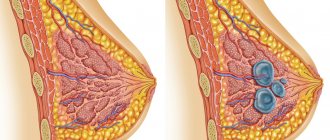
Ovarian neoplasms (tumor of the right ovary in women, as well as tumor of the left ovary in women) are a fairly common pathological condition in gynecological practice. It is difficult to find a woman who has never in her life been diagnosed with an “ovarian tumor,” be it benign or having a different histological basis. An ovarian tumor is a space-occupying formation that is formed from the tissue of this uterine appendage. The neoplasms are united only by the additional volume that forms on the ovary. The remaining characteristics of the tumor have a fairly diverse palette, both in etiology and pathogenesis, and in histological structure and signs of benignity.
Ovarian tumors have a fairly extensive classification according to their histological structure. However, the most general classification can be called the following.
All tumors can be divided into benign (benign ovarian tumor in women) and malignant. Benign ovarian tumors grow slowly, they do not affect adjacent organs, and also do not have the ability to metastatically spread. Gynecology notes that malignant ovarian tumors grow quickly, have the ability to metastasize, grow into surrounding organs and tissues, and also affect the lymphatic system.
If a benign tumor is diagnosed, then you should not relax and let the problem take its course. This does not mean at all that a benign tumor will not pose a significant risk to a woman’s health. Benign tumors have a pronounced and confirmed tendency to malignancy.
Hormone-producing neoplasms can also be distinguished among ovarian tumors. They are able to secrete hormones and change the hormonal background of a woman to something unusual for the physiological one.
Get a free doctor's consultation
Ovarian tumor: dangerous or not, causes
The question of the cause of the formation of both benign and malignant tumors remains open.
- Among the theories of the occurrence of these processes, one can highlight the hereditary one, which is based on genetic aspects that have the ability to be transmitted from mother or father to a girl.
- Viral theory, which also takes place in the etiopathogenesis of neoplasms. Viral agents, affecting the ovary, provoke the formation of a tumor.
- The hormonal cause is also the most commonly used theory in explaining the appearance of this type of neoplasm. The fact that the background of hyperestrogenism, a condition in which an increased amount of estrogen predominates in a woman’s body, often causes diffuse or focal hyperplasia, and subsequently the formation of tumors.
Malignant and benign ovarian tumors: clinical guidelines and risk factors
Risk factors for the occurrence of such pathological conditions are:
- Early menarche, that is, the early onset of menstruation in a girl.
- Late menopause, late decline in the reproductive function of the body (ovarian tumors in women during menopause).
- Some scientists suggest the development of formations against the background of the physiological processes of ovulation. When follicles rupture, tissue trauma occurs monthly. This is followed by restoration, regeneration, and epithelization of the damaged areas. As a result of these actions, ovarian cells begin to actively divide, and under the influence of certain provoking factors, this process can be disrupted and can lead to uncontrolled division.
That is why a large number of ovulations is considered a high risk factor for the occurrence of tumors. - How to reduce the amount of ovulation? A physiological decrease in the number of eggs released from the follicles is pregnancy. During pregnancy, this phenomenon does not occur, and, accordingly, the risk of neoplasms is reduced.
- It is also possible to use combined oral contraceptives, which create an artificial hormonal background and prevent the cascade of reactions in the regulation of the woman’s reproductive system that lead to ovulation. No ovulation means a low risk of developing pathology in terms of ovarian neoplasms.
- Frequent episodes of inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs are also fundamental for the occurrence of ovarian neoplasms.
- Invasive manipulations of the uterus in the form of abortions using curettage or vacuum extraction.
- Carrying out surgical interventions on the ovaries themselves also provokes the development of tumor formations.
- Women with metabolic disorders, which are expressed in obesity of varying severity, also have a greater risk of developing ovarian neoplasms.
- Ionizing radiation is a high risk factor for the development of ovarian tumors.
- Diet is a proven factor that increases the risk of malignant neoplasms. A large amount of consumed animal fats leads to an increase in the possibility of developing tumor processes.
The prognosis for women with any ovarian tumors is a rather vague question. It all depends on the histological structure of the tumor. After all, the difference between a follicular cyst and malignant neoplasms is significant.
Symptoms and signs
As mentioned earlier, a woman’s ovarian tumor does not show any symptoms during its development for a long time. There are only very rare cases when, already at the first stage of the disease, a woman herself suspects some signs of benign tumors and consults a doctor. Usually, even with special diagnostics, it is difficult to suspect the first stage of an ovarian tumor; it rarely happens that during an ultrasound or at an appointment with a gynecologist, a specialist finds a pathology.
