What is the cervical canal
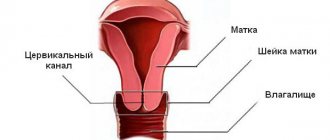
The cervical canal is the canal of the cervix, connecting the vagina and the cavity of this organ. It has two small holes - the internal and external pharynx, the normal diameter of which is 2-3 millimeters. The external pharynx is visible during a standard examination, has a dotted shape if the woman has not given birth, and after childbirth or abortion it becomes slit-like. The layer of mucous membrane covering the cervix is called the endocervix.
Atresia of the cervical canal
A disorder that results in fusion or obstruction of the cervix is called cervical atresia. The disease can be a congenital pathology or acquired as a result of illness or injury. Congenital disorders are cases of abnormal formation and development of internal organs. Acquired atresia in most cases is caused by abortion, cervical cancer, inflammation in the inner and outer layers of the canal tissue.
The cervical canal is closed, what does this mean?
Whether the sperm will pass through to the egg largely depends on the condition of the cervix. When the cervix is completely or partially closed, doctors diagnose stenosis. It can be distinguished by the following symptoms: absence or painful menstruation, infertility, pain during sexual intercourse. A narrow cervical canal and conception are poorly compatible; first you need to eliminate the cause, then carry out bougienage. If you still manage to get pregnant with this disease, there is a high probability of incoordination of labor and subsequent cesarean section.
The cervical canal is dilated, what does this mean?
At any stage of pregnancy, the doctor can report the news that the cervical canal is dilated - what does this mean? This means that the cervix cannot perform its functions of holding the fetus. Enlargement of the cervical canal can be caused by an increased amount of male hormones that soften the cervix, multiple pregnancies, developmental abnormalities and injuries. The following steps can be taken to prevent a possible miscarriage:
- medications are prescribed that strengthen the cervix;
- installation of a special ring, which will be removed only at 37 weeks;
- stitches were placed around the cervix.
Features of the structure of the cervical canal
The cervical canal performs a connecting function and provides communication between the internal and external organs of the reproductive system. It gradually increases from the moment the girl is born until puberty. Then it changes its appearance after childbirth, the hole becomes slit-like.
The following structure of a girl’s genital organs is considered normal: the uterine cavity begins with the internal os and passes into the cervical canal of the cervix, which passes into the cervix and ends with the external os, and then the vagina. Due to this structure, the process of natural delivery is ensured.
The os of the uterus opens gradually. The process of opening during childbirth begins with the internal pharynx, and then, as contractions progress, it spreads to the external pharynx. The reverse process of closing the cervical canal follows the same pattern, but lasts not several hours, but about 3 weeks. The peculiarity is that the external pharynx does not completely restore its appearance; it becomes slit-like, which significantly speeds up the process of opening during repeated births. That is why they say that in those who have given birth, the cervical canal is dilated.
A gynecologist can suspect the development of pathology of the cervical canal immediately during an examination of the vagina in the speculum. The doctor not only assesses the condition of the epithelium, but also pays attention to the compliance of the anatomical structures with the reference parameters.
A normal length is considered to be about 3.5-4.5 cm, with a width of no more than 5 mm. Inconsistency with these indicators indicates the risk of developing pathology. The exception is physiological shortening at the end of the 3rd trimester of pregnancy. Such a change is necessary to ensure normal delivery. If the canal is shortened before the 30th week of pregnancy, the risks of an unfavorable outcome appear, and the likelihood of premature birth or miscarriage increases. The acute condition is treated by applying an obstetric ligature or pessary. Such methods are designed to help a woman carry her pregnancy to 8 months and prevent premature dilatation.
Attention! The diagnosis of enlarged cervical canal does not pose a danger to a non-pregnant woman, but such a disorder may indicate the development of pathological processes in the reproductive system.
The extension is determined by the following criteria:
- The internal os on ultrasound is dilated by more than 2 mm, the diameter of the remaining parts is within normal limits;
- a slit-like expansion can be seen in the upper third with an increase in the number of cervical glands;
- the deformation has a funnel-shaped structure;
- expansion can be seen along its entire length against the background of softening and shortening.
