Conization of the cervix is a gentle and less invasive method of treating female diseases. The pathological process occurring in the genital area is not always amenable to therapeutic treatment.
In these cases, surgical manipulation of the organ is required to remove the changed tissue and prevent the progression of the pathological process. Such a modern method is conization of the cervix, which is carried out through the vagina.
What is cervical conization surgery?
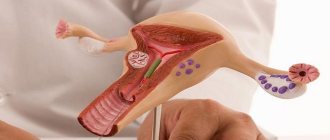
This is a cone-shaped removal of affected tissue from the cervical part of the organ and the cervical canal. The pathological focus is operated on, including healthy tissue.
The operation of conization of the cervix allows you to effectively treat pathology of the mucous membrane, while maintaining the possibility of pregnancy and bearing a healthy child.
For the outcome of the intervention to be positive, the patient must be aware of what cone-shaped resection is on the female genital organs and how it is performed. The operation is performed under local anesthesia and with minimal time.
Conization is carried out inpatiently, but hospitalization is not always necessary. A few hours later, after resection and examination by the attending physician, the patient is sent home.
Diathermoconization
Diathermoconization is an electrosurgical cone-shaped excision of pathologically altered tissue of the cervix with the apex of the cone facing the internal pharynx.
The diathermoconization method can and should be used when the pathology of the ectocervix (outer epithelium of the cervix) is combined with hypertrophy and deformation of the cervix.
Indications for diathermoconization:
- deformation of the cervix after childbirth,
- hypertrophy with moderate and severe dysplasia,
- chronic endocervicosis.
Usually the operation is performed on days 6-8 of the menstrual cycle. Intravenous anesthesia is used.
The advantage of this method is the possibility of serial-stage histological examination of removed tissues and the detection of intraepithelial cancer.
However, there are a number of complications that may accompany this manipulation:
- bleeding,
- menstrual irregularities,
- cervical canal stenosis,
- fusion of the cervical canal.
To correctly diagnose cervical diseases and select the most appropriate treatment method, a preliminary consultation with a gynecologist is necessary.
| Electroconization of the cervix | A16.20.051 | RUR 5,880 |
| Diathermocoagulation of the cervix (1cm) | A 16.20.036.001 | RUR 1,945 |
Service cost
When is conization prescribed?
The following indications are relevant for conization of the cervix:
- Dysplasia is a pathological change in the structure of an area of organ tissue, which is a precancerous disease and requires mandatory treatment. Surgical treatment is necessary at any stage of pathology development. Conization of the cervix for grade 3 dysplasia is a mandatory surgical procedure;
- the presence of atypical cells in the upper epithelial layer of the organ tissue (for cancer);
- polyps and cystic formations inside the cervical canal;
- scars due to medical procedures or ruptures during childbirth;
- migration of atypical cells into the cervical canal, especially with a rapidly growing pathological focus;
- ectropion , organ leukoplakia;
- erosion of the cervical uterus , which, with various treatment methods, does not give a positive result and progresses
Purpose of the operation
The main goal is to remove the affected tissue. However, during conization, a fairly large volume of pathological material can be sent for histological examination. The laboratory determines the cause and gives a conclusion about the presence of cancer or chronic infection.
That is, the purpose of this manipulation is both therapeutic and diagnostic measures.
Repeated conization of the cervix is rarely performed, but can be performed in case of relapse after previous treatment of the pathological focus.
Indications
Electrodiathermoconization of the cervix is prescribed when pathogenic changes, epithelial dysplasia are detected. The main indications are:
- identifying areas of change in the cervical epithelium;
- detection of pathogenic cells;
- organ dysplasia of 2–3 degrees – the patient does not feel symptoms of the disease, but if left untreated, complications may develop;
- erosive changes in the cervix;
- keratinization of the organ mucosa (leukoplakia);
- cicatricial changes in the cervix - develops due to ruptures during injury;
- formation of polyps;
- recurrent dysplasia after surgery (electrodiathermoconization of the cervix, cryodestruction, laser vaporization);
- ectropion - eversion of the organ mucosa.
The main reasons for electroconization are considered to be: obtaining biological material for histological examination, treatment of malignant neoplasms.
Preparing for surgery
Conization of the organ is carried out 3-5 days after menstruation. This is the optimal time during which the body recovers before the next cycle and the absence of pregnancy is guaranteed.
