Using folk recipes
Chronic inflammation of the ovaries in women with mild symptoms is supplemented with treatment with folk remedies.
It is recommended to use infusions of medicinal herbs for internal use and douching. A decoction of yarrow helps a lot. One large spoon of dry crushed herb should be brewed with boiling water (200 ml). Leave covered for 15 minutes, filter. Drink a third of a glass every 6 hours.
A decoction of white acacia has a positive effect on the body. One small spoon of dry raw materials should be poured with boiling water (200 ml). Simmer in a water bath for 15 minutes, filter. Take 100 ml 4 times a day. This decoction is recommended for douching.
Calendula decoction is suitable for douching. 3 g of dried flowers are poured with boiling water (250 ml). Leave for 1 hour, filter. All douching solutions should be of low concentration to avoid drying out the vaginal mucous layer and disturbing the microflora balance. The course of douching should be at least 10 days with daily procedures.
For inflammation of the ovaries in women and symptoms of other gynecological diseases, treatment with folk remedies and healthy lifestyle recipes should be agreed with the attending physician. Self-medication of the disease is dangerous.
Ointments and creams
To prepare ointments and creams, use a base to which plant components are added:
- the cream consists of a water base, gelatin and vegetable oil (pink, peach). You can add solutions of vitamins A and E to it;
- The ointment consists of a fatty base (vaseline, glycerin), to which oils are added in small quantities.
After preparing the base, infusions and decoctions are added to it so that the consistency of the product does not become too liquid. Vaginal tampons are soaked in the prepared ointment or cream or compresses are applied to the lower abdomen (under the patch). The course of treatment is 10-14 days.
Drug treatment of inflammation of the appendages: antibiotics
Unfortunately, in recent years, many pathogenic microorganisms have acquired resistance to the antibiotics most often prescribed for adnexitis. We are mainly talking about tetracycline drugs.
Many doctors today prescribe Doxycycline as a drug that has minimal side effects and is quite effective. In addition, unlike other drugs in this group, Doxycycline is eliminated from the body quite quickly. But in general, tetracyclines will not be the best choice - both due to the developed resistance of pathogenic microbes and due to the large number of side effects.
When treating ovarian inflammation in women with antibiotics, drugs from the macrolide group are also used. They are often prescribed orally, since such drugs are practically not destroyed in the stomach. Due to their long half-life, they remain in the body for a long time and can even accumulate, which increases the effectiveness of their use. From this group, “Klatsid” and “Sumamed” are considered the best choices; their effectiveness has been proven by many studies.
The advantage of these drugs is that they act on some pathogenic microorganisms that remain “undetected” by other drugs because they live inside cells, causing inflammatory processes.
Another group of antibiotics that is prescribed to treat inflammation of the appendages and ovaries in women are fluoroquinolones. Their advantage is that resistance to them develops extremely slowly, so the drug does not need to be changed. In this group, the most effective drugs are Lomefloxacin, Ofloxacin, Norfloxacin.
Very often, when treating adnexitis, not one, but two antibiotics from different groups are prescribed. This is due to the fact that inflammation of the appendages is rarely caused by just one pathogen; much more often we are talking about several pathogenic microorganisms at once, both aerobic and anaerobic groups. Tinidazole and Metronidazole can be used to combat aerobes.
For symptoms of ovarian inflammation, treatment with antibiotics gives positive results. In this case, drugs can be used in different forms of release - both in the form of intramuscular injections and in the form of solutions for intravenous administration. Usually, antibiotics for injection are prescribed first, then medications in tablet form are prescribed. Candles are used much less frequently in such cases.
But there are antibiotics that are mainly produced in capsules - these are “Cedex” and “Ceftributen”. They are considered the most effective against pathogens such as streptococci, gonococci and enterococci.
The fluoroquinolones mentioned above—Ciprofloxacin and Ceftriaxone—can be prescribed both by injection and in tablet form. They cope with almost all types of microorganisms.
“Azithromycin” and “Zoomax” also have a wide spectrum of action. In any case, the dosage and method of administration should be selected by the doctor. Of course, contraindications to such drugs, the patient’s allergies, etc. are taken into account.
It is especially important to choose the right antibiotic during pregnancy. It is impossible to avoid taking such tablets when treating inflammation of the ovaries (right, left or both), since the disease can lead to miscarriage or premature birth
Since self-medication is contraindicated for pregnant women, we will refrain from providing even introductory information about the prescribed medications. Only a doctor can assess the likely risks and draw up a treatment plan.
This is the treatment prescribed to patients with ovarian inflammation. Men are also often diagnosed with inflammation of the epididymis (orchiepidymitis). For treatment, the same antibiotics are prescribed, but taking into account the clinical picture and characteristics of the patient’s body.
Treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome with chamomile: contraindications and side effects
Treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome with chamomile should begin only after eliminating contraindications:
- individual intolerance to the plant;
- pregnancy.
Use with caution during breastfeeding.
