurs with pathologies, which poses a threat to the health and life of the unborn child.
- Unfavorable environmental conditions. The environmental conditions in which the expectant mother lives also make a certain contribution to the well-being of pregnancy. The release of harmful substances into the atmosphere from factories and industrial facilities, increased air pollution from vehicles, and poorly purified water negatively affect the quality of life of a pregnant woman, which accordingly leads to a deterioration in the health of the woman and her fetus.
- Diseases in future parents. Genetic diseases, alcohol abuse and smoking, as well as drug addiction of one of the parents can lead to serious problems with the baby’s health. Mother's diseases (asthma, diabetes, heart disease, vascular disease, kidney disease) can cause pathologies in the child.
- Age of the woman in labor. Complications that arise during pregnancy and childbirth are often caused by the too young (under 16 years old) or mature (over 35 years old) age of the first-time mother. This is explained by the physiological characteristics of the female body, which best copes with bearing and giving birth to children between the ages of 18 and 30.
- Complications of the current pregnancy. These include pelvic or transverse presentation of the fetus, infection of the fetus or internal genital organs of the mother, severe toxicosis, gestosis, premature placental abruption.
Oga during pregnancy: what is it, what is the interpretation, what to do about it?
The term OAGA (complicated obstetric and gynecological history) refers to the totality of information about a woman’s gynecological health - unfavorable factors that can negatively affect the current pregnancy and childbirth.
In other words, OGA during pregnancy can be diagnosed to an expectant mother who has problems associated with childbearing function.
An obstetric and gynecological history is carried out individually for each woman during a real pregnancy.
Components of the OAS
A pregnant woman may have a burdened obstetric-gynecological history if the following factors have been present in the past:
- Abortion. Artificial termination of pregnancy negatively affects women's health - a hormonal imbalance occurs, leading the body to stress, and the risks of inflammatory and infectious diseases of the reproductive system increase.
- Miscarriage. This includes miscarriages (before 28 weeks of gestation) and preterm birth (28 to 37 weeks). If spontaneous abortion occurs 2 or more times in a row, then the woman is diagnosed with recurrent miscarriage, in which each subsequent pregnancy is in danger of being terminated.
- Early placental abruption. Premature placental abruption can occur at any stage of pregnancy and can be partial or complete. In any case, this is a serious pathology that requires treatment and careful monitoring of the pregnancy.
- Complications during childbirth. Trauma to the birth canal, ruptures, abnormal labor, large blood loss - all this and much more can lead to problems in subsequent births.
- Pathologies in previously born children. In this case, doctors carefully monitor the pregnant woman and find out the causes of the pathologies of the previously born child in order to exclude the same problem.
Thus, OAGA accompanies pregnancy when one or more points are identified. In this case, indications for establishing a complicated medical history can also be the stillbirth of a baby or his death in the first 4 weeks, Rh conflict of parents, pathologies of the woman’s genital organs, hormonal imbalance and menstrual irregularities, etc.
Placental abruption is one of the reasons for the diagnosis of OGA in the future
Like most pregnant women, my medical record for pregnancy management included the inscription “OAGA”. The diagnosis was made due to previous two failed pregnancies - spontaneous miscarriages in the early stages.
In this regard, from the 4th week of gestation, the doctor prescribed Duphaston as a maintenance hormonal drug and additional ultrasound examinations in the first and second trimesters.
Otherwise, the management of my pregnancy differed little from other uncomplicated ones - a scheduled visit to the gynecologist, regular urine and blood tests, ultrasound in each trimester. The pregnancy ended successfully, delivery occurred on time.
COVID-19 Case Definition
The ranking of COVID-19 cases in pregnant women, women in labor and postpartum is carried out in accordance with standard approaches.
Suspicious case of COVID-19
Clinical manifestations of acute respiratory infection (body temperature above 37.5 °C and one or more of the following: cough, shortness of breath, chest tightness, blood oxygen saturation by pulse oximetry (SpO2) ≤ 95%, sore throat, runny nose , decreased sense of smell and taste, signs of conjunctivitis) in the absence of other known causes that explain the clinical picture, regardless of the epidemiological history.
Probable case of COVID-19
Clinical manifestations of acute respiratory infection (body temperature above 37.5 °C and one or more signs: cough, shortness of breath, feeling of chest congestion, blood oxygen saturation according to pulse oximetry (SpO2) ≤ 94%, sore throat, runny nose, decreased smell and taste, signs of conjunctivitis) in the presence of at least one of the epidemiological signs:
- returning from a trip abroad 14 days before the onset of symptoms;
- having close contact over the past 14 days with a person under observation for COVID-19 who subsequently became ill;
- presence of close contacts over the past 14 days with a person who has a laboratory confirmed diagnosis of COVID-19;
- working with patients with confirmed and suspected cases of COVID-19.
