Histology after frozen pregnancy
Histology – studies the structure of tissues of living organisms. The main research methods are microscopy. It is used to study the normal structure of tissues and their pathology, which causes changes and damage.
Identifying the cause of missed abortion
Nowadays, histology methods are used to determine the disease of the female body. This method is used after a miscarriage, if there is a frozen pregnancy, when there is a suspicion of cancer and other similar cases.
Why is pathology dangerous?
A stop in the development of the embryo and the death of the fetus in the later stages is a moral and physical test for a failed mother. In any of the options, the problem is solved by removing the embryo from the uterine cavity. The degree of risk and consequences depend on the period at which the pathology was discovered and the cleaning method.
For example, curettage can lead to uterine bleeding with the appearance of infections and the subsequent development of adhesions. All these are real problems that can prevent you from getting pregnant in the future.
Quite often, cleaning a frozen pregnancy leads to disruption of the intestinal microflora due to serious antibacterial therapy and surgery.
A huge problem is the bitterness of loss. A woman manages to get used to the role of a mother even during those short months while life begins to emerge inside. After the fetus has died, she may become depressed, have trouble sleeping, and live in constant fear. In such cases, expectant mothers need to realize that a lost child is a bitter, but the only true lesson. It is important to be able to extract the most important things from what you have experienced and do everything to ensure that the next pregnancy goes as smoothly as possible and gives you the happiness of long-awaited motherhood.
Essence and stages of research
In the modern world, this is an indispensable procedure that can determine even the most complex pathology. Such an analysis is associated with cytology (the study of cells), embryology (the study of the structure of the embryo), thanks to it it is possible to study the exact structure of tissues.
In order to conduct histological studies, a piece of tissue (small) is taken, a smear, a print or a small section from the organ that is being examined is enough. The test period usually varies from five to ten days; in rare cases where urgent results are needed, a rapid test can be done within twenty-four hours.
But such research is not always accurate. Research is carried out in seven stages:
- fixation. Tissue fragments are treated with a special composition in order to prevent the breakdown of cells and structure. This is done so that the material does not deteriorate during study;
- wiring. The materials are degreased so that they become compacted;
- filling. Impregnated with paraffin to prepare a hard cut;
- cutting. Using a microtome, the hardened material is cut into thin layers;
- coloring. These layers are placed on special glasses, stained with a special composition to determine different tissue structures (DNA, RNA, cytoplasm, etc.);
- conclusion. Sections on glass are covered with another glass on top to preserve the layers;
- study. The obtained samples are studied by histologists or pathomorphologists using a light microscope.
They are directly involved in deciphering the histology results if a frozen pregnancy, miscarriage, etc. occurs. Why does my left side ache during pregnancy?
In gynecology, histology is prescribed to study the fetus. Such a pregnancy is the same as a miscarriage that has not yet occurred. After determining the death of the fetus, cleansing is prescribed so that putrefaction does not begin in the woman’s body.
The material is cut directly from the uterus. You cannot have sexual intercourse within 24 hours. Everything is done under sterile conditions, local anesthesia is given, and a piece of flesh is taken for analysis. The material is sent to the pathology laboratory and examined there. If abnormalities are detected, treatment is prescribed.
What the results say
The results of histological studies carried out after a frozen pregnancy are very important. Determine the causes of the disease, malignant or benign tumor process. And the early stages of diseases are detected.
Can determine the origins of the disease
The extracted matter (placenta) is always sent for histology. Histology is carried out along with tests for infections, hormones, etc. This allows you to accurately determine the cause of the incident. This is necessary to avoid a repetition of the situation.
Gynecologists prescribe histology for inflammatory processes in the uterine cavity, neoplasms on it, after curettage, and during a frozen pregnancy. If multiple ovarian cysts are present.
It also helps to identify cancer at an early stage. Histology is also prescribed:
- with prolonged bleeding;
- pain in the lower abdomen that appears for no particular reason;
- leukoplakia;
- uneven surface of the organ;
- painful menstruation;
- for infertility;
- irregular periods;
- neoplasms on organs, etc.
The cost of such an analysis
Histology tests carried out after a frozen pregnancy come in several types: for urgent examination and for planned examination. Making a diagnosis depends on:
- the quality of the material that was examined;
- quality of diagnostic equipment and qualifications of laboratory staff;
- qualifications and experience of pathomorphologists.
The price of histological analysis is from 2 to 3 thousand rubles
The cost of such a procedure ranges from two to three thousand rubles. Decoding and description is about five hundred rubles. Re-examination of glass costs about two thousand rubles. Immunohistochemistry costs approximately three to five thousand rubles.