There are also side effects from chamomile, mainly due to an overdose. These include:
- acute allergy - Quincke's edema, urticaria;
- bronchospasm;
- allergic itching;
- nausea and vomiting;
- uterine bleeding;
- increased blood pressure;
- insomnia and irritability.
If acute reactions occur, you should immediately consult a doctor, and if the condition is life-threatening, call an ambulance.
How to properly treat oophoritis with folk remedies
Treatment of oophoritis is carried out using a significant number of various means: baths, douching, the introduction of medicinal tampons, the use of tinctures and decoctions, etc.
Steam baths
It is useful to make baths in which a little hay is added. Instead of hay, you can add cabbage boiled in milk. You cannot sit in the water: the steam must penetrate into the vagina. Other bath compositions:
- a mixture of black radish juice and olive oil;
- decoction of chamomile and oak bark;
- a decoction of yarrow, nettle, chamomile (all herbs should be taken in equal proportions).
Douching solutions
It is recommended to irrigate the vaginal mucosa daily. The temperature of the solution should not exceed body temperature. The compositions for douching are as follows.
- An infusion of a mixture of oak bark, shepherd's purse, water pepper and nettle. Take 15 g of all components and add 1 liter of boiling water.
- A decoction of marigolds is prepared as follows: boil 4 tbsp for 2 minutes. flowers in 1.5 liters of water. Keep in a sealed container for 20 minutes, then strain.
- Take 25 g of rosemary, yarrow, sage and 50 g of oak bark, mix them. For 1 liter of water you need to add 1 tbsp. collection, bring to a boil and heat for 30 minutes in a water bath.
Therapeutic tampons
To prepare tampons, you need to soak sterile cotton wool with one of the medicinal tampons. Inserted deep into the vagina. Medicinal compositions:
- juice from aloe and fresh cabbage;
- a mixture of honey and propolis;
- a mixture of a few drops of eucalyptus oil with olive oil.
Infusions for internal use
They should be taken for inflammation and various associated conditions.
- Infusion of sage and chamomile. Boil it for 2 minutes, leave for 20 minutes. Drink a glass before meals 2 times a day.
- For stress, it is useful to take teas made from mint, lemon balm and valerian root. It’s great if the tea is infused in a thermos. You should drink 0.5 liters of this tea 3 times after meals.
- A mixture of aloe juice and honey has pronounced anti-inflammatory characteristics. To provide a therapeutic effect, it is enough to take 2 tbsp. funds per day.
- To improve metabolism, you will need to prepare a decoction of licorice, horsetail, rose hips and immortelle. For 1 liter of boiling water you need to take 2 tbsp. medicinal mixture. Take 150 ml after meals 3 times a day.
List of herbs
The following herbs are used to treat inflammation of the ovaries:
- Potentilla gossamer;
- blueberries (leaves);
- small-leaved linden inflorescences;
- dry barberry roots;
- lemon balm and mint;
- yarrow;
- thorn;
- corn silk;
- field grass;
- sweet clover;
- mat-and-stepmother;
- centaury;
- rose hip;
- black currant;
- chamomile flowers;
- calendula flowers.
Infusions and decoctions
Infusions and decoctions for inflammation are prepared from the above list. Usually take 1 tbsp for 0.5 liters of water. herbs or mixtures of herbs.
Decoctions for inflammation are best prepared in a water bath.
Juices and teas
To treat inflammation of the ovaries, teas from:
Aloe juice is considered the best for getting rid of ovarian inflammation. Contains a huge amount of highly active organic substances. Has a high antibacterial effect against staphylococci, streptococci and other bacteria.
To significantly reduce pain and inflammation, compresses made from ichthyol ointment are used.
Some doctors recommend using compresses with medicinal clay for inflammation. It fights swelling and inflammation, and “pulls out” toxins.
Steam baths
Some recipes for steam baths for inflammation in the ovaries:
- Boil hay in a large saucepan. The patient should be placed over this pan until it cools down.
- Pour unwashed sheep's wool over it and place the sick one over it.
- Boil gorse in a large saucepan, pour olive oil over it, place the patient on it while there is steam.
How to treat ovarian inflammation: baths, tampons and douching
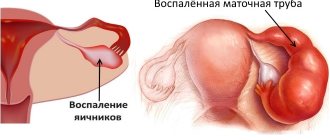
Inflammation of the ovaries (other medical terms: oophoritis, adnexitis) is a disease that poses a danger to health and, especially, to the reproductive function of the female body. Very often, the development of diseases of these paired sex glands is caused by pathogenic bacteria: chlamydia, gonococci, trichomonas, mycoplasmas, streptococci, staphylococci and others.
However, often the inflammatory process in the ovaries begins after ordinary hypothermia, abortion, childbirth, or the use of intrauterine devices.
Symptoms of ovarian inflammation (adnexitis, oophoritis)
The symptoms of this disease depend on the form of inflammation. This may be acute or chronic oophoritis. The main signs of ovarian inflammation are:
- pain in the lower abdomen and vagina during sexual intercourse,
- discharge,
- disruptions in the menstrual cycle.
