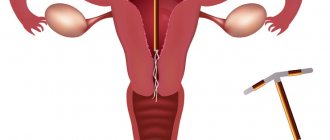
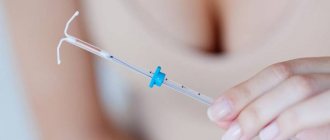
Intrauterine devices (IUDs) are contraceptive devices that perform their functions while inside the uterus. IUDs have a high degree of reliability and at the same time protect against unwanted pregnancy for a long period of time.
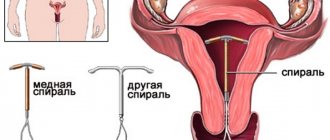
There are two types of intrauterine devices - hormonal and non-hormonal. Both species prevent pregnancy by releasing specific substances into the woman's reproductive tract. Hormonal IUDs produce synthetic hormones, while non-hormonal or copper-containing IUDs release small amounts of copper.
IUDs can affect your periods in different ways. Both types of IUDs can cause heavy or irregular bleeding soon after they are inserted into the uterus.
Changes in the menstrual cycle or other side effects mainly depend on the type of IUD used. Women who use hormonal IUDs are more likely to experience weaker or irregular periods. Copper IUDs usually cause menstrual bleeding to be heavier than usual.
In the current article, we will explain how two types of IUDs can affect menstruation. In addition, we will provide important information to women who are considering switching to other methods of contraception.
How does the nature of menstruation change after the installation of a non-hormonal IUD?
After the insertion of an intrauterine device, the body takes time to adapt to the contraceptive. We'll look at which ones below.
First menstruation
In most patients, the nature of bleeding changes - it becomes intense and prolonged. This occurs because the IUD irritates the endometrium. Menstruation becomes so heavy that a woman has to use more than 1 pad for 3-4 hours. A nagging pain in the lower abdomen and weakness appear. Sometimes you have to use antispasmodics to relieve discomfort.
In 3 months
During the first month after installation of the IUD, the woman’s body adapts to the foreign body. Menstruation remains abundant and long. There is a nagging pain in the lower abdomen. According to reviews, on average, the duration of menstrual flow increases by 1-2 days. Don't worry: this is a normal reaction of the reproductive system to the introduction of a foreign object into the uterine cavity.
After installing an intrauterine device, spotting and spotting between periods cannot be ruled out. This is also a symptom of the reproductive system adapting to a contraceptive. If they last more than three months and do not disappear, you must definitely visit a gynecologist.
In 6 months
During this period, menstruation returns to its physiological norm. Menstruation may be more abundant, but does not exceed the acceptable limit. In some cases, the pain is stronger than before the contraception was introduced into the uterine cavity.
If the bleeding is very heavy and prolonged, you should consult a gynecologist. The IUD may need to be removed because its side effects outweigh its contraceptive effectiveness. If the IUD is not removed in time, anemia develops.
What to do in case of cycle disorders due to a non-hormonal IUD?
For moderate cycle disorders:
- If spotting between menstruation or light bleeding occurs during the first 6 months after installation of a non-hormonal IUD, treatment is not carried out. This is a completely normal phenomenon and does not pose a danger to a woman.
- If you complain of nagging pain in the lower abdomen during menstruation, anti-inflammatory drugs (ibuprofen, etc.) are prescribed in a short course (3-5 days).
- If there is continuous bleeding, pathology of the pelvic organs should be excluded. An examination by a gynecologist, colposcopy, and ultrasound are indicated. When a disease is detected, its treatment is indicated. The question of removing the coil is decided individually and depends on the diagnosis.
- If there is a significant disruption to normal life due to bleeding, removal of the IUD is indicated.
If there is heavy or prolonged bleeding:
- During the first six months after insertion of the IUD, prolonged or intense bleeding may occur, which does not pose a danger to the woman. No treatment required.
- If the woman’s general condition worsens, anemia develops, or bleeding increases, removal of the IUD is indicated.
Gynecologists point out that the use of copper-containing coils quite often leads to menstrual irregularities in the form of spotting or bleeding. Such symptoms occur in the first 6 months and often become the reason for removing the IUD. Various medications can be used to combat cycle disorders, but their effectiveness is questionable.
What is an IUD and what is it for?