Already in the second or third stage, some symptoms appear that indicate benign tumors in the body in women. Already these signs of an ovarian tumor are definitely worth paying attention to and urgently going to the hospital. In such cases, the disease, which does not stop developing, produces pronounced symptoms.
List of signs of ovarian tumors:
- menstruation periodically disappears or is completely absent;
- nausea, vomiting and discomfort appear after each meal;
- the ovaries constantly hurt, even if they do not have a cold due to external factors;
- symptoms such as pain and discomfort during sexual intercourse are highlighted;
- sometimes a tumor of the ovary of women provokes an increase in the size of the abdomen;
- when going to the toilet, the girl experiences urinary retention or, on the contrary, she suffers from too frequent urges;
- due to ovarian tumors there may be very frequent constipation;
- damaged ovaries can cause symptoms such as varicose veins, constant swelling of the feet;
- If a girl has too frequent rashes on her face, her voice has become rough and unnecessary hairs appear, then it is likely that the problem is in tumors that have affected the ovaries.
These are not all the symptoms that provoke a woman’s ovarian tumor, since each stage of the disease produces its own factors that characterize it. There are cases when women have to fight infected types of tumor, which is considered the most advanced option. In this case, the disease in the ovary is characterized by such symptoms of benign neoplasms as:
- rapid heartbeat and too fast pulse;
- signs of fever;
- there may be bleeding from the genitals, supported by constant pain with such tumors;
- also, a benign ovarian tumor may be accompanied by pathological vaginal discharge;
- In addition, constant sharp pain may be felt in the ovaries.
The female body must always be under supervision, so it is best to periodically visit a gynecologist, since, as already mentioned, sometimes a disease can be discovered at a random appointment. It is best not to ignore possible signs of illness, keep the ovaries warm and do less physical activity. If you experience the slightest discomfort, you should urgently make an appointment with a doctor for diagnostics.
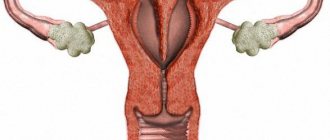
Types of ovarian tumors
These include neoplasms that can increase in size due to the division of cells of their own tissues. It is possible to affect only one ovary or both at the same time.
Tumors that develop only within the ovary are called benign. Another type, malignant neoplasms, grow rapidly, spreading first to neighboring and then to distant organs, which leads to complete destruction of the body. Cancerous tumors are primary (occur directly in the ovary) and secondary (metastatic, that is, formed as a result of the development of malignant diseases of other organs).
Tumors of both types are divided into the following types:
- Epithelial, formed from epithelial cells. These include, for example, serous and mucinous cystadenomas, endometrioid neoplasms (benign), as well as adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma (malignant).
- Stromal (hormone-forming). They consist of tissues that produce sex hormones: estrogens (thecoma), androgens (androblastoma). Such tumors are easier to recognize in the early stages than others, since hormonal changes are manifested by characteristic changes in appearance and specific menstrual cycle disorders.
- Germinogenic (their laying occurs simultaneously with the ovaries during the period of intrauterine development). These include, for example, a teratoma, which forms from the same tissues as the embryo. Fragments of bones, skin, fat, teeth, and hair are found in it.
Diagnostics
Nowadays, diagnosing a tumor is a fairly common and progressive event, since, unfortunately, a significant part of the female population suffers from such a disease and complications. In a professional medical institution, the diagnosis of any tumor takes place in several stages. This approach allows you to make the most accurate diagnosis and select a very effective and quick treatment method. Diagnostics is carried out in the field of medicine known as gynecology. The primary diagnosis can be made in the gynecology department.
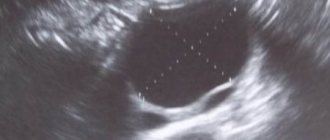
It all starts with the fact that the patient must undergo a general classical examination by a gynecologist. Already at this stage, a large tumor or the formation of a benign cyst can be detected. If the neoplasm that affects a woman’s ovaries is quite large, then she herself can feel it. Most often, such formation does not cause cancer and can be treated. After a gynecological examination, the clinic usually offers ultrasound radiation, which provides more opportunities for making a diagnosis. Such a diagnosis reveals the stage of the disease and possible complications; it is only important to determine whether the formation is malignant or benign.
