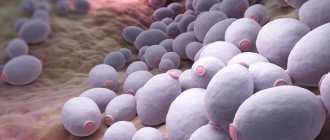
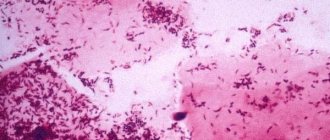
Trichomonas are single-celled protozoan microorganisms; only three types of parasites pose a threat to human health: intestinal, oral, vaginal (genital, genitourinary). A sexually transmitted disease is caused by Trichomonas vaginalis. Both men and women are equally susceptible to the disease.
If in a man the focus of pathology is in the seminiferous tubules, prostate gland and urethra, then in a woman the mucous membranes of the vagina are affected. The infection enters the body through unprotected sexual contact with a carrier of the disease.
What to do in such a situation? To get started, we recommend reading this article. This article describes in detail methods of controlling parasites. We also recommend that you consult a specialist. Read the article >>>
Doctors distinguish several forms of the disease: acute, chronic, carriage. Each is characterized by specific symptoms. The danger of the disease is that the patient spreads the infection for a long time and does not even know it.
Trichomonas
Signs of illness
Trichomoniasis in women is manifested by cutting, burning and tingling in the genital area. The patient is bothered by foamy, mucous discharge with an unpleasant odor, usually it has a yellowish tint.
Sometimes, during the acute course of the disease, the body temperature rises and nagging and aching pain occurs in the abdominal cavity. During sexual intercourse, a woman will notice uncomfortable and even painful sensations.
When an infection enters the urethra, it makes itself felt by frequent urination. The genitals become hot to the touch, swell, become inflamed, and redness begins to appear.
The disease immediately becomes chronic, periods of remission alternate with exacerbation (Trichomonas colpitis, vaginitis).
The man has no symptoms. This is explained simply. The bacterium enters the urethra and often comes out with urine. It happens that the pathological process is accompanied by symptoms:
- foamy discharge;
- frequent urge to go to the toilet;
- pain in the urethra.
The manifestations of trichomoniasis are significantly enhanced by the consumption of alcoholic beverages, smoking, poor diet, self-medication with antibiotics, and exacerbation of existing chronic diseases.
If a woman is sick, she experiences deterioration during pregnancy or during menstruation. A smear will be required to make a diagnosis. In a woman, an analysis is taken from the cervical canal, urethra, and posterior vaginal fornix.
A man is checked for infection by scraping the urethra and examining semen and prostate fluid.
There are several methods for studying biological material. Thanks to the cultural method, the number of bacteria, the degree of the inflammatory process, and resistance to certain medications are determined.
Bacterial DNA is determined by PCR (polymerase chain reaction).
Installations
This procedure involves the introduction of a special antibacterial solution into the man’s urethra, which has an inhibitory effect on the infection. Additionally, such substances enhance cell regeneration and allow the epithelial layer to recover faster.
When treating trichomoniasis, mercury oxycyanide (1 ml per 1 liter of water), silver nitrate (1 ml per 1000 ml of water), ethacridine lactate (1 ml per 2 liters of water) is administered. The solution in an individually selected dose is administered for 15 minutes and washed off.
Installations are characterized by unpleasant sensations, but when treating the chronic stage of trichomoniasis, their use increases the chances of a complete recovery and preventing the occurrence of complications.
Trichomoniasis is a dangerous disease that can lead to chronic damage to the urinary and reproductive systems. If even a small number of mild symptoms of the disease appear, you should immediately seek help from a venereologist. In the absence of regular partners, you should always use a condom and, if possible, get tested every 4-6 months to identify the latent stage of the pathology.
Length of incubation period
The first symptoms of the disease can manifest themselves in different ways - from several days to 2 months from infection. It also happens that the disease occurs in a latent form, and thus the symptoms appear several months later and accompany other diseases.
Therefore, the length of the incubation period depends on several factors:
- Presence of other pathologies in the anamnesis. In this case, the incubation period is short, only a few days. The reason for this is that the body is already weakened by other pathologies.