A month before conization, the preparation of the patient begins, when it is necessary to take the necessary tests and conduct the following studies:
- colposcopy of the cervical uterus;
- analysis of smears from the vagina and cervix for the presence of microflora and atypical cells;
- ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs;
- ECG of the heart;
- fluorography of the lungs;
- blood for hemoglobin, leukocytosis, ESR;
- blood for clotting;
- blood to determine the group and Rh factor;
- blood biochemistry for hepatitis;
- blood for AIDS and syphilis;
- urine for general analysis.
Contraindications
If there is an inflammatory process, electroconization is prohibited. The main contraindications include:
- invasive form of cancer;
- acute form of infectious pathologies, inflammatory processes;
- it is impossible to determine the boundaries of the affected tissues;
- the area affected by cancer cells is larger than the technical capabilities of surgical intervention;
- poor blood clotting;
- chronic pathologies (diabetes mellitus, heart failure, hypertension, liver disease, renal failure).
What types of conization are there?
Depending on the type of pathological process, age and individual characteristics of the patient, conization is done using various techniques. Only the doctor decides which surgical intervention to perform.
There are several instrumental approaches for performing the operation:
- The loop technique is the most common method of removing pathological formations on an organ, which is carried out using a cone-shaped loop and a diathermocoagulation device.
- The knife technique is conization using a scalpel, which is currently not used due to numerous complications.
Electroconization
- Electroconization of the cervix for dysplasia of any degree allows you to remove the pathological focus and stop the further development of the negative process;
- Electrodiathermoconization of the cervix can be in the form of a deep procedure using triangular attachments;
- Diathermoelectroconization is carried out using nozzles of shorter length, from one to three centimeters. It is important that when carrying out this method, gross deformation of the tissue does not occur in the future, and the operation does not have a negative effect on the woman’s reproductive function.
Laser conization of the cervix
When using a laser technique, the pathology is affected by a laser beam. Laser conization of the cervix provides a minimum of postoperative complications and the ability to regulate the volume of material taken for examination.
This conization technique has virtually no effect on planning the possibility of conceiving and bearing a child.
Radio wave conization
- The radio wave technique is aimed at destroying a pathologically changed area of an organ by exposing tissue cells to high-frequency alternating current. In this case, for radio wave conization of the cervix, surgeons use the Surgitron apparatus with a set of various electrodes. The value of the technique lies in the fact that when tissue is dissected, blood vessels coagulate, which reduces the possibility of postoperative bleeding.
- Radioconization of the cervix provides precise exposure to the pathological focus in the organ. The method is characterized by low pain and quick recovery after surgery. Complications such as wound infection are rare.
- Radiosurgical conization eliminates burns and destruction of healthy organ tissue. After manipulation, the function for childbearing is completely preserved.
Cryoconization
Cryoconization is the use of liquid nitrogen to destroy an area of organ pathology by freezing. The method is relatively inexpensive and painless, since the organ is anesthetized by nitric oxide.
Now this type of operation is not used, since it is not possible to accurately calculate the power of the freezing factor’s effect on pathology. In addition, there is no possibility for histological examination of the area of the affected organ tissue.
Methodology
Conization of the mucous layer of the cervix can be performed in different ways:
- knife involves surgical cutting out pathological areas;
- laser is carried out using a laser beam and is more gentle;
- Electroconization involves the use of a radio wave device.
The method of cervical treatment is selected according to the individual characteristics of the patient. The realization of the reproductive function is of no small importance.
If the patient wishes to have children in the future, preference is given to the most gentle method. Based on the volume of surgical intervention, one can distinguish economical conization, in which the removed area is no more than one and a half centimeters, and high conization, in which 2/3 of the cervical canal is excised.
Knife
About 40 years ago this technique was the only one. Removal of pathological areas was carried out with a conventional scalpel. The procedure is quite painful, despite the absence of nerve endings on the cervical mucosa, so it is performed under general anesthesia.
Currently, the knife method remains the preferred method for patients with confirmed cancer. The main advantage of this procedure is that it allows one to obtain more complete material for histological examination than modern conization methods.
Disadvantages of knife therapy include: a high risk of complications, the likelihood of bleeding, the possibility of infection, the formation of large scar areas and loss of cervical functionality.
Laser
This technique is considered more preferable than a radical method of treatment. Laser conization is carried out by treating the cervix with a special beam. The operation is performed without bleeding and is practically painless. However, not all medical institutions can do it.
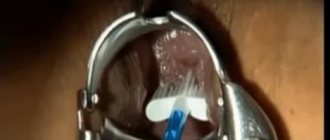
How is conization surgery performed?
