FAM of the breast - what kind of diagnosis is it, its types: diffuse, localized
Benign formations are one of the most common forms of mammary gland pathologies in women. They appear in more than 50 forms and are adenofibromatosis, fibromatosis, etc.
What is it - FAM of the mammary gland? FAM stands for fibroadenomatosis. This is a benign disease that occurs in the connective tissue of the mammary gland, where fibrous tissue grows under the influence of hormones.
Depending on the ongoing pathological process, this disease takes various forms, which differ from each other in the nature and extent of the lesion.
Causes and risk factors
The main reason for the development of such problems is hormonal imbalance in women. This may happen for some reasons:
- Stress – constant stress overexertion affects the functioning of the endocrine glands, which disrupts the functioning of many body systems.
- Problems in the sexual sphere - irregular sexual intercourse, no permanent partner, etc., changes in hormonal levels.
- Gynecological diseases - problems with the functional functioning of the ovaries; failure of the menstrual cycle leads to disruption of the normal production of hormones. Of particular importance in provoking the disease is abortion.
- Early cessation of breastfeeding before the child is one year old, as well as refusal to feed the child after his birth, provokes stagnation in the milk ducts, hence, inflammatory diseases in the breast.
- Thyroid diseases cause improper production of hormones.
- Some diseases of the liver, which removes hormonal breakdown products from the body, which can lead to hormonal imbalance.
In addition, there are provoking factors, the presence of which suggests an increase in the likelihood of developing FAM of the mammary glands.
They are based on a chemical and hormonal nature:
- work in hazardous production;
- unhealthy lifestyle, alcohol abuse and smoking;
- tight underwear;
- taking oral contraceptives;
- frequent pregnancies or refusal to bear children.
Symptoms
There are different types of lumps in the mammary gland, so the mammologist relies on the accompanying symptoms to make the correct diagnosis:
- frequently recurring stabbing chest pains that occur during the premenstrual period;
- a feeling of pressure or burning in the chest during the premenstrual period;
- discharge from the nipples that appears independently or when squeezed;
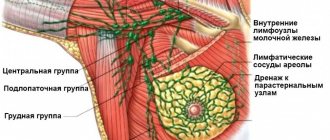
- possible enlargement of lymph nodes in the axillary region;
- The mammary glands swell and become denser.
It is worth noting that the manifestations of these symptoms intensify during periods of nervous overstrain and physical fatigue.
Forms
FAM of the breast has several forms:
- Diffuse. This form is considered the first stage of the disease. What is it - diffuse FAM of the mammary glands? The examination reveals several nodules, which are usually located in the upper parts of the chest. Seals are detected in one or both mammary glands. Associated symptoms are hardening of the mammary glands before menstruation and increased sensitivity. They can disappear on their own, which happens after childbirth and completion of breastfeeding.
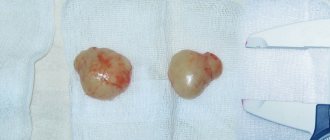
- Localized. The question often arises, what is FAM lock of the mammary gland? In this case, a single formation is clearly defined in size from 1 to 6 cm. The compaction is a dense knot with clear boundaries, a bumpy surface and may have a granular structure. When palpated, it causes slight pain.
- Localized FAM of the breast is a form of the disease that in 40% of cases occurs in nulliparous and unmarried women aged 30 to 40 years, of the remaining cases, 38% are women who have had multiple abortions.
- Cystic. Multiple and multi-chamber cysts develop, which are heterogeneous in nature and arise in the ducts or alveoli. The disease often affects 2 breasts at once, where the cysts are located one at a time or in groups. Diagnosis requires x-rays, as well as puncture and trephine biopsies.
- Focal. This form is similar to diffuse FAM, where the compactions also consist of glandular tissue, which is replaced by fibrous tissue. But in this case, there is no clear boundary between the tissues, and the patient feels constant pain.
- Fibrous. In this form of the disease, compactions are formed due to the proliferation of fibrous tissue. Most often, such processes occur as a consequence of injury or an infectious-allergic disease.
- Nodal. Small lumps appear locally, and the patient feels pain in the area of the lumps. This form occurs in close connection with diffuse fibroadenomatosis.
Only a specialist can determine the form of the disease after a thorough diagnosis.
Diagnostics
What is the diagnosis of FAM of the breast, and what methods are used to accurately diagnose it? To make a correct diagnosis, a mammologist, in addition to standard ultrasound and x-rays, can prescribe a number of special and additional studies. For example, aspiration and stereotactic biopsies, trephine biopsy, ductography help determine benign or malignant formation in each specific case.
