The effectiveness of oncology treatment depends on the stage at which the disease was diagnosed. Its detection at the beginning of development allows you to avoid undesirable consequences and save the woman’s life. The Rom index is an indicator indicating the presence of benign or malignant tumors. To determine it, a blood sample is sent for testing of tumor markers HE4 and CA125.
What is the Roma Index
In most cases, cancer is detected in late stages. Early diagnosis is considered the key to successful treatment. To assess the degree of risk, it is necessary to undergo an analysis, the result of which will be the Roma index. It is considered the average value of tumor markers CA125 and HE4. The name is an acronym that literally translates as “algorithm for calculating the probability of a cancerous tumor.”
Blood is drawn from a vein. The study is prescribed in the presence of alarming symptoms and in preparation for surgery. Involving two indicators in the study at once reduces the risk of error in the presence of inflammatory processes and age-related changes in the body. Rom's algorithm allows for timely detection of a malignant tumor, thereby increasing a woman's chances of survival. You can find out about the disease long before the first symptoms appear.
The CA125 marker makes it possible to identify the disease at an early stage of its development. It is produced in the epithelial layers of tissues. The marker is produced not only by the ovaries, but also by other internal organs. Therefore, it is involved in the diagnosis of cancer of the liver, pancreas, breast, respiratory tract, uterine and rectal mucosa. An increase in the indicator indicates the presence of cancerous tumors. In this case, additional research is carried out, since a number of factors may influence the result.
Features of the CA125 marker include protein production by the epithelium and low sensitivity. It cannot always be detected at the beginning of the development of pathological processes, therefore the detection of CA125 is usually combined with HE4, which has greater sensitivity.
The level of the HE4 marker increases in transitional cell carcinoma, endometrial and breast cancer. It is impossible to determine a mucinous tumor with its help, therefore, if its presence is suspected, other types of studies are prescribed. An increase in HE4 levels may indicate hormonal imbalances, but it does not respond to inflammatory processes in the body. Additional tests are always required to make a final diagnosis.
Deciphering the analysis for tumor markers and calculating the ROMA 1 and 2 indices
09.11.2017
Deciphering the analysis for tumor markers and calculating the ROMA 1 and 2 indices
The tumor marker or ROMA index is the most accurate way to determine the risk of gonadal cancer in women. It is an algorithm that, based on the ratio of two antigens and depending on the patient’s age, calculates the likelihood of malignant neoplasia occurring in the ovaries.
What is the ROMA index?
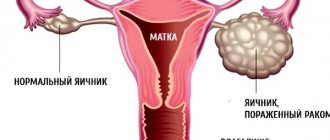
Ovarian cancer is one of the most dangerous cancers in women. As a rule, it does not have specific symptoms and is often diagnosed in late stages, which significantly reduces the chances of successful therapy and 5-year survival rates.
The name of the calculation algorithm is an acronym (“Risk of Ovarian Malignancy Algorithm”), literally meaning “algorithm for calculating the risk of ovarian cancer.”
Calculation of the probability of malignant neoplasia using two ovarian cancer markers at once is used both for patients at risk and in standard diagnostic packages and oncology panels of laboratories.
One of the tumor markers used in the calculation of POMA is CA 125. It is the main antigen of ovarian neoplasia. Its sensitivity in the first stages of gonadal cancer is not high enough for an unambiguous diagnosis, so it is often combined with the more specific and accurate tumor marker HE 4.
The normal concentration of CA 125 does not reach 35 U/ml (the results of patients during pregnancy or menstruation may approach the reference values). In most inflammatory diseases and benign neoplasms, its level does not exceed 100 U/ml.
The normal concentration of HE 4 depends on the patient’s menopausal status: before menopause it does not exceed 70 Pmol/ml, after it it doubles. The second tumor marker is more specific for malignant neoplasms, although it can also give a false-positive result for endometriosis and benign tumors.