2. The presence of clinical manifestations of severe pneumonia, ARDS, sepsis or the presence of pneumonia with characteristic changes in the lungs according to computed tomography or plain chest radiography, regardless of the results of laboratory testing for the presence of SARS-CoV-2 RNA using PCR and epidemiological history.
3. A case suspected of COVID-19 if it is impossible to conduct a laboratory test for the presence of SARS-CoV-2 RNA using the PCR method.
Confirmed case of COVID-19
Positive laboratory test result for the presence of SARS-CoV-2 RNA using polymerase chain reaction (PCR), regardless of clinical manifestations.
Statistics for Russia
According to statistics in Russia, the number of pregnant women diagnosed with OHA is increasing every year. Currently, a complicated medical history accompanies about 80% of pregnancies, i.e. 8 out of 10 expectant mothers have certain risk factors during the period of bearing a child.
In 50% of pregnancies with a complicated obstetric-gynecological history, patients require inpatient hospitalization, where close monitoring and timely treatment are provided.
Factors leading to aggravated medical history during pregnancy
Among the reasons why a woman may be diagnosed with OHA are:
- Socio-biological disadvantage. The absence or insufficient amount of funds to purchase the necessary medicines, vitamins, quality food, clothing and much more often leads the expectant mother to stress, which negatively affects the pregnancy. This group includes women without education and without work (or with low-paid work), leading an immoral lifestyle, as well as pregnant women who are forced to earn money through hard physical labor. In this case, pregnancy most often occurs with pathologies, which poses a threat to the health and life of the unborn child.
- Unfavorable environmental conditions. The environmental conditions in which the expectant mother lives also make a certain contribution to the well-being of pregnancy. The release of harmful substances into the atmosphere from factories and industrial facilities, increased air pollution from vehicles, and poorly purified water negatively affect the quality of life of a pregnant woman, which accordingly leads to a deterioration in the health of the woman and her fetus.
- Diseases in future parents. Genetic diseases, alcohol abuse and smoking, as well as drug addiction of one of the parents can lead to serious problems with the baby’s health. Mother's diseases (asthma, diabetes, heart disease, vascular disease, kidney disease) can cause pathologies in the child.
- Age of the woman in labor. Complications that arise during pregnancy and childbirth are often caused by the too young (under 16 years old) or mature (over 35 years old) age of the first-time mother. This is explained by the physiological characteristics of the female body, which best copes with bearing and giving birth to children between the ages of 18 and 30.
- Complications of the current pregnancy. These include pelvic or transverse presentation of the fetus, infection of the fetus or internal genital organs of the mother, severe toxicosis, gestosis, premature placental abruption.
Most of the factors leading to OGA are controllable. Therefore, future parents are obliged to adequately analyze the situation and plan the pregnancy responsibly.
Source: https://Wellness2You.ru/besplodie/oaga-v-ginekologii-rasshifrovka.html
Preparing for a new pregnancy and preventing complications
A woman who has had failed or complicated pregnancies and childbirths, gynecological operations or diseases, and other negative episodes in the past should not despair. In this case, you need to carefully prepare for a new pregnancy and take measures to prevent possible complications.
A woman diagnosed with OGA should plan a new pregnancy after consulting a doctor.
So, at the stage of preparation for pregnancy, the expectant mother should:
- seek advice from a gynecologist and at the same time describe to him as accurately as possible all previous situations related to “women’s” health - this will allow the doctor to draw up a complete medical history of the patient;
- take a test for TORCH infections (rubella, herpes, cytomegalovirus, toxoplasmosis, STDs);
- take hormone tests and, if necessary, adjust hormonal levels;
- do an ultrasound examination of the internal genital organs;
- visit a geneticist, psychologist (on the recommendation of the attending physician).
These measures when planning pregnancy are minimal. In each individual case, the doctor may prescribe additional examination necessary for a particular patient.
With the onset of pregnancy with a concomitant diagnosis of a complicated obstetric and gynecological history, a pregnant woman is obliged to adhere to preventive measures to prevent the development of complications. These include:
- regular scheduled visits to your doctor;
- examination by specialized specialists, to whom the gynecologist refers according to an individual pregnancy management plan;
- diagnosis and treatment of identified abnormalities and diseases.