An IUD is installed for a contraceptive effect. The method is used not only in Russia, but also in Scandinavian countries and Asia. There are two types of agents: inert and medicinal. The former are made of plastic and come in various shapes, while the latter have a plastic base with the addition of copper or silver wire, or with a hormone. Hormonal drugs increase effectiveness and reduce the risk of complications. The installation of the IUD is carried out on the 4th-8th day of the start of menstruation. During this period, the cervical canal is slightly open, and installation of the drug is painless and easy. It is recommended to insert an IUD immediately after an abortion, two months after childbirth and six months after a cesarean section. After inserting an IUD, you should limit yourself to physical activity for a week, avoid hot baths, saunas, steam baths, do not take laxatives and diuretics, and avoid sexual activity. The doctor will inform you about the service life of the drug, possible complications and their symptoms. The IUD is removed after the expiration date, if complications develop, at the request of the patient.
Complications
The first periods after installation of the coil are heavy and long. Main complications after IUD installation:
- perforation of the uterus;
- displacement of the contraceptive into the abdominal cavity;
- pain;
- inflammatory diseases;
- increased body temperature;
- purulent or sanguineous discharge;
- anemia.
Cramping pain in the lower abdomen and bleeding indicate expulsion of the drug. An increase in temperature and the appearance of discharge indicate inflammatory reactions. After installation of the IUD, heavy periods occur, which leads to the development of menorrhagia. With heavy blood loss, iron deficiency anemia develops. If heavy periods continue after insertion of the IUD, you should contact a specialist to remove the IUD.
Menstruation after installation of the IUD
Menstruation and the IUD: how does our body behave after the installation of an IUD? Normally, after the installation of an IUD, the complications described above are possible; gradually, with each month, the effect decreases and disappears altogether. Menstruation does not come regularly during the spiral. During the first few months, light bleeding may appear at first, but after that your periods will become heavier and last a couple of days longer than usual. Over time, hormone levels will level out, and your periods will come on time and with the same duration. Heavy periods with the IUD will go away on their own after a couple of months, but if it continues for a long time, consult a specialist.
Indications and contraindications
Indications for the use of IUDs are: unwanted pregnancy, dangerous partner, high fertility and contraindications to pregnancy.
Contraindications:
- inflammation of the pelvic organs;
- malignant formations of the cervix and uterine body;
- pregnancy;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- algomenorrhea;
- metrorrhagia;
- hypoplasia;
- abnormalities in the development of the uterus and genital organs;
- anemia;
- etc.
Advantages of the method
- long-term use;
- efficiency;
- instant contraceptive effect;
- restoration of fertility after removal;
- use during lactation;
- The IUD has a therapeutic effect;
- low cost.
What is hyperplastic candidiasis? This difficult name is given to oral candidiasis, caused by opportunistic fungi of the genus Candida. It is curious that this pathogen is in... Definition of intertriginous candidiasis Intertriginous candidiasis is a lesion of skin folds in which clearly defined erosions are formed, often accompanied by weeping. With this view...
How does the nature of menstruation change after installing Mirena?
Unlike the non-hormonal intrauterine device, Mirena affects menstruation in a different way:
- Menstruation becomes moderate or scanty, and its volume noticeably decreases.
- The duration of monthly discharge is shortened by 1-2 days.
- Painful sensations in the lower abdomen disappear.
Some patients experience reversible amenorrhea, in which menstruation does not come at all. This is considered normal with Mirena and does not require treatment. If the IUD is removed from the uterus, periods will eventually return. The use of Mirena contributes to the regularity of the cycle and the comfort of menstruation.
Other symptoms after installation of a hormonal IUD:
- Spotting in the middle of the cycle occurs in the first 6 months after the introduction of Mirena and is considered normal. No treatment required.
- If bleeding intensifies or does not stop after six months, you should be examined by a gynecologist. If a pathology is identified, its treatment is indicated.
- If there is severe discomfort due to spotting or bleeding, the Mirena intrauterine system is removed.
To prevent anemia, iron supplements are prescribed and nutrition is adjusted.
Advantages of the uterine device
The IUD has many advantages:
- Small price.
- After removing the IUD from the body, reproductive capacity is quickly restored.
- Can be used even while breastfeeding.
- A very high degree of contraception, can be compared with a condom, as it prevents unwanted pregnancy by 98%.