The final sensitivity of the double test, taking into account the hormonal status of the woman, reaches 96% of cases of epithelial cancer of the gonads, which occurs in 8-9 out of 10 patients with ovarian cancer.
Thanks to the combination of two antigens, the likelihood of error due to inflammatory processes in the pelvic area and menopause is reduced.
Indications for testing
Calculation of the ROMA index is used not only to assess the effectiveness of treatment and monitor the patient in remission, but also for screening for ovarian cancer. The use of antigens separately is not recommended by experts as an accurate test, especially if the woman is at risk for this disease.
The main indications for testing for the POMA tumor marker include:
- early diagnosis of malignant ovarian tumors (the index increases due to an increase in HE 4, while in benign tumors the concentration of CA 125 or both tumor markers increases);
- predicting the degree of malignancy of a neoplasm in the pelvic area (for benign tumors, the ROMA index does not exceed the reference values, is consistently slightly increased or decreases over time in the absence of therapy);
- determining the effectiveness of surgical treatment of malignant ovarian tumors (in combination with other tests).
To check the effectiveness of a course of treatment, the dynamics of one of the indicators is monitored, but in some cases a full study and calculation of ROMA is used. A decrease in this index demonstrates the effectiveness of the chemotherapy course.
The ROMA test is not performed for patients under 18 years of age or who have previously undergone treatment for cancer.
How is the result calculated?
The formula for calculating the result and the name of the test (ROMA 1, ROMA 2) differs depending on the woman’s menopausal status. The POMA indicator is calculated based on the prognostic index, which, in turn, already depends on the concentration of tumor markers CA 125 and HE 4.
PI 1 (before menopause) = - 12 + 2.38*Ln(HE concentration 4) + 0.0626* Ln(CA concentration 125), where Ln is the natural logarithm (the degree of exponentiation to obtain the specified value).
PI 2 (after menopause) = - 8.09 + 1.04*Ln (HE concentration 4) + 0.732* Ln (CA concentration 125).
The calculation of the final index for tumor markers ROMA 2 and ROMA 1 occurs according to a single formula:
ROMA = (exp(PI1,2)/[1 + exp(PI1,2)]) * 100, where the exp indicator is raised to the power of the prognostic index.
In premenopause, the POMA index should not exceed 11.4%. After menopause, the reference value rises to 29.9%. Depending on the limits used for the concentration of each tumor marker, the norm for the ROMA index can vary from 7.39% (25.29) to 12.9% (24.7). Reference values are indicated in a special column for analysis results.
If these indicators are exceeded, the question arises of more detailed diagnostics, which includes ultrasound of the pelvic organs, CT, MRI and biopsy of tumor tissue if a neoplasm is detected by hardware examination.
An additional and less common (due to greater labor intensity) algorithm for calculating cancer risk is OVA1. To determine it, 5 indicators are required: concentrations of tumor marker CA 125, transferrin, alipoprotein A1, microglobulin B2 and prealbumin. Typically, a comprehensive comprehensive evaluation is used after surgery for ovarian cancer.
The concentration of tumor markers is determined using the immunoelectrochemiluminescent technique. The reliability of the analysis depends entirely on the characteristics of the test systems and the correct implementation of the research protocol by personnel. It is very important to carry out the analysis in the same laboratory, because a change in the average level of errors may be reflected in the dynamics of the index.
Rules for taking the analysis
As with other types of studies for which venous blood is taken, patients are prohibited from eating any food for 8 hours before taking biomaterial and are advised to report all medications they are taking. If they are not vital medications, you should completely avoid their use 2 days before the test.
Within a few days, a woman needs to stop drinking alcohol and eating foods that irritate the gastrointestinal tract (spicy, fried and fatty foods, smoked foods). Immediately before the test, you can drink only still water. You must stop smoking 3 hours before blood sampling.
The analysis should take place in a state of physical and psycho-emotional peace. It is recommended to eliminate heavy physical activity and stress for 1-3 days.