During the acute phase of the disease, the following are often observed:
- uterine bleeding,
- heat
- and purulent-bloody discharge.
Such symptoms require immediate and qualified medical attention.
Chronic inflammation of the ovaries, along with prescriptions from a gynecologist, can be treated with proven folk remedies. Significant success in treatment can be achieved by using medicinal baths, tampons and rinsing (douching):
Douching solutions
Washing the vagina with a decoction from the aerial part of the cinquefoil will relieve pain, reduce inflammation and have a bactericidal effect. Add five tablespoons of dry plant to half a liter of boiling water.
Place on fire and bring to a boil. Leave in a thermos for at least half an hour. Strain the broth through multi-layer gauze and syringe with the warm extract before bed. After the procedure, be sure to put on warm pajamas and cover yourself well with a blanket. Potentilla infusion is also taken orally. This drug effectively regulates the menstrual cycle and stops uterine bleeding.
Place two tablespoons of finely crushed flowers in 400 ml of boiling water. Leave for an hour in a warm place. Drink the infusion strictly before each meal, 0.5 cups.
Therapeutic tampons
You can use these medicinal tampons at night for inflammation of the appendages. To do this, first prepare a decoction of herbs: chamomile, oak bark and sage. It is recommended to adhere to this ratio in the amount of raw materials 5:2:3.
One spoon of herbal mixture is poured with one cup of boiling water (300 ml). Let it boil, strain well through cheesecloth, cool until warm. Moisten cotton swabs and place them in the vagina until the morning. In the morning you can douche with an infusion from the same collection.
Take two full tablespoons of herb per liter of hot water.
According to the empirical experience of traditional medicine, it is recommended to treat inflammatory processes in the ovaries by douching the vagina with a decoction of the following medicinal herbs: marshmallow root, oak bark and mother herb (oregano).
The amount of each plant material is taken in the ratio: 2:5:4. Next, pour 7 tablespoons of the herbal mixture into a saucepan and pour 300 ml of boiling water. Bring the mixture to a boil and leave for another half an hour.
The strained, warm decoction is doused daily in the morning and evening.
Preventive measures
To protect yourself from oophoritis, you should avoid hypothermia. You should know that medical abortion can also cause inflammation in the ovaries due to pathogenic bacteria entering the vagina.
Move more, control your immunity, avoid casual sex without protection.
At the first symptoms of the disease, be sure to undergo an examination and consult your gynecologist.
Source: https://NarodnymiSredstvami.ru/lechenie-vospaleniya-yaichnikov-narodnyimi-sredstvami/
Characteristic symptoms
The clinical picture may vary depending on the pathology. Common symptoms of inflammation in women are pain in the lower abdomen of various types (aching, shooting), changes in the consistency, color and smell of discharge, a feeling of severe itching and burning. An inflammatory process can also be suspected based on irregularities in the menstrual cycle.
The acute severity of symptoms increases the woman’s nervous excitability, she becomes irritable. In severe inflammatory processes, a disturbance in the general condition may occur: signs of intoxication and body temperature appear.
female inflammation
Overview of specific inflammations and typical symptoms:
| Name | What part of the reproductive system is affected? | Signs |
| Endometritis | Uterine mucosa |
|
| Ovarian cold | Ovaries |
|
| Vulvitis | External vulva | Redness may appear on the labia, and the woman feels itching. The nature of the discharge depends on the cause. As it progresses, the vulva swells and becomes painful. |
| Cervicitis | Cervix | Asymptomatic. Atypical discharge rarely appears. |
Treatment of the disease
Treatment tactics are determined after an accurate diagnosis has been established. The choice of treatment option depends on several factors:
- stages of the disease;
- causes of pathology;
- symptoms.
Only the acute form of oophoritis is treated in a hospital setting. The remaining stages of ovarian inflammation with mild symptoms can be treated at home.
Antibiotic therapy
When ovarian inflammation is detected in women with acute symptoms, treatment with these drugs is mandatory. During diagnosis, it is only necessary to identify the type of pathogen and its sensitivity to the drug. The dosage is selected individually to ensure the required concentration of the antimicrobial component. In severe cases of the pathology, several medications may be prescribed at once.
You cannot self-medicate, as there are several groups of antibiotics with their own characteristics. A doctor can figure them out; he prescribes medications, taking into account diagnostic data.
For inflammation of the ovaries in women with pronounced symptoms, prescribe treatment at home, and a quick recovery can only be achieved with the help of properly selected antibiotics. The table presents the main medications for the treatment of ovarian inflammation.
| Antibiotic group | Medications | Description |
| Sulfonamides | Streptocide, Sulfasalazine, Co-Trimoxazole | Strong drugs with a wide spectrum of action. Used as injections. |
| Aminoglycosides | Kanamycin, Gentamicin | They show high efficiency and are used in the form of injections and tablets. |
| Penicillins | Oxacillin, Ampicillin | They have few side effects, but are low in effectiveness. |
| Cephalosporins | Cephalexin, Cefazolin | Has many side effects. |
| Tetracyclines | Tetracycline, Doxycycline | Often prescribed and well tolerated. |
To achieve maximum antimicrobial effect, antibiotics are often combined.