For a more complete diagnosis, which allows you to determine the most successful treatment regimen, the following are performed: thermography, chest x-ray, MRI or CT, examination of lymph nodes, and various laboratory tests.
Treatment
The main directions of treatment are optimization of hormonal balance and tissue restoration, as well as symptomatic therapy. The use of different drugs will depend on many factors, such as age, stage of the disease, etc.
In general, hormonal agents, vitamins, homeopathic drugs, antidepressants, adaptogens, and anti-inflammatory drugs are used. In some cases, medications for the liver and thyroid gland.
Surgical
In cases where drug treatment is ineffective or in cases of advanced disease, surgical intervention may be used. This treatment is also indicated for some localized forms of FAM.
The operation can be performed under general anesthesia or local anesthesia, depending on the complexity of each case. During the operation, the necessary histology tests are taken.
Traditional methods
The use of folk remedies in the treatment of fibroadenomatosis is aimed primarily at optimizing hormone levels, normalizing metabolism and relieving nervous tension.
Many plants contain essential oils and active ingredients that have a positive effect on the treatment of the disease and the patient’s condition as a whole. A special advantage of such methods is the absence of side effects.
For example, to treat the mammary glands, burdock or cabbage leaves are applied to the breast. Some plants, such as valerian root, nettle, rose hips and others, have a mild effect by stabilizing hormonal levels.
But you should not think that by using only such means you can easily cure fibroadenomatosis, and especially its advanced stage. Traditional methods can be used as an addition to conservative treatment. Before use, you should consult your doctor.
Forecast and danger
With timely diagnosis, the diagnosis of FAM is not dangerous and responds well to treatment. What is FAM of the breast when compared to cancer?
It is worth noting that fibroadenomatosis is a benign formation, but these cells have the ability to develop into malignant ones over time. This explains the need for early diagnosis.
Prevention
Preventive measures are aimed at maintaining general health, the absence of sudden changes in hormone levels, as well as breast renewal during lactation:
- healthy lifestyle, physical activity;
- comfortable underwear that helps avoid chest compression;
- early diagnosis - involves self-examination of the breast and regular visits to a mammologist;
- breastfeeding - from the moment the child is born until 1-1.5 years;
- refusal of abortion;
- regular sex life.
If you detect the first signs and the presence of seals, you should immediately consult a doctor for early diagnosis and initiation of treatment.
Video
From our video you will learn about the causes, prevention and treatment of breast diseases.
molzheleza.ru
Causes of localized fibroadenomatosis in women: diagnosis and treatment methods
Local fibroadenomatosis of the mammary glands, what is it? In a broad sense, local fibroadenomatosis is a process that results in the formation of many nodules with clear boundaries in the mammary glands.
The disease is a benign tumor, but it must be treated in a timely manner.
Otherwise, complications can lead to serious consequences and the need for surgical intervention.
In the article we will talk about the treatment of localized fibroadenomatosis of the mammary gland, we will tell you what it is, what are the causes and symptoms of the disease.
Localized fibroadenomatosis or localized mastopathy is a disease that is accompanied by a complex of processes that promote the proliferation of immature cells of breast tissue.
The result of the development of the disease is the formation of an atypical ratio of epithelial and connective tissue components. Changes in the mammary glands manifest themselves in the form of swelling, swelling and the formation of compactions that cause discomfort. The nodes can reach 6 cm in diameter.
There are several names for the disease:
- adenofibrosis;
- fibrocystic disease;
- Reclus disease;
- mastopathy;
- cystic mastopathy;
- fibromatosis.
Localized mastopathy: what is it? Localized mastopathy is a disease whose risk group includes patients with hormonal abnormalities and liver diseases.
These factors are among the most common causes of nodules in the mammary glands. In some cases, fibromatosis develops against the background of a hereditary predisposition.
The causes of the disease also include the following factors:
- pathologies of the thyroid gland (thyroid hormones are in close relationship with sex hormones);
- frequent stressful situations (in fact, negatively affects the state of the endocrine system);
- carrying out induced abortions (procedures provoke disruption of the functioning of sex hormones);
- late onset of menstruation or late pregnancy (factors relate to the causes of subsequent hormonal abnormalities);
- gynecological diseases (this type of disease can provoke a hormone imbalance);
- early cessation of lactation (the factor provokes a deviation in the performance of the mammary glands and the formation of stagnation in them);
- problems of a sexual nature (lack of a regular sexual partner, irregular intimate relationships, as well as other sexual problems cause hormonal imbalance).
