Can the spiral move?
In medical practice, there are often cases when the IUD moves or falls out completely. Most often this happens after menstruation. Excessive bleeding and rejected tissue, coming out, can cause displacement. In some cases, the IUD is dislodged immediately after insertion. As a rule, this is due to the unskilled work of the doctor who installed it.
Spiral displacement. Symptoms
Pain in the lower abdomen, discomfort during sexual intercourse, bleeding - these are the main signs of displacement of the spiral. Incorrect placement of the IUD significantly reduces its contraceptive effect. Therefore, if the above symptoms are detected, it is very important to use additional methods of birth control. For some women, the incorrect position of the IUD does not cause any pain, i.e. is asymptomatic. To detect a defect in time, you must follow some recommendations:
- You need to independently control the length of the threads coming out of the cervix. How can you tell if the spiral has shifted? If the antennae have disappeared or become significantly shorter, this may indicate that the device has fallen out. Most often this happens unnoticed when visiting the toilet. In this case, it is necessary to do an ultrasound and check for pregnancy. Elongated strands indicate helix displacement.
- You should visit a gynecologist's office once a year and perform an ultrasound diagnosis. Following these simple rules will allow you to identify the incorrect position of the IUD in time and avoid unplanned conception.
Negative consequences
This natural remedy will 100% relieve pain during menstruation! If you guess what it is, you will get rid of it forever!
If the spiral has become dislodged (moved), in addition to heavy menstruation and pain in the abdominal area, more serious consequences are possible. In 15% of cases, women are diagnosed with damage or injury to nearby organs, especially the intestines.
Treatment
An ultrasound examination should determine the position of the device in the uterine cavity.
If the diagnosis is confirmed, the IUD needs to be removed. After this, you can install a new one or choose a different method of protection. The device cannot be reused. If no inflammatory processes occur during wearing, removal is almost painless. It is very important that the procedure is performed by a specialist and takes place under sterile conditions. This will avoid damage to the uterine mucosa and infection. Typically, the IUD is removed during the menstrual cycle. Doctors have found that women who have had a vaginal birth have virtually no complications associated with the use of such a contraceptive method as the intrauterine device. Displacement is most often observed in women with suspected adenomyosis.
This remedy relieved all Chinese women from menstrual pain! It will help you too! You stick it on the groin and forget about the pain!
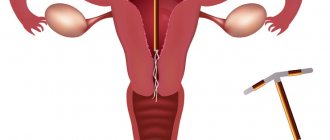
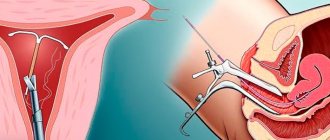
Intrauterine devices (IUDs) are a reversible and long-term method of protection against unwanted pregnancy. The vast majority of IUDs are T-shaped devices that are placed in the uterus and remain there for an extended period of time. Sometimes the spirals randomly shift and come out.
In girls aged 14 to 19 years, the spirals are displaced more often than in women from other age categories. Additionally, IUD prolapse is more common in women who have recently had a vaginal birth or medical abortion.
The doctor will have to remove the IUD if it has become dislodged or partially removed from the uterus.
WHEN SHOULD IT BE REMOVED?
Removal of the intrauterine device is carried out in the following cases:
- displacement or expulsion (spontaneous prolapse) of the IUD. If after replacing the contraceptive the problem recurs, then the woman should think about changing the method of protection against pregnancy
- the end of the IUD service life specified by the manufacturer. Most often, spirals are designed for 3-5 (rarely 10) years. If the annotation of the intrauterine device does not indicate the period of use, then by default it is equal to 5 years
- pregnancy. The effectiveness of the IUD is 98%, however, unfortunately, in very rare cases, pregnancy can occur (including ectopic)
- woman's desire to have a child
- development of uterine fibroids. A small fibroid, which is not accompanied by deformation of the uterus, does not prevent the installation of an IUD (it is advisable to opt for a product with a gestagen). If, after the introduction of a contraceptive, the fibroid begins to grow or a new one appears, then the product must be removed immediately
- the occurrence of diseases of the pelvic organs. In this case, removal of the IUD is accompanied by antibacterial therapy
How likely is the IUD to come out?
Intrauterine devices may come out in women recovering from natural childbirth.
The categories of women who are associated with a higher risk of IUD failure are detailed below.