After you have received the results of histology, which was carried out after a frozen pregnancy, each woman must undergo certain examinations:
- to identify TORCH infections, it is necessary to undergo examination a few days after curettage (no later), otherwise there will be no accurate result;
- undergo an examination to determine the level of hormones - progesterone, estradiol, thyroid hormone;
- undergo a pelvic ultrasound several times during one menstrual cycle;
- do an immunogram, immunological examinations, yourself and do the same for your spouse (partner);
- it is necessary to undergo a biocenosis study, sowing the flora of discharge from the genital organs. Determine sensitivity to the main spectrum of antibiotics, bacteriophages;
- identify infections that can be sexually transmitted;
- identify hemostasis indicators Fibrinogen, Prothrombin, Thrombin time, APTT, Antithrombin 3, Lupus anticoagulant;
- identify genetic risks in case of repeat pregnancy;
- determine blood clotting.
Of course, an accurate examination is prescribed by the attending physician. He takes into account the specifics of your case and prescribes the course that you need to take. This is usually from three to six months. You should not plan pregnancy for this period.
Partners, after they have received the results of your histology after a frozen pregnancy, need to carefully monitor their health, lead a healthy lifestyle, and eliminate bad habits and stressful situations. Spend more time outdoors and play sports. A woman needs to avoid heavy exercise, get more rest and eat right.
About the author : Borovikova Olga
Proper preparation for the procedure
At least two days before curettage, it is necessary to exclude:
- sexual intercourse;
- douching;
- washing the external genitalia using cosmetics.
Taking any medications must be agreed upon with your doctor. The fact is that many drugs can affect blood clotting, which can cause serious blood loss after surgery.
The curettage procedure is carried out in the second half of the menstrual cycle, when the woman does not have menstruation. Otherwise, the result may not be entirely correct, and surgery at the beginning of the cycle will provoke prolonged bleeding. This happens because the uterine mucosa grows before ovulation, stops developing closer to menstruation, and then is completely rejected.
If the time of curettage is chosen incorrectly, then the hormones synthesized by the ovaries will come into conflict with the endometrial layer that is unnaturally small for this time of the cycle and will not allow it to grow to the required size.
What is histology?
Histology is the science of the state of the body at the tissue level.
The analysis is closely related to cytology (the study of cells) and embryology (the study of the structure of the fetus) and allows one to study the exact structure of any tissue, so it is often prescribed to identify various abnormalities and pathologies.
To conduct a histological examination, a small piece of tissue is taken from a person: sometimes it is just a smear or print, but it can also be a thin section directly from the organ being examined.
The study lasts on average 5-10 days (in rare cases, urgent histology is performed from 1 to 24 hours, but it is less reliable) and is carried out in 7 stages:
- Fixation - the tissue fragment is treated with a liquid that prevents the breakdown of cells and structures so that the material does not rot during the study.
- Wiring - the material is dewatered for compaction.
- Embedding - The tissue is impregnated with paraffin or another embedding preparation to prepare a solid block for sectioning.
- Cutting - using special equipment - a microtome - the solid block is cut into the thinnest plates.
- Staining - sections are laid out on glass slides and stained with special preparations to determine different tissue structures (DNA, RNA, cytoplasm, etc.).
- Conclusion - the prepared sections on glass slides are covered with a second layer of glass with the medium necessary to preserve the material for a long time.
- Research - the resulting histological preparations are studied by histologists or pathomorphologists using an electron or light microscope.
In gynecology, histology is usually prescribed to study tissues of the fetus, uterus and cervix.
In the USA, many people are vaccinated against HPV, but in our country few people know about it; you can use the link to fill in your knowledge gaps.
Recommendations
After miscarriage and curettage, the first step is a histological examination. Only after receiving the results of this diagnosis will the physician be able to decide on the next steps. To determine the exact cause of the misfortune, additional diagnostic methods may be needed:
- Hormonal blood test of the patient.
- Study on TORCH infection.
- Ultrasound of the reproductive system. Additional examination of the adrenal glands and thyroid gland is possible.
- Immunogram analysis.
- Genetic analysis. We need to study samples from both partners.
- Analysis of sperm activity and viability (for men).
- Vaginal biocenosis, microflora smear.
- Blood chemistry.
- Study of venous blood coagulation.
After histology and a comprehensive study, the patient should undergo treatment that will allow her to fully recover and avoid similar problems during future pregnancies. This therapy can last from 4 to 6 months.