IMPORTANT! During breastfeeding, the risk of local fibroadenomatosis increases. Premature interruption of lactation leads to stagnation in the mammary glands. It is strictly not recommended to stop breastfeeding before three months after birth.
Local fibroadenomatosis of the mammary gland never develops asymptomatically. The presence of nodules can be detected by palpation. When palpated, compactions with clear boundaries are clearly felt, and discomfort of varying degrees occurs.
Associated symptoms include menstrual irregularities, deterioration of the condition of nails, hair and skin, and emotional instability.
Localized mastopathy can cause difficulty in conceiving and bearing a child. If the disease occurs during pregnancy, then the course of treatment must be carried out at an accelerated pace and always under the supervision of a specialist.
Breast cancer - what is it and signs of its appearance
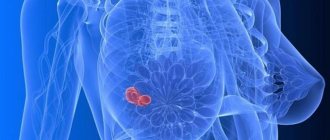
Femme mammary gland what is it? Fibroadenoma (FAM) is a disease of a tumor nature that develops in the tissues of the mammary glands. By its nature, it is a benign tumor, usually of hormonal origin. Its development is provoked by too high levels of sex hormones - estrogen, progesterone or prolactin. Women under 35 most often develop diffuse estrogenic type of mammary glands, and after 40, when the processes of decline of reproductive function begin, prolactin type.
Peculiarities
What are the essence and symptoms of this disease? Under the influence of pathological processes, the glandular tissue of the mammary gland grows, and fibrocystic neoplasms are formed. They can be single or multiple, covering one breast or both at once. Cysts and fibroids are filled with fluid inside. There is no need to ignore FAM - this is fraught with serious consequences, there is a risk of degeneration of a benign neoplasm into a malignant one.
There are several reasons for the development of FAM:
- chronic stress or severe nervous shock;
- disturbances in the functioning of the ovaries;
- poor blood supply to the pelvic organs;
- hormonal imbalance (including those caused by taking oral contraceptives);
- frequent childbirth or refusal to have children;
- wearing tight or ill-fitting underwear;
- lack of lactation or inability to breastfeed;
- heredity.
There are nodular and leaf forms of fibroadenoma. Nodular forms never degenerate into cancer, but every 10th case of leaf FAM ends in breast sarcoma.
A mammologist treats fibroadenoma of the mammary glands. His task is to find out the causes of the tumor and prescribe adequate treatment aimed at eliminating them.
Symptoms of FAM
In the early stages, FAM occurs without symptoms. At a later date, a woman can feel the tumor on her own. There are also signs of breast fibroadenoma that indicate the presence of FAM:
- before menstruation, a stabbing pain appears in the chest, which intensifies with physical activity;
- sometimes tumor growth is accompanied by a feeling of pressure and burning in the chest;
- When pressed, a clear, odorless liquid may be released from the nipples;
- the nipples themselves may crack and become covered with painful sores;
- breast tissue swells and thickens;
- Lymph nodes in the axillary area may become enlarged.
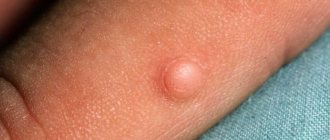
The main symptoms of the disease are the appearance of a small tubercle in the breast tissue, which rolls under the fingers, but does not change location when changing body position.
Diagnosis of the disease
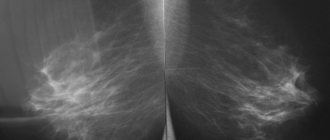
FAM is detected in early stages by mammography. The increase in the number of tumor diseases of the mammary glands has become the reason for the inclusion of mammography in the list of mandatory diagnostic tests during medical examination.
In mammography images, the doctor clearly sees fibrocystic neoplasms - cavities filled with fluid. In addition to mammography, the patient must undergo an ultrasound examination of the surrounding tissues and organs, and is also sent for a consultation with related specialists - a gynecologist and an endocrinologist (with a full diagnosis of the condition of the endocrine glands involved in the production of sex hormones).
If FAM is detected, a puncture of the tumor-like formation is prescribed, and if necessary, a biopsy of the affected glandular tissue is taken. This is done to determine the likelihood of cancer cells appearing and determine the strategy for further treatment - conservative or surgical.
Note! User recommendation! For the treatment and prevention of breast diseases, our readers successfully use an effective remedy to combat these ailments. Cedar resin will improve blood circulation, relieve swelling, and bee venom will relieve pain. Get rid of pain..."
