Certain types of cancer lead to characteristic changes throughout the body, including at the molecular level. Such changes can be detected using relatively simple laboratory tests for tumor markers. With certain malignant tumors, an increase in one or another indicator is observed. In particular, carbohydrate antigen 125 (or CA-125) makes it possible to suspect ovarian cancer and some other oncological pathology, as well as monitor the patient’s condition after treatment has already been carried out.
CA 125
The presence of the CA 125 marker (high molecular weight glycoprotein) is present in the body of any healthy person, although it is extremely small. In medical circles it can be heard under the name carbohydrate antigen 125, cancer antigen CA 125. The following body tissues have the presence of this antigen:
- endometrium of the uterus;
- the fallopian tubes;
- ovaries;
- pericardium of the heart;
- pleura of the lungs;
- pancreas;
- gallbladder;
- kidneys;
- bronchi;
- stomach;
- intestines.
With various inflammations or tumor formation, the amount of the CA 125 marker increases, and by analyzing blood or organ tissue, the presence of the disease can be determined. The resulting cyst or tumor begins to rapidly grow the CA 125 protein. This makes it possible to use testing for this substance to confirm the presence of cancer.
Norm CA 125
In the body of a healthy woman, the level of the CA125 marker ranges from 11 to 15 U/ml; during menstruation there is an increase to 35 U/ml. During menopause, the amount of protein is no more than 20 U/ml.
The reason for this is a drop in estrogen production, and as a result, the inactive endometrium of the uterus and ovaries. In women who have undergone surgery to remove female organs, regardless of age, artificial menopause begins, and normal CA 125 numbers do not rise above 5 U/ml. Menopause with elevated CA 125 can mean a fairly wide range of problems.
Ovarian cancer
Ovarian cancer ranks fifth among cancer problems of the female organs, ending in death in forty-five percent of cases.
Menopause is a dangerous time for this disease to occur. It mainly affects women between 50 and 75 years of age. Symptoms of ovarian cancer:
- pain in the lower abdomen and lower back;
- problems with urination;
- disruption of monthly cycles if the woman is still premenopausal;
- feeling of nausea;
- no appetite;
- pain during sex;
- bleeding from the uterus;
- enlarged abdomen or inguinal lymph nodes;
- emaciation.
These symptoms begin with large sizes of ovarian cancer, when treatment may be late, and metastases grow to other organs near the appendages. Symptoms of earlier manifestations of ovarian cancer look different:
- depression;
- apathetic state of mind;
- weak muscles;
- getting tired quickly when working;
- loss of interest in life;
- reluctance to eat.
If these manifestations seem to be unrelated to a terrible disease, sound the alarm and go to the doctor.
The early stages of the disease have no symptoms, so when signs of the disease appear, it is often too late for treatment. But it’s not for nothing that CA 125 is called an ovarian tumor marker. In the early stages, during tests, it detects the onset of tumor growth in half of the cases.
In nine out of ten cases, the disease detected by analysis of the CA 125 marker can be successfully defeated.
At the onset of premenopause, it is advisable for every woman to undergo an annual blood serum examination for the CA 125 marker, especially if there have been cases of ovarian cancer in your family.
The tumor marker indicator for malignant lesions of the appendages begins to increase one and a half to two and a half years before the higher signs of the disease appear, at the first stage of cancer, and this is a good chance for patients to survive after such a test of fate. Antigen levels in this disease range from 115 to 1200 U/ml. If treatment is successful and tests are good, the doctor continues to monitor CA 125 levels to eliminate the risk of tumor recurrence.
The frequency of testing the CA 125 marker after cancer treatment is every three months to prevent its reoccurrence.
The test for the CA 125 tumor marker is carried out in combination with the HE 4 marker - this analysis is called the roma index. The HE 4 protein is much more sensitive than the CA 125 marker to ovarian cancer, and increases in levels already at the first stage of cancer. Therefore, most often modern gynecology uses the roma index to identify oncology of the appendages. At the same time, to determine ovarian cancer, a complete gynecological examination of the woman, hysteroscopy, laparoscopy, and CT scan of the female organs are performed.