At the same time, future parents should not forget about the importance of maintaining a healthy lifestyle both throughout pregnancy and at the planning stage. A pregnant woman, including those with OHA, is strongly recommended to eat a nutritious and varied diet, breathe fresh air, and maintain a regime of wakefulness and rest. And also one of the key components of a successful pregnancy is a positive attitude and psychological balance.
Every woman expecting a baby is required to visit the attending physician according to the pregnancy management plan
Child health and OAA
Do you have OAA during pregnancy? What is it and how can it affect the child’s health? This diagnosis can have a significant impact on the baby’s health. For example, the presence of infectious diseases of the genital tract, due to which this diagnosis was made, can lead to infection of the child during childbirth. But if the doctor is a competent specialist, then this simply cannot happen.
It is also necessary to remember that hereditary factors can have a huge impact on bearing a child. A pregnant woman with diseases such as hypertension and diabetes can pass them on to her daughter, for whom they will become a real problem when she is expecting her child.
OAA itself is not hereditary. However, often hereditary diseases can appear precisely during the period of waiting for a child. Therefore, at the stage of pregnancy planning, you need to be well aware of detailed information about the health of relatives. It doesn’t hurt to undergo genetic testing.
Reviews from women from OSA
I have OAA. KS (uterine scar), large fetus, frozen, 2 KS, anemia.
Strawberry*
https://deti.mail.ru/forum/v_ozhidanii_chuda/beremennost/otjagoshhennyj_akusherskij_anamnez/?page=2
I had. 2 missed births, 2 miscarriages. 5 IVF. When they saw me at the maternity hospital, they told me to lie down until the birth. At 35 weeks I was admitted and at 36 my waters broke. Everything ended well. With the next pregnancy, a year later, TAA was no longer diagnosed.
Elena Dubenskaya
https://deti.mail.ru/forum/v_ozhidanii_chuda/beremennost/otjagoshhennyj_akusherskij_anamnez/?page=2
I have such a diagnosis, it was made due to inflammation of the appendages and gastrointestinal tract, although it is written in two abbreviations OAA, OGA.
Perula
https://www.baby.ru/blogs/post/38138027–28433837/
Despite all sorts of difficulties of pregnancy and childbirth, the expectant mother should be confident in the positive outcome of this stage of her life. With a diagnosis of OHA, most women easily carry and give birth to healthy children - it is important not to neglect the opinion of doctors and follow the recommendations of specialists.
OAS: the essence of the problem
The abbreviation OAGA stands for burdened obstetric and gynecological history. This is the presence in each individual patient of factors associated with past pregnancies, as well as with gynecological health, which can complicate the current condition and have a negative impact on the fetus. In medical practice, this diagnosis is made when a woman has premature birth, miscarriages, stillbirths, abortions, the birth of children with developmental defects, and the death of a child within 28 days after birth. The medical history is also complicated by pathologies of the uterus and ovaries, infertility of any origin, hormonal imbalance, and Rh conflict.
What can trigger the development of CPRF?
There are some factors that can lead to the development of placental insufficiency:
- The presence of chronic diseases in a pregnant woman, especially with regard to heart and vascular diseases, thyroid pathologies, diabetes mellitus and heart disease.
- Infectious diseases of the respiratory system.
- Viral diseases.
- Venereal diseases.
- Complications during pregnancy in the form of gestosis, Rh conflict or threat of miscarriage can also cause the development of fetoplacental insufficiency.
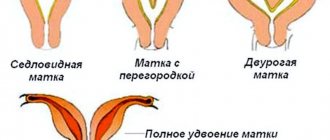
- The presence of pathologies of the uterus and reproductive system.
- Disturbances in the attachment of the placenta.
- A history of abortions or miscarriages.
- Love of cigarettes during pregnancy greatly increases the risk of developing anemia, and therefore CFRD.
- Unsatisfactory living conditions.
- Late or early pregnancy.
What can a woman do
If a woman has already had unsuccessful pregnancies or has gynecological diseases in her medical history, then each new conception plan should be approached very seriously. Accidental pregnancies should not be allowed, especially if the timing recommended by the gynecologist is not followed after miscarriages, childbirth and induced abortions. It is important for a woman with OGA to register with a antenatal clinic or private clinic as early as possible, since, for example, the first screening to detect genetic pathologies in the fetus must be carried out strictly before 12 weeks of gestation. The patient should inform the gynecologist about each episode associated with previous pregnancies, abortions, surgical treatment of the uterus and appendages, and chronic gynecological diseases. Only with the woman’s complete frankness will the doctor be able to minimize the factors that complicate the course of pregnancy and lead to pathology or death of the fetus.