A modern diagnostic method that helps fight ovarian tumors, such as Doppler ultrasound, is actively used. In this case, the Doppler effect is used, which makes it possible to determine the type of blood flow pathology, identify the stage of the disease, and the consequences. The clinic also uses computed tomography, one of the most accurate diagnostic methods that checks a woman’s ovaries. Tomography allows you to assess the condition of the body, find metastases, and obtain various images.
Sometimes diagnostics are used that allow one to identify markers left by tumors directly in the blood. Then the patient must give her blood for several tests, but it is best to use a couple more methods to make an accurate diagnosis. Sometimes it is impossible to understand in one diagnosis what type of tumor is present, so this is a step-by-step study.
Lead tactics
If after 2 months the cyst does not disappear, then surgical intervention is necessary, which is explained primarily by oncological alertness. When formed on the ovary, it is much higher than with other tumor processes of the female genital area, for example, uterine fibroids.
The task of general gynecologists is to prevent the development of an oncological process at any cost, and this task today has been greatly facilitated by the advent of ultrasound and laparoscopy. If a cyst and not a tumor is clearly identified, then the operation is limited to cystectomy - removal of the cyst with a capsule (to prevent relapse). Laparoscopy makes it possible to remove the cyst without damaging healthy ovarian tissue, and with minimal intervention to remove the paraovarian cyst. If complications develop, surgical intervention is also indicated.
Causes
As for the reasons why this disease can develop, scientists still cannot name an exact list, because the disease is still being studied. There are several already proven factors that can definitely affect the occurrence of a tumor. Each patient may have one or more factors. It is not necessary for all of them to be present.
Common causes of ovarian tumors:
- The problem may be a hormonal imbalance in the female body;
- it is likely that the disease can begin due to genetic predisposition and heredity;
- excessive consumption of animal fats and other specific addictions can affect the development of the disease, especially when it comes to Asian food;
- harmful impurities, and especially talc, which is often used for skin care, can cause a woman to develop an ovarian tumor.
Hormone-producing neoplasms
The main cause of tumors is genetic disorders. A hormone-producing neoplasm on the left ovary (or on the right) can be caused by the following predisposing factors:
- heredity;
- complications during pregnancy, for example, gestosis;
- chronic liver diseases;
- low level of immunity;
- menstrual cycle lasting less than 24 days;
- inflammatory processes in the pelvis;
- conservative treatment of uterine fibroids;
- early onset of the menstrual cycle.
The occurrence of tumors can be facilitated by a woman living in an area contaminated with radiation. A negative factor is the patient's constant state of stress. If a woman suspects she has a tumor, for example, an inflammatory neoplasm of the ovary, then she should consult a gynecologist. The doctor will suggest you undergo the following examinations:
- magnetic resonance imaging;
- tumor markers;
- ultrasonography;
- laparoscopy with the condition of taking a biopsy.
Women may experience some symptoms, such as uterine bleeding, breast swelling or increased libido. In little girls, hormone-producing ovarian tumors cause premature puberty. In some cases, fluid may appear in a woman’s abdomen, that is, ascites. Sometimes the disease causes breast shrinkage and increased hair growth. Some types of hormone-producing tumors can degenerate into cancerous tumors.
Treatment
Ovarian tumors can only be effectively cured by surgery. Of course, the course of treatment will include medications that will help to dull the pain and slightly slow down the development of the disease. But the best way to get rid of this problem is to remove the tumor, followed by long professional treatment and recovery. After surgery to remove a benign or malignant tumor is completed, the specialist conducts a differential diagnosis. It allows you to identify whether there are other neoplasms and how the body behaves. Then you can think about treatment and develop a plan.
During surgery, the doctor removes the uterus, ovaries and the omentum that covers the abdominal cavity. If a girl who has never given birth before and plans to bear a child in the future agrees to the operation, then the doctor can remove only one affected ovary. For this option, it is important that the tumor affects only one organ, is at an early stage and there are no metastases.
After surgical treatment is completed, postoperative chemotherapy begins. Typically, the course of treatment can take a month or a month and a half, depending on how complex the operation was. If the operation was performed at the first stage, the patient is not prescribed chemotherapy. Then she is treated with medication under the supervision of a doctor.
Complications possible with the formation of an ovarian tumor
Benign neoplasms prevent the onset and normal course of pregnancy. Their increase leads to disruption of the functioning of other organs. Some tumors are attached to the ovary by a thin stalk, the twisting of which leads to tissue necrosis. The neoplasm can burst, which leads to bleeding and peritonitis. A benign disease can turn into cancer.
Malignant lesions of the ovaries pose a threat to life. The likelihood of recovery depends on the size and growth rate of tumors and the presence of metastases.