Tumor marker ca 125 is the norm in women over 50 years old, antigen ca 125 for ovarian cysts
Testing for tumor markers is recommended annually after 40 years of age, since the risk of malignant tumors increases with age.
In women after menopause, the reproductive system is especially vulnerable, so an analysis for the specific “female” antigen CA 125 is mandatory for them.
An increase in its level signals ovarian cancer, benign tumors and the presence of other gynecological diseases that require treatment.
Norm CA 125 in women with cysts and other conditions
This tumor marker is a glycoprotein produced by epithelial cells of the digestive tract, kidneys, and pancreas. But the maximum concentration is found in the ovaries, which allows the antigen to be used as a marker of diseases of the female reproductive system. The maximum permissible value is 35 U/ml; venous blood is taken for research.
The specificity of CA 125 is low, since its level can increase in tumors of various locations:
- ovaries;
- uterus;
- pancreas;
- intestines and stomach;
- lungs.
Concentration indicators also increase in benign formations - ovarian cysts, fibroids. A physiological increase in the norm is typical for the first trimester of pregnancy and menstruation.
To diagnose ovarian cancer in women of fertile age, CA 125 is rarely used because it is characterized by low sensitivity.
In addition, in the first stages, when there are no metastases yet, the amount of glycoprotein increases slightly. To suggest adenocarcinoma, additional tests for antigens HE4, CA 15-3, CA 72-4, CEA and others are required.
The tumor marker is of practical value at the stages of monitoring treatment and after it, for predicting relapses.
The information content of the analysis increases in the postmenopausal period, in women over 50. It is for this age category that CA 125 is recommended as the main tumor marker for ovarian cancer. In addition, specific values make it possible to judge the presence of certain diseases.
Thus, the norms of CA 125 in women do not differ by age, and the table shows the concentrations of the antigen in the blood under certain conditions and pathologies:
| Patient's condition | Analysis results, U/ml |
| Healthy woman | 10-15 |
| Pregnancy, 1st trimester | Upper limit of normal (35) |
| Cyst | 35-60 |
| Endometriosis, fibroids | up to 110 |
| Ovarian cancer | From 100 and above, most often five times higher than the maximum permissible value |
Ovarian cyst
This benign formation is diagnosed in women of different ages. With an ovarian cyst, which is a cavity with fluid or tissue proliferation, the CA 125 value rises to 60 U/ml.
This indicator is normal, but it is necessary to constantly monitor the antigen level, since the tumor can degenerate into malignant.
More information about the characteristics of the disease can be found in the video about tumor markers for cysts.
Endometriosis
A fairly common pathology in women of reproductive age. It is a growth of the muscular layer (endometrium) of the uterus. It may be accompanied by painful sensations, inter-cycle bleeding, and in advanced cases – an increase in abdominal volume. The values of the CA 125 marker reach 100 U/ml.
After additional diagnostics that exclude cancer, hormonal therapy is prescribed, and surgery is also indicated. In this case, systematic monitoring of the antigen level is mandatory, since malignant degeneration of endometrial cells is possible.
Myoma
Against the background of hormonal imbalances, benign tumors of the uterus - fibroids - often arise. They can be localized both in the thickness of the muscular wall of the organ and in the cavity (connecting to the uterus with the help of the so-called stalk).
CA 125 values in this case are higher than with ovarian cysts, reaching 110 U/ml. Myoma itself is not life-threatening, but the cells of such a formation are prone to degeneration into malignant ones.
Therefore, it is recommended to take hormonal drugs to reduce the tumor or undergo surgery to remove it.
Pregnancy
Changes in hormonal levels also occur in the initial stages of pregnancy, which affects the increase in the level of antigen in a woman’s blood. In addition, the glycoprotein is also synthesized by fetal cells, also entering the bloodstream. Thus, in the first trimester, an increase in CA 125 above the permissible 35 U/ml is a physiological norm, and should be alarming only if it is significantly exceeded.
How to get tested for tumor marker CA 125
If there are malfunctions in the functioning of the female reproductive system (menstrual irregularities), pain in the pelvis, or after menopause, you should definitely undergo an examination.