How is FAM different from cancer?
Multiple fibroadenomas are a benign neoplasm. If the size of the tumor does not exceed 10 mm, then the mammologist registers the woman and assesses the condition of the tumor every six months without treatment.
Breast fibroadenoma has differences from a malignant tumor that every woman needs to know:
- Fibroadenoma is a small round or oval lump that has a dense but elastic structure, does not hurt when pressed and moves under the fingers (floating effect). FAM always has clear boundaries. The tumor does not change the color, structure and temperature of the surrounding skin. With cancer, the following may occur: changes in the color of the halo and nipple, the boundaries of the halo, hemorrhages in the skin of the mammary glands.
- The cancerous tumor is not enclosed in a capsule, but is located in the lobules of the mammary gland, so it does not roll under the fingers. In addition, unlike FAM, it does not have clear outlines.
- When palpating a malignant tumor, cords always stand out, which are clearly visible in a standing position. The cords are directed upward or to the sides, like the claws of a crayfish. Which was the reason for the name of the disease.
- With fibroadenoma, axillary lymph nodes rarely enlarge, while with cancer this is one of the main diagnostic signs indicating imminent metastasis. If a painless soft ball of tumor is felt in the chest, and another in the axillary lymph node, then it is necessary to urgently go for a consultation with an oncologist.
- Discharge from the nipple with FAM is clear and odorless, with cancer it is dark and foul-smelling, sometimes mixed with blood.
- Both fibroadenoma and malignant tumor are hormone dependent. In this case, FAM can change size and density in accordance with the schedule of the menstrual cycle, but the cancerous tumor, which has a direct connection with the genital organs, remains unchanged.
Doctors never consider these symptoms to be 100% diagnostic; rather, they indirectly confirm the assumptions of specialists. Each woman’s body is deeply individual and the disease can occur in different ways. In any case, the diagnosis of breast fibroadenoma or cancer is established according to objective studies: mammography, ultrasound, CT or MRI.
Treatment
Doctors always try to treat fibroadenoma with conservative methods; excision is used only in extreme cases. Since it is associated with improper production of estrogen and prolactin, a course of oral medications is prescribed. They contain iodine and sex hormones - antagonists of estrogen, prolactin and progesterone in small quantities. Such treatment is prescribed according to the condition of the endocrine glands, if a deficiency of thyroid hormones is detected, or, conversely, excessive releases of pituitary, ovarian and adrenal hormones into the blood.
In the complex treatment of FAM, the doctor will definitely advise you to follow a diet. It is advisable to give up strong drinks - tea and coffee, meat broths cooked on bones, and limit the consumption of chocolate and other sweet and flour products. The diet should be varied with seasonal vegetables and fruits. A healthy diet will contribute to a mild form of the disease and a speedy recovery.
Breast fibroadenoma is a wake-up call for a woman to reconsider her life priorities - give up bad habits, and perhaps think about motherhood.
All cases of FAM of the mammary glands require constant medical supervision. It is required to undergo mammography and ultrasound examination once every 6 months. Surgical removal of breast fibroadenoma is prescribed if the doctor sees that:
- conservative treatment does not produce results;
- fibroadenoma increases in size;
- In biopsy analyses, single degenerated cancer cells appear.
The indication for removal of breast fibroadenoma is its shape. For example, leaf FAM is considered a borderline condition and is treated surgically.
A woman is prescribed surgical treatment - laser removal of fibroadenoma in the mammary gland. This operation is fundamentally different from that for cancerous tumors. Through a small incision, the cystic capsule is removed from the mammary gland while preserving the surrounding tissue. An exception is leaf-shaped fibroadenoma of the mammary gland, which is removed by sectoral resection along with the affected glandular tissue.
Prevention of fibroadenoma
Every woman must learn breast self-examination methods and conduct it monthly 10-14 days before the onset of menstruation. Those who have already been diagnosed with small fibrocystic nodules should be careful about their health. Follow the doctor's instructions, undergo courses of conservative therapy and regular examinations with a mammologist.
If you are reading these lines, we can conclude that all your attempts to combat chest pain have not been successful... Have you even read anything about medications designed to defeat the infection? And this is not surprising, because mastopathy can be fatal to humans - it can develop very quickly.
- Frequent chest pain
- Discomfort
- Experiences
- Discharge
- Skin changes
Surely you know these symptoms firsthand.