Recent women giving birth
In 2021, American scientists conducted a study involving 162 women who had intrauterine devices inserted immediately after natural birth. It turned out that during the first 6 months of using the coils, 8% of the study participants experienced complete withdrawal, and 16% experienced partial withdrawal.
Recovery period after IUD removal
For 5-6 days after removal of the IUD, a woman should refrain from intimacy, the use of vaginal tampons and suppositories (suppositories). It is also not recommended to douche, visit the sauna and bathhouse, engage in heavy physical activity and sports, take a hot bath and take medications that contain acetylsalicylic acid. Some women, after removal of the IUD, may experience a pulling, aching pain in the lower abdomen, as well as the appearance of minor bleeding or spotting. The appearance of such pathological conditions is considered normal. They do not require treatment as they should disappear on their own within a few days. The next menstruation may begin with a slight delay, which is also considered normal. If a hormonal IUD was inserted, it may take a little longer for your menstrual cycle to return.
After removal of the intrauterine contraceptive device, pregnancy occurs in 30% of patients within the first month, and in 60% during the first three months. Within 1 year after removal of the IUD, pregnancy occurs in 90-95% of women, provided that at this time they do not use other contraceptives.
Source: ginekologi-msk.ru
Symptoms of release and displacement of the intrauterine device
When the doctor places the intrauterine device in the uterus, he explains to the woman how to monitor the threads of the device.
If the IUD comes out or becomes dislodged, a woman may notice at least one of the following changes when checking the strings:
- the threads become shorter than usual;
- the threads seem uneven;
- the threads change location;
- there are no threads.
Women may also notice that they cannot feel their IUD.
In some cases, a dislodged or prolapsed IUD can cause physical symptoms. These symptoms include the following:
- severe bleeding;
- acute spasms;
- deviations in the nature of vaginal discharge.
Sometimes, when the coils come out, there are signs of infection, such as fever and malaise.
If a woman experiences the listed symptoms, then she needs to visit a gynecologist.
What could be the consequences of installing a spiral?
When removing the intrauterine device, sometimes more serious difficulties arise. In some cases, the spiral antennae are not detected. Then it is necessary to determine the location of the device and determine whether it is there at all. For this purpose, visual examination methods (ultrasound or radiography) are used. If during the study it turns out that the spiral has perforated the wall of the uterus and is located outside its cavity, emergency surgery is required.
There are situations when the antennae of the spiral are in place, but the gynecologist is unable to remove it. In such cases, an ultrasound or x-ray is needed to determine the cause of the immobility of the spiral. It happens that the device fits too tightly to the walls of the uterus.
Much more dangerous is the situation when a foreign body grows into living tissue. Most often, this consequence occurs if the spiral is not removed in due time, that is, the validity period of the medical device has been exceeded. In such cases, invasive surgery is necessary to remove the coil.
How does the release of an intrauterine device affect the risk of pregnancy?
When the intrauterine device is displaced, the risk of unwanted pregnancy increases
If the intrauterine device falls out or becomes dislodged, the risk of unwanted pregnancy increases.
If the IUD remains in the uterus during pregnancy, it can lead to health problems for both the mother and her baby. In particular, the risk of miscarriage and ectopic pregnancy will increase.
An ectopic pregnancy is a condition in which a fertilized egg begins to develop outside the uterus. This usually occurs in the fallopian tubes.
An ectopic pregnancy is a problem that requires emergency medical attention.
Due to the increased risks, the doctor will pay special attention to a woman who becomes pregnant while having an IUD in the uterus.
When should you see a doctor?
It is necessary to meet with a doctor if pregnancy occurs while there is a device in the uterus.
A woman should see her doctor if she suspects that the IUD has come out or become dislodged. The specialist will likely perform a gynecological examination or suggest an ultrasound examination to check the correct placement of the IUD.
In addition, a woman should consult a doctor if she becomes pregnant while having an IUD inside the uterus, since in such situations the risk of miscarriage and ectopic pregnancy increases.
A visit to the hospital is also necessary if a woman experiences one of the following symptoms:
- severe cramps;
- severe bleeding;
- fever;
- deviations in the nature of vaginal discharge;
- constant pain in the uterus or persistent discomfort.
The listed symptoms may indicate that the displacement of the spiral can lead to serious complications.
Expulsion concept
Expulsion of the IUD is the spontaneous expulsion of the intrauterine device from the uterine cavity. This complication is more often observed in young nulliparous women or older women. It can also occur after an increase in the number of pregnancies (including those ending in abortion), the likelihood of displacement or loss of a contraceptive is significantly reduced.
