Pregnancy, especially the first one, is a rather exciting process for every expectant mother. Screenings either help relieve anxiety or, on the contrary, increase it. The growing belly begins to cause discomfort, and the baby beating in the womb is already a reminder that childbirth is coming soon.
Having heard the phrase, the internal pharynx is expanded in a funnel shape; what this means and what to do now - the woman will want to know right away. Often, specialists scare patients with premature birth due to the pathology found. Therefore, let's figure out in which case the risks are especially great.
Childbirth
Childbirth is considered premature if it occurs from 22 to 37 weeks of pregnancy and a baby weighing from 500 to 2500 grams is born. It is important to note that the period in weeks is calculated for a regular cycle, starting from the first day of the last menstruation.
According to statistics, premature birth occurs in 5 to 10% of cases on the entire planet. Even the latest developments in the field of medicine cannot prevent them with a 100% guarantee. Patients from developed countries who use artificial insemination methods for conception experience premature birth most often.
During screening, an ultrasound diagnostic specialist may find that the internal os is expanded in a funnel-shaped manner. If the patient has a history of giving birth prematurely or having miscarriages, then this is a cause for concern. There are about 15% of such women.
There is a connection between past and current pregnancies: the earlier labor began in the previous pregnancy, the higher the risk of encountering the same problem now.
Doctors provide special care to women whose uterus has a septum or is considered unicornuate. In addition, various injuries and treatment of the cervix before pregnancy also increases the chances of premature birth.
The funnel-shaped expansion of the pharynx and the diameter of the cervix normally does not exceed 1 centimeter. The situation is complicated by the fact that premature birth often occurs in primiparous patients, and the pathology can be sudden in nature, when previous pregnancies were resolved according to all the rules - at the end of the gestational period. This is why it is so important to closely monitor any pregnant woman.
Treatment
We have already mentioned cervical cerclage, in which stitches are placed on the cervix. This measure helps prevent childbirth before the 34th week of pregnancy by 25% if the patient has already encountered this problem.
The suturing procedure is performed from 11 to 13 weeks of gestation. Another tactic is also possible: regular ultrasound monitoring of the length of the neck, and as soon as it is shortened to 25 mm, a cerclage is immediately applied. With the latter approach, unnecessary suturing can be avoided by 50%.
If the length of the cervix does not reach 15 mm, then thanks to cerclage the risk of early delivery can be reduced by 15%. It is important that there is no history of such pathology. In case of multiple pregnancy, cerclage is not used.
Progesterone therapy is carried out from 20 to 34 weeks. Its effectiveness is 25% if there is a history of premature birth. In women with a shortened cervix without a complicated medical history, the effectiveness is higher - 45%. We are talking about childbirth before 34 weeks of gestation.
Progesterone is used only locally - the drug is injected into the vagina. The daily dose is no more than 200 mg.
The pessary is made of silicone because it bends well. With its help, the uterus is directed to the sacral spine, thereby relieving the load on the cervix that the fetus puts on. If the internal os is expanded funnel-shaped and the neck is shortened, then it makes no sense to use a pessary and cerclage at once. Some experts have a different opinion, combining two methods at once.
When measures have been taken to correct the condition of the cervix, regular ultrasound monitoring does not make sense.
As you can see, for modern medicine there is nothing critical, even if the internal os is expanded funnel-shaped and if the cervix is shortened. A timely visit to a gynecologist and undergoing screenings will help you detect the problem and take appropriate measures to bear a healthy baby. Also, if labor begins prematurely, the highest-level perinatal centers will provide the child with first-class care, placing him in a special unit for premature babies.
The condition of the cervix affects the course of pregnancy. Much attention is paid to the processes of its maturation. The cervix remains tight and closed during pregnancy unless there are complications. Only towards the end of the term are natural changes possible. At the end of pregnancy, the cervix changes as follows:
- - consistency changes - softens;
- - shortened (smoothed);
- - gradually opens up.
Premature cervical ripening
Normally, the cervix ripens only in the third trimester. Prematurity is diagnosed in the second trimester. Most often, this situation occurs in women who have already suffered miscarriages or premature births. The development of such a complication may be associated with developmental anomalies, connective tissue diseases, after some surgical interventions, traumatic injuries, etc. In some women, cervical incompetence is diagnosed for the first time and for no apparent reason. Pathological shortening of the cervix during pregnancy requires immediate medical attention.