How to minimize risks?
Since TAA is directly related to the health status of the pregnant woman, it is first of all necessary to prepare for the new expectation of a child in advance. There is special preconception preparation for such women, which can be completed without OAA, but in this case it will be simpler.
OAA during pregnancy - what is it and how to minimize risks? With this diagnosis, a woman must undergo a number of examinations, as well as preventive measures:
- Be examined for infections, and if they are detected, be cured.
- Examine hormonal levels and correct them if necessary.
- Treatment of pregnancy-related diseases of various systems and many others.
Thanks to such methods, the risk of possible involuntary termination of pregnancy is significantly reduced and the health of the expectant mother is maintained.
In addition, if a woman knows that she has OAA, then it is important to register as early as possible, since lost time can affect the preservation of the child’s life and its proper development.
The doctor should be aware of everything that concerns the health of the pregnant woman. It happens that a woman previously terminated her pregnancy with medication or had a miscarriage for some reason. In this case, during a new pregnancy, these factors may still remain. Moreover, termination of pregnancy causes trauma to the uterus. Therefore, the presence and influence of such factors on a new pregnancy cannot be excluded.
Also, the presence of complications in previous pregnancies may be due to the fact that there were features in the structure of the organs that cannot be changed.
OAGA: medical tactics
Whether the expectant mother belongs to a certain risk group, taking into account the OGA, is determined by an obstetrician-gynecologist after clinical and laboratory tests. An individual observation plan is entered into the patient’s chart with the appointment of modern methods of examining the mother and fetus. It also contains information about recommended preventive hospitalizations, as well as an indication of where the birth will take place - in a regular or specialized maternity hospital.
At-risk groups
In Russia, obstetricians and gynecologists use a systematic approach to determine the degree of perinatal risk. The first - low - includes repeat pregnant women with a maximum of three quiet births in the anamnesis. This group also includes primary pregnant women who have no obstetric complications or non-gynecological pathologies; one uncomplicated abortion is allowed in their medical history. The second degree of risk is childbirth in women with compensated pathological conditions of the cardiovascular system, mild diabetes mellitus, kidney disease, hepatitis, and blood diseases.
Also complicating the medical history:
- pregnancy after 30 years;
- placenta previa;
- clinically narrow pelvis;
- large fruit;
- its wrong position;
- perinatal mortality recorded in previous pregnancies;
- gestosis;
- operations on the uterus.
The third degree of risk includes women with severe pathologies of the heart and blood vessels, exacerbation of systemic diseases of connective tissue, blood, placental abruption, shock during childbirth, and complications during anesthesia.
Just what the doctor ordered
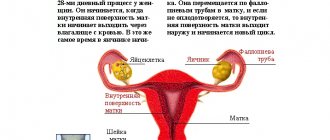
Pregnant women of high risk groups may be prescribed a consultation with a geneticist with a possible chorionic villus biopsy, amnio-, cordo-, placentocentesis to determine abnormalities in the development of the unborn child. The most accessible of all these studies is amniocentesis. With it, by micropuncture of the amniotic membrane, a portion of amniotic fluid is obtained, which contains embryonic cells. They are examined for the presence or absence of genetic damage.
Examination of amniotic fluid will help determine fetal pathologies
Oaga during pregnancy what is it?
» Miscellaneous » Oaga during pregnancy what is it
OGA is a term that accompanies pregnancy management with any deviation from the norm. According to statistics, in Russia about 80% of women have OGA, and their number does not decrease from year to year. When compiling an anamnesis, all previous pregnancies are taken into account, regardless of their outcome, as well as gynecological diseases and operations.
OAS: the essence of the problem
The abbreviation OAGA stands for burdened obstetric and gynecological history. This is the presence in each individual patient of factors associated with past pregnancies, as well as with gynecological health, which can complicate the current condition and have a negative impact on the fetus.
In medical practice, this diagnosis is made when a woman has premature birth, miscarriages, stillbirths, abortions, the birth of children with developmental defects, and the death of a child within 28 days after birth.
The medical history is also complicated by pathologies of the uterus and ovaries, infertility of any origin, hormonal imbalance, and Rh conflict.
What can a woman do
If a woman has already had unsuccessful pregnancies or has gynecological diseases in her medical history, then each new conception plan should be approached very seriously.
