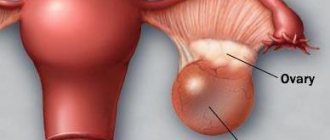
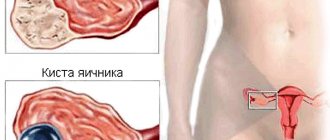
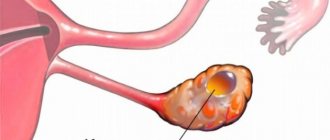
Fluid in the ovary is one of the pathologies of the reproductive organs, which raises many questions among women. The current lifestyle, diet, well-being in the family, social environment, working conditions and even worldview - everything influences the formation of diseases of the genital organs. Overexertion and stress necessarily affect the functioning of the endocrine system. This leads to dysfunction of the gonads, which provokes the risk of the occurrence and development of cysts. An ovarian cyst is a neoplasm in the form of a cavity where pathological fluid accumulates.
Pathological fluid differs radically in its structure depending on the etiology of its occurrence. It can be viscous, oily-dense and watery-mucous.
Causes of pathology
Fluid in the ovarian cavity is a consequence of disorders in the woman’s body. It cannot form on its own and appears during the following diseases and conditions:
- Hormonal imbalance. It entails the appearance of functional, less commonly, epithelial cysts. In the first case, the cause of fluid accumulation in the ovary in women is a disruption of the process of ovulation and follicle maturation.
- Inflammatory or infectious lesion of the appendages. Causes swelling of the tissues of the organ, which provokes its enlargement. As fluid comes out, cysts often form. It is also possible that they will appear multiple times, i.e. development of polycystic appendage syndrome.
- The presence of gynecological diseases, childbirth, abortions, miscarriages, including a history. Diseases of the genital area disrupt the functioning of the ovaries, reducing their endocrine and reproductive functions.
- The course of endometriosis. With prolonged presence, this pathology affects the fallopian tubes, and then the appendages. Endometriosis is characterized by the proliferation of the uterine endometrium. When the ovaries are damaged, fluid accumulates, from which pathological formations are formed.
- Stagnant processes. Increase the likelihood of neoplasms appearing in the pelvis.
The likelihood of cysts is influenced not only by the course of the disease, but also by the woman’s lifestyle. The impact on the genitals also occurs due to some individual characteristics of her body. Additional factors that increase the risk of fluid accumulation in the ovaries:
- early onset of menstruation;
- late menopause;
- harmful working conditions;
- poor environmental conditions;
- irregular sex life;
- taking oral contraceptives without a doctor's prescription;
- frequent stress, chronic fatigue;
- non-compliance with the daily routine;
- smoking and alcohol abuse.
Corpus luteum cyst during pregnancy
If a corpus luteum cyst is found in a woman during pregnancy, then this is not a threat to either the fetus or the woman; in most cases it does not affect pregnancy; it should be monitored using ultrasound. If its size becomes more than 5 cm and does not decrease over time, doctors will consider surgery to avoid complications. But, as a rule, the ovarian corpus luteum cyst should be eliminated on its own by the 18-20th week of pregnancy, at which time the functions of the corpus luteum in producing hormones are completely transferred to the formed placenta. Even in cases where a woman had a corpus luteum cyst and pregnancy occurred due to it, it should completely resolve by 20 weeks.
Development mechanism
Cysts come in various types and differ in their cause, structure and likelihood of degeneration into a malignant formation. Liquid accumulation occurs at different rates. Sometimes such diseases do not require treatment due to the high probability of disappearing on their own.
Functional
In the first phase of a woman's menstrual cycle, the follicles containing the egg mature in the ovaries.
In the normal course of this process, the release of the latter occurs by rupture of the follicle membrane. In the remaining space, the corpus luteum is formed, which is necessary for the production of progesterone, which stimulates the movement of the female cell through the fallopian tube and further fixes the fertilized egg in the walls of the uterus. Functional cysts appear when the folliculogenesis process fails. They develop from an unruptured follicle. They are a small formation with a diameter of 2-6 cm. Most often, they disappear on their own within 2-3 menstrual cycles and do not require treatment. If there are a large number of them or further growth of the cyst, drug therapy is required.