Cervical assessment
The cervix during pregnancy is often assessed during a vaginal examination. The assessment is carried out in points.
In addition to vaginal examination, ultrasound is also used. This is a more accurate method. Using ultrasound, you can clearly see shortening, changes in the anatomy of the internal pharynx, expansion of the cervical canal, etc. Transabdominal and transvaginal access (vaginal sensor) can be used for examination. Transvaginal ultrasound is most often used. Before the test, the woman is asked to empty her bladder. She lies on her back, bends her legs at the knees, puts a special cover on the sensor, applies sound-conducting gel, and carefully inserts the sensor into the vagina.
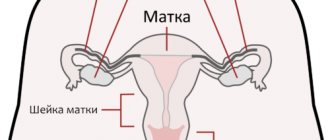
Cervix
The absence of pathological changes in the cervix is the key to a healthy pregnancy, since it is the cervix that is responsible for its safety and also determines the nature of the birth process. Essentially, the cervix is a barrier that prevents the fetus from leaving the mother's womb.
Thanks to the inner mucous layer of the cervix, called the endocervix, a plug is formed, created from mucus secreted by special glands. Its function is to prevent various microorganisms from entering the uterus.
The expansion of the internal os and a cervical length of 22 mm or less indicate that labor may begin soon. If this happens in the late stages of pregnancy, when it is already considered full-term, then there is no problem. When such a situation is discovered in the second or early third trimester, you should immediately discuss your condition with your doctor.
In some women, the cervix ripens quite early - it shortens and the pharynx gradually opens, which means that its barrier function is impaired. This process has no symptoms; it can only be seen during an ultrasound examination at the next screening. At a later stage of gestation, the mucus plug also begins to come off. It is easy to notice by the discharge from the genital tract - mucus with blood streaks.
As already mentioned, it may be that initially the internal pharynx is funnel-shaped, the norm is no more than 1 centimeter. Typically, this opening of the throat is observed if there are scars on the cervix.
The internal pharynx is funnel-shaped: what does this mean, what is the norm, what to do?
The area where the cervix meets the vagina is called the external os in gynecology.
If a woman has a second or subsequent pregnancy, its shape will normally be slit-like; when carrying her first child, the external os remains round. The norm during pregnancy is the opening of the external pharynx to 0.2-0.3 cm (but not more than 0.6 cm, 10 mm is a dangerous condition). The internal os is the muscular ring between the uterine cavity and its cervix. Normally, during gestation it is closed and begins to open before the process of delivery.
The internal os performs a protective function, preventing the penetration of pathogens into the uterus and the premature birth of the baby.
Reasons for opening the pharynx
Premature opening of the throat during pregnancy is a dangerous condition. It occurs without pronounced symptoms, so it is difficult to detect and treat in a timely manner, but the lack of therapy leads to pregnancy failure and fetal death. A pregnant woman's pharynx may open due to the following reasons:
- isthmic-cervical insufficiency - characterized by weakness of the cervical muscles, which, under the influence of the weight of the fetus, contracts in the early stages of pregnancy, leading to premature opening of the pharynx and spontaneous termination of pregnancy;
- pathological changes in the cervical canal due to injury or illness;
- multiple pregnancy - several embryos put more pressure on the cervix than one fetus;
- hormonal imbalance - early cervical ripening can be triggered by an excess of male hormones in the body of a pregnant woman.
Treatment tactics
A doctor can diagnose the opening of the external pharynx during a routine gynecological examination, while a funnel-shaped expansion of the internal pharynx can only be detected using an ultrasound examination. This pathology is a threat to the fetus, so urgent measures must be taken to eliminate the pathology.
Surgical intervention
If the pharynx is dilated in a v-shape, but prolapse of the fetal bladder from the uterine cavity has not yet occurred, it is possible to save the pregnancy with the help of surgical intervention. Typically, a circular suture is placed on the cervix while maintaining a small drainage lumen (this technique reduces the risk of infection).
Obstetric pessary
To strengthen the walls of the cervix and stop the process of opening the pharynx, the doctor may decide to install an obstetric pessary. This is a ring-shaped device made of plastic or silicone. It is inserted through the vagina without anesthesia (the procedure is unpleasant, but not painful). In some cases, two methods are used at once - stitches are applied and a pessary is placed.