- Unlike the same hormonal pills, a woman’s hormonal levels do not change
- The spiral can be taken for a very long time, from 3 to 10 years.
- Installation and removal is straightforward.
- It does not cause discomfort and is not felt either in everyday life or during sexual intercourse.
- There is no need for oral contraceptives.
Dangerous symptoms: when you urgently need to see a doctor
Sometimes a woman notices certain signs that may threaten her health. These include:
- There is no intrauterine device thread in the vagina.
- A spiral is detected in the genital tract, which indicates its loss.
- There was profuse bleeding.
- Intermenstrual discharge occurred six months or more after the insertion of the IUD.
- Menstruation disappeared and did not appear for more than 90 days.
- The appearance of severe or cramping pain in the lower abdomen. Such a symptom may indicate an ectopic pregnancy, ingrowth of the contraceptive into the uterine wall, or perforation of the uterus.
- There was a high temperature, fever with pain in the lower abdomen and vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor. Such manifestations may be a sign of an inflammatory process.
Useful video
Watch this video about the advantages and disadvantages of the intrauterine device:
For those who have not experienced it, it is difficult to understand what is happening - uterine bleeding or menstruation, how to distinguish them and whether to panic. Indeed, heavy periods are similar to uterine bleeding. However, there are important differences worth knowing.
It can be very difficult to independently understand whether it is heavy periods or bleeding. However, there are clear signs of menstruation and bleeding, as well as additional symptoms for which it is important to see a doctor.
Sometimes long periods become quite common and normal (after an abortion, due to heredity). If they last more than 7 days, with severe pain and red clots, then this is a reason to consult a doctor. It is highly undesirable to carry out treatment on your own.
Menstruation after IUD removal
To protect yourself from unwanted effects, removal of the IUD from the uterine cavity should be done exclusively by an experienced gynecologist. Most patients visit the doctor with a complaint about the absence of menstruation after removing a contraceptive. However, practice shows that the disappearance of menstruation depends on the period of use of the contraceptive product, as well as on the degree of thinning of the endometrium. Experts say that if the IUD has been in the uterine cavity for a long time, it will take more time to restore its inner lining.
What does the absence of menstruation while using an IUD indicate?
When a woman does not have her period, a natural question arises: why did they disappear? Many people worry that unplanned fertilization has occurred. There's really no need to worry. The reason for the absence of menstruation for up to 3 months is considered to be hormonal changes and ovarian dysfunction. Such features occur if other factors are excluded: pelvic inflammation, sexually transmitted infections or conception of a child.
If a woman is worried about the disappearance of her periods, the first step is to rule out pregnancy. To do this, it is worth purchasing a rapid test to determine the “interesting position”. If the test gives a positive reaction, you should immediately consult a gynecologist. If several repeated studies show a negative result, we can conclude that fertilization has not occurred.
Experts say that when using a hormonal intrauterine device, menstruation may normally be absent for up to 3 months. If this period is exceeded, it is recommended to visit a female doctor to rule out diseases of the genital organs. The doctor will prescribe appropriate tests and studies that will help determine the cause of the disappearance of menstruation.
After installation of an intrauterine device, many women notice a change in the nature of menstruation. Sometimes the changes do not go beyond the norm, but in some cases they can be manifestations of a serious pathology. To prevent health problems, you need to carefully monitor your menstrual cycle, and if various abnormalities appear, immediately seek help from a gynecologist.
The uterine device can, if not solve, then slow down many female diseases, and also protects against unwanted pregnancies. The most favorable time for installing an IUD is 3-7 days of the menstrual cycle , when a woman still has slight spotting. This is due to the following: the cervical canal is “slightly open” for the unhindered release of menstrual flow, so it is easier to insert an IUD; Pregnancy is definitely ruled out.
You should not install an IUD during heavy discharge , as it may not be fixed and may even come out on its own. Direct insertion of the spiral is a painless procedure and takes 3-5 minutes.
Theoretically, an IUD can be inserted on any day of the cycle. There is even a method of emergency contraception - inserting an IUD within 24 hours after unprotected sexual intercourse.
The disadvantages of inserting an IUD are not critical: pregnancy cannot be ruled out for sure; the procedure is more painful. During this period, it is recommended to take a blood test for hCG to exclude pregnancy, and immediately before the procedure, take an intramuscular injection of an anesthetic or at least take a tablet orally half an hour before.