Despite the fact that the POMA analysis is often performed after detection of neoplasia in the pelvic area, in parallel with other clarifying studies, it is necessary to take a break for the test. For 1-3 days before laboratory diagnostics, MRI, CT, ultrasound, radiography and physiotherapeutic procedures cannot be performed.
Timely diagnosis using the highly accurate ROMA algorithm is a chance to detect a malignant tumor at an early stage and increase the patient’s chances of survival. A woman’s task is to regularly undergo preventive examinations (studies) and follow all the rules of preparation for them.
Published at Tue, 07 Nov 2021 16:31:10 +0000
(0, average: 5 out of 5)
Source: https://clinicsisrael.com/article/rasshifrovka-analiza-na-onkomarkery-i-raschet-indeksov-roma-1-i-2/
Roma Index in Gynecology
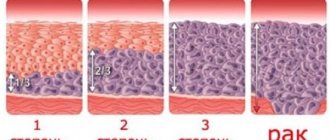
Most often, this method of assessing women's health is used in the field of medicine, which studies ailments associated with the reproductive system. Ovarian cancer is a common disease with an increased mortality rate. If the development of the disease is detected at an early stage, the probability of a positive treatment outcome increases to 90%. The Roma Index helps to diagnose ovarian cancer in time and take appropriate measures. The need for analysis is confirmed by the following statistical data:
- A favorable prognosis when cancer is detected at the first stage is 90%. During this period, the disease is diagnosed in 30% of cases.
- On the second, cancer is detected even less often - only in 10%. The probability of a positive outcome is 70%.
- In most cases (about 60%), cancerous tumors are detected precisely at the third stage of development, when the survival rate decreases. It is 40%.
- Women with the fourth visit a doctor in 17% of cases. The chances of a complete cure are much lower. They make up less than 25%.
What does the Roma 1 indicator consist of?
To determine Roma 1, you need to test your blood for the presence, concentration and ratio of two substances in it. Moreover, this is done in dynamics, since temporary changes in the indicator or their absence are important.
The need to determine it is caused by the presence of a benign neoplasm on the ovaries or other gynecological pathologies in which the likelihood of cancer is increased. In premenopause, a drop in the level of sex hormones can provoke cell degeneration if a tumor already exists, or there are other factors favorable for pathological changes. Blood for roma 1 is taken from a vein; the patient must not eat for 8 hours before collection.
CA 125
Atypical cells that form in healthy ovarian tissues reveal themselves in blood tests. The presence of tumor marker CA 125 is read in the biological fluid. This is a substance that the body increases when cancer cells appear in the tissues of the gonads. What is dangerous regarding the occurrence of ovarian malignancy is not the presence, but the increase in the level of the indicator in a short time.
Its detection is not a 100% method of detecting cancer. Without a refined analysis of Roma 1, the calculation of CA 125 before menopause may give a false positive result in the following cases:
- Pregnancy up to 12 weeks. This is possible in premenopause, when rare menstruation causes a woman to lose her vigilance and take less careful precautions;
- The presence of various types of inflammation in the uterus and appendages;
- Endometriosis;
- Adhesive process in the pelvic area.
Another substance is present in the female body - HE 4, which is a protein of the epidermis. It is produced by the epithelium of the upper respiratory tract and tissues of the reproductive organs in minimal quantities, but production increases in response to the appearance of atypical cells in certain parts of the body.
If elevated HE 4 values are detected, a false diagnosis may also be made, since this happens when a benign ovarian tumor and renal failure are combined, as well as:
- Myoma;
- Inflammation in the pelvic area;
- Hepatitis or cirrhosis.
A mucinous tumor, on the contrary, does not cause an increase in the concentration of the protein compound. And relying only on it, it is easy to start the process of its development.
Indications for the procedure
Analysis for tumor markers is not carried out as part of a regular preventive examination. It is prescribed for patients with an increased risk of developing cancer. In some cases, testing is necessary after removal of benign or malignant tumors. Constant monitoring helps prevent possible complications. The following indications for testing are noted:
- menopause period;
- hereditary factor;
- preparation for genital surgery;
- presence of malignant tumors in the anamnesis;
- long-term use of oral contraceptives.