Functional formations cause a delay in menstruation. The onset of menstrual bleeding occurs with a pronounced pain syndrome.
Corpus luteum cyst is a consequence of insufficient production of progesterone by the appendages. It is formed in the absence of regression of the gland itself, which should disappear with the onset of menstruation. Like follicular formation, yellow fluid in the ovary can disappear on its own and rarely requires treatment.
Organic
They belong to the epithelial types of cysts. Most common in postmenopausal women. Unlike functional formations, they have a tendency to become malignant. Need surgical treatment.
Types of organic cysts:
| Name | Description |
| Mucinous (cystadenoma) | It can reach enormous sizes - from 15 to 50 cm in diameter. It has a smooth shell and many chambers containing mucus. Highly likely to develop into cancer |
| Dermoid | Congenital pathology can form already in the womb. It begins to grow actively due to natural or pathological hormonal imbalance, most often in adolescence. Contains elements of bone and soft tissue |
| Endometrioid | Consequence of a long course of endometriosis. Inside the capsule there is a brown liquid mixed with blood clots. Rarely degenerates into oncology. If small in size, can be treated with medication |
Symptoms of ovarian cysts
Ovarian cysts, regardless of whether they are benign or malignant, do not cause symptoms in the initial stage of development. A benign cyst usually disappears within a few weeks. If the formation does not disappear, it can cause the following abnormalities:
- bleeding;
- abdominal pain;
- nausea and vomiting;
- lack of ovulation;
- feeling of bloating;
- pain during intercourse;
- irregular menstrual cycle;
- pain in the lower back or hip.
All these symptoms are not specific to ovarian cysts and may be signs of other diseases, such as uterine fibroids.
How to detect fluid in the ovaries
To identify pathology, a woman should undergo a comprehensive examination. Diagnostic methods are prescribed by a gynecologist:
| Name | Description |
| Gynecological examination | Palpation of the internal genital organs, approximate determination of the volume of the tumor |
| Ultrasound | Detection of fluid in the ovaries, the nature of its origin, detailed examination of the pelvic organs |
| Vaginal smear | Analysis of local microflora, presence of infections |
| General blood and urine tests | Assessing the condition of the whole body, identifying the inflammatory process |
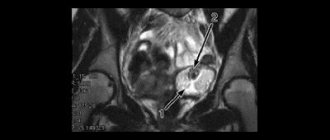
| CT or MRI | Necessary when ultrasound is of little information; it allows a detailed assessment of the structure of the pathology, the presence and volume of free fluid in the left or right ovary |
| Diagnostic laparoscopy | Prescribed when instrumental types of examinations are ineffective, it allows you to analyze the condition of the appendages, conduct a biopsy of the formation for its further examination |
If a woman is suspected of having an oncological process, she needs to be tested for tumor markers. If cancer is present, the nearest pelvic organs and lungs are additionally examined to detect metastasis.
Ovarian cyst: what is it?
A common pathology most often becomes a consequence of hormonal imbalances: changes in ovarian tissue lead to the appearance of bubbles of various diameters. In most cases, cystic formations are benign; only serous cysts, in the presence of provoking factors, are susceptible to malignancy.
Inside the cavity with thin, elastic walls there is liquid. The size of the cyst is from 13 mm to 8 cm or more. Against the background of the pathological process, the affected ovary swells and enlarges.
In 80% or more cases, cysts are not true tumors; it is no coincidence that they are called tumor-like formations. The true form of cysts is often characterized by large sizes, the membrane ruptures, and the contents enter the surrounding tissues.
Large cavities compress adjacent areas and interfere with the functioning of neighboring organs. Pain syndrome rarely manifests itself with a small diameter of cystic formations, discomfort is a sign of active growth of the cavity, less often evidence of the development of a malignant process.