Accidental pregnancies should not be allowed, especially if the timing recommended by the gynecologist is not followed after miscarriages, childbirth and induced abortions.
It is important for a woman with OGA to register with a antenatal clinic or private clinic as early as possible, since, for example, the first screening to detect genetic pathologies in the fetus must be carried out strictly before 12 weeks of gestation.
The patient should inform the gynecologist about each episode associated with previous pregnancies, abortions, surgical treatment of the uterus and appendages, and chronic gynecological diseases. Only with the woman’s complete frankness will the doctor be able to minimize the factors that complicate the course of pregnancy and lead to pathology or death of the fetus.
Fight infections!
A mandatory test before conception is a test for TORCH infections - determination of antibodies to rubella, cytomegalovirus, herpes and toxoplasmosis, as well as sexually transmitted diseases.
Remember: infection with rubella during pregnancy is almost always an indication for its artificial termination at any stage, since it entails pathologies of the fetus - deafness, blindness, and other developmental defects. As gestation continues, intrauterine fetal death occurs in 20 percent of cases.
If there are no antibodies to the rubella virus, you should get vaccinated against it no later than two months before the planned conception.
Rubella infection during pregnancy is an indication for abortion
With toxoplasmosis, the severity of the prognosis directly depends on the time of infection. When Toxoplasma is introduced into the fetus in the first trimester, spontaneous abortions and severe developmental pathologies are possible.
Late congenital toxoplasmosis is characterized by intracranial calcification, chorioretinitis, convulsions, and edema of the brain. Intrauterine growth retardation is recorded. CMV infection during pregnancy also provokes the onset of perinatal pathology - prematurity, stillbirth, defects of organs and systems.
Infection with herpes is most dangerous in the first 20 weeks of pregnancy; vertical infection of the fetus is possible with subsequent development of pathologies.
What is important to remember regarding infection? You can become infected at any time, even a few days before conception, which means that the absence of certain pathogens in your body does not guarantee a positive outcome of your pregnancy.
Therefore, most doctors argue that carriage of a number of infectious pathogens (not all, of course) is much better than their absence in the body. Why? Because if you come into contact with a sick person, you are not in danger of being reinfected - you already have protection against this type of pathogen.
This does not apply to bacteria and fungi, where the mechanism of defense against these microorganisms is different, so you can become infected with many bacterial and fungal infections more than once.
Elena Berezovskaya
https://lib.komarovskiy.net/mify-ob-infekciyax.html
Hormonal swing
During pregnancy planning, it is important for a woman to have her hormonal levels examined and normalized. A good place to start is with thyroid hormones.
This organ produces triiodothyronine (T3) and tetraiodothyronine (T4, thyroxine). Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) is produced in the pituitary gland.
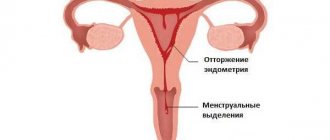
Thyroid dysfunction can cause menstrual irregularities, miscarriage, and fetal pathology.
By gender
Sex hormones should be checked in case of menstrual irregularities, male-pattern body hair growth, a history of missed pregnancies, excess weight, and PCOS.
Ultrasound will show the exit
The release of an egg from the ovary, which will help a woman determine the period of possible conception, and also give an objective picture of the condition of the uterus and appendages. The procedure is prescribed on days 9–10 of a 28-day cycle (to control ovulation) or on days 5–7 to detect possible pathological changes.
OAGA: medical tactics
Whether the expectant mother belongs to a certain risk group, taking into account the OGA, is determined by an obstetrician-gynecologist after clinical and laboratory tests.
An individual observation plan is entered into the patient’s chart with the appointment of modern methods of examining the mother and fetus.
It also contains information about recommended preventive hospitalizations, as well as an indication of where the birth will take place - in a regular or specialized maternity hospital.
At-risk groups
In Russia, obstetricians and gynecologists use a systematic approach to determine the degree of perinatal risk. The first - low - includes repeat pregnant women with a maximum of three quiet births in the anamnesis.
This group also includes primary pregnant women who have no obstetric complications or non-gynecological pathologies; one uncomplicated abortion is allowed in their medical history.
The second degree of risk is childbirth in women with compensated pathological conditions of the cardiovascular system, mild diabetes mellitus, kidney disease, hepatitis, and blood diseases.
Also complicating the medical history:
- pregnancy after 30 years;
- placenta previa;
- clinically narrow pelvis;
- large fruit;
- its wrong position;
- perinatal mortality recorded in previous pregnancies;
- gestosis;
- operations on the uterus.
