It is a rare woman who clearly and correctly reacts to emerging problems: at the first pain in the lower abdomen, at the first disruptions in the menstrual cycle, she immediately turns to a gynecologist. In the majority of cases, the acute phase turns into chronic adnexitis, and treatment begins too late. Many people do not even suspect that pain radiating to the lower back is not always related to pathologies affecting the spine. Symptoms of inflammation of the appendages very often mimic other diseases, and only a doctor can recognize them and prescribe adequate treatment.
Any pain in the lower back and pelvis should be a warning sign. Treatment of inflammation of the appendages, the symptoms of which so often mislead the patient, is always long and complex, and it is almost impossible to carry it out on your own. In case of acute pain, a hospital is always required, and then there will be home treatment, sanatorium-resort treatment, massage sessions and numerous procedures in the clinic’s physiotherapy room. Even the diet must be special: spices, salt, carbohydrates and much more are limited.
For what diseases are they used?
Antibiotics in gynecology are prescribed only if indicated. The main reason is that medications of this type are not effective against fungi and viruses.
Antibiotics used in gynecology can be prescribed for:
- inflammation of the ovaries;
- uterine tubes;
- inflammation of the labia;
- uterine body;
- cervical canal;
- vaginal inflammation.
Medicines of this class are effective against the following pathogens:
- gonococci;
- chlamydia;
- streptococci;
- staphylococci.
It should be noted that even one of the most ancient sexually transmitted diseases, syphilis, must be treated with antibacterial agents. The causative agent of the infection is the bacterium Treponema pallidum. Therapy for syphilis is long-term, however, if it is carried out in a timely manner, it ends successfully for the patient.
In case of inflammation of the reproductive organs, an antibiotic in gynecology is prescribed individually. Immediately before the course, an analysis is done for the sensitivity of strains to the drug (bacterial culture of microflora to determine sensitivity), which helps to choose the most effective remedy and optimize treatment.
The following indications exist for antibacterial therapy:
- temperature increase;
- severe pain syndrome;
- the appearance of vaginal discharge;
- symptoms of intoxication.
All gynecological diseases require different treatment methods; both monotherapy and combination therapy can be carried out.
Indications
To treat ovarian inflammation, it is necessary to select antibiotics, the instructions for which may describe the following indications for use:
- infectious diseases of the upper and lower respiratory tract;
- urinary system infections;
- infectious lesion of the genital organs;
- infections of the skin, bone, soft and connective tissues;
- biliary tract infections.
All this helps eliminate pathogenic microorganisms that cause inflammation. When they are completely destroyed, the patient recovers.
What medications are prescribed?
There are two main types of antibiotics. In gynecology, medications can be used whose action is either bacteriostatic or bactericidal.
The latter affect pathogenic microflora, killing bacteria. Their mass death causes intoxication or an increase in its symptoms, however, as harmful pathogens are removed from the body, the patient’s condition improves.
Bacteriostatic drugs act differently on microorganisms; they block the mechanisms of their reproduction and growth. This causes the death of pathogenic microflora. In other words, medications create an unfavorable environment for the reproduction and growth of pathogenic bacteria, which can help cope with the symptoms of the disease and speed up the patient’s recovery.
Interaction with other medications
Most types of antibiotics are prohibited from being combined with each other - with the same
exposure to the body can lead to deterioration of the condition or overdose.
It is not recommended to take these drugs simultaneously with anticoagulants or oral contraceptives - the effect of the latter may be reduced. When combined with medications that contain disulfiram, the patient's condition may worsen. It is prohibited to use antibiotics simultaneously with dextran, glucose, proteins, and lipids. When administering an injection, mixing drug solutions in one syringe is prohibited.
Advantages and disadvantages of treatment
Antibacterial drugs have their disadvantages and advantages; their use allows:
- stop the inflammation process at the stage of its development before complications arise;
- to conceive a healthy child, carry him to term and give birth without any problems;
- avoid problems in the future with the reproductive system.
It is very important to carry out treatment promptly using broad-spectrum antibiotics in gynecology. Thanks to this, it is possible to avoid the transition of the inflammation process to the chronic stage and various complications.
A protracted disease is usually in a latent state, but under unfavorable factors it can develop into an acute form. This happens because bacteria are constantly present in the body; treatment does not help get rid of them, but only reduces the activity of pathogens.