Sometimes it is practiced to insert an IUD into women immediately after childbirth. However, the doctor must be sure that there are no membranes inside the uterine cavity or inflammation. Installation of the IUD is also allowed during breastfeeding if the woman has not yet menstruated. In this case, it is also necessary to first take a blood test for hCG.
Dates for the start of menstruation with a spiral . If the IUD is inserted in the last days of menstruation, then the next one, as a rule, arrives on time. However, there are some features:
- First menstruation and its features. Immediately after installation, there may be slight spotting or even a re-start of menstruation - they extend to 10-14 days. If it drags on for more than two weeks, you should consult a doctor. The first next menstruation comes as usual in the cycle. They are often more abundant and there may be clots. Many people report pain, even if there was none before.
- Second period after installation. They can be ordinary and familiar to a girl. Sometimes they change so much that they force you to remove the IUD - they become extremely abundant, long-lasting and painful.
- How are things going in the third month? By this time, the body adapts to the IUD - accepts or rejects it. The cycle is either getting better, or you need to choose other methods of protection.
- With Mirena , periods become less abundant, the duration of critical days decreases, the cycle becomes more regular, and menstruation is less painful. But it causes breakthrough bleeding, pain, and the coil can come out on its own or move into the uterine cavity.
After removal, the woman’s menstrual cycle gradually returns to the norms that were before its installation. If you have doubts or suspicions of any disease, it is better to consult a doctor.
Read more in our article about how menstruation occurs with the IUD, how the cycle afterward is established, and also about when to install or remove the product.
Read in this article
Installation of the spiral
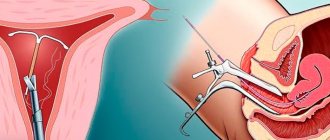
Only a doctor should insert an IUD after a thorough examination of the woman for the absence of pregnancy, infectious diseases and inflammatory processes in the uterus. Since it must be located in the cavity of the organ, the natural question is: when is the IUD placed before or after menstruation?
Access to the uterine space is through the cervical canal. This is a rather narrow “corridor,” especially for nulliparous women. Traumatizing it is extremely undesirable, as it carries the risk of infection and the appearance of erosive changes. Damage to the cervix may be a negative circumstance for subsequent births.
It is more advisable to insert the IUD during menstruation:
- The cervix is slightly open more widely than usual and has a soft consistency;
- The insertion of the IUD will be precise and painless;
- The reproductive system is undergoing an update, which will help it quickly adapt to the presence of a foreign object.
But what about the discharge? Can't it interfere with the doctor? This consideration leads to the question of what day of menstruation the IUD is placed on. With a 3-day menstruation, it is better to do this on the last day. If it lasts 4-7 days, it is also closer to the end, for example, 2-3 days before it. In this case, by the time the IUD is inserted, menstruation is no longer so intense as to prevent the gynecologist from seeing the working field. But the cervix has not yet narrowed enough to make inserting the IUD difficult.
What about other days?
Installation of an intrauterine device
For some women, the doctor prescribes the installation in addition to their critical days. But they doubt whether the IUD is inserted without menstruation. In principle, doing this on other days of the cycle is not prohibited. It’s just that many specialists prefer to do the installation in the last days of menstruation. This way you can be sure that the patient is not pregnant.
But if there is urgency in protection, you should not be afraid and doubt whether it is possible to insert the IUD without menstruation. This is often done to women who have recently had a successful birth. In order for the hormonal IUD to work immediately, it is administered a week after the start of the cycle.
For many, their critical days are already over by this time, and the IUD is thus installed “dry”. The process may be a little more painful. But local anesthetics will help relieve the sensations, and the manipulation itself lasts no longer than 5 minutes.
The effect of the IUD on the reproductive system
The intrauterine device is a reliable and popular method of contraception among women who have given birth. Protection against pregnancy is carried out in the following ways:
- Aseptic inflammation in the uterine cavity. The IUD is installed under sterile conditions, the likelihood of infection is minimal. However, even in such cases, aseptic (without pathogenic bacteria) inflammation begins in response to a foreign body in the uterine cavity. As a result, a layer of defective cells forms on the inner surface of the uterus, which prevents the implantation of the fertilized egg if fertilization does occur.