- Immune system activity. Various types of diseases, especially infectious ones, are activated precisely during the period of weakened immunity. Because if Trichomonas enters an organism with normal immunity, it activates the defense and they may not survive. Otherwise, the incubation period will be long. If a woman has normal flora in the vagina, then infection will not occur at all.
- Taking antibacterial drugs. When a person is treated with such drugs for other diseases, they also affect Trichomonas. And if this drug has a different focus, then it will only increase the incubation period. Very often, at the first symptoms, people begin to self-medicate, without suspecting that their partner also needs medications, thus, the incubation period not only increases, but the disease also becomes chronic.
- In women, the incubation period is long if the vaginal microflora is normal, namely if there are a large number of lactic acid bacteria.
The duration of the incubation period is also affected by the number of bacteria that enter the body. If there are few of them, then the symptoms will appear after a longer time.
And accordingly, on the contrary, if infection occurs immediately with a large number of bacteria, then the incubation period is much shorter.
Due to such an unstable incubation period, diagnosis is difficult. And to determine the presence of the disease, you need to undergo a series of laboratory tests.
After the incubation period, signs of trichomoniasis already appear. These include: discomfort in the lower abdomen.
- First there is discomfort in the lower abdomen, and as the disease develops, pain also appears;
- increased body temperature;
- discomfort when urinating, namely itching and pain;
- There may be pain during sexual intercourse;
- there will be redness on the genitals, as well as burning and itching;
- Women will have discharge from the genitals, it has an unpleasant odor and a yellow color, and it looks like purulent discharge.
With asymptomatic trichomoniasis in women, the epithelium of the cervix is severely affected. Such a lesion is usually diagnosed during colposcopy. In this case, the woman will have symptoms that are not similar to trichomoniasis. Sometimes inflammation of the uterus still appears due to the spread of infection.
Danger
The disease requires mandatory therapy. Lack of treatment leads to the following dangerous processes:
- high risk of developing HIV and transmitting other sexually transmitted diseases;
- pregnancy pathologies, including miscarriage and stillbirth;
- development of male and female infertility;
- cervical oncology;
- chronic inflammation of the genitourinary system;
- prostatitis and cancer processes in the prostate gland.
You cannot self-medicate the disease. Trichomonas, in the absence of a competent plan, begin to reproduce more actively, and treatment can become difficult due to the transition of the disorder to an atypical and latent form. Diagnosis of trichomoniasis in this case is only possible in a laboratory - during a random preventive examination.
How does the incubation period differ between men and women?
The Trichomonas pathogen may not manifest itself in any way during its incubation in women. However, some patients may experience the following symptoms in the first days:
- whitish vaginal discharge, scanty or copious;
- unpleasant odor from the genitals;
- pain when emptying the bladder, accompanied by a slight burning sensation;
- swelling and redness of the vulva.
After the incubation period is completed, women may notice the appearance of aching pain in the lower abdomen. Upon examination, the doctor discovers that the cervix has become softer. The addition of another infection to trichomoniasis can be expressed in the form of small ulcers on the mucous membranes of the vagina.
In men, the asymptomatic stage often occurs without any discomfort. Sometimes the patient may notice a pulling sensation when urinating. As this period continues for a long time, the symptoms appear and then disappear.
If other types of pathogenic microorganisms are attached, the man develops a false urge to empty the bladder, copious discharge from the urethra, and a burning sensation in the groin area.
Treatment
Treatment of the disease must be carried out simultaneously in both sexual partners, even if Trichomonas is not sown in one of them. During treatment and control, sexual activity is prohibited .
During the acute and subacute process, general therapy is used (medicines in the form of tablets are taken orally).
If the disease is chronic or occurs with complications, local treatment must be added.