Application of candles
For severe inflammation of the ovaries in women with complex symptoms, treatment with antibiotics is supplemented with suppositories. Vaginal suppositories that contain:
- oak bark;
- walnut extract;
- propolis.
A positive result is shown by the use of Clindamycin suppositories. They are administered at night. Metronidazole suppositories are used morning and evening. Voltaren suppositories have a calming effect and are recommended for complex treatment.
For chronic inflammation of the ovaries in women with mild symptoms, treatment with suppositories is recommended to be carried out regularly in courses for the purpose of prevention.
Inflammation of the ovaries in women: signs and treatment at home
Inflammation of the ovaries and fallopian tubes is called adnexitis. The infection affects one or both glands at once. When inflammation of the ovaries occurs in women, only a gynecologist can determine the symptoms and treatment.
The disease is classified as a dangerous pathology. In 20% of patients who have had adnexitis, infertility occurs. In advanced states, the disease leads to peritonitis, a life-threatening complication. Emergency surgery is the only thing that helps prevent death.
Causes
The ovaries can become inflamed if they are penetrated by:
- pathogens that cause sexually transmitted infections (eg, gonorrhea agents);
- opportunistic microorganisms (streptococci, staphylococci, candida).
The development of adnexitis is also provoked by:
- childbirth;
- abortion;
- intrauterine devices;
- genital surgery;
- careless performance of diagnostic procedures.
If a woman has a cold in her ovaries, then there is a high probability that an inflammatory process will break out in the glands.
Adnexitis is not the root cause, but a consequence of infectious processes occurring in the uterus and fallopian tubes . Occasionally, pathogens enter the ovaries with blood or lymph if a woman is sick with tuberculosis, tonsillitis, or has carious teeth.
The infectious and inflammatory process moves from the uterus to the tubes. Purulent exudate appears in the fallopian tubes and adhesions form. Their walls become denser, and the lumen narrows.
If treatment is not started at this stage, the gonads are drawn into the inflammatory process. The tube is soldered to the ovary. In severe cases, the peritoneal tissues undergo destructive changes. Ultimately, it all ends with rupture of the fallopian tube and peritonitis.
Symptoms
When ovarian inflammation occurs in women, symptoms and treatment vary. The disease is acute, subacute and chronic. Each type of disease is accompanied by characteristic symptoms.
Exacerbation stage
When adnexitis worsens, the following symptoms occur:
- severe pain, pain when urinating;
- constant pain radiating to the lower back or sacrum, lower abdomen, above the pubis;
- a sharp increase in temperature, sometimes up to 39 degrees;
- feverish condition;
- weakness, fatigue;
- bleeding between periods;
- excessive pain during intimacy;
- copious discharge of serous or purulent exudate.
An exacerbation is manifested by another pronounced symptom: inflammatory processes lead to a significant enlargement of the ovaries, the palpation procedure causes pain to the woman. This symptom is determined by the gynecologist when examining the patient. Treatment of adnexitis in the acute stage is carried out in a hospital setting.
Signs of the subacute form
This type of illness is a rare occurrence. The disease develops against the background of mycoplasmosis or tuberculosis. The signs of the subacute phase of the disease are similar to the symptoms of the acute form, but are less pronounced.
Symptoms of chronic inflammation
If not cured immediately, the disease develops into a chronic form. The disease either worsens or subsides. In the acute stage, chronic inflammation of the ovaries manifests itself as follows:
- soreness in the groin, above the pubis;
- increased pain during menstruation;
- sexual dysfunction (low libido, pain during intimacy);
- poorly discharged leucorrhoea;
- menstruation disorder;
- ovarian dysfunction;
- It is impossible to conceive a child even with regular sex life.
The size of the inflamed ovary is increased. When palpating it, pain occurs. Women burdened with adnexitis:
- irritable;
- lethargic;
- suffer from increased fatigue, sleep disturbances, and decreased performance.
Drug therapy
The choice of treatment method is influenced by the form of the disease, severity, symptoms and causes of adnexitis. The acute form is treated in a hospital setting. Sick women are prescribed:
- antibiotics;
- pain relievers;
- restorative drugs (immunomodulators, multivitamins).
In subacute adnexitis, therapy is supplemented with physiotherapy. In the chronic course of the disease, methods of physiotherapeutic and balneological treatment are used.
Chronic adnexitis is a difficult-to-treat pathology. Treatment for chronic ovarian inflammation takes longer. The disease is more difficult to treat and produces severe complications that can only be eliminated surgically.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics are absolutely necessary to treat ovarian inflammation. To suppress inflammation, an antibiotic is selected that can destroy the pathogen that caused the disease.