Cervical length indicators by week
Normally, the internal and external os of the uterus are closed until 36-41 weeks of gestation. In this case, the length of the smooth muscle ring gradually shortens, and the opening diameter increases. This facilitates the passage of the fetus along the birth canal at the time of delivery.
Reference: in most cases, changes in the size of the cervical canal occur from the 20th week of gestation, however, a gynecological examination is recommended from the 14th week.
The length of the external and internal pharynx during pregnancy is the norm by week:
- up to the 10th week – 45 mm;
- 16-20 weeks – 40-45 mm;
- 25-27 weeks – 35-40 mm;
- 32-36 weeks – 30-35 mm.
Too short a uterine os between 14 and 24 weeks indicates a high risk of preterm birth:
- up to 10 mm – delivery at 32 weeks of gestation;
- no more than 15 mm – the gestational age of the child will not exceed 33 weeks;
- less than 20 mm – the child will be born at 34 weeks of gestation;
- no more than 25 weeks - the labor process will begin at 36-37 weeks of pregnancy.
Based on the condition of the internal os, you can determine the approximate date of birth of the child, as well as prevent premature birth in the early stages of gestation.
2 weeks before the birth process, the uterus matures almost completely, while the length of the cervix is shortened to 10 mm.
Under pressure from the fetus, the pharynx begins to gradually open, which can be easily determined using ultrasound and gynecological examination.
The internal os is open during pregnancy: pathology control
Diagnosing the opening of the internal pharynx requires taking action. Which ones exactly depends on both the degree of expansion of the canal and the duration of pregnancy.
- Drug therapy. In a hospital setting and on bed rest, the woman undergoes treatment using hormonal agents, vitamins and antispasmodics, and magnesia.
- Installation of a special ring on the neck - a pessary. A structure made of plastic or silicone is placed on the neck, thereby strengthening its walls. As a result, the process of opening the pharynx can be restrained. The ring is most often applied after the 20th week and removed at the 37th week. The procedure is performed without anesthesia. The doctor lubricates the pessary with silicone, inserts it through the vagina and places it on the cervix.
- Surgical intervention - suturing the neck. In this case, either a circular suture can be applied, leaving a drainage gap, or the external pharynx - the anterior and posterior lips of the cervix - can be completely sutured. The second method is less popular, because the created closed space is a favorable environment for the development of infection. The operation is performed before the 28th week of pregnancy.
Unfortunately, taking even radical measures is not always able to save a pregnancy.
If the cervical canal is dilated
An ultrasound or examination may reveal that the cervical canal is dilated
– isthmic-cervical insufficiency, that is, the cervix is not able to perform its functions, retain the fertilized egg, and already in the early stages of pregnancy there is a threat of miscarriage.
Source: https://GolovaNeBoli.ru/beremennost/vnutrennij-zev-voronkoobrazno-rashshiren-chto-eto-znachit-kakaya-norma-chto-delat.html
ICN
The term isthmic-cervical insufficiency means that the cervix dilates in the 2nd or 3rd trimester without uterine contractions. The likelihood of premature delivery or termination of pregnancy depends on the width of the opening. With such a pathology, a woman should regularly visit an obstetrician-gynecologist.
It is possible that with a diagnosis of ICI, labor may end in a timely manner. Thanks to transvaginal ultrasound, cervicometry is performed, in which the length of the closed zone of the cervix is determined, as well as the shape and size of the expansion of the pharynx.
If there is a risk of premature birth, then an ultrasound scan should be performed every 14 days, starting from the 14th week of pregnancy. The last study is carried out at 24 weeks of gestation. For women outside the risk group, an ultrasound examination of the cervix is prescribed from 20 to 24 weeks of pregnancy.
Cervicometry
The patient should empty her bladder and lie on her back with her knees bent. Very carefully, the doctor inserts a transvaginal sensor protected by a condom into the vagina. It is important not to put pressure on the neck so that its length does not artificially increase. The sensor is directed to the anterior fornix.
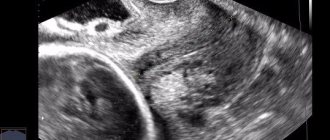
On the monitor, the specialist sees the left and right parts of the cervix, as if separated by a vertical line. If the internal os is funnel-shaped, the doctor will immediately explain what this means and show it on the screen.