Diagnosis of pathology is provided by ultrasound techniques, but an experienced doctor may suspect a problem during a vaginal examination and bimanual examination.
Inflammation
The causes of inflammation of the cervical canal can be infectious or non-infectious. Inflammation can be caused by: gonococci, streptococci, E. coli, chlamydia, herpes viruses, candida and papillomas. Non-infectious causes include:
- erosion;
- injuries;
- neoplasms;
- cervical prolapse.
To determine the cause of the disease and treatment options, it is necessary to undergo an examination and submit a scraping for analysis. Inflammation of the cervical canal is visible during the initial examination - redness, swelling is observed, and purulent discharge is possible. To determine the pathogen, it is necessary to submit diagnostic material - a smear, bacteriological culture of secretions - and conduct a study to detect sexually transmitted infections.
Cyst
In cases of blockage of the glands of the mucous membrane of the uterine passage, cysts are formed. This is explained by the fact that the outflow of mucus is difficult and when it accumulates, the ducts begin to expand. Common causes are inflammation of the cervix, cauterization of erosion. A cervical canal cyst is a benign neoplasm containing fluid, often found in women of childbearing age.
Cysts can be single or multiple and often they do not require treatment because they do not cause any complications and do not harm health. Cysts have no effect on pregnancy and may disappear spontaneously after childbirth. Only those neoplasms that are large in size and continuous growth are subject to autopsy.
Cervical canal during pregnancy
After the moment of fertilization, the cervix closes tightly and is in tension until labor begins. It is very important to monitor the cervical canal during pregnancy, because the positive outcome of childbirth depends on its condition. The cervix smoothes and opens, its length decreases one to two weeks before birth. If this happens earlier, we can talk about a serious risk of miscarriage.
The outside of the cervix is covered with a layer of cells that secrete mucus, which forms a dense plug during pregnancy. Its main functions:
- separate the uterus from the vagina;
- protect the fetus from harmful microorganisms that may be in the vagina.
Functions performed by the cervical canal
The functional activity of the cervical canal is aimed at protecting the woman’s internal genital organs from the penetration of pathogenic bacteria and viruses. Even a healthy woman has a number of different microorganisms in the vaginal space, including pathogens. However, the uterine cavity has a sterile environment. This is due to the activity of special cells located in the thickness of the cervical canal and producing mucous secretion. Its amount varies depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle under the influence of hormones produced by the body.
In the initial and final phases of the cycle, the mucous secretion acquires a viscous, viscous consistency, and its environment becomes acidic. Such conditions are unfavorable for pathogenic microorganisms, do not allow them to reproduce and lead to their death. If sperm enter the cervical canal at this time, their activity is disrupted, which naturally prevents fertilization.
Closer to the beginning of the ovulatory period, due to the action of estrogen, the mucous secretion becomes more watery, with an alkaline pH, so this time is optimal for sperm, allowing male reproductive cells to easily penetrate the uterine cavity and fertilize the egg. After sexual contact, which results in fertilization, the mucus produced changes its structure, which is due to the action of progesterone. The secretion acquires viscousness and viscosity to provide the fertilized egg and developing placenta with reliable protection from the possible penetration of pathogenic flora.
Bougienage
The procedure for dilating the cervix is called bougienage of the cervical canal. The reason for this operation may be partial or complete atresia. The operation is performed under local anesthesia if the narrowing is minor, under general anesthesia if the closure is complete. Before the operation, you must undergo the following examinations:
- smear for infections, white blood cell count;
- blood tests - general, biochemical, AIDS, hepatitis B, C;
- colposcopy;
- coagulogram;
- smear microscopy;
- fluorography;
- culture from the vagina and CC;
Progress of the operation
When bougienaging the cervical canal, probes are inserted in a certain order into the site of overgrowth, the diameter of which is gradually increased. The size of the initial bougie is usually 0.5 mm, the final one is 1 mm.
On average, the operation lasts no longer than 30 minutes.
Gynecological surgery takes place in the following sequence:
- The anesthesiologist puts the patient under anesthesia. Local anesthesia is used much less frequently and for exceptional indications for pain relief.