The availability of modern techniques for carrying out therapeutic and diagnostic manipulations on a woman’s reproductive organs makes it possible to perform surgery on the uterus in the shortest possible time. The operation is performed in a day hospital setting.
No special preparation is required before the manipulation. It is recommended to shave pubic hair and empty the bowels and bladder. Conization is carried out in the morning on an empty stomach. How quickly the operation takes place depends on the type of technique chosen by the doctor.
In general, resection lasts about half an hour.
The surgery is performed on a gynecological chair under local anesthesia with the use of sedatives or under short-term intravenous anesthesia.
The operation begins with a visual examination of the cervix on the mirrors and treating it with Lugol's solution or acetic acid.
The pathological segment, after applying one or another solution, changes its color.
After the tests, the organ is infiltrated with novocaine or lidocaine, followed by conization of the affected tissue area, about 5 mm thick.
The early postoperative period lasts two hours, during which the patient must remain in a day hospital. After this time, the woman is sent home.
After operation
Conization does not have a negative impact on a woman’s health, since modern equipment used for manipulation makes it quick and less painful.
Basically, the recovery period after conization proceeds without complications. Minor pain in the lower abdomen and discharge persist, lasting up to three weeks. The nature of the secretion may be bloody or brown.
During the recovery period, treatment after conization of the cervix is predominantly symptomatic.
After resection, a scab forms on the organ, which begins to be rejected and come out in the second week from the moment of surgery. During this time, the volume of discharge may increase.
Basic restrictions
In order for the postoperative period of cervical conization to go smoothly and without any complications in the patient’s condition, she must follow certain rules, which involve restrictions for six weeks:
- peace in intimate life;
- exclusion of visiting the pool , sauna, bath and bath;
- Limitation of lifting weights up to three kilograms;
- exclusion of tampons from use in personal hygiene;
- exclusion from the use of medications that thin the blood (aspirin).
If after conization a fever appears or the general condition worsens, this is an indication for immediate consultation with a doctor.
How does the cervix heal?
Healing after conization of the cervix, if the recovery period goes smoothly, occurs quite quickly. Within one and a half to two weeks, the scab comes off, after which the wound epithelializes. Complete healing occurs within three to four months.
During this period, it is necessary to visit a doctor who will give recommendations on what the patient should know about her body after conization and how the cervix is healing.
These may be the following manifestations:
- increased amount of bleeding for more than four weeks;
- burning and itching in the vulva area;
- pain in the abdominal area after a quiet period;
- resumption of discharge after its cessation.
During this period, no therapeutic measures are carried out, but according to indications, taking into account the type of operation performed, the doctor may prescribe suppositories or douching.
How does the scab come off after conization?
After resection, a crust forms on the wound surface, which is a layer of dead cells.
What does a scab look like?
It can be grayish or yellow in color and have a soft consistency. The removal of the scab goes unnoticed in most women.
The crust covering the wound protects it from penetration of pathogenic microbes. A new layer of epithelial cells is formed under it, and when it is formed, the scab begins to come off. On average, its rejection begins to occur on the 5th or 7th day after conization.
In this case, the type of surgical intervention plays a role, when the period of removal of the crust can increase to 7–10 days and the possibility of an increase in the volume of bloody discharge.
Diathermocoagulation
Diathermocoagulation is a method of treating benign diseases of the cervix. Under the influence of high-frequency current, endogenous heat is formed in the tissues with an increase in temperature to 60-100 ° C, which causes irreversible coagulation of proteins and tissue fluids. A white scab forms on the surface of the vaginal part of the cervix, which is rejected 10-12 days after diathermocoagulation. Epithelization (healing) of the wound surface ends after 1.5-2 months.
During the operation, a passive electrode is placed under the woman’s sacrum, and the second electrode is manipulated. For ease of impact, the tip of the working electrode can be used in the most suitable shape: a needle, a ball or a loop. Diathermocoagulation is characterized by almost complete bloodlessness, ablasticity, and a low risk of spreading infection. Recovery after diathermocoagulation is observed in 93-97% of patients.
Today, diathermocoagulation is one of the most common methods of treating erosion and other pathologies of the cervix.
After the procedure, minor bleeding and menstrual irregularities are possible.
Possible complications
Complications after cervical conization are rare, but possible.
It can be:
- prolonged and heavy bleeding;
- inflammatory processes in the genital area;
- scar changes;
- cervical organ insufficiency during pregnancy;
- endometriosis.