As a rule, the movement of the spiral occurs in the first few hours after installation, and therefore, at the end of the procedure, it is rational to undergo an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs in the longitudinal direction. If the drug is detected in the cervix or the contraceptive is found fragmentarily, in the cavity or cervix, expulsion is noted and a serious chance arises. This promotes migration of the intrauterine device (IUD) into the fallopian tube , which can cause severe damage and perforation of soft tissue.
Advantages characteristic of an IUD in the uterine cavity:
- high effectiveness of the contraceptive - over 98% ;
- effective from the moment of establishment;
- rapid restoration of fertility after removal;
- does not affect sexual intercourse;
- does not affect breastfeeding;
- suitable for use by women who cannot use hormonal medications;
- duration of action: from 2 to 10 years ;
- relatively low cost;
- no need for daily monitoring.
Disadvantages characteristic of intrauterine devices:
- the procedure of insertion and removal is carried out only by a doctor ;
- there is no protection against sexually transmitted infections;
- an increase in the amount of discharge and the degree of pain during menstruation during the first 2-3 months after the installation of the IUD;
- not recommended for young nulliparous women;
- the risk of inflammatory diseases increases, because the cervix remains open;
- damage and depletion of the endometrium , which negatively affects subsequent pregnancies;
- possibility of IUD expulsion ;
- not recommended for women with prolonged/painful menstruation;
- Before administration, an examination by a gynecologist and tests for the presence of sexually transmitted infections are required.
The essence of the procedure
Hysteroscopy is the main method for diagnosing an ingrown intrauterine device. The examination allows you to determine the exact location of the contraceptive and the degree of ingrowth. Over time, the IUD becomes covered with the endometrium and is embedded in the myometrium. The choice of removal tactics largely depends on the location of the spiral. Being near internal organs and large vessels significantly complicates the operation.
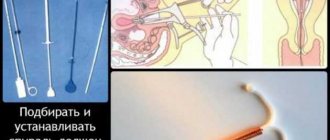
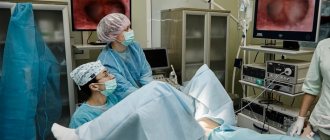
Removal of an ingrown IUD is carried out in several stages under local anesthesia in an operating room. First, the genital organs are sanitized. Dilators are placed in the cervical canal. Gynecological devices facilitate access to the uterus. Then a hysteroscope is inserted into the cavity and the walls are carefully examined. After detection, the spiral is removed with special forceps or a curette. If a significant part of the contraceptive has grown into the abdominal cavity, laparoscopy is prescribed. If the IUD is located near the bladder or the walls of large vessels, laparotomy is indicated. At the end of the operation, the doctor scrapes out the overgrown endometrium.
It is recommended to remove the IUD on days 5-7 of the menstrual cycle. For two weeks after surgery, it is necessary to limit physical activity and carefully monitor personal hygiene. If you feel worse, you should immediately consult a doctor.
The medical center in Maryino invites everyone to consultations. To make an appointment with a gynecologist, call the phone number listed on the website. We will select a time convenient for you.
Р'СЃРµ статьи
Source: www.euromeds.ru
IUD extraction is performed in the following cases:
- The end of the recommended period of use of the IUD (intrauterine devices can be used for 5-10 years);
- The presence of uncontrolled bleeding from the uterine cavity, which is caused by the insertion of an IUD;
- Pregnancy that occurred while an IUD was installed;
- Change in the growth activity of a benign tumor in the uterine cavity after the introduction of an intrauterine device (fibroids, fibroids);
- Detection of malignant tumor processes of the pelvic organs;
- Expulsion of the IUD - displacement of the intrauterine contraceptive relative to its correct initial position;
- The appearance of an ascending infectious process (gonorrhea);
- The presence of acute inflammatory pathologies of the pelvic organs.
Reasons for appearance
The main reasons for the expulsion of the IUD are the discrepancy between its shape and size , the distance from the cervix to the bottom of the uterine cavity and its volume.
As a result, painful sensations and strong muscle contractions are observed, which lead to the displacement of the contraceptive outside the organ - into the cervical canal, and from there into the vagina. A similar situation results from the inability of the isthmus muscles to retain the drug in the cavity. In addition to individual physiological etiology, the following are equally sources of expulsion:
- use of an IUD by women with a deformed or open cervix ;
- excessive mechanical loads ;
- Incorrect installation of the spiral.