- Effect on sperm. A foreign body in the uterine cavity is a mechanical obstacle to the further advancement of male germ cells.
- The contractility of the uterus increases. The intrauterine device, being in the uterine cavity and irritating its walls, stimulates the activity of the myometrium. This can be expressed in periodic nagging pain in the lower abdomen. In addition, this mechanism prevents the implantation of the fertilized egg into the endometrium.
There are also spirals with metal additives - copper, gold, silver. They have an additional effect and increase the contraceptive effect. In particular, copper-containing IUDs interfere with the activity and motility of sperm, thereby reducing the chances of pregnancy.
In addition, copper ions can influence the peristalsis of the fallopian tubes, which reduces the likelihood of developing an ectopic. Spirals based on silver and gold are more preferable to women who have once suffered from inflammatory processes of the genital organs - endometritis, adnexitis, cervicitis and others.
However, all these are only hypothetical effects of the IUD on a woman’s body. How they prevent pregnancy has not been fully studied. However, even in ancient times, to protect against pregnancy, women placed a spool - a ring of gold - into the uterine cavity immediately after childbirth. Thus, peculiar spirals existed back in Ancient Egypt.
Hormonal IUDs (the most popular and well-known Mirena), in addition to the effect inherent in all IUDs, have a contraceptive effect due to the regular release of gestagens.
And here is more information about dysfunctional uterine bleeding.
Is it possible to place it outside of menstruation?
Theoretically, an IUD can be inserted on any day of the cycle. There is even a method of emergency contraception - inserting an IUD within 24 hours after unprotected sexual intercourse. However, in this case, there is a possibility of infection of the uterine lining if the woman was simultaneously infected with an STI during sex.
The disadvantage of inserting an IUD not on critical days is the following:
- pregnancy cannot be ruled out for sure - the fertilized egg may not be visible in the uterine cavity if it has not yet descended, and the test does not always give a reliable result;
- the procedure is more painful - the cervix is often in a spasmodic state on ordinary days.
It is also sometimes practiced to insert an IUD into women immediately after childbirth. However, the doctor must be sure that there are no membranes inside the uterine cavity or inflammation. Otherwise, the procedure risks serious complications. Installation of the IUD is also allowed during breastfeeding if the woman has not yet menstruated. In this case, it is also necessary to first take a blood test for hCG.
Dates for the start of menstruation with a spiral
IUDs, with the exception of hormonal ones, do not affect the onset of the menstrual cycle. And if the IUD is inserted in the last days of menstruation, then the next one, as a rule, arrives on time. However, there are some peculiarities.
First menstruation and its features
Immediately after installation of the IUD, a woman may notice slight spotting or even the re-start of menstruation - thus extending it to 10-14 days. This does not always happen and such features vary from person to person. If the critical days drag on for more than two weeks, you should consult a doctor to prescribe, at a minimum, hemostatic drugs.
The first next menstruation comes as usual in a woman’s cycle - after 21-35 days. They are often more abundant and there may be clots. Many people report pain, even if there was none before.
Second period after installation
Based on the next menstruation, one can already judge how the critical days will pass in the future. They can be ordinary and familiar to a girl. Sometimes periods change so much that they force a woman to have the IUD removed - they become extremely heavy, long-lasting and painful.
How are things going in the third month?
By this time, the body has already fully adapted to the IUD - either accepts it or rejects it. If an IUD brings a lot of inconvenience to a woman, you shouldn’t think that it will go away later—it’s better to use another method of contraception.
All these features are characteristic of classic IUDs. If the system is with hormones (for example, Mirena), the nature and duration of menstruation is completely different, since the body is under the influence of gestagens.
Features of Mirena and menstruation after it
This is a hormone-containing spiral, its analogue is Levonov’s. They are used for contraception, but also have a therapeutic effect. More often prescribed to women over 35 years of age for the prevention and treatment of gynecological pathologies.
Contains Levonorgestrel as an active ingredient. It is also included in such tablets as Postinor, Escapelle, Mirolut. The only difference is in the dose of the substance and the method of entry into the body.
Hormonal IUDs have all the properties of conventional IUDs, plus their action is supplemented by the following points:
- Levonorgestrel has an antiestrogenic and progestogenic effect, which improves the balance of female sex hormones. Therefore, Mirena is prescribed for endometrial polyps, hyperplasia, and recurrent uterine bleeding.