Where and how to get tested for the CA 125 tumor marker? Numerous paid medical centers offer their services at prices starting from 300 rubles. Blood is taken from a vein, after which it is examined for 1 to 3 days.
To obtain the most reliable result, you need to prepare in a certain way:
- A blood test for CA 125 for ovarian cysts is taken strictly on an empty stomach, in the first half (up to 12 o’clock) of the day. Therefore, when donating blood in the morning, you cannot have breakfast.
- It is advisable to drink only water the night before and on the day of delivery; you should not smoke during this period of time.
- Three days before your scheduled visit to the laboratory, you should adjust your diet by eliminating marinades, fatty, spicy and fried foods, as well as alcohol.
- Stop taking any medications a few days before the procedure as they may affect the results.
- Limit physical activity the day before, immediately before donating blood, calm down and catch your breath (sit for 15 minutes in front of the office).
- If the test is taken by a woman who has not yet reached menopause, the procedure should be prescribed in the first phase of the cycle, before ovulation.
What to do if, according to the results of the study, the tumor marker CA 125 is higher than normal in a woman after 40 years of age? First of all, do not get upset and do not try to make diagnoses yourself, but go to a doctor who will prescribe an additional examination. Even if laboratory error or other factors are excluded, an increase in antigen levels is often observed in cases of non-life-threatening pathologies.
Does the tumor marker CA 125 always indicate cancer?
No, in most cases, an increase in this glycoprotein indicates pathological, but not oncological processes in the female reproductive system. Only very high values indicate malignancy. Typically, the cause of an increase in antigen concentration is:
- borderline (prone to transformation into cancer) benign tumors;
- inflammatory and infectious processes affecting the serous membranes of various organs (peritonitis, pleurisy, pericarditis);
- endometriosis or uterine fibroids;
- ovarian cysts.
As a rule, in these cases the result does not exceed 100 U/ml. Laboratory errors and the influence of extraneous factors also cannot be ruled out. For example, if proper preparation was not carried out before donating blood: the woman took medications, did not follow a diet, smoked, etc. The antigen concentration also increases during menstruation.
Cyst symptoms and how they differ from cancer symptoms
According to the classification, there are three main types of these benign formations.
The first is functional cysts, which go away on their own within a couple of months. They represent the accumulation of fluid in the follicle or its growth if ovulation has not occurred.
The second type , an endometroid cyst, is a cavity in the tissues of an organ filled with blood.
The third (or true tumor) is cystic, developing from its tissues. Rarer types of cysts are hemorrhagic or ordinary cysts of the corpus luteum, retention, mucinous, dermoid, paraovarian cysts, etc.
Regardless of their origin, all cysts present with similar symptoms:
- pulling pain in the lower abdomen, on the right or left, sometimes intense (up to nausea, vomiting, spreading throughout the pelvis and radiating to the rectum);
- disruption of the menstrual cycle - intermenstrual bleeding or delays;
- with a significant size of the cystic tumor, the abdomen enlarges.
If the norm of the tumor marker CA 125 in women after 50 years of age is exceeded two or more times, a suspicion of ovarian cancer arises. Risk factors should also be taken into account: most often, adenocarcinoma develops in women who have not given birth or have a family history of cancer. Although scientists and doctors cannot yet name the exact reasons for the degeneration of cells.
How are the symptoms of cancer different from the signs of a cyst? Both pathologies are often virtually asymptomatic at the very beginning.
While the tumor is localized in the organ itself, it can manifest itself as pain only when the leg is torsed (sudden and sharp pain).
As it grows, symptoms characteristic of cancer of any location appear in the form of low-grade fever, weakness, loss of appetite, weight loss, menstrual irregularities, and the development of anemia.
Already at the second stage of adenocarcinoma, the abdomen enlarges, which also happens with a cyst. But the difference is that in the case of cancer it is an accumulation of fluid (ascites), and in the case of a cyst it is overgrown tissue.