But is it possible to defeat the infection without harming yourself? Read the article about effective, modern ways to effectively combat mastopathy and not only... Read the article... Women who have undergone surgery to remove the leaf form of FAM must register not only with a mammologist, but also with a gynecologist and endocrinologist. They need to monitor the condition of the genital organs and endocrine glands. In general, breast fibroadenoma is a disease that does not threaten life and does not change its quality.
bolivgrudi.ru
Kinds
Adenofibrosis comes in nodular and leaf (diffuse) forms. Diffuse fibroadenomatosis of the mammary glands is more common and is divided into:
- adenosis – a tumor with a predominance of the glandular component;
- fibroadenosis (fibrous fibroadenomatosis) – a neoplasm with most of the fibrous tissue;
- fibrocystic – cystic fibroadenoma of the breast.
There is also a mixed form of pathology, in which all the above-mentioned tissues are present in equal parts, or two of them, for example, when a fibrocystic neoplasm occurs. Depending on the severity of the clinical picture, diffuse fibroadenomatosis of the mammary gland can be insignificant, moderate or severe. Depending on the location, number of tumors and nature of the disease, there may be:
- Focal fibroadenomatosis - a large number of nodules form throughout the breast. Neoplasms do not have clear boundaries and are accompanied by constant painful sensations.
- Localized fibroadenomatosis – one or several tumors appear in the breast, but in one quadrant or segment. The size of the formation varies from one to six centimeters. This is a compaction that has clear boundaries and a heterogeneous bumpy or granular surface.
Women encounter localized fibroadenomatosis of the mammary gland much more often, and tumors can affect both breasts at the same time. The superior outer quadrant is affected more often because this VNK contains more fibrous and adipose tissue.
What is FAM of the breast and how to treat it
FAM of the mammary gland - few people know what it is. Therefore, having heard such a diagnosis, they are at a loss, not understanding what exactly is happening to them. Fibroadenomatosis, or mastopathy, is a disease that consists of the formation of single or massive cysts in the tissues of the mammary gland. FAM is usually diagnosed in women after 30 years of age, although there are cases of the disease developing in younger women. This is especially true in cases where a woman has already had several periods of lactation.
The disease has several forms:
- local FAM;
- diffuse FAM.
Diffuse FAM of the mammary glands is much more common than nodular FAM. Diffuse fam is considered to be the initial form of the disease. Without appropriate drug treatment, a localized type of disease develops, which poses a great threat to the patient.
Modern doctors and scientists tend to believe that the main reason for the development of FAM a is hormonal imbalance, and it can be triggered by various factors.
Among these provocateurs are:
- liver diseases;
- dysfunction of the endocrine system and thyroid gland;
- ovarian diseases;
- sexual problems and abstinence;
- constant stressful situations and emotional stress;
- induced abortions and miscarriages;
- refusal to breastfeed a child or early termination of lactation.
Congenital pathologies of organs that are involved in the production of hormones or the removal of their breakdown products also play a huge role.
Symptoms
The first symptoms are a feeling of heaviness and fullness in the breasts before menstruation. Women may experience a burning and tingling sensation in their breasts during ovulation. When the nipples are squeezed, a clear fluid may be released. Cracks often appear on the nipple halo.
The lymph nodes in the groin area become enlarged, and the mammary gland itself swells greatly and is characterized by a certain density when palpated. Diffuse cysts that form in the gland at an early stage may not be palpable. After nervous tension or physical work, pain in the gland appears.
If we consider the diffuse and local forms separately, we can say that diffuse FAM is characterized by numerous small nodules that have a granular structure and can cause slight pain when pressed. Localized FAM is characterized by a clear shape; the edge of the formation can be clearly felt upon palpation. When pressed, a sharp pain occurs. The texture of the formation is lumpy; it feels good when pressed.
The peculiarity of the disease is that it can remain in the body for a long time and not cause significant discomfort. It can be detected during a routine examination or during the diagnosis of another disease. FAM can cause problems in women with conception, disruptions in the menstrual cycle, mental instability, and general weakness in the body.
Diagnostics
A mammologist can diagnose the disease based on laboratory and instrumental studies.
Standard diagnostic procedures include:
- mammography, which is performed in two projections;
- ultrasound examination.
In order to get a clearer picture of the woman’s condition, it is necessary to conduct an aspiration biopsy with further cytology, histological examination of the removed tissue, and also do ductography.
If there is a suspicion of a malignant tumor, then do:
- thermography;
- chest x-ray;
- magnetic resonance or computed tomography;
- examination of lymph nodes;
- General laboratory tests and blood tests for hormones.
Treatment
Based on the data obtained, the doctor develops a treatment regimen.