The development of a primary malignant tumor occurs in stages and is manifested by corresponding symptoms.
At stage 1, cancer cells are found only in the ovary itself. Its capsule is gradually damaged. First one and then the second organ is affected, and fluid begins to accumulate in the abdominal cavity.
At stage 2, cancer spreads to other pelvic organs (primarily the uterus).
At stage 3, metastases form, in addition, cancer cells appear in the nearest lymph nodes.
At stage 4, cancer cells are found in distant parts of the body (in the lungs, liver and other organs), where they travel through the blood and lymph.
Video: Signs of tumors in the ovaries
Doctors treating this disease
Ovarian tumors are treated by gynecologists and surgeons, since we are talking about the complex restoration of the female body. A gynecologist usually identifies the problem using modern equipment. He calculates what stage the patient is at and how best to remove the tumor in order to cause minimal harm to her body. The gynecologist also carries out preventive measures and is engaged in the complete recovery and recovery of the patient. As for the surgeon, he performs surgery, without which it is impossible to get rid of the disease. By consulting with each other, doctors find the most beneficial treatment option for the disease.
Without attending the initial appointment, it is completely impossible to predict which specialist out of all the clinic employees will take care of the treatment. The thing is that the stage and type of disease determines which doctor will treat you. To have the slightest idea, you can familiarize yourself with the list of doctors at the clinic.
Diet
Diet for ovarian cancer
- Efficacy: no data
- Duration: until recovery/lifelong
- Cost of food: 3200-4300 rubles per week
For ovarian cancer, nutrition should be rational and as natural as possible. It is important to practice these basic nutritional principles:
- Products must be natural and healthy. Canned food, as well as food with stabilizers and preservatives, should be kept to a minimum.
- The menu should contain as many vegetables, fruits, berries, and nuts as possible.
- The diet should be formulated so that it contains all the vitamins and minerals necessary for the body.
- The menu should include those foods that help cleanse the blood of toxins and stimulate the functions of the immune system. These are sea fish, grains, beets, broccoli, cabbage, nuts, etc.
- You need to drink about 2 liters of water per day.
It is recommended to include the following products in the diet:
- Seeds and nuts.
- Fresh vegetables, herbs, berries, fruits.
- Fish oil, seafood, sea fish.
- Various vegetable oils.
- Eggs.
- Lean meats.
- Bran, muesli, cereal.
- Wholemeal bread.
- Dairy products.
- Honey.
- Fresh juices, berry fruit drinks.
It is very important to eat well after chemotherapy to avoid deficiencies of minerals and vitamins.
At the same time, the following products should be minimized:
- Salt.
- Smoked meats, marinades, sauces.
- Semi-finished products.
- Soda.
- Coffee, strong tea.
- Sugar and weaknesses.
- Baking, white bread.
- Saturated fats.
- Fat meat.
Indications
Experts highlight some indications that all women should pay attention to. This will probably make it possible to predict the disease or take preventive measures. The most common indication is a regular preventive examination by a gynecologist. It is recommended to periodically undergo ultrasound tomography, which, if anything happens, will allow you to quickly determine the disease. Women's health is worth monitoring, so it is recommended to track the menstrual cycle, monitor hormonal levels, and periodically visit a gynecologist for a routine examination.
Gynecologist's recommendations
Tumors often occur in people who have a hereditary predisposition. But this is not a death sentence, you just need to eliminate some provoking factors from your life, and the risk of developing cancer will noticeably decrease.
Gynecologists recommend that women give up bad habits such as smoking and drinking alcohol. It is advisable to start playing sports, for example, race walking or swimming. Junk foods should be excluded from your diet: fast food, fatty foods, fried foods.
Taking modern hormonal contraceptives will have a beneficial effect on a woman's health. They not only protect against unwanted pregnancy, but also reduce the likelihood of tumors on the ovaries. A woman should refrain from having an abortion. At least 2 times a year you need to visit a gynecologist and undergo an ultrasound examination.
It is advisable for a woman to donate blood for hormones from time to time in order to detect any violations in time. And if the disease is still found, then the patient must follow all clinical recommendations for ovarian tumors.
Advantages of treatment at the clinic of JSC "Medicine"
JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitberg) is a medical institution in which specialists will provide you with high-quality care. During treatment, doctors use only modern equipment and innovative treatment methods. Each patient in the clinic has his own individual approach, which means that each will have his own therapist and attending physician. Treatment in the professional clinic of Meditsina JSC is worth it, because in a very short time each patient will be able to return to their old life and forget about health problems.