You can distinguish a benign tumor from a cancerous one by the resumption of uterine bleeding during cancer. With the formation of metastases, problems with the gastrointestinal tract, heart and respiratory failure appear.
At this stage of the disease, the prognosis is already unfavorable, so you need to be examined as early as possible, even with minor symptoms of the disease.
Read further: Tumor marker ca 19 9 - what it shows and means, the norm in women
Source: https://medseen.ru/onkomarker-sa-125-norma-u-zhenshhin-posle-50-let-antigen-sa-125-pri-kiste-yaichnikov/
Ovarian or endometrial cyst
The cyst is not malignant, but it secretes a glycoprotein, and an excess amount of CA 125 can cause the cyst to degenerate into cancer. The normal amount of marker for ovarian cyst disease is no more than 60 units/ml. A cyst can often appear during menopause, and often the disease occurs without symptoms, so blood tests must be performed regularly during menopause. After operations to remove cysts, it is necessary to keep the level of CA 125 antigen in the blood serum under control to avoid relapse of the disease.
Uterine fibroids
Myoma is a benign formation of the uterine cavity, which occurs in twenty-five percent of women seeking help from a gynecologist. The premenopausal period is a common time for the occurrence of this disease, and the causes of the disease are varied:
- heredity;
- changes in hormonal balance during menopause;
- inflammation in the reproductive system;
- impaired metabolism;
- presence of diabetes mellitus;
- stressful situations;
- lack of physical activity and movement;
- growth of adipose tissue;
- surgical termination of pregnancies, wearing spirals;
- inability to experience orgasm during sex.
The amount of carbohydrate antigen in fibroids increases to 110 U/ml, but this is not relevant for making a diagnosis.
Along with it, an ultrasound examination of the female organ, MRI and other tests are carried out.
What types of disease are there?
Depending on the location of fibroids, they are distinguished:
- Subserous fibroma - a benign formation that forms on the outer mucous layer of the myometrium and grows towards the pelvic cavity, does not lead to an enlargement of the uterus, is considered the most benign type that can occur with fibroids;
- Submucosal fibroma - forms under the mucous membrane of the female genital organ, while growing into the lumen of the organ. Accompanied by long, heavy menstruation and uterine bleeding not associated with the menstrual cycle, which lead to swelling of the mucous membrane, accompanied by cramping pain;
- Intramuscular fibroids - formed in the muscular wall of the myometrium, accompanied by intramuscular hemorrhage, which is very dangerous for the female body;
- A pedunculated fibroid is located on a narrow base connecting the neoplasm to the wall of the uterus. This location causes poor circulation in the node (from the cervix to the vagina), which leads to increased intra-abdominal pressure and, as a result, the onset of bleeding, aggravated by severe pain.
Uterine fibroids can contribute to the development of ovarian cancer and are among the main risk factors for its development.
Endometriosis
Endometriosis is an overgrowth of the lining of the uterus that occurs during childbearing years. But during menopause it also appears for the first time due to an increase in adipose tissue, diabetes mellitus, chronic infections, surgical interventions that cause scars, and as a result, the growth of the endometrium. The CA 125 indicator for endometriosis is up to 100 U/ml. Simultaneously with the CA 125 tumor marker, the doctor prescribes a test for CA 199 and CEA markers, and other studies: ultrasound, MRI, colposcopy, hysteroscopy, laparoscopy.
This far from harmless disease can, under some circumstances, develop into cancer, so you need to see a doctor regularly.
Other cancers
If a blood test reveals an increase in the level of CA 125, the growth of cancer cells in other organs of the woman’s body is possible. Cancer can attack the following organs:
- stomach;
- pancreas;
- lungs;
- mammary gland;
- liver;
- Lymphomas occur in the lymph nodes of the thymus, spleen, tonsils, and on lymph plaques of the small intestine.
The CA 125 tumor marker is studied for these lesions in combination with other markers and diagnostic methods, because its quantitative value is not indicative of these diseases. They also include the study of carbohydrate antigen during treatment to monitor how its amount in the patient’s blood changes over time. Tests are ordered by the attending physician.