In most cases, the scheme consists of two stages:
- restoration of the normal balance of hormones in the body;
- relief of symptoms and restoration of gland tissue damaged by cysts.
Treatment uses hormonal drugs, homeopathic remedies, vitamins and antidepressants. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may be prescribed to relieve pain in the breast area. The duration and course of treatment are decided by the doctor, taking into account the patient’s condition, her age and body weight.
To treat the disease the following is prescribed:
- antiestrogens, which normalize the balance of female hormones (Fareston, Tamoxifen);
- androgen drugs, which are designed to suppress the production of hormones (Danazol);
- antiprolactin agents such as bromocriptine;
- means regulating menstruation (Zhanine, Non-ovlon, Tri-regol);
- drugs containing progesterone - Progestogel, Utrozhestan;
- painkillers - Ketanov, drugs with analgin;
- drugs that facilitate liver function (Essentiale, Hofitol, Artichoke, Karsil, Gepabene).
If therapy does not bring results, then surgery is required. The surgical intervention will consist of a sectoral resection, as a result of which the cysts and tissue located nearby will be removed. The seized material will be sent for histological examination to exclude oncology.
The feasibility of the operation is decided individually, since with a diffuse type of disease it is not always possible to achieve the expected result, and surgical intervention can provoke a multiplication of formations.
After surgery and during the period of conservative treatment, a woman should give up strong alcoholic drinks, black tea, coffee and smoking for a long time.
Alternative Treatments
Nature has created a huge number of natural remedies that will help normalize the balance of hormones without side effects.
Plants that help prevent or eliminate the formation of cysts in the mammary gland include: corn silk, valerian root, birch buds, rose hips, currant leaves, nettle, burdock root. Decoctions are made from the above herbs and combined voluntarily. These plants do not cause allergic reactions, so they can be used for a long time.
Ficus leaves are crushed and mixed with honey. Take orally before each meal.
For local treatment and relief of chest pain, you can make compresses from cabbage leaves and burdock.
Compresses made from yeast dough, eggs and unsalted butter have a good effect on the patient’s condition. The cake is applied to the breast once a day for three hours.
A good effect can be obtained using tar and onions. The onion head is baked and the skin is removed. Then the baked onion is chopped and a fly in the ointment is added; The product is applied to the area of the seal once a day before bedtime.
Whatever treatment method you choose, remember that you cannot let the disease take its course, because it is fraught with malignant degeneration. As for prevention, it consists of leading a healthy lifestyle and visiting a mammologist at least once a year.
Video
In this video, a mammologist talks about diagnostic methods and treatment methods for FAM.
comments powered by HyperComments
grud.guru
Diagnostics
What is the diagnosis of FAM of the breast, and what methods are used to accurately diagnose it? To make a correct diagnosis, a mammologist, in addition to standard ultrasound and x-rays, can prescribe a number of special and additional studies. For example, aspiration and stereotactic biopsies, trephine biopsy, ductography help determine benign or malignant formation in each specific case.
For a more complete diagnosis, which allows you to determine the most successful treatment regimen, the following are performed: thermography, chest x-ray, MRI or CT, examination of lymph nodes, and various laboratory tests.
Fem breast
Fibroadenomatosis of the mammary glands (mastopathy), what it is, may be of interest to any woman after the age of thirty. This is a benign disease caused by hormonal imbalances and affecting the mammary glands.
This diagnosis can be made based on complaints and examination by a mammologist. The main symptoms of fibroadenomatosis of the mammary glands include the following manifestations:
- Frequent and recurring stabbing pain in the chest associated with premenstrual syndrome;
- Sometimes, instead of the first sign, there is a feeling of pressure and burning in the same place and at the same period;
- It is possible that discharge from the nipples may appear, both when squeezed and spontaneously;
- The growth of lymph nodes located in the axillary area cannot be excluded;
- Swelling and hardening of the mammary glands.
Stress and physical strain can increase pain.
When examined by a mammologist, he can immediately palpate the tumor, if necessary, do a mammogram and perform ultrasound diagnostics.
As mentioned earlier, this disease has a dishormonal nature of origin. Hormone imbalance can occur:
- When you are under regular stress. Due to nervous breakdowns and psycho-emotional disorders, various pathological processes can develop in any system of the body. The mammary glands are often more vulnerable than others.
- Due to the presence of sexual problems in a woman’s life. This could be irregular sexual contact (due to the lack of a regular partner, etc.), interruption of sexual intercourse, or general sexual dissatisfaction.