The true position of the pharynx cannot be confused with the lower part of the uterus, since the mucous membrane of the endocervix has a special echogenicity - either increased or decreased. Measurements are taken from the outer to the inner pharynx, namely, to the notch in the form of the letter V.
The neck is naturally uneven, it has some bends, so measurements are taken in a straight line. That's why its length turns out to be shorter than it actually is. You can also do them along the cervical canal. And yet there is no particular importance in how to take measurements, because when it is shortened, the output is always a straight line. You cannot examine the cervix for more than 3 minutes.
With natural uterine contractions, the length of the cervix also changes. Always choose the smaller value. The length is also affected by the position of the fetus in the 2nd trimester, when it is already quite large.
It is possible to detect the fact that the internal os is expanded funnel-shaped, and also determine the length of the neck using a transabdominal sensor. However, the values are not so accurate. Deviations compared to cervicometry will be +/- 5 mm.
results
With a cervical length of 30 mm or more, the risk of premature birth is reduced to 1%. If such patients have complaints of pain and heavy discharge without blood, then hospitalization is still not indicated.
The length is less than 15 mm in the case of a singleton pregnancy, as well as 25 mm if there is more than one fetus, it is considered dangerous and requires urgent medical intervention. Such women are hospitalized and everything necessary is prepared if labor suddenly begins.
The clinical picture, in which a funnel-shaped expansion of the internal pharynx and a neck length of 22 mm is detected, requires an urgent visit to a gynecologist so that he can decide what therapy is indicated. Microdoses of progesterone are usually prescribed. Or the neck is closed using a cerclage - stitching, and they may also offer the installation of a pessary.
For particularly suspicious patients, it is worth noting that a shortened cervix detected during cervicometry does not mean that you will certainly have a premature birth, just that the risk is higher than that of other women who do not have this feature.
Enlargement of the cervical canal: normal or pathological?
Determining the condition of the cervix is a mandatory element of a gynecological examination. Such an examination can reveal not only a variety of pathological changes in the mucous membrane, but also an expansion of the cervical canal.
This symptom in some cases is a formidable sign of ongoing pathological processes, although sometimes it is considered as a component of natural changes in the reproductive system. Therefore, an isolated conclusion about the presence of dilatation of the cervical canal is not a clear cause for alarm. It must be assessed in relation to a specific clinical situation.
Cervical canal - what is it and what is its function?
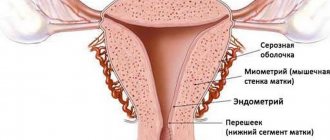
The cervical canal (canalis cervicis uteri) is a natural linear space inside the cervix that connects the uterine cavity with the lumen of the vagina. Under normal conditions, it has a spindle-shaped shape due to 2 physiological terminal narrowings. They are called the external and internal pharynx.
The cervical canal is lined with a special cylindrical epithelium, which performs a barrier and secretory function.
The mucus produced by its cells contains a large amount of glycoproteins and is essentially a hydrogel with a finely porous structure.
Moreover, its consistency, acidity and permeability are not constant, but change depending on the woman’s hormonal background, the day of her cycle and a number of other factors.
The mucus contained in the lumen of the canal is a natural obstacle to bacteria and viruses, forming a “plug” and thereby preventing ascending infection of the uterine cavity.
In addition, the cervical tissues have a local immune system that provides additional protection against most microorganisms. It is represented by immunocompetent cells, the humoral factors and antibodies they produce.
It is thanks to the cervix that the uterine cavity maintains its sterility.
- Creation of a selectively acting barrier on the path of spermatozoa
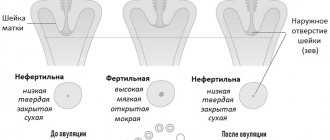
Hormonal levels that change during the ovarian-menstrual cycle affect the acidity and viscosity of cervical mucus, which has a regulatory effect on male germ cells.
Before ovulation, the mucus plug liquefies, its pores increase in diameter, the pH becomes alkaline, and the cervical canal opens slightly. All this creates favorable conditions for the penetration of sperm from the vagina into the uterine cavity.