What is euthyroidism of the thyroid gland and how to treat the disease?
Read useful information. Methods for treating subclinical hypothyroidism with folk remedies at home are collected in this article.
Effective Treatment Options
How to treat an ovarian cyst? If a cystic formation is detected, the doctor must rule out a malignant process before choosing the optimal type of therapy. MRI in combination with analysis for tumor markers HE4 and CA125 provides an answer to the question about the nature of pathological changes. If cancer cells are detected, treatment is carried out by a gynecological oncologist.
Learn about the first signs of thyroiditis of the thyroid gland, as well as methods for treating the pathology.
What is mastopathy of the mammary glands and how to treat the disease using folk remedies? Read the answer in this article.On the page https://fr-dc.ru/zabolevaniya/diabet/pitanie-pri-vtorom-tipe.html, see the list of permitted and prohibited foods for type 2 diabetes.
Recommendations for the treatment of ovarian cysts:
- in case of a malignant process, removal of the ovary, radiation therapy, and the use of cytostatics to prevent relapses are indicated,
- a woman should strengthen her immune system, take vitamin supplements and immunomodulators,
- it is important to reduce the risk of influence of factors that provoke the development of the tumor process. You need to give up alcohol, smoking, not consume foods with carcinogens, and in difficult environmental conditions, change your region of residence,
- it is necessary to treat gynecological diseases, normalize the production of important regulators to optimize hormonal levels. It is endocrine pathologies and fluctuations in the level of sex hormones, according to doctors, that most often provoke the appearance of cystic formations in the ovaries.
Waiting tactics and conservative treatment
What is this method? In the absence of a malignant process and the small size of the cysts, doctors recommend that the patient periodically monitor the condition of the cysts. Experts conduct observation for three months. Monitoring dynamics using ultrasound allows you to notice the growth of education in time. The study is carried out immediately after the end of the next menstruation, on the 68th day of the cycle.
If an ovarian cyst is detected, the patient takes medications to normalize hormonal balance, containing progesterone or other types of regulators. In the presence of an inflammatory process, antibiotics, NSAIDs, and vitamins are indicated.
If after 3 months the cavity with fluid does not resolve, then surgery is indicated. If there is a sharp deterioration in the condition, rupture of the cyst, bleeding outside the menstrual period, rapid growth of the formation, or the appearance of signs indicating the development of a malignant process, surgery is prescribed earlier or as an emergency.
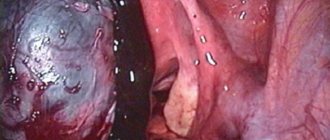
Surgical intervention
Two methods are used to remove cysts:
- Laparotomy. Traditional method of resection of tumor formations. The doctor makes an incision in the anterior wall of the peritoneum to gain access to the organs located in this area. After the operation, a noticeable scar remains, complications include: bleeding, tissue inflammation, poor healing of the postoperative suture. The technique is used for large cysts, severe obesity, when it is difficult for a surgeon to reach the ovary using endoscopic instruments. Another indication for open surgery is rupture of a cystic formation, effusion of contents into the abdominal cavity. The traditional method is also used for complete removal of the ovaries due to a malignant process.
- Laparoscopy. A modern minimally invasive technique reduces the risk of complications, prevents active blood loss, and relieves the patient of ugly scars on the abdomen. The operation is performed using endoscopic instruments under the control of a miniature video camera. To access the internal organs, two incisions no larger than 1 cm are sufficient. The surgeon sees the progress of the operation on the monitor. In case of incomplete desquamation of tissues, re-growth of the cavity and accumulation of fluid are possible. Ovarian laparoscopy is often performed on young women and teenage girls to remove the cyst, but preserve as much intact tissue as possible from important organs. For mature women, resection of the tumor with part of the ovary or its complete removal from the affected side is indicated to reduce the risk of malignancy and prevent relapses.