- For gynecological diseases. Any pathologies that cause inflammation in the ovaries contribute to disruption of their production of female hormones. Any form of abortion, even medication, can accompany the pathological process.
- Against the background of early cessation or refusal to feed the newborn with breast milk. If the mother has no problems with the amount of milk, then breastfeeding should be continued for at least one year.
- For thyroid dysfunction. Both a deficiency and an excess of thyroid hormones can shake the balance of sex hormones.
- Due to liver disease. One of its functions includes the removal of products formed during the breakdown of hormones. If for some reason a violation occurs, substances are not eliminated immediately or not completely, this is reflected in the hormonal level.
At the moment, medical practice knows about several forms of this disease. We will get to know each of them further.
Diffuse femme of the mammary gland
Diffuse fibroadenomatosis is considered the initial stage of this pathology. It is characterized by increased sensitivity of the mammary glands and their hardening before menstruation. If you palpate, you can feel several elastic nodules distributed throughout the upper tissues of the breast. At the end of menstruation they disappear. In some women, after pregnancy and prolonged breastfeeding, this phenomenon no longer appears at all. Although other ladies continue to experience discomfort due to flaccid breasts, along which small cysts (the size of a grain of rice) are common, increasing at the end of the menstrual cycle. In this case, nipple discharge is also possible, which can be transparent and light, or greenish-brown.
We figured out what it is, but what should women do with diffuse fibroadenomatosis?
Doctors recommend a timely visit to a mammologist for early initiation of conservative treatment based on hormone therapy and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Localized breast fam.
When it comes to a single lump in the breast tissue, it is generally accepted that this is a localized form of fibroadenomatosis. The diameter of the nodule can be from 1 centimeter. Sometimes it grows up to 6 centimeters. In most cases, compaction has clear boundaries, although a more vague nature is not excluded. The formation is characterized by a dense consistency, lumpy surface, possibly with a granular structure.
Usually these patients are between 30 and 40 years old, where more than 40% are those who are not married, have no children and have never been pregnant. At the same time, about 38% of the rest had repeated abortions. A disc-shaped tumor can affect both individual areas of the gland and the entire tissue of the organ. All this is accompanied by moderate pain.
A localized form of fibroadenomatosis is typical for women during premenopause or during menopause, but medical sources contain cases of such a diagnosis among patients from 30 to 75 years old.
For accurate diagnosis, they resort to x-ray and cytological examination, in combination with thermography.
Cystic breast cancer
What is cystic fibroadenomatosis? In this form of the disease, mammary gland cysts are heterogeneous. The place of their origin is small ducts and alveoli. The tissues of ductal cysts are formed by epithelium, and alveolar cysts are growing gaps between adjacent lobules. In case of
Papillary growths, possibly of a solid type, cannot be excluded first. Small cysts are most often grouped. The chest lesion is bilateral.
It is not possible to make a diagnosis based on X-ray examination alone. A more effective diagnosis requires puncture and trephine biopsy of the mammary glands.
Focal femma of the mammary gland
The fact that this is also a benign process is immediately clear. Focal fibroadenomatosis is very similar to the diffuse form of the lesion. The main difference is that the pain is felt almost continuously. Foci of compaction are also formed by a replacement process, which involves glandular tissue being replaced by fibrous tissue. However, the difference is that they are not clearly differentiated.
The administration of the portal categorically does not recommend self-medication and advises consulting a doctor at the first symptoms of the disease. Our portal presents the best medical specialists with whom you can make an appointment online or by phone. You can choose the right doctor yourself or we will select one for you absolutely free. Also, only when you make an appointment through us, the price for a consultation will be lower than in the clinic itself. This is our little gift for our visitors. Be healthy!
Friends! If the article was useful to you, please share it with your friends or leave a comment.
medportal.net
Prevention
Preventive measures are aimed at maintaining general health, the absence of sudden changes in hormone levels, as well as breast renewal during lactation:
- healthy lifestyle, physical activity,
- comfortable underwear that helps avoid chest compression,
- early diagnosis - involves self-examination of the breast and regular visits to the mammologist,
- breastfeeding - from the moment the child is born until 1-1.5 years,
- refusal of abortion,
- regular sex life.
If you detect the first signs and the presence of seals, you should immediately consult a doctor for early diagnosis and initiation of treatment.
Complications and consequences
If a woman discovers lumps of any size in her breasts, she should definitely visit a mammologist. Only a doctor after an examination will be able to tell what their origin is and what health hazard they pose.