- The cervix is prepared, treated with disinfectants and a spoon-shaped speculum is inserted into the vagina.
- Using special holders, the doctor fixes the labia and moves it towards the entrance to the vagina.
- To determine the position and size of the uterus, a uterine probe is carefully inserted into its cavity.
- The surgeon expands the cervical canal with careful movements.
- As soon as the bougie passes the cervical canal, Hegar dilators are inserted - a metal rod with a rounded end. It is enough for the device to penetrate the internal os of the cervix. Small diameter dilators enter the cervical canal relatively freely. But as soon as the channel expands, bougienage becomes more difficult. As soon as the expander has passed the canal, it must be carefully removed and a larger probe must be immediately inserted to prevent the internal pharynx from shrinking.
If the next probe cannot be passed through the cervical canal, it is removed and a bougie of smaller diameter is reinserted. It is left in the canal for 1 minute, then they try to continue expansion with a larger probe.
After the operation is completed, the cervix and genital organs are sanitized.
After the patient comes to her senses after anesthesia, she may be sent home or left in the hospital for 24 hours.
Scraping
In cases where drug treatment no longer helps, doctors resort to an extreme measure - surgery. Curettage of the cervical canal - what is it and what are the indications for the operation? This is a simple procedure performed by a gynecologist under general anesthesia. Before the operation, you must undergo a standard examination, take a blood test, culture, and a smear for infections.
One of the reasons for the formation of polyps and indications for their removal, polypectomy, may be the onset of postmenopause, but more often it is not treated in a timely manner for inflammatory processes of the cervix. Such an operation may be prescribed if the following diseases are detected:
- myoma;
- decidual polyps;
- fibrous polyp;
- oncological diseases;
- hyperplasia endothermy;
- calcifications;
- uterine dysplasia.
Video
Cervical canal
- a spindle-shaped hollow area that connects the uterine cavity and vagina. Normally, this area is tightly closed. It performs a protective function - the infection should not penetrate the uterus. The inner layer of cells produces mucus, which creates a kind of plug in the cervix.
During pregnancy, a mucous seal forms in the canal, which tightly closes the cervix and protects the embryo.
For manipulations in the uterine cavity and diagnostic procedures, the doctor must expand the cervical canal.
Indications and contraindications for the procedure
Dilatation of the cervical canal is prescribed in the following cases:
The procedure is not performed if:
- suspected ectopic pregnancy;
- established ectopic pregnancy;
- inflammatory process in the acute period of any localization - gynecological and other organs;
- infectious diseases
Other cases are discussed individually with each patient.
How does the procedure work?
Manipulations are carried out only in a medical facility
. Observance of asepsis rules and practical skills by medical personnel is mandatory.
1
.
the patient is on the gynecological chair; 2
.
external genitalia and vagina are treated with disinfectants; 3
.
The gynecologist conducts a manual examination of the patient - both intravaginal and rectal; 4
.
Speculums are inserted into the vagina and the cervix is exposed; 5
.
the anterior lip of the cervix is grabbed with forceps; 6
.
the uterine cavity is examined, the direction of insertion of instruments is determined; 7
.
expand the cervical canal to 8 mm. For this purpose, special dilators are used; 8
. Then the required manipulations are carried out in the uterine cavity - examination, surgery, termination of pregnancy.
After the procedure, the gynecologist examines the lips of the cervix. If there are signs of bleeding, appropriate treatment is carried out.
Complications after the dilation procedure
The procedure for expanding the cervical canal is an invasive procedure. Therefore, after the procedure, the following complications may arise:
- bleeding;
- rupture or perforation of the walls of the cervical canal;
- infection of internal organs;
- allergic reactions to anesthesia materials, medications;
- psychological problems in the patient.
If gynecological manipulation is carried out in a medical institution, then the risk of complications is minimized.
Patients with various female diseases come to our clinic. Among them, the clinic’s doctors often diagnose pathologies of the cervical canal of the cervix: polyps, cysts, inflammation, etc.
The main function of the genital organs is reproductive, and it is very important that their diseases cannot lead to infertility or menstrual dysfunction. Therefore, every woman should undergo preventive examinations at least once a year.