A woman can also get tested at her own request. Timely care of your health helps to detect the development of pathological processes and increase the chances of a positive outcome. Doctors recommend diagnosis at least every five years. Mature women should be tested for tumor markers more often.
Tumor marker: roma index indicators in premenopause and postmenopause
During the menopausal period, female organs are constantly at risk of getting diseases. A woman is plagued not only by inflammatory problems of the reproductive system, but the possibility of oncological problems increases. Cancer is not easy to detect and can be noticed in later stages. But the roma premenopause index allows you to find out the presence of a tumor at the beginning of growth, that is, at a time that is favorable for recovery.
How to prepare
The reliability of the result depends on compliance with certain rules. The biomaterial is collected on an empty stomach in the morning. If a woman visits the treatment room during the day, at least four hours must have passed since her last meal. If you have psycho-emotional disorders, you must first consult with a specialist, since the result of the analysis in this case may be distorted. The principles of preparation are as follows:
- You must stop drinking alcohol 5 days before the test.
- The day before visiting the treatment room, it is recommended to avoid sexual intercourse.
- Drawing blood during menstruation is strictly prohibited.
- You should stop smoking 12 hours before donating blood.
- The day before the procedure, you should not eat heavy or fatty foods.
- If drug therapy is carried out, the study must be rescheduled for another time.
- It is advisable to limit physical activity the day before.
Carrying out Roma1 analysis
Blood for this analysis is taken from a vein on an empty stomach. The doctor prescribes the order of repeated tests, because the definition of the disease must be in the dynamics of time. Blood serum analysis is carried out by any gynecology laboratory. An accurate test result requires following the following rules before drawing blood:
- morning time: from seven to eleven o'clock;
- do not eat for 8 hours before the test;
- exclude alcohol, smoking, fried and fatty foods;
- be in a calm spirit, do not be nervous;
- do not exert too much physical effort;
- the doctor must know about the medications the patient is taking;
- ultrasound examination, radiography, magnetic resonance imaging are excluded; – all these conditions for several days.
The analysis is carried out quickly - within a day, in some clinics - within three days.
Rules for taking the analysis
The cost of a blood test for tumor markers ranges from 550 to 1000 rubles. It includes the price of reagents and the work of medical personnel. Research is not carried out in government institutions. Blood sampling is carried out in the treatment room of specialized clinics. The patient is placed in a chair with an armrest. Using a sterile syringe, blood is drawn from a vein. For 15-20 minutes after the procedure, you must keep your arm bent.
The test is not prescribed for cancer patients, persons under 18 years of age, and those with a rheumatoid factor level of 250 IU/ml. The test result will be ready 1-3 days after blood sampling. It is carried out using the immunoelectrochemiluminescence method for assessing blood serum. The reliability of the data depends on the qualifications of the personnel and the serviceability of the test systems. If a questionable result is obtained, the analysis is repeated. To prevent errors, the study is carried out in the same laboratory.
What it is
Tumor markers are protein indicators in the human body that indicate the likelihood of a person developing cancer. ROMA 1 is a tumor marker that is most often used in the field of gynecology. It indicates pathological processes in the epithelial part of the ovaries.
Note: this test can also be used as an additional method for diagnosing pancreatic, breast, uterine, and lung cancer.
To carry out the analysis, venous blood is taken. Next, it is necessary to identify the presence of specific protein compounds - HE-4 and CA-125, which in large quantities indicate oncology. Their ratio, calculated using a special formula, is the Roma index.
For the study, blood is drawn from a vein.
Decoding the results
The diagnosis is made by a gynecologist or oncologist based on the data obtained. The Roma index is calculated using special formulas. They vary depending on the phase of menopause and the age of the woman. It is quite difficult to make calculations on your own. An increase in the indicator does not always indicate the presence of cancerous tumors. The following factors can provoke an increase in CA125:
- liver diseases;
- cystic formations in the ovaries;
- pregnancy;
- pathologies of the thyroid gland;
- infections in the genital tract;
- endometriosis;
- appendicitis.