The third degree of risk includes women with severe pathologies of the heart and blood vessels, exacerbation of systemic diseases of connective tissue, blood, placental abruption, shock during childbirth, and complications during anesthesia.
Just what the doctor ordered
Pregnant women of high risk groups may be prescribed a consultation with a geneticist with a possible chorionic villus biopsy, amnio-, cordo-, placentocentesis to determine abnormalities in the development of the unborn child.
The most accessible of all these studies is amniocentesis. With it, by micropuncture of the amniotic membrane, a portion of amniotic fluid is obtained, which contains embryonic cells. They are examined for the presence or absence of genetic damage.
Examination of amniotic fluid will help determine fetal pathologies
All pregnant women with OGA, according to indications, are referred for consultation to specialists to resolve the issue of prolonging pregnancy. In cases where it is necessary to conduct examinations in a hospital setting, the patient is placed in the gynecological department of the hospital or maternity hospital.
Important attitude
Women with OGA often experience pessimism during pregnancy. The need to visit the doctor more often and stay in the hospital worsens their mood. Constant thoughts about the upcoming birth and the health of the unborn child also add to the problems.
Soft psychological relaxation techniques, which are used by specialist psychologists who conduct courses for expectant mothers in maternity hospitals and antenatal clinics, can come to the rescue. Physical activity is also indicated, of course, with the permission of the gynecologist observing the woman: walking, swimming in the pool, yoga.
It must be remembered that the OAGA is not a sentence, but an instruction to the doctor in choosing the optimal way to manage the pregnancy. Yoga is good for you during pregnancy
Forecast for the future
It is worth knowing that childbirth with a burdened obstetric and gynecological history, as a rule, ends in the birth of a healthy child. Only in some cases, the mother’s simple medical history can affect the health of the newborn.
For example, if a woman has sexually transmitted infections, the fetus may become infected during childbirth. A predisposition to certain diseases - hypertension, diabetes - is also inherited. They can complicate future pregnancies for the girl born.
But OAGA itself is by no means a hereditary phenomenon, but the medical history of a particular person.
The importance of obstetric history for the current pregnancy is difficult to overestimate. The collected and analyzed data should always be taken into account when deciding on the tactics of managing the patient, her childbirth, and also when referring for an abortion.
Source: https://firstdone.ru/raznoe/oaga-pri-beremennosti-chto-eto-takoe.html
Important attitude
Women with OGA often experience pessimism during pregnancy. The need to visit the doctor more often and stay in the hospital worsens their mood. Constant thoughts about the upcoming birth and the health of the unborn child also add to the problems. Soft psychological relaxation techniques, which are used by specialist psychologists who conduct courses for expectant mothers in maternity hospitals and antenatal clinics, can come to the rescue. Physical activity is also indicated, of course, with the permission of the gynecologist observing the woman: walking, swimming in the pool, yoga. It must be remembered that the OAGA is not a sentence, but an instruction to the doctor in choosing the optimal way to manage the pregnancy.
Yoga is good for you during pregnancy
Forecast for the future
It is worth knowing that childbirth with a burdened obstetric and gynecological history, as a rule, ends in the birth of a healthy child. Only in some cases, the mother’s simple medical history can affect the health of the newborn. For example, if a woman has sexually transmitted infections, the fetus may become infected during childbirth. A predisposition to certain diseases - hypertension, diabetes - is also inherited. They can complicate future pregnancies for the girl born. But OAGA itself is by no means a hereditary phenomenon, but the medical history of a particular person.
The importance of obstetric history for the current pregnancy is difficult to overestimate. The collected and analyzed data should always be taken into account when deciding on the tactics of managing the patient, her childbirth, and also when referring for an abortion.
Complicated obstetric history
The concept of “complicated obstetric history” includes a possible serious threat to fetal development and successful delivery. In medical practice, this diagnosis is made based on the presence of concomitant problems that arose during previous pregnancies, as well as in the case of miscarriages or the birth of a stillborn baby.
Numerous abortions, pathologies of the uterus and ovaries pose a certain danger and can lead to unforeseen consequences.
What is considered a burdened obstetric history in medical practice?