Childbirth after conization of the cervix may be premature due to disturbances in the organ, that is, the weakness of its muscle layer.
Growing pregnancy, putting pressure on the incompetent cervical organ, causes prolapse of the fetus and premature opening of the birth canal.
In rare cases, stenosis of the cervical canal develops in the postoperative period, which leads to the impossibility of conception. Therefore, women planning a pregnancy are not recommended to undergo conization before conception, but to treat the disease conservatively.
Bleeding after conization
Uterine bleeding, as a consequence of conization of the cervix, is rare, in only 2% of cases, since the operation takes place in tissues in a place where large vessels do not anatomically pass through.
The cause of this complication may be technical errors during the operation, as well as disruption of the menstrual cycle. If damage to the vessel occurs, then the help of a doctor and the use of hemostatic agents are required.
Discharge
The organ can bleed for a long time, even up to four months. Healing occurs naturally, so this process cannot be accelerated. Discharge after conization of the cervix appears immediately after surgery.
After a week or a week and a half, when the scab begins to come off, the discharge is greater than normal and may stop seven days after the scab comes off, or may persist for a month after the operation. Sometimes the operated uterus secretes blood for up to three to four months.
Pain in the postoperative period
Recovery after conization occurs with minor pain, which is localized in the lower abdomen and is similar in nature to pain during menstruation.
This is a normal recovery process after surgery and does not cause any particular discomfort. The doctor, in this case, may prescribe painkillers.
The stomach stops hurting a few days after resection. But if the pain becomes more intense, a mandatory consultation with a doctor is necessary.
Basic restrictions
The cervix after conization is an open wound. Therefore, as for healing any wound, it is necessary to minimize the impact on it. Namely:
- Do not have vaginal intercourse for a month.
- Do not use vaginal tampons.
- Do not take a bath (wash in the shower).
- Do not lift weights exceeding 3 kg.
- Bathhouses and saunas are excluded.
- Don't swim.
- Avoid overheating.
- Do not take drugs that prevent blood clotting (aspirin).
Pregnancy after conization
The availability of modern equipment allows surgical intervention to be performed with minimal complications. For patients planning conization of the cervix and pregnancy, resection is carried out using the most minimally invasive techniques, that is, radio wave or laser.
After the operation, conception recommended by the doctor can be carried out a year after the complete restoration of the body and function of the woman’s reproductive system.
Pregnancy after conization generally proceeds normally. If postoperative insufficiency of the cervical canal appears, it is easily corrected by applying an obstetric pessary to the organ.
It consists of rings made of silicone or plastic, interconnected and having three sizes, which are installed at 20 and removed at 38 weeks.
Pregnancy after conization of the cervix is successfully carried to term, and the child is born naturally.
Contraindications
If a woman has cervical dysplasia, conization is not always carried out. This type of treatment is contraindicated in patients with confirmed cancer. In this case, the entire organ is usually removed, after which long-term treatment is prescribed, including chemotherapy and radiation.
It is forbidden to perform conization if a woman has an inflammatory process in the vagina. It is necessary to first undergo treatment, and then carry out the chosen method of surgical intervention. Conization is contraindicated for patients during pregnancy, as this may cause its termination. Before conization is performed, preparation and examination are required.
Restoration of the menstrual cycle
Surgery does not affect the menstrual cycle. Menstruation after conization of the cervix comes at the right time, but in abundance. In some cases, the doctor prescribes iron supplements to compensate for blood loss.
The risk of bleeding is associated with hormonal changes in the body caused by the operation, but their regularity remains.
Complete recovery of the organ after surgery occurs within three to four months, so the abundance of discharge during this period is functional in nature and does not require specific treatment.
In some cases, if hemoglobin drops and the color of the blood changes, symptomatic treatment is carried out.
Therefore, pregnancy after conization occurs after its final restoration. Hormonal imbalance with pathological changes in the menstrual cycle is observed in 20% of cases. In this case, such a contingent of patients needs medical therapy prescribed by a doctor.
Childbirth after cervical conization can be natural or by caesarean section. Cone-shaped resection does not have any effect on the development of the baby.
The tactics of labor management depend on the size of the postoperative scar on the organ:
- If the suture is small , then under the strict supervision of a doctor, the woman gives birth herself or with the help of forceps.
- If there is a large scar , a cesarean section may be permitted.
But in any case, pregnancy and successful birth after resection are possible, both the first and subsequent ones.