An increase in HE4 almost always indicates the presence of malignant tumors. But in some cases it is the result of impaired kidney function, cirrhosis of the liver or the formation of fibroids. A diagnosis cannot be made based on data from one of the indicators. Both parameters need to be assessed. A false negative result is rare. It is possible only in the early stages, when the malignant tumor does not produce cells.
The doctor makes a conclusion about the patient’s health only after receiving the results of other studies. These include ultrasound monitoring of the pelvic organs, biopsy and gynecological examination. If the study was carried out in preparation for surgery, then the woman’s hereditary predisposition to cancer is determined. Surgical intervention is possible only if the woman does not have any problems.
ROMI calculator
ROMI (Return on Marketing Investment) is an indicator of the profitability of advertising campaigns and overall investments in marketing. Calculated using the formula: ROMI = (Advertising Revenue - Advertising Expense) / Advertising Expense * 100%.
Enter the values below and the free calculator will easily calculate the total value online.
- Save link
- Send to colleagues
In marketing, ROMI is used to calculate the effectiveness of advertising campaigns minus marketing costs. Investments in promotion will be considered justified if the final indicator is positive. The purpose of ROMI is to measure the extent to which marketing expenditures contribute to profits.
Now the metric is actively used to measure the impact of Internet promotion. However, it migrated precisely from classical marketing. The ROMI concept first gained prominence in the 1990s.
There are two forms of marketing ROI:
- Short term . Measured as a simple assessment of the effectiveness of each dollar invested in marketing channels;
- Long-term . Used to determine the added value of marketing in the overall process of promoting a brand or introducing a new product to the market, increasing awareness, increasing the share of presence and coverage.
Long-term ROMI models are often used in parallel with customer lifetime value (LTV) models to demonstrate the long-term value of incremental customer acquisition or reduced churn rates. Some more sophisticated approaches involve multi-year long-term ROMI, including CLV-type analysis.
What is considered normal ROMI?
The difficulty of measuring ROMI varies depending on the business sector. Findings from a recent US study show that ROI on media (such as TV and radio) is more difficult to measure than on digital channels such as PPC, email marketing or social media marketing.
Since the early 2010s, the first SaaS platforms for corporate use began to appear, which automate calculations and help marketers measure ROMI in real time for various business sectors and communication channels with the target audience.
The difference between ROMI and ROI
Many still do not see the difference between the two metrics, although a correct assessment and correct understanding of the differences between ROMI and ROI (Return On Investment) can save a campaign from negative dynamics and scaling of losses.
The confusion arose because the term ROI is more general, while ROMI is more universal for marketing, as it relates specifically to advertising investments. Marketers do not always take into account financial and accounting expenses, warehouse balances, logistics, office rent, salaries, etc. in their calculations.
Examples
You can calculate ROMI using two values known to business:
- Profit from the results of advertising activities;
- Costs of advertising activities.
Let’s say you invested 1,000 rubles in advertising, and received 2,000 rubles as a return. The return on investment was 100%. If you receive only 1500 rubles - 50%, and earned 3000 rubles - already 200%.
Important! Strive for constant growth and increasing the dynamics of the coefficient. A negative index indicates that the marketing program is not profitable, i.e. funds invested in advertising are not returned.
How to increase ROMI
Some obvious tips to improve your results:
- Improve the quality of your advertisements - work on your click-through rate (CTR);
- Increase website conversion: from optimizing landing pages to advertising channels;
- Constantly work with clients and analyze at what stage the deal failed, identify the reasons, find bottlenecks in the sales funnel;
- Analyze current campaigns and distribute the budget taking into account the effectiveness of campaigns / ad groups / individual key phrases;
- Expand your semantic core based on the analysis of key phrases that can bring in new customers.