Those working in the clinic will help diagnose and treat the disease in a timely manner. The earlier the disease is detected, the greater the chance of curing it and not turning it into a chronic form.
Postoperative period and healing of the cervix
After bougienage of the cervix, the patient can return to normal life in about 2 weeks. During this time, all pain completely disappears.
If the pain intensifies within 14 days, you should urgently visit a doctor. A woman may experience a recurrence of infection. For this purpose, it is possible to install an alloplastic channel.
During postoperative treatment, the patient should take anti-inflammatory drugs and suppositories to speed up the wound healing process. They are prescribed only by a gynecologist, focusing on the woman’s health condition and the presence of individual intolerance to certain medications.
You should immediately consult a doctor if the following symptoms appear:
- discharge of blood and mucus from the genitals;
- persistent pain in the lower abdomen;
- increase in body temperature.
To prevent the development of negative consequences of bougienage of the cervical canal, the patient should take antibacterial drugs.
The choice of anti-inflammatory drugs is made by the attending gynecologist
Depending on the severity of the clinical case, tablet or injection forms are used. To prevent the development of thrush, you need to take antifungal agents (most often they are prescribed in the form of suppositories).
To prevent infection, the following measures must be taken:
- promptly treat inflammatory processes in the uterus and cervical canal;
- undergo regular medical examinations to detect inflammatory pathologies and malignant neoplasms (such examinations should be carried out starting from adolescence);
- abortions should be performed only in a hospital setting and only by qualified personnel;
- do not use douching without control and the need, do not use aggressive solutions;
- from childhood you need to adhere to the rules of a healthy lifestyle and exercise regularly;
- do not use chemical contraceptives without supervision;
- avoid infection with infectious pathologies;
- During pregnancy
, do not take medications that have a toxic effect on the baby.
Cryodestruction is a modern method of treating cervical diseases
What is the cervical canal
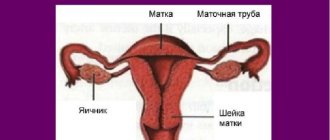
The internal female genital organs are located in the lower part of the abdominal cavity and consist of the cervix, which is visible when examined in mirrors, and the body of the uterus, which is located in the abdominal cavity (pelvis). The fallopian tubes extend from the uterus (from its corners), and under the fallopian tubes, on both sides, are the ovaries. The cervix can be cylindrical or conical in shape.
Nature has thought through a lot, and in order to protect the female body from water coming from the vagina and to maintain pregnancy during gestation, there are 2 narrowings in the cervical canal, the so-called pharynx (internal pharynx and external pharynx). The doctor examines the external pharynx during a speculum examination. A dotted pharynx is typical for nulliparous women, a slit-like pharynx is typical for women who have given birth or had an abortion.
Inside the cervix is the cervical canal
. It is the cervical canal that forms the connection between the external and internal organs. It is through this that an infection can enter from the vagina and spread into the abdominal cavity. During childbirth, the cervix shortens and the baby is born through the smoothed cervical canal. The canal, uterus and vagina form the birth canal.
Inner layer
The cervical canal is lined with epithelium, which produces mucus. The epithelium is hormone-dependent and produces different secretions, depending on the day of the menstrual cycle. It is by the mucus in the cervical canal, in the middle of the menstrual cycle, that the doctor determines the “pupil symptom” - a sign of ovulation. During pregnancy, it is in the cervical canal that the epithelium forms mucus - a plug, the discharge of which is a harbinger of the onset of labor.
When examining on mirrors, the doctor pays attention to the surface of the cervix
. If it is smooth and light pink in color, then there is no problem. The doctor examines the border of the cervical epithelium and the epithelium of the cervical canal. If the epithelial border is displaced or there is an erosive surface, the doctor describes the location and size of the identified pathology. In addition to a visual examination, the doctor can perform a Schiller test with staining of the cervical mucosa with an iodine-containing solution. In addition, a colposcopy can be performed.
During postmenopause
, as well as during
pregnancy
and after childbirth, the cervix undergoes changes. Thus, during menopause, the mucous membrane becomes paler, secretions are not produced, and vaginal dryness is noted. Every year, the doctor performs scrapings on the woman for oncocytology using a special brush from the cervical canal and from the surface of the cervix in order to identify oncological and pre-cancer diseases in time. During pregnancy, the cervix has a cyanotic color.