The following therapeutic regimens exist:
- Metronidazole (analogues – Trichopolum, Rozex, Flagyl): 250 mg twice a day for 10 days;
- Metronidazole: 4 days, 250 mg 3 times a day, then 4 days, 250 mg 2 times a day;
- The same drug: the first day 500 mg 2 times, the second day – 250 mg 3 times, then for 3 days 250 mg twice a day;
- Tinidazole (Tsiprolet) – 2 g once;
- Atrican - 250 mg twice a day for 4 days;
- Naxojin – 500 mg 2 times a day for 6 days;
- For chronic and complicated course of Metronidazole: first day – 750 mg 4 times, second day – 500 mg 4 times. Then a break.
After therapy, recovery is not observed in all patients. another course is necessary .
After starting the main treatment, women can do douching or herbal baths (chamomile flowers, sage).
Additionally, suppositories such as Klion D, Ginalgin, Metronidazole (1 vaginal tablet for 10 days) are used for local therapy.
In pregnant women, trichomoniasis can only be treated from the beginning of the second trimester .
Treatment monitoring is carried out 7-10 days after taking the last drug, and then repeated twice within a month.
How to understand that the incubation period has ended
Both patients and doctors are not always able to identify the beginning of the active phase of trichomoniasis, since often the incubation stage smoothly and imperceptibly flows into the manifested stage. It is possible to mark the end of the asymptomatic period when the following symptoms develop:
- The appearance of a strong burning sensation during urination. Patients also note increased itching in the genitals, which causes severe discomfort.
- The desire to empty the bladder immediately after passing urine. Patients develop a feeling of overcrowding, reminiscent of signs of cystitis and urethritis.
- The appearance of discharge in the form of mucus from the urinary tract and vagina.
- Narrowing of the urethral canal resulting from an inflammatory process. Patients complain of pain when urinating, urine retention, and discomfort in the lumbar region associated with the development of pyelonephritis.
In representatives of the stronger sex, trichomoniasis may not make itself felt for several years and proceed in a latent form. Clinical signs may develop 2-4 years after infection.
Diseases of the genitourinary system, the addition of other infections, deterioration of the immune system due to stress, hypothermia, and nutritional deficiencies can lead to the activation of pathogenic microorganisms.
Trichominiasis and pregnancy
Trichomoniasis, according to most doctors, is not one of those diseases that can have a detrimental effect on the fetus; it does not cause malformations in the fetus. But, of course, trichomoniasis during pregnancy is an extremely undesirable condition. There are several reasons for this.
The aggressive environment that forms in the vagina of a pregnant woman with trichomoniasis can “melt” the lower pole of the amniotic sac and lead to premature rupture of amniotic fluid, which means miscarriage or premature birth.
Trichomoniasis - symptoms. The likelihood of contracting trichomoniasis during childbirth is especially high for a newborn girl, which is due to the characteristics of her body (the girl has a short urethra, through which Trichomonas can easily penetrate the bladder).
Trichomonas themselves do not penetrate the fetus through the placenta, but can serve as a “tram” in which chlamydia, gonococci and other pathogenic microbes quickly move into the uterine cavity. This is due to the ability of Trichomonas to absorb microorganisms without killing them.
Microbes inside Trichomonas are protected from antibiotics and cannot be detected during diagnosis. Often, after treatment for trichomoniasis, infections that have been treated for a long time or have never been detected in a given woman suddenly become apparent. In addition, it is possible for a child to become infected when passing through the birth canal affected by Trichomonas.
Under what conditions does the incubation period change?
Under the influence of certain factors, the incubation time of the pathogen may vary. The state of the human immune system can speed up or shorten the duration of the period. Often infectious diseases develop when the body's defenses are weakened. Their symptoms begin to appear earlier.
With a normally functioning immune system, even when harmful bacteria invade organs, signs may not be observed for a long time, since the pathogen does not become activated. In such patients, the incubation period is longer than in weakened people.
The age of the patient also plays a certain role: in older people, the immune system works worse, which leads to the rapid onset of symptoms of trichomoniasis. If, at the time of introduction of the infectious agent into the body, a person suffers from chronic pathologies or acute diseases, the incubation period is 2-4 days. This phenomenon is associated with the orientation of the immune system to fight inflammatory processes.