And the parietal reverse flow of mucus that occurs during this period is a factor that allows us to “weed out” functionally incomplete male germ cells that are not capable of progressive, targeted movement.
- Removal of menstrual and postpartum discharge from the uterine cavity
The cervix is the natural and only route for the evacuation of blood, rejected endometrium, physiological and pathological secretions. Violation of its patency leads to the accumulation of secretions, progressive expansion of the uterine cavity with the reflux of contents into the fallopian tubes, and provokes an inflammatory process.
- Formation of the birth canal, ensuring the natural expulsion of the fetus, its membranes and separated placenta
This is ensured by the expansion, shortening and centralization of the position of the cervix during contractions in the 1st labor period.
The cervical canal is often considered as a special anatomical formation, paying special attention to it when examining a woman.
What does it mean - the cervical canal is dilated?
Normally, in an adult nulliparous woman with sufficiently developed genitals, the length of the cervical canal is on average 3.5-4.5 cm, and the diameter at the widest part does not exceed 8 mm.
Its external pharynx has a round shape and a diameter of 5-6 mm.
And after childbirth, it naturally takes on a slit-like shape with several radiating traces of tissue tears along the edges and no longer closes so tightly.
The permissible width of the lumen of the cervical canal outside the process of labor is up to 8 mm. An increase in diameter above this indicator is the basis for diagnosing enlargement (dilatation). This is complemented by shortening of the cervix, which is sometimes used as an independent criterion.
A closed cervical canal is the norm during pregnancy until the onset of labor. Its expansion exceeding the average statistical size is spoken of in several cases:
- there is an expansion of the internal pharynx up to 2 mm or more already at the end of the first trimester of gestation, with a normal diameter of the remaining parts of the cervical canal;
- the cervical canal is slit-like expanded in the upper third, and there is often a significant increase in the number of cervical glands;
- there is a funnel-shaped deformation of the internal os; when performing a 3D ultrasound and sufficient specialist skills, it is often possible to record prolapse of the membranes;
- expansion of the canal along its entire length, with a simultaneous decrease in the length of the cervix and its softening.
Diagnostics
Confirmation of the presence of dilation during a routine basic gynecological examination is usually not possible, except in cases of gaping of the external os.
Reliable diagnosis requires intravital imaging techniques, and ultrasound is usually sufficient. In this case, preference is given to a vaginal sensor, although it is also possible to use a conventional transabdominal one.
Measuring the cervix during an ultrasound is called cervicometry.
A more accurate imaging method is MRI of the pelvic organs. Of course, this technique is not used for the primary diagnosis of cervical pathology. MRI is performed at the second stage of examining the patient to reliably determine the nature of her changes.
Smear analysis during dilation of the cervical canal is an additional diagnostic method that allows you to confirm the presence of an inflammatory process and determine its nature. To exclude STDs as the cause of cervicitis, a serological blood test is performed for major infections.
Why is this dangerous?
If the cervical canal is dilated in the absence of pregnancy, this does not pose an immediate danger to the woman’s life. But such dilatation is a symptom of various pathological processes in the cervix or body of the uterus, which requires adequate diagnosis and timely, comprehensive treatment.
Enlargement of the cervical canal during pregnancy is clearly a pathological sign. It may be a manifestation of:
- Threatened spontaneous abortion in early pregnancy. At the same time, in addition to the expansion of the cervical canal on ultrasound, there are signs of pathological hypertonicity of the uterus. Incipient detachment of the ovum with a retrochorial hematoma can also be detected, while maintaining the viability of the embryo.
- Isthmic-cervical insufficiency, which is diagnosed from the 2nd trimmeter of pregnancy. Additional diagnostic ultrasound signs of this condition are a funnel-shaped expansion of the internal os, a decrease in the length of the cervix at less than 20 weeks to 3 cm, a decrease in the ratio of the length of the cervix to its diameter (at the level of the internal os) to less than 1.5. Isthmic-cervical insufficiency is the cause of recurrent miscarriage.
- Abortion in progress or incomplete spontaneous abortion (in early pregnancy), premature birth (after 26 weeks of gestation).
Therefore, if dilation of the cervical canal is diagnosed during pregnancy, the doctor needs to decide on treatment tactics as soon as possible and assess the advisability of urgent hospitalization of the patient.