These are normal physiological changes that occur over a period of time.
The cervical canal does not undergo cyclic changes associated with the menstrual cycle. Only during ovulation does secretion increase.
Cervical canal - where does it lead?
The cervical canal is the inner part of the cervix, which is the transition between the main female organ and the vagina.
It is covered by a layer of epithelium that has the ability to secrete mucus. Its quantity and composition vary, depending on the period of the menstrual cycle. These secretions are the thinnest and smallest during ovulation, when the body creates the most favorable opportunities for fertilization of the female reproductive cell. The rest of the time, the mucus is quite thick, and its maximum amount occurs before menstruation.
In women of reproductive age, the cervical canal has a width of 7-8 mm. This is enough for the penetration of sperm and the removal of menstrual fluid, part of which is the secretion secreted by its epithelium.
Changes during menopause
How are menopause and the cervical canal related? It has already been said that the reproductive system undergoes changes during this period. This small area is no exception. It changes under the influence of a new hormonal balance, like all reproductive organs, that is, it decreases.
A decrease in estrogens and progestins affects the uterus in such a way that its muscle tissue atrophies, being replaced by connective tissue, and the blood vessels narrow. The organ shrinks so much that, compared to what it was before menopause, it becomes one and a half times smaller. Accordingly, the sizes of the cervical canal in menopause are:
- Length 20-25 mm;
- Width 3-5 mm.
For some, the latter value may be even more modest due to the process of tissue fusion. The thinned epithelium also produces significantly less mucus, which for many leads to vaginal dryness.
The biological meaning of the changes is clear: the woman is no longer in danger of becoming a mother, therefore, she does not need a passage in the uterus for sperm and menstrual flow.
Changes in the cervical canal during menopause are caused by hormonal imbalance
Pathologies of the cervical canal of the cervix
Often women come to our clinic who complain of increased discharge from the genital tract, its unpleasant odor, and spotting after sexual intercourse.
During the examination, the doctor sees only the cervix and the external os of the cervical canal. The main diseases diagnosed in patients based on speculum examination and microbiological examination:
. Cervicitis
, which is an inflammation of the cervical canal of the cervix (the diagnosis can be made after examining smears). With prolonged untreated cervicitis, fusion of the walls or fusion of the cervical canal may occur. Treatment of cervicitis boils down to prescribing anti-inflammatory therapy and local treatment of the cervix and vagina.
. Polyps
- These are benign neoplasms, the cause of which is the same inflammatory process. The growth of a polyp in the cervical canal can be triggered by hormonal disorders, as well as trauma to the cervix during childbirth or abortion. Our doctors remove polyps surgically. In addition, concomitant therapy is prescribed. Polyps require surgical treatment and after they are examined for histology, adequate therapy is prescribed.
. Narrowing, curvature
cervical canal - when conducting, the doctor must describe the length and course of the cervical canal, describe the invisible part of the cervix. If a narrowing, curvature of the cervical canal or partial closure of the canal is detected or suspected, the doctor suggests examining the cervical canal using an optical one. If it is planned, then the doctor performing the manipulation of insemination or embryo transfer must take into account all the nuances of the structure of the cervical canal and its location relative to the uterus. If necessary, carried out
Content
Enlargement of the cervical canal can be interpreted in two ways. Sometimes this is a sign of an ongoing pathological process, but in some cases, expansion (dilatation) of the cervical canal is a natural change that does not threaten women’s health. For this reason, doctors do not consider enlargement of the cervical canal as an isolated symptom.
Causes of cervical canal occlusion
The cervical canal is located inside the cervix.
It protects the uterine cavity from the penetration of pathogenic bacteria, is responsible for the transportation of sperm and is the birth canal. The cervical canal stretches well, but due to edema and swelling of the mucous membrane, it can narrow, and as a result of scarring or proliferation of connective tissue, it can become overgrown. For a woman, infection of the cervical canal is dangerous, as the risk of chronic inflammatory processes and even cancer pathology increases. In addition, a woman with a narrow cervical canal will not be able to get pregnant.