ROMI allows companies to analyze segments whose returns are not worth the investment and distribute investments in promising areas.
Norm and deviation
The Roma index rate ranges from 11.4% to 29.9%. Premenopausal women are at risk with rates above 7.4%. In postmenopause, the possible development of oncology is indicated by a result of more than 25.3%. When interpreting analyses, various nuances are taken into account. If the indicator decreases over time, then the neoplasm is benign. An increase in the index over time indicates the presence of cancer. The results of ultrasound, biopsy, laparoscopy and additional tests are of great importance in making a diagnosis. Borderline indicators require special attention from women in relation to their health. In this case, there is a risk of developing cancer in the future. It is advisable to carry out additional diagnostic procedures to ensure the absence of a tumor.
Norm of the ROMA index for women, table and explanation
According to the current instructions of the World Health Organization, the ROMA index is deciphered as follows:
- Roma index 1 - premenopause (age of reproductive activity) - permissible rate up to 7.39%;
- Roma index 2 - postmenopause (after the extinction of reproductive activity) - the permissible rate is up to 25.29%.
That is, in premenopausal women, an index below 7.39% indicates a low risk of epithelial (superficial) ovarian cancer, above 7.39% indicates an increased risk .
Similarly, in postmenopausal women, an indicator of up to 25.29% indicates a low risk, and above 25.29% indicates a high risk. Naturally, these indicators are not a reason for making a final diagnosis, but in 90% of cases the preliminary result is subsequently confirmed.
(The picture is clickable, click to enlarge)
Tumor markers
Tumor markers are substances secreted by a tumor that appear in the blood of a cancer patient. A tumor marker consists of hormones, proteins, antigens and metabolic products. This is a kind of indicator that shows the likelihood of cancer. The tumor marker also determines the tumor structure and stage of development.
Using this test, you can determine treatment methods not only for cancer, but also for inflammatory processes. Elevated blood test results for the level of tumor markers indicate the likelihood of disorders in the ovaries or other pelvic organs with a suspected oncological genesis.
To identify a malignant neoplasm, the following is usually used:
- the main ones are CA-125 and CA 19-9 (normal result is from 9 to 37 units/ml.);
- secondary - HE-4;
- additional – AFP and CEA (CEA).
Tumor marker CA-125
CA-125 is a type of tumor marker found in the blood of every person.
Its level in the blood increases with cancer and for some other reasons. This antigen is found in the uterus, endometrium, ovaries, eye tissues, intestines, stomach, pancreas, kidneys, and bronchi. In rare cases, in the first trimester of pregnancy it is found in blood plasma and breast milk. CA-125 increases in the initial stages of disease development only in 50% of cases. Using this tumor marker or in combination with other markers, the presence of cancer in the mammary gland, uterine mucosa, respiratory organs, rectum, liver, and stomach is determined.
For example, if there is no pathology, the analysis will show a CA-125 level of 10 to 15 units/ml. The normal level of this tumor marker in women in the absence of cancer is allowed up to 35 units/ml. Exceeding this CA-125 value indicates the presence of a cancerous tumor in the body.
A high level of this marker in the blood can also occur in some other diseases:
- ovarian cyst;
- pleurisy of the lungs;
- inflammatory or infectious diseases of the female reproductive system;
- liver diseases;
- purulent appendicitis;
- pregnancy;
- bleeding;
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland;
- endometriosis.
Therefore, an increase in CA-125 levels does not always accurately indicate a malignant neoplasm in the ovaries. But a comprehensive examination will help to accurately determine the cause of the high level of tumor marker in the blood.
Need to know! The level of tumor marker CA-125 for ovarian cancer is above 130 units/ml. In order for the result to be more accurate, it is combined with the level of another tumor marker - HE-4.
Tumor marker HE-4
What is HE-4 tumor marker?