Since the process of bearing a child and its birth require a serious, responsible approach on the part of the supervising specialists, any difficult circumstances that occurred before the current pregnancy are taken into account. It is possible that artificial termination of pregnancy, which doctors had to resort to during the previous pregnancy, will not have a detrimental effect on the development of the child and will not complicate childbirth. In medical practice, there are frequent cases of unfavorable outcomes of events in the presence of a burdened obstetric history. Such a conditional, but quite serious diagnosis, requiring a special approach from medical personnel, is made in the following cases:
- stillbirth,
- death of a child in the first days after birth,
- artificial birth,
- abortions,
- miscarriage (habitual),
- surgeries on the uterus, ovaries, tubes,
- birth of a sick child (developmental defects),
- bleeding during a previous pregnancy,
- polyhydramnios,
- hormonal disorders,
- metabolic disorders,
- premature birth in previous pregnancies,
- unfavorable heredity (miscarriages, fetal death in the mother or other close relatives, etc.).
Among the adverse consequences of a burdened obstetric history are placental abruption before the due date (which causes premature birth and fetal death), its improper attachment to the wall of the uterus, weakness of labor and other dangerous consequences. The threat of death of the fetus, newborn or uterine rupture are the most dangerous complications that should be prevented in time and all necessary measures taken if they are likely to occur.
What does OAA refer to?
We learned a little about the concept of OAA during pregnancy. We know the decoding, but the essence is not yet entirely clear. This term includes:
- abortions;
- miscarriage;
- childbirth that occurred prematurely;
- the birth of a child with various defects, malnutrition;
- stillbirth;
- early placental abruption;
- abnormalities of placenta attachment;
- birth canal injuries;
- adhesions, scars;
- narrowness of the pelvis;
- fetal asphyxia;
- condition of other children after birth;
- congenital defects and complications in previous children;
- other complications.
These factors have a huge impact on the course of subsequent pregnancies and their outcome, and therefore must be taken into account by the doctor in order to reduce possible risks to the maximum.
There is a concept similar to OAA - OGA, which means “burdened gynecological history.” It includes everything related to a woman’s health in terms of gynecology: the course of menstrual cycles, disruptions in them, past sexual diseases. The concept of OGA is closely related to OAA, which is why they are often referred to in the general terms “complicated obstetric and gynecological history.”
It should be noted that the diagnosis of OAA during pregnancy (what it is, we explained above) is given to many women. So in Russia their number is approximately 80 percent. A high risk of miscarriage is, unfortunately, not uncommon.
Preventing complications
Since surgery on the uterus in any case involves the presence of a scar. Caesarean section is also a risk factor for a woman who is pregnant with her second child. The risk of uterine rupture cannot be excluded, which can cause the death of the child and mother. For subsequent births after uterine surgery, a caesarean section is indicated; the birth of a child naturally is not allowed in order to reduce the risk. During birth planning, specialists fill out the pregnant woman’s exchange card, carefully study the anamnesis, medical history, find out the presence of unfavorable heredity, and then decide on the issue of delivery by Caesarean section or natural way.
Often the second pregnancy has the same tragic ending as the previous one, as a result of which the intrauterine death of the child was determined for a certain reason. It is extremely important for medical personnel to identify possible pathological processes in a woman’s body and prevent a disastrous outcome of events. In order to avoid serious consequences, it is recommended to plan pregnancy in advance.
Modern diagnostic methods, consultation with specialists, and a healthy lifestyle are necessary conditions for the full development of pregnancy and the timely elimination of serious problems. Pregnant women are advised to visit a supervising doctor within a clearly specified period; possible hospitalization in many cases is the only correct decision to preserve the health of the unborn child and his mother.
OAA during pregnancy: what is it, how to decipher it?
Pregnancy is a difficult period for many women, associated with difficult pregnancy, anxiety and unrest, and an unstable emotional state.
In addition, doctors often frighten the expectant mother with the diagnoses they give her. In exchange cards you can sometimes find an abbreviation such as OAA during pregnancy.
What is it and how scary is it? You will find answers to these questions in the article.
OAA during pregnancy: explanation
The abbreviation “OAA” means “complicated obstetric history.” Let's break it down piece by piece. Anamnesis is the history of the disease from its onset to the visit to the doctor. But pregnancy is not a disease, but a condition.
Therefore, in this area, obstetric history is everything that is interconnected with other pregnancies and their course.
What does the word “burdened” mean? Previously, there may have been some risk factors that influenced the carrying of the unborn baby and a successful delivery.
How to minimize risks?
Since TAA is directly related to the health status of the pregnant woman, it is first of all necessary to prepare for the new expectation of a child in advance. There is special preconception preparation for such women, which can be completed without OAA, but in this case it will be simpler.
OAA during pregnancy - what is it and how to minimize risks? With this diagnosis, a woman must undergo a number of examinations, as well as preventive measures:
- Be examined for infections, and if they are detected, be cured.