The cervical canal can narrow in women of different ages. In this case, the causes of the pathology will be different: in teenage girls, stenosis can be congenital, in young women it can arise as a result of injuries to the mucous membrane of the cervix. In patients over 40 years of age, the cause may be neoplasms or age-related changes characteristic of menopause: due to a decrease in estrogen production, follicle-stimulating hormone increases, but sensitivity to it decreases and the cervical canal becomes shorter, thinner and more vulnerable.
The main causes of cervical canal occlusion are considered to be:
- Chronic endocervicitis is an inflammatory process in the mucous membrane of the cervical canal that lasts more than two months. More often it affects young women who are sexually active and often change sexual partners. The main causative agents of the disease are chlamydia, myco- and ureaplasma, genital herpes, gonococci and other pathogenic microorganisms. With a long-term inflammatory process, swelling of the mucous membrane is complicated by fibrotic changes in the cervix. Because of this, the lumen of the cervical canal narrows.
- Injuries of the cervical canal. Narrowing of the lumen can result from rupture of the cervix during childbirth, damage during abortion, careless probing, and curettage, which are performed for diagnostic purposes. The cervical canal can be damaged as a result of different types of operations on the cervix: cryodestruction, loop electroexcision, radio wave coagulation, diatheromocaugulation, laser vaporization.
- Growth of neoplasms. In this case, the channel will be blocked as a result of mechanical action. The growth of polyps and fibroids and malignant tumors may be critical. If cancerous lesions are treated with radiation therapy, this further increases the risk of stenosis.
- Involution of the cervix. In this case, the narrowing of the lumen occurs as a consequence of dystrophic changes in the genital organs during menopause.
- Lack of pregnancies and physiologically natural childbirth.
Main reasons
If the cervical canal is dilated outside of gestation, then dilatation does not pose a certain danger.
But expansion above the permissible norm may be a sign of the following pathologies:
- polypous formation located in the lumen of the cervical canal, which is why it is expanded;
- cystic lesion of the cervix - Nabotov's cyst - is defined on ultrasound as a formation with anechoic contents; the cyst can be represented by multiple formations with a diameter of up to 1 - 3 mm;
- benign neoplasms of the cervix - leiomyoma, hemangioma, fibromyoma;
- adenocarcinomas;
- adenomyosis;
- polyp of endometrial tissue;
- “born” fibroids;
- cervicitis (acute or chronic form), including those provoked by STDs;
- tumors of the body of the uterus, causing stretching of the internal os.
Symptoms and signs of a closed state of the cervical canal
A pathology in which there is a closure of the lumen in the cervical canal is often diagnosed in women experiencing problems with conception. With this condition of the canal, the entry of sperm into the uterine cavity seems problematic. In this case, we talk about stenosis of the cervical canal, which can be partial or complete. Among the reasons causing the closure of the canal tissues are:
- consequences of curettage of the uterine cavity;
- improper performance of manipulations in the cervical area, for example, coagulation of erosions;
- the presence of a polypous formation in the lumen of the canal;
- infection of the canal tissue;
- oncopathology.
Canal fusion can be suspected by the following symptoms:
- the presence of pain during the onset of menstruation, scant discharge;
- a feeling of heaviness in the vagina caused by pressure on the cervix due to delayed menstrual flow (hematometer);
- pain in the groin area due to hemorrhages in the fallopian tubes (hematosalpinx);
- disturbances in the activity of the urinary tract;
- pain in the bladder area.
For women of reproductive age planning to conceive and give birth to a child, doctors recommend first diagnosing and establishing the causes of the pathology, and then, if possible, performing a canal bougienage procedure. If a pathology is detected in a pregnant woman, doctors need to solve the problem of possible complications during natural delivery, so the option of performing a cesarean section is considered.
Postmenopausal period
Menopause is accompanied by multiple changes in the female body, affecting specifically the reproductive organs. This also applies to the cervical canal. Reacting to the new level of hormones, it becomes somewhat narrower.
But what does dilation of the cervical canal mean? The period of menopause is a dangerous time for a woman, since many dangerous diseases can begin to develop right now.