- Levonorgestrel stimulates the thickening of cervical mucus, which makes it difficult for sperm to penetrate into the uterine cavity.
- The active substance leads to endometrial atrophy, so the fertilized egg, even in the event of conception, has “nowhere” to implant.
- The drug does not directly affect ovulation in such a minimal dosage, but has an effect on the secretion of FSH and LH by the pituitary gland.
Considering the action and influence of Mirena and similar IUDs on the body, there are features of the menstrual cycle when using them. Namely:
- menstruation becomes less abundant;
- the duration of critical days decreases;
- the cycle becomes more regular;
- menstruation is less painful.
However, Mirena is not a panacea. Some women are not suitable for this method of treatment and contraception; they experience breakthrough bleeding, pain, and the IUD may come out on its own or become dislodged in the uterine cavity.
Removing the IUD
The average period of use of intrauterine contraception is 5 years. This condition should not be neglected and “forget” about the spiral, which often occurs in women who are not sexually active. Such exceeding of the terms of use threatens various complications - from inflammatory to infertility and cancer.
It is also ideal to remove the IUD in the last days of your period. This way the procedure will be less painful and the possibility of pregnancy will be excluded (rare, but still possible with the use of an IUD). Immediately after removal of the IUD, a woman can become pregnant, so protection should be taken from the first day. The extraction procedure itself takes no more than 5 minutes.
Restoring the cycle after removing the IUD
After removal, the woman’s menstrual cycle gradually returns to the norms that were before its installation. If you have doubts or suspicions of any disease, it is better to consult a doctor.
Heavy periods
If a woman had decent discharge in the uterine cavity during menstruation against the background of an IUD, similar discharge may persist for another couple of months. But if your critical days are accompanied by pain, discharge with clots and an unpleasant odor, you should consult a doctor. Long-term use of an IUD is a risk factor for endometritis. Moreover, while wearing the spiral, a woman could develop fibroids and other pathologies.
Scanty menstruation
They are more common in women who had light periods before the IUD was installed. In addition, pregnancy should be excluded if the discharge is spotting.
Time after IUD removal
In terms of duration, periods also usually become shorter, since the coil itself provokes long-term spotting after the completion of the main discharge.
And here is more information about how to distinguish uterine bleeding from menstruation.
The intrauterine device is a reliable and inexpensive way to prevent pregnancy. But a foreign body in the uterine cavity provokes a change in the nature and duration of menstruation. For some, IUDs are not suitable at all - menstruation becomes so heavy and painful. The doctor’s task is to choose the most suitable IUD option for a woman; the variety of coils produced allows this to be done.
How do IUDs affect menstruation?
Depending on the type of IUD used, women may experience different changes in the nature of their menstrual cycle.
Hormonal IUDs
IUDs can affect your periods in different ways
Hormonal IUDs release artificial progesterone into the uterus, which is called levonorgestrel.
While in the uterus, this substance prevents pregnancy in the following ways.
- Thickens cervical mucus. More viscous cervical mucus makes it difficult for sperm to move toward the egg.
- Thinning of the endometrium. The endometrium is the mucous membrane lining the inner wall of the uterus. It periodically thickens in order to receive and subsequently nourish a fertilized egg.
- Prevents ovulation. Levonorgestrel may prevent the release of an egg from the ovary, but it should be understood that this property of the hormone is unstable. That is, the prevention of unwanted pregnancy is mainly achieved due to the thickening of cervical mucus and thinning of the endometrium.
Hormonal IUDs can relieve menstrual symptoms, such as prolonged or excessive bleeding.
Menstruation is the rejection of the endometrium by the uterus and its subsequent exit from the body through the vagina. Because levonorgestrel thins the lining, women may have lighter or shorter periods while using an IUD.
Four types of hormonal IUDs are currently widely used in world medicine. They all contain the same hormone, but affect the body for different periods of time:
- Mirena - up to 7 years;
- Liletta - up to 7 years;
- Kyleena - up to 5 years;
- Skyla - up to 3 years old.
IUDs that are designed for longer-term use include larger volumes of levonorgestrel. The higher the concentration of this hormone, the higher the likelihood of developing light menstruation or its complete absence.