Disadvantages of antibiotics in gynecology for inflammation:
- candidiasis appears;
- after antibiotics, digestive problems may occur;
- the activity of the immune system weakens.
When treating an infectious or inflammatory pathology with antibacterial drugs, beneficial bacteria in the body die en masse, which occurs due to the effect of the drug on the body as a whole. It kills both harmful and beneficial microorganisms, which can cause certain consequences.
It will take time to restore the natural microflora. To do this, several medications are prescribed at once that can correct the situation.
Let's see what types of antibiotics in gynecology help against the inflammatory process?
Nuances of pathology
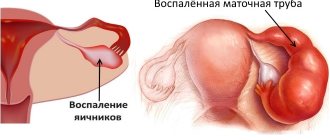
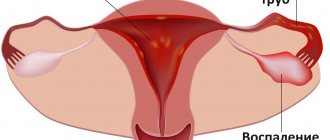
Inflammation of the uterine appendages, which occurs in the acute stage, is accompanied by symptoms:
- pain in the lower segment of the peritoneum,
- discomfort during intimacy,
- unusual discharge from the genital tract that has a yellowish color and an unpleasant odor,
- increase in body temperature,
- general malaise,
- menstrual irregularities.
If such signs occur, it is important not to miss the moment and get examined in time. Based on laboratory diagnostics, the cause of poor health is established, which is most often a sexually acquired disease.
If you ignore the signs of the inflammatory process, then after 2-3 weeks their intensity will begin to decline. A woman may mistakenly assume that recovery has occurred.
However, the causative agent of the pathology remained in the body. The chronic course of adnexitis is accompanied by a less pronounced clinical picture with periodic exacerbations.
At this stage, the following changes may occur in a woman’s body:
- dysfunction of the gonads,
- imbalance of hormones synthesized by the ovaries,
- formation of adhesive process,
- spread of the pathogen to nearby organs,
- penetration of infection into the lymph flow and damage to systems not related to reproductive function,
- cervical deformity,
- decreased fertility.
Types of antibiotics prescribed
To treat the infection, medications of different release forms are used. A doctor may prescribe to a woman: tablets, suppositories, solutions for subcutaneous or intramuscular injections, that is, injections.
In tablet form, the drugs are taken orally and come with some risks. Having penetrated the stomach, they have a detrimental effect on beneficial microorganisms and cause the appearance of dysbacteriosis and other digestive disorders.
Injections are the most effective and are used mainly in hospital settings. Various injections enhance the effect of antibacterial drugs. Help reduce their negative impact on the gastrointestinal organs.
The prescription of antibiotics in suppositories in gynecology is perceived as an auxiliary treatment. In fact, these drugs are noticeably effective, act locally on problems, and minimize the risks associated with such treatment.
It should be noted that in gynecology, vaginal suppositories are used for women. Rectal suppositories are used to treat men.
Antibacterial suppositories
When it is necessary to deliver the active substance of an antibacterial drug directly to the site of the lesion, bypassing the digestive system, suppositories are used for vaginal administration. Antibiotics in the form of suppositories have a much faster effect; they have a bactericidal and anti-inflammatory effect.
We can highlight Hexicon, Polygynax and Terzhinan. Additionally, Diclofenac, Movalis and Indomethacin suppositories can be prescribed to relieve inflammation and relieve pain. For hormonal disorders, Ovestin suppositories are prescribed.
Classification of antibiotics and their features
In gynecology, a wide variety of antibiotics are used for inflammation and infections. The drugs used have a wide range of effects; such drugs are universal and are produced in the form of injections or tablets. There is also a new generation of antibiotics, they are less toxic and at the same time effective.
There are universal antibiotics in gynecology. The list of such drugs is given below:
- “Ampicillin” is a medicine familiar to many people, of semi-synthetic origin, often prescribed by doctors, but has a number of disadvantages.
- “Erythromycin” is a drug that is well tolerated by the body and is one of the macrolides that disrupts the bonds between molecules and causes the death of pathogenic microorganisms.
- Tetracycline is an inexpensive drug used to treat inflammatory and infectious diseases.
- Metronidazole is an antimicrobial and antiprotozoal medication that is available in several forms (injection solution, vaginal gel and tablets).