If during a gynecological examination the cervical canal is dilated, then this is a sign of an existing pathology. Most often, cervical dilatation during postmenopause is caused by:
- inflammation of the vaginal segment - cervicitis;
- serozometer;
- myoma;
- polypous formations;
- endometrial hyperplasia.
But the main cause of these pathological processes is insufficient production of estrogen, which is considered a prerequisite and basis for the expansion of the cervical canal.
Cervicitis
The chronic form of cervicitis occurs without characteristic symptoms. In some cases, a woman notes the presence of slight cloudy serous-purulent discharge.
The cause of the development of the disease is prolapse of the uterus and/or vagina, characteristic of the menopause, and subsequent inflammation.
Serozometer
The cervical canal can be dilated as a result of the formed serozometra. The cause is a violation of the ability of the endometrial mucosa to self-regenerate. Its degradation occurs. As a result of the pathological process, serous exudate accumulates inside the uterus.
The following factors can provoke or enhance the production of serous secretion:
- Smoking. Nicotine worsens existing hormonal imbalances, which causes more active degradation of the endometrium.
- Poor nutrition, including a significant proportion of fatty foods. The resulting energy from a large amount of fat is not spent, which leads to an increase in fat reserves. And this also negatively affects hormonal changes.
- Lack of physical activity. During menopause and postmenopause, many women, fearing the manifestations of osteoporosis, reduce physical activity to a minimum. This fact only aggravates the already existing metabolic disorder.
In addition to the expansion of the cervical canal, the patient develops the following symptoms:
- liquid gray vaginal discharge, intensifying after sexual contact or exertion;
- discomfort and pain in the lower abdomen;
- problems with emptying the bladder.
Serozometra creates a favorable background for the development of endometrial hyperplasia, polyps and endometrial cancer, and therefore requires careful diagnosis and treatment. Dilatation of the cervical canal may be an indicator of the serosometer.
Myoma
Uterine fibroids become a common cause of dilated cervical canal. The disease is usually diagnosed long before the onset of menopause.
The following factors can provoke the development of fibroids:
- hormonal imbalance;
- heredity;
- being overweight;
- disturbances in the process of carbohydrate metabolism;
- state of habitual stress;
- thyroid diseases;
- previous abortions and difficult births.
Myoma, which causes expansion of the cervical canal, is localized in the isthmus or cervix, initiating deformation.
If the cervical canal is dilated and the diagnosis of fibroids is confirmed, then gynecologists recommend undergoing a transvaginal ultrasound examination - the woman is under observation and receives conservative treatment. With the progressive growth of fibroids and further deformation and expansion of the cervical canal, minimally invasive or radical intervention is performed. Myoma that disrupts the normal anatomy of the cervical canal in the form of its partial expansion is removed by embolization of the uterine arteries or by excision.
Polyps
Polyps are another common cause of enlargement of the cervical canal in young and postmenopausal women. Pathology can be provoked by:
- hormonal fluctuations;
- diabetes;
- hypertonic disease;
- obesity;
- psychological problems;
- abnormalities in the functioning of the thyroid gland.
The polyp may not manifest itself in any way. In such cases, pathology is revealed only during an ultrasound examination, when a specialist notes that the cervical canal is dilated.
Endometrial hyperplasia
Endometrial hyperplasia, which occurs more often during menopause and postmenopause, can also cause dilation of the cervical canal.
The reason that the cervical canal is dilated is the abnormal proliferation of cells, the structure of which resembles endometrial cells. Provoking factors may be:
- hypertonic disease;
- being overweight;
- diabetes;
- liver pathologies.
Taking medications containing estrogens can also provoke the activation of hyperplastic processes. They help the female body adapt to the new condition, but also increase the risk of hyperplasia.
The disease can occur either in a latent form or have visible signs. These include:
- bleeding;
- bloody "daub".
Quite often the pathology occurs in combination with cystic and polypous formations. It is most often detected in the absence of clear pathological symptoms - during an ultrasound examination.
Enlargement of the cervical canal, detected during the postmenopausal period, is a serious symptom that requires a full medical examination and the appointment of therapy adequate to the condition.