Ca 125 on which day of the cycle to take: how to take it correctly, when is it better, preparation, rules for taking it
Oncology poses a threat to every person. A huge number of provoking factors are attracting more and more attention to modern diagnostics.
Questions about what CA 125 is on what day of the cycle to take become relevant when examining a woman to identify gynecological diseases. Timely examination of tumor markers makes it possible to detect a tumor at an early stage.
Thanks to this, the likelihood of the prescribed treatment being effective increases significantly.
What is the tumor marker CA 125
There are a huge number of tumor markers, the determination of the level of which allows us to identify malignant tumors developing in the body. Each of them is sensitive to diseases of different systems. There are universal substances that help identify a wide range of pathologies.
Tumor marker CA 125 is used in the diagnosis of malignant tumors of the female reproductive system. In most cases, it is used as a substance that is sensitive to the development of malignant cells in the gonads.
In addition, it detects tumors:
- uterus,
- fallopian tubes,
- mammary glands,
- pancreas,
- large intestine,
- stomach,
- liver.
An increase in the level of a tumor marker does not always indicate the presence of a malignant tumor. In some situations, this is a signal about the development of inflammatory processes, for example, in the uterus, liver or gonads.
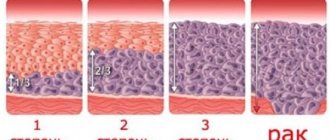
Indicators for ovarian cancer
Malignant ovarian tumors can go through 4 stages of development. In the first stage, the spread of cancer cells into the layers of the organ itself is observed. At this stage, the tumor marker level is normal. In this regard, diagnosis at the onset of the disease is ineffective. At subsequent stages of the disease, the amount of CA 125 increases, which is detected after blood sampling.
The CA 125 study is carried out at the therapy stage to reflect the degree of its effectiveness. When tumor marker values decrease, they indicate the effectiveness of treatment and the need for its further continuation.
After the entire course of therapy has been completed, analysis is carried out to identify the current development of the disease.
If the indicators are significantly reduced over time, then they speak of remission or recovery.
If the situation is absolutely opposite, then the analysis is included in a full examination in order to determine the cause of the exacerbation and the possible development of metastases.
Sometimes the test results are false positive. In such cases, the question often arises about why the level for CA 125 is elevated and how to properly take the test to obtain the correct data. It is necessary to follow all the rules for donating biological material and the doctor’s recommendations. In addition, other diagnostic procedures are additionally performed to help clarify the diagnosis.
The study of tumor markers provides a person with great opportunities. Timely preventive examination helps maintain invaluable health.
Answers to questions: what is tumor marker 125, how to prepare for the test, when is the best time to donate blood will help you properly prepare for the diagnostic procedure. The decryption of the data should be carried out by the doctor, not the patient.
This will avoid complications and prevent the development of more serious conditions. Loading…
Source: https://hk-krasnodar.ru/krov/na-kakoj-den-czikla-pravilno-sdavat-onkomarker-sa-125
CA 125 and serous inflammation of organs
As we saw above, the quantitative indicator of carbohydrate antigen in the analysis may indicate inflammation of the serous membranes of various organs, causing the development of the following diseases:
- exudative pleurisy of the lungs;
- cardiac pericarditis;
- peritonitis;
- acute pancreatitis;
- liver cirrhosis;
- inflammation of the thyroid gland;
- hepatitis A;
- pneumonia;
- renal failure.
The tumor marker level in women with these diseases is no more than 110 U/ml, and is carried out in tandem with various other examinations and tests.
CA 125 and pregnancy
Since menstruation is present during premenopause, although its rhythm is disturbed and ovulation is unstable, this cannot exclude the occurrence of pregnancy at this time. CA 125 levels are elevated to eighty-five U/ml before three months of pregnancy. The presence of this protein during pregnancy is concentrated in the amniotic fluid, blood serum and milk of a woman. A slight increase in antigen is also observed during menstruation. Gynecology does not practice prescribing this test to women under these circumstances.
Tumor markers and their significance
Tumor markers are specific proteins that are produced by malignant tumors or normal tissues in quantities exceeding the permissible limits due to the entry of cancer cells.