While taking antibacterial medications, the duration of incubation is reduced. This is especially true when using broad-spectrum drugs. Acute symptoms of trichomoniasis when exposed to this factor are smoothed out, or may not develop at all.
The incubation period also depends on the state of the vaginal microflora. It is lengthened if a large number of lactic acid rod bacteria are present. These beneficial microorganisms successfully fight pathogens and prevent them from becoming active, as a result of which the symptoms of trichomoniasis may not develop for a long time.
The number of harmful bacteria entering the body also plays a certain role. When single pathogens of an infectious disease are introduced, its symptoms may not appear for a long time. With the penetration of a large number of Trichomonas, the acute stage occurs much earlier.
The length of the incubation period is influenced by many factors. The active phase develops in many patients after 2-3 weeks, but can appear after 2 years or more.
The patient is considered infectious for the entire duration of the unmanifested phase of trichomoniasis.
Pathogenic microorganisms enter the body of healthy people during intimate contact. It is also possible to become infected through household means if personal hygiene rules are not followed.
Recovery stage
The recovery stage is an important component of effective treatment of chronic trichomoniasis. It is carried out after each course of basic therapy and involves the following steps:
- Taking hepatoprotectors that restore the liver weakened by antibiotics.
- Topical use of antioxidants.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures.
- Vitamin therapy.
- Diet therapy.
After completing the course of treatment for trichomoniasis, restoration of the intestinal microflora becomes mandatory. For this, patients are prescribed a 10-day course with probiotics.
Chronic course
Chronic trichomoniasis is the most dangerous form of the disease, since it is characterized by an asymptomatic or low-symptomatic course, which is characterized by frequent alternation of periods of exacerbation and remission.
As a rule, during an exacerbation, there is a tingling sensation or itching in the genitals, as well as discomfort when urinating. During the period of remission there are no pathological symptoms.
Provoking factors for the development of exacerbation can be alcohol consumption, hypothermia, heavy physical activity, hormonal imbalances, and improper hygiene of the intimate area.
In case of self-medication, refusal of therapy or uncontrolled use of drugs, acute trichomoniasis can become chronic, which will lead to epididymitis, prostatitis and infertility.
Symptoms of trichomoniasis manifest themselves differently in men. The difficulty in diagnosing pathology lies in the fact that its signs are not always available, and treatment does not begin on time.
In medicine, cases are often identified when a man is a chronic carrier of the infection for several months and there are no symptoms.
Manifestation of this disease:
- the first signs of the disease in men are itching and burning during urination;
- discharge from the urethra. They can be different - light and transparent, whitish and gray, in some cases purulent or in the form of foam;
- single scanty discharge occurs in the morning, it looks like a transparent drop.
The first symptoms of trichomoniasis are enhanced by eating foods with spicy seasonings and alcoholic drinks.
Further symptoms increase and manifest themselves as follows:
- inflammation and slight swelling can be observed at the opening of the urethra;
- pain is observed in the perineum, genitals, rarely - pain spreads to the pelvic area;
- in some cases, a small amount of blood appears in the urine and semen;
- There is a suppression of sexual desire and a decrease in potency.
The sensations of trichomoniasis are often confused with the symptoms of a disease such as radiculitis, and independent treatment is carried out for it, which, as a rule, ends unsuccessfully.
If the disease is not detected in time by the first signs and treatment is not started, serious complications can occur.
These include:
- pain in the testicles and scrotum caused by increased body temperature;
- inflammatory processes of the genital organs - swelling and redness of the penis, its head, the appearance of wounds and ulcers on it;
- inflammatory processes caused by this pathology often lead to prostatitis;
- if the causative agent of the disease Trichomonas vaginalis penetrates the urethra, an inflammatory process develops, which often leads to urethritis. When inflammation intensifies or is not treated, damage occurs to the organs of the genitourinary system - the ureters, bladder and kidneys;
- As a result of infection, the quality of biological (semen) material decreases in a man and sperm become less mobile. In most cases, such changes lead to infertility that cannot be treated.