At this stage, you need to use reliable contraceptives. Then both partners must undergo a control examination, and if everything is in order, you can begin planning conception. It is recommended to pay special attention to the emotional state of the expectant mother. You need to experience only positive emotions, forget about the fear of another miscarriage, and tune in to a positive end to your pregnancy.
A miscarriage occurred at 14 weeks. The histology results showed: when examining the placenta, its infectious pathology was established, subchorial intervillusitis +/++, basal deciduitis++, purulent parietal choriodeciduititis +++ with focal necrosis of the membranes, vascular funiculitis +. A pathological examination revealed signs of antenatal fetal death, which may have developed due to maternal pathology and infectious pathology of the placenta. No developmental defects were found in the fetus. I have no idea where this infection came from. Before IVF, I took so many tests, as if they were training to be an astronaut, all the tests were good. In short, I broke my whole head.
Girls, please tell me who has encountered such a conclusion from a histological examination after a spontaneous miscarriage: “Reliable signs of an interrupted intrauterine pregnancy in early gestation.” What could this mean? The miscarriage occurred at 10 weeks 1 day. Before this, I had an ultrasound at 8 weeks 5 days, everything was fine.
Histological examination of a frozen pregnancy or after a miscarriage
A frozen pregnancy in the medical sense is the same miscarriage, it just hasn’t happened yet. In both cases, the doctor cleanses the uterus to avoid rotting of the embryo in the female body, which can lead to inflammation and severe illness.
The extracted material (placenta) must be sent for histological examination.
Histology after a miscarriage in combination with testing for viruses, hormonal imbalance, etc. helps determine the exact cause of spontaneous abortion or fetal death in the womb. Knowing the cause will help you avoid recurrence of problems in your next pregnancy.
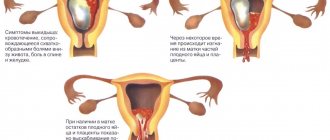
Signs of fetal freezing
In the very early stages of pregnancy, pathology makes itself almost invisible. The expectant mother experiences mild symptoms of toxicosis, breast swelling, and mood changes. Only after a while the symptoms of pregnancy will begin to subside little by little, giving way to pain and bleeding. The latter indicate the beginning of the process of detachment of the fertilized egg and the risk of miscarriage.
A week or two after pregnancy fading, the symptoms of toxicosis will disappear completely, the breasts will become soft and stop hurting, and the basal temperature will drop. All these are signs of fading pregnancy, which a woman can and should pay attention to even before visiting a doctor. At later stages, after the 16th week, when the baby is already making itself felt with kicks and movements, his tragic death is indicated by silence with the absence of any activity inside the womb.
***
In addition to the obvious visual signs of a frozen pregnancy, which a woman may not pay attention to, the problem can be learned from the test results. The supervising doctor should prescribe a blood test for the level of the hCG hormone and an ultrasound.
If the fetus does not develop, the hCG level will be significantly lower than normal. Using ultrasound equipment, the doctor will be able to determine the absence of the baby's heartbeat. Pathology can also be detected during a routine gynecological examination - the size of the uterus will not correspond to the duration of pregnancy.
To eliminate the problem in cases of asymptomatic frozen pregnancy, women are advised to register as early as possible and not miss routine examinations with doctors.
The diagnosis of “frozen pregnancy” leaves no hope for further pregnancy and childbirth. The baby inside the womb has died and must be removed from the uterine cavity as quickly as possible before the decaying tissue enters the mother's bloodstream. Depending on the duration of the frozen pregnancy, the doctor prescribes a method of treatment. It could be:
- medicinal method (the patient is asked to take pills that provoke uterine contractions for arbitrary miscarriage, prescribed for up to 5 weeks);
- surgical intervention with curettage during a frozen pregnancy;
- vacuum cleaning.
In extremely rare cases, when the pregnant woman’s body’s reactions allow it to wait, the doctor decides to give the body the opportunity to independently get rid of the dead embryo. During this period, the woman is under strict supervision to avoid the development of complications.
***
Histology for determining gynecological oncological diseases
It can be very difficult to determine the presence of cancer - often in the initial stages they are asymptomatic, so it becomes almost impossible to notice and manage to prevent their development. However, with regular visits to the gynecologist, it is possible to recognize the emerging disease. During the examination, the doctor will notice symptoms that the woman does not feel and will prescribe a histology of the affected organ.
The study allows not only to identify the pathology, but also to carry out the correct treatment: histology shows the category of the neoplasm - benign or malignant.
Histology of the uterus
To prescribe uterine histology, more noticeable symptoms and other studies (ultrasound, blood tests, etc.) . Symptoms for which histology is prescribed include:
- prolonged bleeding;
- causeless pain in the lower abdomen;
- leukoplakia;
- irregularities on the surface of the organ;
- neoplasms on or inside an organ and other symptoms related to tumor diseases.
Under sterile conditions under local anesthesia, the doctor uses gynecological instruments to cut out a piece of the tumor directly from the uterus. The tissue is sent to the pathology laboratory, where it is examined.
If abnormal tissue areas are detected, appropriate gynecological oncological treatment against cancer is prescribed. If the tumor tissue is homogeneous with the tissues of a healthy uterus, then the disease is benign (most often it is fibroids) and it can either be treated or wait until it goes away on its own (in some cases it does) - the gynecologist reports the exact decision.
Ovarian histology
It is carried out to determine the contents of cystic neoplasms on the ovaries or the type of tumor growths. To select the material, a puncture (puncture) is used through the abdominal cavity.
For many women, “these days” do not go as they should; at this address you will find out how long they should last from a medical point of view.
And by following the link you can find out ways to stop your period altogether.
Histology of the cervix
If inflammatory, precancerous or oncological diseases of the cervix are suspected, the gynecologist sends a small piece of it for histology.
The study helps determine the presence of erosion, dysplasia, flat condylomas, cancer and other diseases of the cervix, so that the gynecologist can prescribe correct and effective treatment.
The material is collected in the same way as from the uterus, but there is no need to dilate the cervix.
Other types of histology in gynecology
For histological examination to identify health problems in the female reproductive system, endometrial tissue, part of the mucous membrane from the cervical canal, and fluid from cystic formations in the vagina taken by puncture can be sent.
Doctors' answers
This result of pathohistological examination of tissues indicates the presence of an inflammatory process (there is a disturbance in the blood supply, increased vascular permeability, edema, excessive formation of cells in the altered area of decidual tissue, a large number of blood cells rush to the site of inflammation, decidual tissue appears with leukocyte infiltration, which at first is of an adaptive nature , but as the process progresses, the tissue becomes saturated with a huge number of leukocytes). Necrosis is the death of local tissue that develops at the site of inflammation when the blood supply to the tissue is stopped and exposed to microorganisms and their metabolic products. In this case, the immune, endocrine, and secretory functions of the membrane are disrupted, and the decidual tissue begins to disintegrate and is rejected. Cyto- and syncytiotrophoblast are elements of the outer layer of cells in embryos at the blastocyst (trophoblast) stage, which ensures contact of the embryo with the maternal body and is involved in the implantation of the embryo into the uterine wall and the formation of the placenta. You need to undergo further examination to identify STIs and opportunistic flora as a source of chronic metroendometritis.
Histology: analysis transcript
When filling out a sheet with research results, they use medical terms that are difficult for ordinary people to understand, and often the most unpleasant things from these terms are written in Latin.
The histology results are sent to the gynecologist, and based on them he will make a diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment. It is not recommended to decipher the analysis yourself, so as not to make yourself think about terrible diseases.
Almost all diseases today are curable, so it is better to rely on a doctor and his experience.
Result
The histological results after curettage and their interpretation are of interest to many patients. Each disease has its own characteristic transformations of the endometrial structure. Typical for persistence of the corpus luteum (long-term existence) are pronounced secretory changes in the glands and a decidual reaction of the endometrial stroma. This occurs as a result of a violation of gonadotropic stimulation of progesterone synthesis.
The results of a scraping study with dysfunctional uterine bleeding indicate hyperplasia (pathological proliferation of normal cells) of the endometrium and the absence of a secretion phase.
With prolonged exposure to low levels of estrogen, scrapings are diagnosed with glandular hyperplasia; this condition often accompanies menopause. It can be cystic - the glands grow in the form of cavities. Atypical hyperplasia involves the presence of enlarged nuclei with a changed shape in the cell, irregularly shaped glands. After menopause, endometrial atrophy occurs.
The occurrence of ovulation is indicated with 90% accuracy by secretory changes in the endometrium, removed during curettage of the uterine cavity two to three days before the onset of menstruation. With the help of histologists, they confirm the diagnosis of a chronic inflammatory process in the uterus, an interrupted pregnancy, determine the presence and nature of polyps, benign and malignant processes.
If the histological results after curettage describe uneven infiltration of glands in combination with damaged fibroblast stroma or a desmoplastic reaction, pronounced aggregation of glands with the formation of a lattice pattern in place of the stroma, its replacement with a large amount of desquamated epithelium - we can talk about a malignant transformation of the endometrium into adenocarcinoma (cancer) .