Signs of expulsion
Symptoms of partial expulsion of the contraceptive are:
- severe, cramping pain in the suprapubic area , which is not relieved by analgesics and antispasmodics;
- atypical vaginal discharge;
- bleeding and pain during and after intimate intercourse;
- hemorrhages between menstrual cycles ;
- sensation of the drug at a physiological level in the cervix or vagina;
- increase in the visible length of the IUD threads.
The indicator of absolute expulsion is:
- it is impossible to see and palpate the IUD threads;
- the spiral cannot be detected using standard techniques for examining the genital organs. There is a low probability of doing this using an ultrasound or x-ray examination of the pelvic area.
- the uterus should measure 4.3−5.1 cm ; in women who have given birth - more than 5−5.2 cm; the location has not been changed;
- size - 2−3 cm ;
- the walls of the uterus should have a uniform thickness, without specific formations;
- The IUD should be placed deep in the uterine cavity.
Features of removing an ingrown helix
You cannot remove the IUD yourself; to do this, you should contact a qualified gynecologist. Before the procedure, the specialist will examine the patient in a gynecological chair and refer her for tests. Laboratory tests that a woman must undergo before manipulation:
- Analysis of urine;
- blood analysis;
- microflora smear;
- bacterial culture.
An ultrasound examination of the uterus and colposcopy should also be performed. After the doctor is confident that the IUD has grown into the patient’s organ, the doctor sets the time and day of the operation.
Extraction is carried out in stages using local anesthesia. Intimate organs are sanitized: the woman’s genitals are treated with antiseptic medications. Dilators are installed in the cervix to facilitate access to the uterine cavity. Next, a hysteroscope is inserted through the cervix, with which the gynecologist can examine the muscle walls in detail.
After the specialist detects the IUD, it is removed with sterile forceps or a curette. In cases where most of the contraceptive grows into the abdominal cavity, laparoscopy is prescribed.
If the coil is located near the bladder, urinary tract and large vessels, laparotomy is indicated. At the end of the procedure, the doctor scrapes out the overgrown mucous layer. The duration of the operation varies from 15 to 30 minutes.
If an ingrown intrauterine contraceptive cannot be pulled out through the cervical canal (due to occlusion or atresia), then a specialist removes it through the abdominal cavity. In this case, extraction occurs using laparoscopic methods under general anesthesia. After surgery, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed, and the doctor gives a referral for an ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
Consequences and complications
Expulsion is sometimes accompanied by mild discomfort , less often by severe pain in the suprapubic or periumbilical region of the pelvis. In a normal situation, the pain manifests itself for a short time, otherwise, a visit to a gynecologist is required for further examination.
Partial displacement of the contraceptive can lead to its migration into the fallopian tube , which leads to perforation of the walls of the fallopian tubes. The development of this pathology can be assumed based on the characteristic symptoms :
- persistent pain in the lower abdomen and the appearance of signs of intra-abdominal bleeding;
- weaknesses;
- tachycardia;
- blanching of mucous membranes;
- drop in blood pressure;
- “Volka-stand up ” syndrome - the patient strives to take a “sitting” position to reduce pain.
There is only a surgical way to resolve the pathology. Cervical perforation is mainly a consequence of contraceptive displacement. Therefore, a specialist, during a special examination of the genital organs, can detect an intrauterine device in the area of one of the corners of the vaginal vault. If a perforation of the cervical canal itself is detected, immediate insertion of the IUD into the uterus is prescribed for its further removal.
Asymptomatic drug rejection, coupled with the lack of other methods of birth control, leads to unplanned pregnancy .
Signs of a displaced IUD are painful sensations during sexual intercourse for the woman’s partner.
Also find out what a negative MAP test means, interpretation, results, how a spermogram differs from a MAP test
Why do you need labiaplasty - laser or surgical is written in detail here
6 facts about fetal hypoxia, consequences for the child, the nervous system, what it threatens: https://hochu-detey.ru/plan/gipoksiya-ploda.html
Diagnostics
Subjective signs of displacement of the drug are recorded: a sensation of a spiral in the area of the internal and external pharynx of the cervical canal or vagina and a change in a fixed specific length of the threads.
With absolute expulsion, the threads are not amenable to palpation , and probing, ultrasound and x-ray examination of the pelvis do not detect the spiral.