Copper IUDs
Unlike hormonal IUDs, copper-containing IUDs do not help prevent ovulation. Such IUDs prevent sperm from meeting a fertilized egg.
Even if fertilization somehow occurs, the copper-containing IUD will prevent the embryo from implanting into the endometrium.
Women using copper-containing IUDs may experience heavy and prolonged menstrual bleeding.
Other potential side effects of copper IUDs include the following:
- bleeding or light spotting between periods (breakthrough bleeding);
- spasms or aching pain in the lower back;
- menstrual irregularities.
How it affects the body
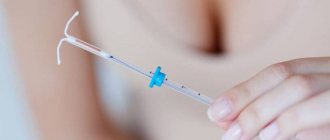
An intrauterine device is a T-shaped device that is inserted into the uterus as a means of contraception to avoid unwanted pregnancy.
The Mirena IUD contains the hormone levonorgestrel, which is released into the uterus. It blocks the growth and rejection of the endometrium and works only inside the uterine cavity, which reduces the risk of hormonal side effects.
As a result of the reaction to the drug, the secretion of cervical mucus increases, which creates an obstacle to the movement of sperm into the uterine cavity. The spiral helps suppress sperm motility inside the uterus and fallopian tubes. Sometimes a contraceptive blocks ovulation, which creates the maximum contraceptive effect.
Only a doctor can install Mirena after a thorough examination:
- It is necessary to take a smear for flora in order to exclude, and in another case, to treat existing inflammations.
- Blood test for hCG.
- Cytological studies are necessary to exclude precancerous and cancerous formations.
- An ultrasound is prescribed to ensure the normal structure of the uterus and ovaries.
Prolonged spotting may be present for six months after installation of the IUD. This is a normal reaction of the reproductive system to the installation of foreign material. If the discharge does not stop after six months, you should voice the problem to your doctor.
Installation of an intrauterine device can sometimes be accompanied by unwanted side effects, the most common of which are:
- migraine;
- acne;
- irregular menstrual flow;
- depressive states;
- heart pain;
- surges in blood pressure.
Disadvantages and side effects of intrauterine devices
Spirals, of course, have disadvantages, and there are only three of them:
- with the IUD, unlike using a condom, there is no protection against sexually transmitted infections;
- Only a doctor can insert and remove the spiral;
- After installation of an intrauterine device, side effects may occur.
Intrauterine devices are one of the safest contraceptives in terms of side effects, since in 95% of cases the use of an IUD occurs without any complications. However, extremely rarely, the development of endometritis and uterine perforation can still occur.
Indications for use
The main indication for the use of an intrauterine device is considered to be the prevention of pregnancy. However, it should be borne in mind that during sexual intercourse it does not protect against STDs, so this type of contraception is not suitable for women who are prone to casual sexual intercourse and chronic infectious pathologies.
Often, an intrauterine device is used for intense menstrual flow for unknown reasons, having previously ruled out possible malignant formations in the organs of the reproductive system. Due to its action, Mirena is prescribed as a prophylaxis against endometrial hyperplasia, fibroids, and during severe menopause.
The nature of menstruation when using an IUD
After installing the Mirena contraceptive, ideally your period should begin at the scheduled time. But it should be taken into account that the body has been subjected to a certain stress, so at first a slight delay is allowed, which should not exceed three weeks. If you don’t have your period after three weeks, you need to go to the hospital immediately. This may be a signal that, despite the installation of the IUD, conception still occurred.
Short delays can last for six months after installation, and they are dangerous for the body.
The first menstruation after installation of the IUD is usually characterized by increased intensity. Why is this happening? Firstly, stress after installation is accompanied by hormonal imbalance, and secondly, the contraceptive changes the composition of cervical mucus and the nature of the endometrium, which directly affects the amount of menstrual fluid. During this period, a woman can use more than one pad every 3 hours and painkillers to eliminate menstrual cramps.
After a few cycles, menstrual flow returns to its normal appearance. Over the course of six months, bleeding may turn into spotting, which is harmless. They indicate that the body is becoming accustomed to a foreign device. There should be no associated pain.
If after several cycles your periods remain as heavy as the first time after installing the contraceptive, you should consult a doctor. A similar phenomenon may indicate side effects of Mirena, which indicates that the body does not accept this contraceptive.