Description of the disease
Urogenital trichomoniasis affects only the urinary and reproductive systems of the infected person.
The causative agent of the pathology is vaginal, intestinal or oral Trichomonas, which enters a healthy body through unprotected sexual contact. After entering a man’s body, trichomoniasis affects his most sensitive parts, which include the urethra, prostate gland, testicles and appendages. The seminal vesicles are affected a little later, but also always suffer from the effects of infection.
In a woman, signs of an inflammatory process appear in the vagina, on the walls of the labia minora, in the area of the cervical and urethra. Patients may be carriers of Trichomonas for a long time, but not know about its presence in the body. Most often, the disorder is detected after the manifestation of obvious symptoms of trichomoniasis or after samples are taken as a stage of a preventive examination.
Women of reproductive age, including girls under 18 years of age who are sexually active, are at risk for the disease.
A sick woman can transmit trichomonas to her newborn baby when it passes through the birth canal during natural childbirth. Infection of this nature occurs in approximately 5% of cases. In recently born children, the disease is often asymptomatic and self-healing.
Men may also not know about the infection for a long time and continue to spread the infection to their partners. Often the real cause of such serious disorders as non-gonococcal urethritis, chronic prostatitis and inflammation of the epididymis is the massive spread of trichomonas. All these diseases lead to decreased sperm motility, which becomes the cause of infertility.
Is trichomoniasis contagious during the incubation period?
Researchers have proven that infection with Trichomonas is possible from the very first day of incubation. A sick person, unaware of the presence of pathogenic pathogens in his body, infects a healthy partner during sexual intercourse.
Trichomoniasis can be transmitted not only through intimate contacts, but also through household contact. Such cases are more rare. Infection occurs when using the patient's personal belongings: washcloths, towels, underwear.
Despite the low viability of Trichomonas in environmental conditions, it is still possible to become infected in this way. Pathogenic bacteria are able to survive in a humid and warm environment for 2-4 hours.
Since Trichomonas parasitize the mucous membranes of the genitourinary tract, the likelihood of infection is high during vaginal sex. During anal or oral contact, the risk of infection is low because the bacteria cannot withstand the conditions of the intestinal and oral cavity.
They die when:
- exposure to antiseptic solutions;
- elevated temperatures (from 40 degrees);
- influence of cold;
- exposure to direct sunlight;
- drying.
Treatment of the genital area with antiseptic solutions (chlorhexidine, miramistin) after questionable sexual contacts helps prevent the development of infection.
Women can avoid infection by using vaginal suppositories that have an antibacterial effect.
Prevention of trichomoniasis
It is already known that this disease is sexually transmitted, which means that promiscuity can cause infection.
What you need to do to avoid getting infected:
- You cannot use other people’s personal hygiene products (towel, razor, comb, shoes);
- A chlorhexedine solution is suitable for disinfection;
- condoms provide reliable protection (if used correctly);
- maintain personal hygiene;
- strengthening the immune system (multivitamins, fresh fruits and vegetables, proper nutrition;
- do not abuse alcoholic beverages and cigarettes.
Routes of transmission
The causes of the disease are most often hidden in promiscuous sexual intercourse, when partners refuse to use a barrier method of protection. The chance of infection in this case is approximately 97-100%.
Trichomoniasis can also be transmitted through household contact. This happens through dirty bedding or underwear, bath accessories and swimwear. But the chance of getting infected this way is extremely small.
Recent studies have shown that the disease becomes an indirect cause of such lesions as diabetes, mastopathy in women and cancer.
It is possible to defeat parasites!
Antiparasitic Complex® - Reliable and safe removal of parasites in 21 days!
- The composition includes only natural ingredients;
- Does not cause side effects;
- Absolutely safe;
- Protects the liver, heart, lungs, stomach, skin from parasites;
- Removes waste products of parasites from the body.
- Effectively destroys most types of helminths in 21 days.
There is now a preferential program for free packaging. Read expert opinion.
Interesting to know: