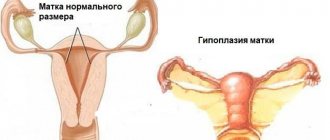
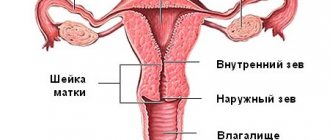
What is the cervical canal?
The cervical canal is the transition from the vagina to the body of the uterus; it has a conical shape with a hole in the center through which the vagina communicates with the uterus. Normally, the length of the canal is 3–4 cm; it is part of the cervix. The external os of the canal exits into the vagina, and the internal os into the uterine cavity.
One of its main functions is protecting the uterus from infections and pathogenic microorganisms; cells located inside the canal produce mucus, its consistency is determined by the stage of the cycle. Mucus at the beginning and end of the menstrual cycle is more viscous with increased acidity; most microorganisms do not survive in such conditions. In the middle of the cycle, the level of estrogen increases, and the mucus changes its structure, becoming more liquid with an alkaline environment. During these few days, sperm have a chance to enter the uterus and meet the egg there.
If pregnancy occurs, under the influence of the hormone progesterone, a plug is formed from the mucus in the cervical canal, which protects the fetus from infections from the outside.
What should not be in a smear?
The presence of certain impurities or pathogens in the smear may indicate the development of severe pathological processes.
Good indicators should exclude the following:
- Increased content of destroyed epithelial cells. This pathology may be a sign of inadequate growth in the number of lactobacilli.
- Key cells. They are epithelial cells inhabited by various pathogenic microorganisms.
- Parabasal cells. An increased content of these cells may indicate the development of an inflammatory reaction or atrophic changes occurring in the vaginal mucosa.
- Abnormal content of pathogenic flora.
- Yeast-like cells. Their presence may indicate the development of thrush.
- Anaerobic bacteria (strict). These pathogens are causative agents of various genitourinary diseases.
- Gonococci. This class of pathogens is the causative agent of gonorrhea.
- Trichomonas. Under the influence of microorganisms, trichomoniasis occurs.
- Atypical cells. The presence of these cells indicates the development of cancer.
To identify some microorganisms, additional blood testing is required, since a microscope is not able to identify all types of bacteria due to their small size.
What is bacterial culture from the cervical canal?
A culture tank is the same as a smear, only it is taken not from the walls of the vagina, but from the opening of the cervical canal. This type of test is not preventive; it is prescribed by a doctor due to elevated white blood cells in a regular smear.
An increased number of leukocytes is a sign of an infectious disease occurring in a woman’s body and requiring immediate treatment.
Also, sowing is required when planning a pregnancy, if sexually transmitted diseases are suspected, in case of infertility, or when registering for pregnancy.
The inoculation is taken using a sterile brush and placed in a flask, into which no foreign microorganisms from the external environment should get. After this, the analysis is sent to the laboratory.
There is no need to be afraid of this procedure; it is not painful at all and is safe. This test is also safe for pregnant women.
IMPORTANT! To obtain a reliable test result, you must abstain from sexual intercourse, do not use vaginal contraceptives, douche, or use perfume gels for intimate hygiene for at least 24 hours. If you have taken antibiotics, the test is prescribed no earlier than 2 weeks after you stop taking the medications.
When is a smear taken for flora in women?
The content of the article
Laboratory testing for the microflora of the genital tract is recommended for every woman to undergo at least once every 6-12 months. Usually, the gynecologist takes material for analysis at each examination of the patient. This is an important preventive measure that allows you to identify hidden infections and other pathologies at an early stage.
The analysis is also prescribed when the following symptoms appear:
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- itching, dryness, burning of the external genitalia;
- pathological discharge from the vagina - blood, pus, leucorrhoea with an unpleasant odor;
- discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- long-term treatment with antibiotics, hormones, cytostatics;
- preparation for pregnancy;
- participation in the IVF program;
- change of sexual partner;
- casual sexual contact with a stranger.
Stomachache
Change of partner
During pregnancy, a smear for the flora is taken from women at least 3 times. This is necessary for the early detection of hidden infections that have a negative impact on fetal development.
How is the analysis done?
In the laboratory, the material is transferred from a test tube to a Petri dish, into conditions that are comfortable for it to develop and reproduce. After 3–5 days, the colony of microorganisms grows in quantities sufficient for diagnostic studies. An antibiogram is also immediately performed to determine the sensitivity of bacteria to antibiotics so that the doctor can prescribe effective treatment.
The bacteriological culture indicator is considered positive when the analysis shows the presence of pathogenic microflora. These indicators are divided into 4 degrees according to the speed of growth and development:
- First degree - scanty growth of microorganisms is present only in a humid environment.
- Second degree - microorganisms of the same type on a solid medium show growth of up to 10 colonies.
- Third degree - the number of colonies on a solid medium reaches 100.
- Fourth degree - the number exceeds 100 colonies.
The third and fourth degrees indicate that there is no infection in the body.
Tank culture is the gold standard in identifying infections; it can be used to identify not only acute, but also latent infections. It is able to identify not only pathogens, but also determine their activity and quantity.
This diagnostic method determines the sensitivity of microorganisms to antibiotics.
An antibioticogram is a complete list of antibacterial drugs to which the isolated bacteria are susceptible.
To identify antibiotics to which the detected microorganism will be vulnerable, 2 methods are used:
- diffusion method - test strips soaked in an antibiotic solution are used. The strips are immersed in a nutrient medium with microbes and the changes are observed;
- standard disc method - special discs impregnated with antibacterial drugs are placed in containers seeded with pathogenic microflora; if the growth of microbes stops, then it is sensitive to this antibiotic. To clarify the level of vulnerability, the diameter of the zone of growth arrest is measured.
What to do if you have a bad smear?
A bad smear in gynecology indicates a number of diseases that need to be treated in a timely manner.
If there are deviations, you must contact a specialist to prescribe therapy. Treatment is carried out comprehensively. Drugs or additional procedures are selected individually, based on the identified disorder.
Treatment with drugs
The use of drugs is an integral part of therapy. In this case, treatment should be comprehensive and include several groups (combination therapy).
Preparations:
- Antibacterial agents. This group includes antimicrobial drugs, the action of which is aimed at suppressing the activity and reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms. Oral forms: Amoxiclav, Trichopolum, Metronidazole. Suppositories (vaginal): Hexicon, Polygynax, Terzhinan.
- Drugs that regulate the balance of vaginal microflora. This group of medications helps restore the acidic environment in the vagina. Moreover, the products have a pronounced antiseptic effect. The most popular drug is vaginal suppositories Vaginorm-C.
- Combined hormonal contraceptives. This group also includes drugs prescribed as hormone replacement therapy. Medicines help increase local immunity and restore hormonal balance.
- Probiotics and prebiotics. This group of products allows you to restore the intestinal microflora and increase the number of lactobacilli in the vagina.
- Phytoestrogens. These drugs are a herbal analogue of hormonal drugs. However, their effect is less pronounced. At the same time, the duration of treatment with this group of drugs increases significantly. List: Remens, Qi-Klim.
The dosage and duration of therapy is established by the treating specialist in each case separately based on the severity of the pathological process and other physiological characteristics of the patients.
Treatment with folk remedies
A bad smear in gynecology can be corrected using traditional methods of treatment. However, such products must be used in combination with medications.
The most popular and effective methods of treatment are lotions made from honey, sea buckthorn and kefir.
All ingredients are mixed and then applied to a cotton swab or pad. The affected areas are lubricated with a tampon 1-2 times a day. The duration of the course is until all symptoms are completely eliminated.
Another effective way to treat thrush, vaginosis and other gynecological diseases is douching with a chamomile solution. The plant has a pronounced antiseptic, soothing and anti-inflammatory effect.
To prepare the decoction you need to take 2 tbsp. l. dried flowers and fill it with 1 liter. boiled water. Then the resulting mixture should be placed on low heat and wait until it boils. For a more pronounced effect, it is recommended to use chamomile together with calendula in a 2:1 ratio.
After the mixture has cooled, it must be strained. For douching, it is recommended to use a special pear or Esmarch mug. To treat vaginal dysbiosis, you can use 1% hydrogen peroxide. Douching must be done 2 times a day.
Duration of use is 1-1.5 weeks. This method helps to quickly eliminate unpleasant symptoms and discomfort and restore the microflora. If you develop any negative symptoms caused by home treatment, you must stop further use.
Before using traditional methods, you should first consult with your gynecologist. If the results of a smear test are poor, you should immediately contact a specialist to prescribe treatment.
All gynecological diseases require a comprehensive therapeutic approach and careful monitoring by a doctor. With proper adherence to treatment rules, the prognosis for complete recovery is favorable in most cases.
Decoding the result
When the analysis is ready, the woman will receive a result form. The analysis form indicates which microorganisms and in what quantity were found in the cervical canal of the subject. If everything is normal, then the analysis will show the absence of fungi and the presence of bifidobacteria and lactobacilli in an amount of at least 107 colonies. It is also considered normal to reproduce E. coli in an amount of no more than 102 and a single number of enterococci.
A smear is considered pathogenic if it contains a large number of enterococci and E. coli, staphylococcus, proteus, yeast, gonococcus, gardnerella, trichomonas, and citrobacter.
Ureaplasmosis, mycoplasmosis and chlamydia invade inside the cell and are not detected by bacteriological culture. To identify these infections, a PCR test is performed.
Cervical canal fusion
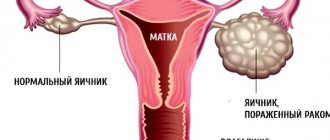
Overgrowth of the cervical canal can be congenital or acquired. Overgrowth (atresia) of the cervical canal leads to partial or complete closure of the walls of the opening and prevents the passage of menstrual blood.
The causes of atresia can be:
- infectious diseases suffered in childhood (diphtheria, mumps);
- poor quality scraping;
- damage by cancer;
- traumatic birth;
- abortion injuries;
- damage by endocervicitis;
- cauterization of the cervical canal;
- advanced inflammatory processes of the internal genital organs;
- elderly age.
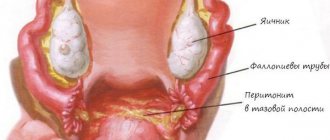
Primary atresia is diagnosed during the first menstruation without finding a way out; menstrual blood accumulates in the uterus and stretches it, the girl feels a general deterioration in health and if she does not consult a doctor in time, the blood further spreads through the fallopian tubes and can cause purulent inflammation.
Acquired (secondary) atresia is diagnosed when a woman consults a doctor about infertility. Stagnant blood clogs the tubes, and the egg does not have the opportunity to enter the uterine cavity. The diagnosis can be established using ultrasound, hysterosalpingoscopy, MRI, and sounding. This pathology is treated by bougienage of the cervical canal.
The bougienage operation is performed in a hospital and takes about 30 minutes. If the infection is complete, then the manipulation is performed under general anesthesia, and if not significant, then under local anesthesia. After the operation, if general anesthesia was used, the patient is discharged for home treatment the next day, and with local anesthesia, the patient is released on the day of the operation. The duration of home treatment lasts 10 days, wound healing drugs and anti-inflammatory suppositories are prescribed.
How to prepare for manipulation?
A smear is made to check the vaginal flora and its sterility, which in principle should not be the case; the study allows one to exclude pathological microorganisms and clarifies the cellular background of the organ. In addition, a cytology smear is used after a PAP test for atypical cells and latent infections (PCR). In all cases, the true cellular composition is studied in order to make a correct diagnosis, so during preparation there is no need to “clean” the genitals by douching or use suppositories “for treatment.” In a couple of days, it is necessary to exclude sexual contacts so that only the female’s own cells are present without the cellular “contribution” of the partner. On the day of the planned collection of material, no personal hygiene measures are taken; the woman comes “as is”; 2 hours before the procedure itself, you should refrain from urinating. As such, there are no contraindications to taking a smear; during menstruation, the picture is not objective due to the abundance of blood cells, so menstruation is the wrong time for diagnosis.
Thickening of the cervical canal
In a woman of reproductive age, the opening of the cervical canal is 7–8 mm wide, which is enough for the removal of menstrual blood and for the penetration of sperm into the uterus.
During the reproductive period, expansion of the pharynx occurs in the middle of the cycle, which is absolutely normal and is associated with approaching ovulation.
With age, a woman’s body undergoes various changes, and the reproductive system also becomes different due to changes in hormonal levels. You need to monitor your health during menopause even more carefully than before. During this period, various diseases, including deadly ones, may appear.
During the examination, some women find that the opening of the canal is greatly expanded, which is a sign of some gynecological disease that needs to be urgently diagnosed and treated.
The cervical canal plays a huge role in the functionality of a woman’s internal reproductive system. This organ takes an important part in the process of childbirth and is of great importance for carrying a pregnancy.
To prevent the appearance of abnormalities in the cervical canal, it is imperative to undergo routine examinations with a gynecologist. Never self-medicate if any ailment occurs!
In addition to attentiveness and accuracy to the patient’s health on the part of doctors. Every woman should take her health seriously. If a woman leads a healthy lifestyle, attends antenatal clinics on time, does not have bad habits, and does not have a promiscuous sex life, her risk of developing inflammatory diseases is much lower.
Video: bacterial culture from the cervical canal
Sowing tank
How do they take a smear for the flora of women?
The collection of biological material is performed by a gynecologist during an examination of the patient in a gynecological chair. In this case, the specialist uses a sterile glass spatula with a wide tip. Speculums are inserted into the lumen of the woman's vagina, after which the secretion of the mucous membrane of the vaginal walls is taken with a spatula. The resulting material is evenly distributed over a sterile glass slide and fixed with a special solution. The glass is marked V, which stands for vagina. The procedure is repeated for the cervix and urethra.
During the collection of material, the patient does not experience pain or discomfort. If discomfort occurs, you should inform your doctor.
Collection of biological material
If the patient needs to examine a smear from the cervical canal for oncocytology, a small brush is used for collection. Rotational movements help remove the top layer of cervical cells. This procedure may cause mild pain and bleeding after collection.