- Examine hormonal levels and correct them if necessary.
- Treatment of pregnancy-related diseases of various systems and many others.
Thanks to such methods, the risk of possible involuntary termination of pregnancy is significantly reduced and the health of the expectant mother is maintained.
In addition, if a woman knows that she has OAA, then it is important to register as early as possible, since lost time can affect the preservation of the child’s life and its proper development.
The doctor should be aware of everything that concerns the health of the pregnant woman. It happens that a woman previously terminated her pregnancy with medication or had a miscarriage for some reason.
In this case, during a new pregnancy, these factors may still remain. Moreover, termination of pregnancy causes trauma to the uterus.
Therefore, the presence and influence of such factors on a new pregnancy cannot be excluded.
Also, the presence of complications in previous pregnancies may be due to the fact that there were features in the structure of the organs that cannot be changed.
Measures being taken
Do you have OAA during pregnancy? How to treat? In this matter, you need to completely trust your doctor and strictly follow his instructions. Knowing that the pregnant woman has had OAA in the past, the specialist must take the necessary measures to prevent possible complications.
To do this, the following is done: the risk group is determined, individual measures are selected to accompany pregnancy. In some cases, for example, a woman needs to be hospitalized at certain times when there is the greatest likelihood of risks.
In addition, women with OAA are most often hospitalized two weeks before the upcoming birth.
Unfortunately, many women do not tell their doctor that they have previously had an abortion or miscarriage. A specialist, not knowing about such phenomena, may underestimate possible risks, and the consequences in the future will be disastrous. It is best to tell your doctor everything.
C-section
For women expecting a second child, cesarean section during the first pregnancy is also a risk factor, since it leaves a scar. Moreover, uterine rupture is possible, which can lead to the death of both the baby and his mother.
After operations on the uterus, a cesarean section is indicated for subsequent births, because in this case the passage of the child through the natural birth canal is risky.
Throughout pregnancy, specialists fill out an exchange card, carefully study the anamnesis and medical history, and determine the presence of unfavorable heredity.
All this information serves to make a decision about what kind of childbirth will be: natural or by cesarean.
Often, the second pregnancy can also end tragically, like the first: with the intrauterine death of the child for some reason. Medical personnel must identify possible pathological processes occurring and take all measures to prevent a tragic outcome. In order to avoid possible dire consequences, it is necessary to plan your pregnancy in advance.
Child health and OAA
Do you have OAA during pregnancy? What is it and how can it affect the child’s health? This diagnosis can have a significant impact on the baby’s health.
For example, the presence of infectious diseases of the genital tract, due to which this diagnosis was made, can lead to infection of the child during childbirth.
But if the doctor is a competent specialist, then this simply cannot happen.
It is also necessary to remember that hereditary factors can have a huge impact on bearing a child. A pregnant woman with diseases such as hypertension and diabetes can pass them on to her daughter, for whom they will become a real problem when she is expecting her child.
OAA itself is not hereditary. However, often hereditary diseases can appear precisely during the period of waiting for a child. Therefore, at the stage of pregnancy planning, you need to be well aware of detailed information about the health of relatives. It doesn’t hurt to undergo genetic testing.
Emotional mood
Women with OAA during/during pregnancy are at risk for possible complications during pregnancy and childbirth. But this is connected not only with physiology. Such women have a completely different attitude towards a new pregnancy than women with a favorable history.
Such pregnant women must attend a variety of preventive and therapeutic measures carried out in antenatal clinics and hospitals.
It must be remembered that OAA during pregnancy is not a death sentence, but rather an indication to the doctor to choose the right way to manage the pregnancy. There is no need to be alarmed if the abbreviation OAA is found on the card. It is quite possible that there will be no complications during pregnancy. But if the doctor does not know about OAA, risks are most likely to arise.
Some advice for pregnant women
Do you have OAA during pregnancy? What it is, you now know. Now there is no need to panic, it is better to listen to some advice.
For the correct and full development of pregnancy, it is necessary to attend consultations with specialists, follow all recommendations and prescriptions prescribed by them, and lead a correct lifestyle.
It is important not to miss appointments with the doctor, and also to tell him truthfully all the necessary information so that the unborn baby is born healthy.
A lot depends on the mother herself, so every effort must be made to ensure that the pregnancy proceeds easily and the upcoming birth is successful.
Source: https://FB.ru/article/256790/oaa-pri-beremennosti-chto-eto-takoe-kak-rasshifrovat