In the affected area, the concentration of the antibiotic should reach a maximum value. For this purpose, treatment of the ovaries is carried out with drugs that have a rather long half-life. When the disease is aggravated, antibiotics are used in various combinations.
How to treat ovarian inflammation caused by opportunistic microorganisms (streptococci, enterobacteria)? Doctors usually prescribe Penicillin to women.
Anaerobic microflora is suppressed with Metronidazole. In mild forms, the medicine is taken orally; in advanced conditions, it is administered intravenously.
To relieve intoxication, patients are recommended to take anti-allergenic medications: Suprastin, Diphenhydramine.
Candles
The main therapy is supplemented with auxiliary means - using suppositories that eliminate adnexitis. For treatment of inflammation of the ovaries, suppositories are used, which contain:
- Oak bark
- propolis;
- Walnut.
Suppositories alone are not able to cope with adnexitis . They are used only in complex treatment of the disease and as a prophylactic agent to prevent chronic inflammatory processes.
Traditional methods
After clarifying the diagnosis and identifying the pathogen, the doctor prescribes a course of supportive and preventive therapy. Drug treatment is supplemented with traditional medicine.
Ovaries are treated at home in different ways. The choice of methods is influenced by the form of the disease. For acute adnexitis, apply cold compresses, take medicinal baths with clay, and wash with herbal decoctions.
In the chronic course of the disease, wrap the lower back and abdomen with insulated bandages, lie in baths with herbal decoctions and medicinal mud. Stuff the pillow with wildflowers, heat it, and fix it in the lower abdomen.
List of plants used for adnexitis
Treatment of ovarian inflammation with folk remedies helps alleviate the course of the disease, prevent the development of complications and relapses, and promotes a speedy recovery.
The following herbs effectively cope with adnexitis:
- Ginseng. Plant extracts suppress inflammatory processes, relieve swelling, and prevent the formation of tumors.
- Juniper. To relieve inflammation and eliminate leucorrhoea, chew the berries and drink infusions.
- Borovaya uterus. Consuming this herb in the form of herbal tea helps get rid of inflammation and prevent the development of tumors.
- Sagebrush. Plant extracts stimulate the glands, have a calming effect, relieve pain, heal wounds, and stop bleeding .
- Badan. Extracts from bergenia suppress blood secretion, inflammation, pain, fight cancer, heal wounds, and restore tissue.
- Bloodroot. Extracts are used for oral administration and douching. They relieve chronic inflammation.
- Coltsfoot. Products based on this herb eliminate inflammation due to adnexitis.
- Centaury. With the help of the plant, chronic infections and inflammations are relieved. Decoctions, infusions, and herbal teas are prepared from it.
- Cranberries, lingonberries and rowan berries are used for therapeutic and prophylactic purposes. They strengthen the immune system, fight vitamin deficiency, suppress pathological microflora, and have a diuretic effect.
- Knotweed. Plant extracts restore reproductive function and eliminate bleeding.
- Ginger. If a woman has colds in her ovaries, warming rubs are prepared with ginger to help eliminate inflammation. Tea with ginger has a detrimental effect on viruses and bacteria that cause adnexitis and eliminates psycho-emotional stress.
How to use plants
For inflammation of the ovaries in women, treatment with folk methods helps eliminate apathy, irritation, increase libido, suppress inflammation, normalize hormonal imbalance, restore the emotional background and the menstrual cycle. Treatment with home remedies lasts 4-6 weeks. After the treatment course, a break is necessary.
Treatment at home is carried out using the following recipes:
- A collection is prepared from centaury, knotweed, horsetail, and cinquefoil. Raw materials are taken in equal quantities. Add 1 tablespoon of the mixture to 200 ml of boiling water. After an hour, the infusion is filtered. Drink 50 ml four times a day.
- Morse made from lingonberries, viburnum, black currants, rowan. Crush the berries, add hot water and leave. Drink a glass throughout the day.
- Make a collection of marshmallow, St. John's wort, nettle, coltsfoot, thyme, yarrow. For the mixture, take equal amounts of herbs. Pour a handful of raw materials into 500 ml of boiling water and leave until cool. Drink 100 ml throughout the day.
- Prepare a collection of the following herbs: coltsfoot, marigold, centaury, chamomile, sweet clover. Place a handful of the mixture in 500 ml of boiling water. Drink the entire infusion in 1 day. Single dose – 50 ml.
- Brew linden blossom with lemon balm, St. John's wort, corn silk and a small amount of oak bark. Drink tea three times a day.
- How to cure ovarian inflammation if adnexitis develops due to a cold? For this purpose, forest hay is brewed in a large saucepan with boiling water and cooled to a comfortable temperature. Take a sitz bath for 15 minutes. After the procedure they go to bed. Duration of treatment – 7 days.
- Add juniper berries, ginger, honey to hot tea.
- Borovaya uterus is brewed and drunk instead of tea, and douching is also done. The product activates the work of the ovaries and normalizes the concentration of hormones .