If the lumps due to fibroadenomatosis do not disappear, they seem to become even larger, treatment cannot be delayed. If you do not get rid of them in time, then pathological processes in the tissues of the mammary glands can develop further: the nodules will merge and large cysts will form. The appearance of atypical and later cancer cells is possible.
Main symptoms
Restructuring of glandular and connective tissues against the background of hormonal disruptions usually occurs asymptomatically or is accompanied by symptoms that are easily confused with PMS. The main symptoms of FAM include:
- aching pain that appears only before menstruation and intensifies with physical activity;
- feeling of burning and pressure;
- swelling and engorgement of the breast;
- irritability and aggressiveness;
- loss of sleep.
In some patients, the lymph nodes in the axillary area become enlarged, and when pressure is applied, clear liquid is released from the nipples. In the later stages, the areolas become covered with cracks and ulcers, and a dense neoplasm can be felt inside the mammary gland.
Many forms of fibroadenomatosis develop against the background of diseases of the reproductive system and thyroid gland.
Treatment
Diffuse fibroadenomatosis of the mammary glands is a disease for which the main treatment method is drug therapy and monitoring the condition of the lumps. Great importance is attached to eliminating the causes of the disease.
A woman is recommended to follow a diet that improves metabolism and accelerates the absorption of healthy food elements. Animal fats are excluded from the diet and more dairy products are included. It is necessary to eat foods containing a lot of fiber.
Drug treatment
In the presence of endocrine disorders, iodine supplements are prescribed. Treatment is carried out with vitamins (A, C, PP, E, Group B), antidepressants, hepatoprotectors, and diuretics.
To restore hormonal levels, drugs are used that reduce the effect of estrogen in the body and regulate the production of other hormones.
Nonsteroidal antiestrogenic agents. Once in the body, they bind to estrogen-sensitive receptors and suppress the activity of these hormones. Toremifene, fareston, raloxifene are used.
Progesterone-based drugs. With their help, they achieve a decrease in estrogen concentration. Duphaston and combined oral contraceptives (COCs) are used.
Drugs that suppress the production of prolactin and somatropin (pituitary hormones). Parlodel is used.
Drugs that block the production of pituitary gonadotropins. Provera and Veraplex are prescribed.
Drugs that block the production of estrogen by adipose tissue (Femara). They are used for menopause.
Any medications are prescribed after a blood test for hormone levels and a study of the patient’s general health.
Surgery
Basically, this is a sectoral resection of the mammary gland. Used only when cancer is suspected. A mandatory histological examination of the removed tissues is carried out. As an independent method of treatment for diffuse adenomatosis, it is ineffective, since the likelihood of relapse is too high.
Other methods
Methods such as physical therapy (with the exception of massage), psychotherapy, laser therapy, electrophoresis, and magnetic therapy are actively used in treatment. Balneological treatment (therapeutic cool baths with mineral salts and mud) is effective.
For this disease, thermal procedures are not prescribed. You should be careful when using folk remedies, such as warming the chest with compresses.
After consulting with your doctor, you can resort to only a few methods to relieve swelling (applying a cabbage leaf to the sore breast, a compress of grated beets). Sometimes doctors allow the use of herbal tinctures containing phytoestrogens.
Always manifests as nipple discharge
Diffuse mastopathy with a predominance of the glandular component is always manifested by fluid discharge from the nipples, most often having a transparent color. As part of the restructuring of the hormonal background and the predominance of the concentration of some hormones over others, a false appearance of colostrum is noted (a secretion normally produced under the influence of prolactin in the very first days after childbirth).
Speaking about the characteristic lump in the breast, women note that there is no connection with the menstrual cycle. Solid formations in the glands remain unchanged at any time. Therefore, it is necessary to clarify the nature of the disease - whether it is benign or malignant.
In addition to compaction, swelling of both glands is simultaneously noted, and the skin color does not change its shade (unlike the inflammatory nature of the disease). Edema is also associated with hormonal changes in a woman’s body. Before the onset of menstruation, there is an increase in the release of prolactin, which is responsible for preparing the mammary glands for breastfeeding. As a result, the lobules enlarge and the breasts become larger, but compression of the blood vessels occurs, the passage of which is already difficult due to the development of mastopathy with a predominance of the glandular component. With the end of menstruation, the volume of the glands returns to its normal state, but the existing seals remain unchanged.
As the disease progresses to a more severe stage, enlarged lymph nodes may be palpated in the axillary region, and sometimes simultaneously above the collarbone. In this case, it is necessary to exclude the oncological process, which is most characterized by lymphadenopathy (enlarged lymph nodes).