Main causes of pathology
Why is the cervical canal enlarged? There are many reasons for this condition:
- Threat of miscarriage.
- Polyp of the cervical canal.
- Cystic lesion of the cervix (the so-called Nabotov cyst), usually with anechoic contents. These can also be multiple small cysts up to 1 mm in diameter.
- Other benign tumor-like formations of the cervix. Possible fibroids, sarcomas, hemangiomas, leiomyomas.
- High-grade adenocarcinoma of the cervix.
- “Born” fibroid or endometrial polyp.
- Endometriosis, adenomyosis.
- Acute or chronic cervicitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal), including those developing as a result of STDs.
- Tumors of the uterine body of significant size, leading to stretching of the internal os.
In women of reproductive age, dilation up to 12 mm or more can be observed for some time after a completed spontaneous or medical abortion, during the recovery period after childbirth, after therapeutic and diagnostic interventions with cervical dilation.
In menopause, dilation may be due to progressive atrophy of uterine tissue against the background of severe estrogen deficiency.
In this case, the cervical canal is usually dilated unevenly, and there may be concomitant prolapse of the vaginal vault and uterus.
And as the process of age-related involution of the reproductive system progresses in the postmenopausal period, dilatation is replaced by narrowing to 3 mm or less, and subsequent atresia (fusion).
What to do?
Therapeutic tactics are determined by the main cause of changes in the cervix.
An obstetric pessary on the cervix to prevent its opening
In the presence of polyps and tumors, the issue of surgical treatment is decided, while in women of reproductive age, preference is given to organ-preserving operations. The exception is adenocarcinoma.
In this case, with extensive damage and signs of malignancy with germination into surrounding tissues, a decision may be made on radical intervention with hysterectomy and subsequent chemotherapy and radiation therapy in accordance with the principles of treatment of cervical cancer.
For cervicitis and endocervical cysts, conservative therapy using systemic and local antibacterial and anti-inflammatory agents is indicated.
Moreover, in the case of a confirmed STD, it is carried out under the supervision of a dermatovenerologist, with simultaneous treatment of all sexual partners and examination of family members.
The woman must subsequently be kept under dynamic registration and regularly undergo control tests for STDs and HIV.
In case of confirmed adenomyosis, therapy is carried out in accordance with current clinical recommendations.
Usually they start with complex conservative treatment using hormonal and anti-inflammatory drugs. Physiotherapy, absorbable agents, and vitamins are prescribed as auxiliary measures.
For adenomyosis that is widespread and not amenable to conservative treatment, surgical treatment is indicated.
The revealed expansion of the cervical canal on ultrasound during pregnancy is the basis for an urgent decision on the issue of hospitalization of the pregnant woman due to threatened abortion or premature birth.
Prescribe hormonal drugs, antispasmodics, magnesium drugs and other tocolytics, and prevent placental insufficiency.
In the case of diagnosed isthmic-cervical insufficiency and a history of miscarriages, additional measures are taken to strengthen the cervix.
These include:
- Special sutures are placed on the neck, which are removed at 38 weeks. Currently, different suturing options are used with approximately equal effectiveness; the choice of method remains with the doctor.
- Installation of a pessary - a special latex ring placed on the cervix to prevent its opening. Possible only in the early stages of isthmic-cervical insufficiency, sometimes in addition to suturing.
- On average, in the presence of isthmic-cervical insufficiency, pregnancy can be prolonged in 2/3 of cases.
Source: https://cmsch71.ru/mammologiya/rashirnie-tservikalnogo-kanala-norma-ili-patologiya.html
Opening forms
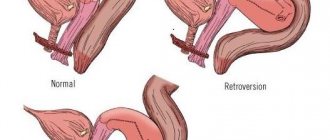
More than once the article mentioned the external and internal pharynx. Let's discuss what forms of expansion the latter has. So, during an ultrasound, you can hear that the internal pharynx is expanded funnel-shaped, and there are also expansions designated by the letters T, U and Y. During pregnancy, the shape of the expansion changes.
The diagnosis of ICI suggests that, along with a shortened and softened cervix, the cervical canal expands, and the internal pharynx changes shape and opens. The study showed that the internal os is funnel-shaped, which is normal if the neck is not shortened. This means you are not at risk of giving birth prematurely.