Often women complain about the cessation of menstruation six months after installing a contraceptive. If the delay lasts for more than two weeks, the first step is to do a pregnancy test or a blood test for hCG. The intrauterine device reliably prevents unwanted pregnancy, but all possible options should be taken into account, in addition, there have been cases when the device has fallen out unnoticed. If the reason for the lack of menstruation is not pregnancy, then there is no reason to worry. Mirena hormones block the growth of the endometrium, which is why there is nothing to come out during the expected period. This is not dangerous for a woman’s body. After removing the IUD, menstruation will return within a couple of months.
Reasons for the delay of critical days
A delay in menstruation after installation of the IUD is not a pathology. The regularity of the cycle will be restored over time. Much will depend on the quality and composition of the installed product.
Normalization of the cycle with the hormonal intrauterine system is faster. Delays in menstruation are more common with metal-containing products. When a failure is accompanied by severe pain, the contraceptive is removed ahead of time.
If you haven't had your period for more than two weeks, take a pregnancy test. If there is no discharge for a long time, conception should not be ruled out. The spirals move from their place, descend into the cervical canal and simply fall out. This is unlikely, but this happens due to the poor quality of the product, improper installation or the individual characteristics of the female body.
Full physiological recovery after installation of an intrauterine contraceptive occurs after 3 months. If during this time the cycle has not returned to normal, and pregnancy is accompanied by painful symptoms, contact a gynecologist.
Contraindications
There are a number of contraindications that do not favor the use of an intrauterine contraceptive:
- pregnancy;
- inflammatory diseases of the genital organs;
- infectious pathologies of the internal genital organs;
- precancerous and cancerous formations in the cervix;
- malignant tumor in the breast;
- do not use a contraceptive immediately after childbirth or abortion;
- abnormalities of the reproductive system;
- jaundice, liver cirrhosis.
Severe diabetes mellitus, thrombophlebitis, arterial hypertension, stroke, as a rule, may be a contraindication. Only after additional examination can the doctor approve the use of Mirena.
A history of ectopic pregnancy is not considered a contraindication to the use of the IUD, but you should be aware that ectopic pregnancy is a very rare undesirable consequence of installing a contraceptive. This complication is characterized by nausea, vomiting, lack of discharge, severe pain in the abdominal area, weakness, and dizziness.
Causes of heavy and prolonged menstruation
The first periods after installation of the IUD are scanty. An increase in discharge is observed from the second month, heavy menstruation should end by the end of the third, when the hormonal levels stabilize. If the course of the cycle follows a different scenario, and their volume does not decrease, visit a gynecologist.
There is a possibility of complications developing. The most common include:
- damage to the uterus;
- displacement of the contraceptive into the abdominal cavity;
- anemia;
- bloody and purulent discharge;
- risk of developing inflammatory processes.
When agreeing to use an intrauterine device, a woman should know how many days her period lasts while wearing the IUD, what is its intensity and how the condition changes with possible complications. Spotting and cramping pain in the abdominal area indicate incorrect positioning or displacement of the contraceptive product.
Prolonged periods, accompanied by an increase in body temperature, indicate the onset of inflammation in the reproductive system. Excessive brown blood loss with increasing pain is a common sign of intrauterine pregnancy.
It is important to understand that all problems of the reproductive system do not go away on their own, and without the participation of a doctor it is impossible to identify the cause of atypical behavior of menstruation after the IUD.
There are several. A separate article on our website will tell you more about them.
Doctors' opinion
In addition to the contraceptive effect, doctors highlight the positive effect of the intrauterine device on the condition of the endometrium. Often, a contraceptive is prescribed for medicinal purposes during severe menopause, for the prevention of fibroids and endometriosis of the uterus. The spiral stops the growth of myomatous nodes, prevents cancer and endometrial hyperplasia, increases hemoglobin, and has a general strengthening effect. After removing Mirena, if you wish, you can become pregnant in the first year. Thanks to the action of hormones, it increases the level of fertility of a woman.
The Mirena intrauterine device is indeed a very convenient and practical means of contraception, however, given the considerable list of contraindications, special attention should be paid to examinations before installing a contraceptive. If you act according to the recommendations of specialists, there should be no health problems during contraception with the intrauterine system.