Douching
Warm solutions are prepared for the douching procedure:
- Juniper fruits are dipped in boiling water and infused. The product is douched daily until the signs of adnexitis disappear.
- An aqueous extract from cinquefoil, centaury, and coltsfoot suppresses inflammation of the ovaries.
- Treatment of inflamed ovaries is carried out with the following solution: steam bergenia in boiling water, dilute with water 1:1.
- Sloes, chamomile and rose hips are poured into a thermos and boiling water is poured in. Insist during the day. Douche before bed.
Using herbal tampons
Hygienic tampons are impregnated with the following agents:
- An extract made from sage herbs, chamomile and oak bark.
- Freshly squeezed aloe juice with honey (1:1).
- Emulsion of calendula extract and sea buckthorn oil. Marigold inflorescences are steamed in boiling water. Add a little sea buckthorn oil to the infusion.
With the help of tampons, colds and inflamed ovaries are treated for 14 days. The procedure is carried out before bedtime. In the morning, the used tampon is removed.
Complex therapy prescribed by a doctor helps to get rid of adnexitis. With the simultaneous use of medications and folk remedies, the inflammatory process quickly subsides and does not cause complications. Women who harden the body, strengthen the immune system, eat right, dress for the season, are protected from the occurrence of disease.
Source: https://FitoOtvet.com/zhenskie-zabolevaniya/vospalenie-yaichnikov-priznaki-i-terapiya.html
Treatment of adnexitis: basic principles
Treatment of adnexitis is a process that requires an integrated approach. First, you need to establish the cause of the disease, which requires laboratory tests, since you need to identify the pathogen and evaluate its resistance to various antibiotics.
Most often, therapy for acute or subacute adnexitis is carried out in a hospital setting, and in the chronic form it is possible to treat it at home. In this case, antibiotics or antibacterial drugs, as well as immunomodulatory, desensitizing and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. This is necessary in order to improve blood microcirculation, relieve pain and inflammation. Physiotherapeutic methods are prescribed only when the temperature becomes normal.
If you consult a doctor in a timely manner, the duration of treatment is 2-3 weeks. Theoretically, it can be treated at home. However, therapy for adnexitis requires bed rest. At home, this is only possible if the family takes on all the responsibilities - cleaning, cooking, etc. Otherwise, there will be no talk of any peace. In addition, it should be remembered that during the treatment of adnexitis, sex is absolutely prohibited.
When treating the chronic form, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, immunocorrectors or biostimulants, vitamins, and enzymes are prescribed.
Non-drug treatment methods play an important role. These are, for example, therapeutic exercises, special massage and intimate warming, and other physiotherapeutic procedures. Antibiotics for the chronic form are rarely prescribed - only in cases where pathogenic bacteria that cause the disease have been detected.
Despite the fact that chronic adnexitis occurs in a milder form than acute adnexitis, it can be more difficult to treat, if only because antibiotics practically do not help. Anti-inflammatory drugs and various physiotherapeutic methods remain. These are, for example, ultrasound and magnetic therapy, electrophoresis, and other procedures whose effect is aimed at improving trophism and microcirculation in tissues.
Mud therapy is considered an effective method, but only if the woman does not have benign tumors in the pelvic organs.
Useful properties of the plant
In folk medicine, chamomile flowers are used, which are collected during the flowering period. They contain a lot of important and beneficial substances for women's health. Essential oil, for example, has a pronounced anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effect. Efficiency in the treatment of problems of the female reproductive system is ensured by the content of medicinal hormone-like substances in chamomile. Doctors agree that chamomile is a safe and effective remedy.
The rich composition of vitamins (nicotinic acid, carotene, ascorbic acid), macro- and microelements (zinc, potassium, copper, boron, selenium) provides the body with the corresponding substances. Chamazulene reduces allergy symptoms and has a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect, while apiin, apigenin and herniarin relieve spasms well.
Chamomile contains organic acids that have bactericidal properties and normalize metabolic processes. Herbal medicines, infusions and decoctions of medicinal plants disinfect, relieve pain and inflammation, have an anti-allergenic effect, relax the muscles of internal organs and accelerate the regeneration processes of damaged tissues.
Symptoms of inflammation of the appendages
The disease begins with an acute form. Its first symptom is pain in the lower abdomen. With unilateral pathology, pain may occur on the left or right, and with bilateral pathology, pain is observed on both sides. Unpleasant sensations radiate to the lower back, sacrum, tailbone, and can spread throughout the abdomen. There is often discomfort during urination and defecation caused by dysfunction of neighboring organs. Purulent vaginal discharge appears, sometimes having an unpleasant odor.
As the disease progresses, chills, fever up to 39 degrees, fever, poor health, loss of appetite, nausea, and aching sensations in the bones occur. Symptoms are caused by intoxication - poisoning of the body with waste products of microbes that cause the disease. Therefore, this phase of the disease is called toxic.
Fever
Nausea
Decreased appetite
If left untreated, the disease progresses to the next, septic, phase, during which purulent foci appear in the pelvic area. At this stage, the patient's condition becomes even more severe. The temperature acquires a wave-like septic character with rises and falls, abundant purulent discharge appears, interruptions in the functioning of the heart are observed, and the functioning of the intestines and bladder is disrupted. There is severe pain in the lower abdomen. Sometimes you can feel a tumor-like formation in the area of the affected organs.
The chronic form occurs in the absence of adequate treatment for acute manifestations. There are two flow options:
- Subacute, in which the disease does not produce pronounced symptoms. There are pulling sensations in the lower abdomen on one or both sides, menstrual irregularities, painful periods, and pathological discharge.
- Recurrent, occurring with remissions - periods of absence of symptoms - and exacerbations, during which acute symptoms occur.
There are 2 types of chronic forms of the disease:
- Infectious-toxic, accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen, discharge, fever, discomfort during intimacy.
- Neuro-vegetative - with this form, a hormonal imbalance occurs due to a disruption in the production of female hormones (estrogens). The patient complains of deterioration in health, mood instability, and menstrual dysfunction. This form of the disease often leads to neuroses.
Neurosis
Types of disease
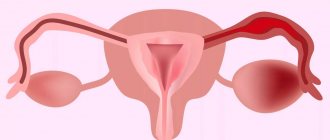
The ovaries have a very infection-resistant outer shell. But the pathology can be transmitted through nearby organs, for example, the fallopian tubes. This is how inflammation of the ovaries or oophoritis develops. A viral infection can spread through blood or lymph. Oophoritis can become a complication after tonsillitis, appendicitis or chronic caries.
There are three types of ovarian inflammation:
- acute;
- subacute;
- chronic.
Without treatment, the pathology becomes chronic, in which periods of exacerbation and remission alternate. Pronounced symptoms are absent or they are confused with other pathologies.
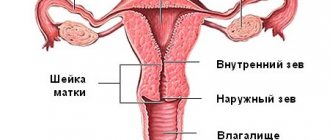
What is ovarian inflammation
To understand what oophoritis is in gynecology (as doctors call inflammation), you need to understand its nature. Oophoritis is provoked by pathogens that rise from the fallopian tubes or cervical canal. Sometimes infection of the ovary occurs through blood or lymph, then even banal caries or tuberculosis can become the causative agent. Symptoms of oophoritis are often confused with other diseases, so diagnosis of inflammation includes ultrasound, blood tests, urine tests, and smears.
Oophoritis can be unilateral (only the right or only the left ovary) and bilateral (both ovaries are inflamed). It can manifest itself in acute (subacute) and chronic forms. Accompanied by a violation of the correct location of the pelvic organs, enlarged ovaries, adhesions, up to an ovarian cyst. There are concomitant diseases: with acute and chronic adnexitis, the appendages become inflamed, with salpingitis – the uterine cavity, the tissue of the fallopian tubes.
Causes
The causative agents of infection are the viruses of chlamydia, trichomoniasis, gonorrhea, tuberculosis, mycoplasmosis, inhabitants of the pathogenic microflora of the female genital organs (streptococci, candida, E. coli). The disease can be triggered by external factors: hypothermia, complications after infectious diseases, abuse of antibiotics, hormonal drugs, injuries during a gynecological examination of a woman, the use of an intrauterine device.
Symptoms
Signs of inflammation of the ovaries and appendages in women in its acute and chronic forms differ. The acute form of the disease is characterized by:
- pain, pain when urinating due to infection of the cervical canal;
- pain in the lower abdomen due to adhesions in the ovarian tissues;
- fever, weakness due to infection;
- dull pain in the lower abdomen during sexual intercourse due to damage to the fallopian tubes;
- disruption of menstruation due to the formation of a persistent focus of inflammation in the pelvis;
- purulent discharge or leucorrhoea.
Symptoms of ovarian inflammation in women in its chronic form (chronic oophoritis):
- dull, aching, nagging pain in the lower abdomen, in the vagina, which intensifies before and during menstruation, during hypothermia, during sexual intercourse;
- leucorrhoea;
- erratic menstruation;
- difficulty conceiving;
- decreased sex drive;
- causeless irritability;
- insomnia, anxiety;
- high fatigue, decreased performance.
Diagnosis and treatment stages
Basically, a gynecologist-endocrinologist deals with the treatment of disorders of the normal functioning of the ovaries. To begin with, the doctor must rule out ectopic pregnancy, tumors, analyze the patient’s menstrual cycle calendar, and conduct an examination. After this, a full diagnostic plan is drawn up.
Classic ways to determine the causes of ovarian failure are:
- ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs
- identifying infections that are transmitted through sexual contact through testing
- checking hormonal levels (donate blood from a vein, urine test)
- establishing the thickness of the uterine mucosa (endometrium)
- histology (scraping required)
- examination of the brain and pituitary gland (MRI, CT).
The main goals of treatment are:
- stabilization of the normal condition of a sick woman
- elimination of the cause of the disease
- normalization of the menstrual cycle.