What is the essence of isthmic-cervical insufficiency?
If, during the process of monitoring a pregnant woman, a diagnosis of isthmic-cervical insufficiency is made, this means that there is a risk of premature dilatation of the cervical portion of the uterus and the onset of labor ahead of schedule.
This pathology indicates the inability of the cervical canal to reliably preserve the developing embryo inside the uterine cavity. With such a violation, there is a threat of termination of pregnancy.
Some expansion of the cervical canal is considered acceptable, within normal limits, during the period of active fetal growth, approximately 16-18 weeks. The increasing weight of the fetus and its active movements put pressure on the cervix, forcing it to open slightly. If the gynecologist, during an ultrasound examination, notes that the canal is enlarged more than normal, the woman is recommended to be hospitalized in an inpatient department to determine the cause of the pathology and take measures aimed at reducing the enlargement and preventing miscarriage.
If this is not the woman’s first pregnancy, the doctor pays special attention to the condition of the cervical canal, since in such pregnant women the cervix has less elasticity. Several factors contribute to the development of isthmic-cervical insufficiency:
- an excess of male sex hormones that have an effect on the tissues of the cervix, in which they soften, lose their firmness and elasticity;
- increased pressure on the cervical area due to the development of two or more embryos during pregnancy;
- existing injuries to the lumen of the cervical canal, neoplasms, inflammatory processes in tissues.
Pregnancy will be maintained if appropriate treatment measures are taken on time. In some situations, it is impossible to do without surgical intervention, which involves placing sutures on the problem cervical area, which will keep the walls of the cervical canal from further expansion.
Pregnancy
If the cervical canal is dilated during pregnancy, then premature labor can begin at any time. The reason for such a deviation may be:
- increased levels of male hormones in the body that stimulate cervical ripening;
- multiple pregnancy;
- trauma and pathology.
The most common pathologies due to which the cervical canal becomes dilated during pregnancy include:
- isthmic-cervical insufficiency;
- pharynx polyp;
- endocervicitis.
Isthmic-cervical insufficiency
This pathology is one of the common reasons why the cervical canal becomes enlarged. The uterus is unable to support a baby that is gaining weight.
Ultrasound helps to detect dilation of the cervical canal in a pregnant woman.
Violations can be caused by:
- abnormalities in hormonal levels;
- polyhydramnios;
- scar deformities.
If the canal is dilated, then the woman is prescribed drugs that strengthen the cervix.
Polyp
Polyps can be true or decidual (pseudopolyp that forms exclusively during gestation). To find out the type of tumor, the pregnant woman is prescribed a colposcopy of the cervix.
Decidual polyp develops against the background of hormonal imbalance and does not require removal. A true polyp is rarely diagnosed during pregnancy. It is removed after the baby is born.
Endocervicitis
The cervical canal can be dilated as a result of inflammation involving its inner surface. The pathology is caused by microorganisms of both pathogenic and opportunistic classes.
The choice of drugs depends on the type of pathogen. Preference is given to local remedies - vaginal suppositories or tablets.
If it turns out that the cervical canal is dilated, this does not always mean the presence of any pathology. The expansion may be physiological, but in any case, the woman will be prescribed an examination.
Changes during pregnancy in the cervical canal area
As soon as conception occurs and pregnancy occurs, a large amount of dense mucous secretion accumulates in the cervical canal, which closes the lumen of the canal like a plug. This kind of blockage of the canal persists throughout the entire pregnancy. Shortly before the onset of labor, the mucus plug peels off, and the woman may see whitish or yellowish mucus coming out with inclusions of blood streaks. This is a signal of approaching birth.
Changes also occur that affect the anatomical structure of the cervical canal. Approximately 7-12 days before the onset of labor, the cervical canal shortens slightly, and right before delivery, which is preceded by contractions, it expands significantly (up to 8-10 cm), its internal surface is smoothed out, forming a single birth canal uterus-cervical canal-vagina. This provides the newborn with an exit from the uterine cavity. Conducting an ultrasound examination of a pregnant woman at different stages, the gynecologist tries to monitor the condition of the cervix, since dilation of the cervical canal is a pathology that contributes to the premature onset of labor.