They cannot be used to make an accurate diagnosis, but detection of these substances in the blood and/or urine allows:
- suspect cancer and its location;
- distinguish a malignant tumor from a benign one;
- study the effectiveness of tumor therapy;
- detect relapse of the disease early;
- detect metastases before their clinical manifestation.
Rules for conducting the CA 125 test
The analysis is carried out as prescribed by the doctor, using blood from a vein. Before taking the analysis, you need to observe some nuances for an accurate result of the procedure:
- do not eat food 8 hours before the test;
- the best hours for delivery are from 7 to 11 am;
- You can only drink clean water in the morning;
- three days before the procedure, avoid alcohol and nicotine;
- do not eat salty, fatty, fried foods a day before delivery;
- consult with your doctor about what medications you can take before the test so that the real CA 125 numbers are not distorted;
- do not conduct a vaginal smear or tissue biopsy before the test;
- do not attend ultrasound, massager, x-ray, colonoscopy, gastroscopy, bronchoscopy a few days before the test;
- do not overwork yourself physically;
- Calm down and don't be nervous before the test.
A qualified physician will decipher the analysis numbers for this marker; do not try to figure out the diagnosis of the disease on your own.
Dear ladies, disciplinedly follow the recommendations of your doctor and come for scheduled gynecological and therapeutic check-ups at the right time, even if you consider yourself healthy. Your health is in your hands!
Educational video on this topic:
About
Who needs to get tested?
- First of all, this test must be taken by every woman who monitors her health. For screening purposes, the analysis is carried out for early detection and most effective treatment of cancer. The sooner an increase in tumor marker levels is detected, the greater the chances of successful treatment of the disease.
- It is important for those women whose relatives have been diagnosed with cancer to undergo the test. For this purpose, it is recommended to carry out the analysis once a year.
- If a woman has previously been diagnosed with benign neoplasms, such as leiomyoma, fibromyoma, functional ovarian cysts, neoplastic lesions, the doctor may prescribe a blood test for tumor markers to diagnose and differentiate tumors.
- It is mandatory for women who have symptoms of a malignant neoplasm to undergo the test. However, do not forget that a positive test for tumor markers is not specific and 100% confirmation of cancer, so additional instrumental research methods (ultrasound, tumor tissue biopsy, MRI) will be prescribed.
- After diagnosing a malignant tumor and carrying out conservative (chemotherapeutic, radiotherapeutic) and surgical (radical removal) treatments, the doctor prescribes repeated blood tests for CA-125 tumor markers. This is done to evaluate the effectiveness of the therapy.
- Subsequent analysis is carried out to identify metastases in distant organs, as well as for the early detection of tumor recurrence. To do this, the test is taken monthly in the first year after treatment, then once every 2 months during the second year, and once every 3 months in the third year. In the absence of relapses and metastases, the test is performed 1-2 times a year until the end of the woman’s life.
To obtain the most accurate result of a tumor marker test, you need to prepare and adhere to simple but very important rules:
- Blood from a vein must be taken on an empty stomach; the patient must not eat 8 hours before taking blood for analysis. Only water is allowed among drinks to prevent distortion of results.
- It is better to take the test in the morning, between 8 and 11 o'clock.
- A woman should give up alcohol and smoking at least three days before taking the test.
- Immediately before the test, you need to calm down, because... Nervous strain, along with nicotine and alcohol, can affect the final result.
- For a certain number of days before the analysis, you should not engage in intense physical activity.
- It is necessary to exclude medical procedures (physiotherapy, massages, ultrasound examinations) 3-4 days before the test.
- It is very important to monitor your diet during the week before the test: avoid fatty, fried and spicy foods.
- Consult your doctor about taking medications before the test, because some of them may affect the result of the analysis.
- If a woman has any inflammatory diseases, the test should be postponed and taken after they are completely eliminated.
- The test cannot be performed during menstruation, because... how this period can be accompanied by a physiological increase in the level of tumor marker in the blood.
If all these rules are followed, the analysis will be clearly and correctly interpreted by the doctor. The result can be expected within 1-2 days after delivery.