At the final stage, the patient may be prescribed hormonal medications that can “trigger” the normalization of monthly bleeding.
Anti-inflammatory suppositories for inflammation of the appendages
The introduction of drugs into the vaginal cavity ensures rapid penetration of the drug into the inflammation zone and a high therapeutic effect of its use. What anti-inflammatory suppositories are used in gynecology for inflammation of the appendages?
Suppositories with NSAIDs
NSAIDs or non-steroidal suppositories for inflammation of the appendages with an anti-inflammatory effect:
- Indomethacin.
- Diclofenac.
- Voltaren.
Also, for adnexitis, hemorrhoidal suppositories with belladonna are prescribed. They are an anti-inflammatory and analgesic at the same time.
The listed drugs are classified as drugs for the treatment of joint diseases and inflammation. They are also successfully used in the treatment of any internal inflammatory processes.
Absorbable suppositories
These drugs prevent the formation of adhesions. They stop adhesions during inflammation and resolve adhesions after treatment of adnexitis.
- Terrylitin suppositories - dilute blood clots and pus, break down necrotic (dead) tissue.
- Longidaza also promotes the resorption of adhesions and stops the adhesive process.
Candles with antiseptics
Vaginal suppositories with antiseptics of antifungal and antibacterial action for the treatment of appendages are ineffective. They are prescribed if, in addition to adnexal inflammation, there is inflammation of the vaginal cavity (colpitis).
Antifungal suppositories:
- Gainomax.
- Myconalosis.
- Gyno-Pevaril.
- Nystatin.
- Primafungin.
- Terzhinan.
Candles with antibacterial action:
- Dalatsin.
- Clindacin.
- Metrovagin.
- Betadine.
- Hexicon.
- Iodoxide.
- Fluomizin.
- Terzhinan (complex drug with antibacterial and antifungal effects and hormonal prednisolone).
Treatment with suppositories, the introduction of medicinal substances into the vaginal or rectal cavity is indicated for various diseases. Medicinal substances enter the bloodstream, bypassing the digestive tract, without partial destruction in the liver. This reduces the incidence of allergic reactions and increases the effectiveness of treatment.
Rectal suppositories with immunomodulatory effects
Preparations with interferon exhibit an antiviral effect. They are broad-spectrum immunomodulators. The most famous of them are Viferon, Genferon, Kipferon.
Note: the drugs listed are rectal suppositories, that is, they are introduced into the rectum through the anus.
Suppositories for normalizing vaginal microflora
Also, during and after treatment with andexide, suppositories are used to normalize the vaginal flora - Acylact, Lactobacterin. They are absolutely necessary during antibiotic treatment. Desirable – in the treatment of viral forms of infections.
For intestinal and stomach infections
The most common intestinal infectious diseases are:
- dysentery;
- acute diarrhea;
- enterocolitis;
- colitis;
- gastroenteritis;
- acute gastritis.
To treat most infections of the digestive tract, the following measures are sufficient:
- change in diet;
- oral or intravenous rehydration;
- symptomatic therapy using intestinal antiseptics: Intestopan;
- Meksaform;
- Chlorquinaldol.
The main causes of such disorders are:
- food poisoning by various microorganisms: salmonella;
- enterococcus;
- anaerobic bacteria;
- staphylococcus;
- sticks;
- streptococcus;
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
food intolerance; secretory disorders; dyskinesia; allergy; binge eating.
If antibiotics are required for healing, then you should choose those that concentrate in the intestinal lumen:
- insoluble sulfonamides:
- Colistin;
- Neomycin;
- Streptomycin.
For staphylococcal enteritis that occurs after long-term treatment with antibiotics (with liquid stools), the following drugs can be prescribed:
- Kanamycin sulfate;
- Rifampicin;
- Erythromycin;
- Cloxacillin;
- Oxacillin.
In such situations, it is recommended to disinfect healthy bacteria carriers and not overuse antibiotics.
To heal bacillary dysentery, in addition to treating symptoms, rest and diet, the following antibiotic drugs (or chemotherapy drugs) are required:
- Levomycetin (Chloramphenicol): 2 g/day (take only in severe cases);
- Tetracycline: 0.5 g/day (3-4 days);
- intestinal antiseptics: Intestopan or Chlorquinaldol: 12 tablets on the first day and 8 tablets in the next 2-3 days;
- Mexaform: half dose.
In the case of resistant forms, Streptomycin or Neomycin with Tetracycline or sulfanilamide is prescribed.
Overuse of antibiotics can cause enteritis with Candida albicans.
Typhoid fever
For typhoid fever, the following antibiotic drugs help:
- Co-trimoxazole;
- Ampicillin;
- Levomycetin (Chloramphenicol).
Cholera
Treatment of cholera is based on restoring the hydroelectrolytic balance, as well as taking the following drugs:
- Co-trimoxazole;
- Levomycetin (Chloramphenicol);
- Tetracycline.