This is a protein found on the mucous membrane of the epithelium of the testicles, epididymis, endometrium, fallopian tubes and respiratory organs. This tumor marker is very susceptible to tumor cells. The level of its content in the blood increases greatly when oncological tumors appear in the body. Among other tumor markers, HE-4 is most suitable for identifying cancerous tumors in the ovaries. A high level of this tumor marker in the blood at the very initial stage of cancer development is observed in more than 95% of cases, and its sensitivity to malignant cells is 85%.
An increase in HE-4 levels confirms the appearance of a malignant tumor in the ovaries, uterine and breast cancer. In some cases, the reason for the elevated levels of this marker is not related to cancer.
False-positive test results for HE-4 determination occur in the following diseases:
- benign tumor in the ovaries;
- uterine fibroids;
- inflammatory process in the female genital organs;
- cystic fibrosis;
- hepatitis;
- renal dysfunction;
- cirrhosis of the liver.
The main advantage of the HE-4 tumor marker is that its level in the blood increases two to three years before a cancer diagnosis is made. HE-4 does not detect mucinous tumor. In the presence of such a neoplasm in the body, the content of this marker in the blood does not increase.
HE-4 levels depend on the menstrual cycle or menopause and are calculated in picomoles per liter. In patients under 45 years of age, the blood level of this tumor marker is normally 60 pm/l. In women aged 50 years and older, the level of indicators is up to 121 pm/l.
A distinctive feature of HE-4 is its very high sensitivity to malignant tumors in the initial stages of development, and CA-125 - in the later stages of the oncological process. The combination of these two tumor markers allows us to achieve maximum sensitivity for detecting cancer in the first two stages and prevent possible relapses.
Early diagnosis method
The speed of recognition of a malignant process in a woman’s body is the key to preserving her life. Thanks to the method of calculating the level of the Roma index, it is possible to make an earlier diagnosis of such a formidable disease as ovarian cancer.
Using the results of the CA 125+HE4 analysis and the algorithm for calculating the prognostic index (PI), it is possible to assess the risk of epithelial ovarian cancer.
The components included in the index calculation formula are each responsible for their own functions:
- HE4 - this tumor marker is synthesized in the body of a healthy person in structures such as epithelial cells of the upper respiratory tract, tissue elements of the reproductive organs, including the ovaries. In its structure it belongs to epidermal proteins. The substance is highly sensitive to the cellular elements that the neoplasm produces. Accordingly, an increase in this tumor marker indicates a high risk of developing ovarian damage. Determining HE4 is invaluable, as its levels rise 2-3 years before ovarian cancer is diagnosed.
- CA125 are atypical cells that are synthesized in the tissues of a healthy ovary and are not highly sensitive in the early stages of the tumor process. In more than 80% of cases, there is an increase in its concentration levels in later stages. The levels of this marker increase approximately 8–10 months before the disease is diagnosed.
The significance of the analysis
The value of the Roma Index study is great. Since in 70-75% of cases a malignant tumor in the ovaries is diagnosed late, then
It is extremely important to carry out effective diagnosis in a timely manner. After all, according to WHO, only up to 30% of women live more than a year.
Despite advances in medicine, the prognosis for ovarian cancer remains dismal:
- Stage 1 – detected in a maximum of 30% of cases, has the most favorable prognosis in terms of five-year survival – up to 90%.
- Stage 2 – determined in up to 10% of cases, prognosis up to 70%.
- Stage 3 – almost 60% of patients apply during this period, when it is often too late. The survival rate is not even 40%.
- Stage 4 – accounts for up to 17% of cases of detection and a dismal prognosis for five-year survival – less than 25%.
Only early diagnosis will allow effective and efficient treatment to begin, because the calculation of the Roma index determines the process:
- Which in the early stages is not amenable to any diagnostic methods.
- In women who already had a history of malignant neoplasms.
- Treatment assessments.
When using Roma index indicators, the sensitivity of the study is almost 93%, and the specificity is 76% in postmenopausal women.
During perimenopause, sensitivity is 100% and specificity is up to 75%. It must be taken into account that such indicators are typical only when determining epithelial ovarian cancer.