- “Cephalosporin” is produced in the form of an injection solution, has excellent tolerability, but is prescribed only if indicated. This is a very popular broad-spectrum antibiotic in gynecology.
List of medicines of the newest generation:
- "Cefamandole" - found in powder form for the preparation of an injection solution, used in the treatment of pathologies of the genitourinary system, infectious diseases of gynecological origin.
- "Rulid" - produced in the form of tablets, perfectly overcomes the barrier of the gastric mucosa. Used once every twelve hours, it is effective in combating many pathogenic microorganisms.
- "Amoxiclav" is an inexpensive and at the same time effective remedy with a wide range of influences. The composition contains amoxicillin and penicillin.
- Ceftazidime is a broad-spectrum drug and is a third-generation antibiotic. Its bactericidal effect is due to the destruction of the cell membrane. It is used in the treatment of severe inflammatory and infectious diseases.
- “Unidox Solutab” is one of the tracyclines; thanks to the action of the composition, it destroys the cell membranes of pathogenic microorganisms and reduces protein synthesis. Available in tablet form. These names of antibiotics in gynecology are known to many.
Also, inflamed reproductive organs can be treated with other drugs, in the form of suppositories. They are:
- With hexicon - they have an anti-inflammatory effect. They are used for prevention or as part of complex treatment. When using this class of suppositories, the likelihood of re-infection is minimized.
- With bactodin - they have a bactericidal effect, creating an unfavorable environment in the vagina for the reproduction and growth of pathogenic microflora.
- With metronidazole – used for the treatment of infectious pathologies caused by Trichomonas.
It must be remembered that the doctor can make antibacterial treatment more effective through suppositories, the effect of which reduces other pathogenic symptoms of the disease. It also reduces the manifestation of pain and reduces temperature.
Acute inflammation of the appendages: how to relieve pain
Anti-inflammatory drugs should be used especially carefully and in no case should you choose them for yourself, since the most important thing here is the duration of the course and the dose, and all this can only be calculated by a specialist. The main symptoms of inflammation of the appendages - primarily pain - are eliminated with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. It must be borne in mind that they cannot treat or cure anything, and if the pain has subsided, this does not mean that the treatment can be completed and the disease has already been defeated. Only acute inflammation is relieved, only pain is relieved. The rest of the infection in the body is alive and well.
NSAIDs are used in the form of injections or tablets, and suppositories are often used. The doctor will always select the necessary medications, and he will also determine the dose and duration of the course. It is impossible to treat acute inflammation of the appendages on your own. Drugs such as Nurofen, Ibuklin, Diclofenac, Ibuprofen and all the others are very capable of ruining your health for the rest of your life. Next, all these drugs that relieve the main symptoms of inflammation of the appendages in women will be discussed, and treatment with these drugs will be discussed in more detail. These are effective anti-inflammatory drugs, but taking them is fraught with negative side effects, and the most dangerous thing is an overdose.
Regenerative treatment
In gynecology, restoration of microflora is carried out after completion of a treatment course with antibiotics. Such procedures are aimed at eliminating unpleasant symptoms, vaginal dysbiosis and gastrointestinal problems.
Restorative treatment is carried out through various means; to restore the vaginal microflora, you can use the following suppositories: “Gynoflor”, “Vagilak”, “Ecofemi”. These products contain lactobacilli, which help restore flora and eliminate painful symptoms.
You can also use the following medications:
- "Genekotex" - produces an anti-inflammatory effect and is a contraceptive medication.
- "Acilact" - enhance local immune activity.
- "Genferon" - has a noticeable anti-inflammatory effect, can be part of a combination treatment for diseases of urological and gynecological types.
List of drugs for restoring intestinal microflora:
- “Smecta” is one of the sorbents that perfectly absorbs toxins remaining in the patient’s body after the death of pathogenic microflora.
- “Bifidumbacterin” - it contains beneficial bacteria that help deal with digestive problems.
- "Hilak-Forte" is a drug that creates a favorable environment in the stomach and intestines for the reproduction and growth of beneficial microorganisms.
To restore the microflora after treatment, you will also need to follow a diet. It is advisable to adhere to some principles in the diet:
- include fermented milk products in the menu;
- eat fresh vegetables and fruits;
- drink mineral water and fresh juices.
For reference: thanks to proper nutrition, the functioning of the immune system will be improved, and the body will recover faster from illness and toxic treatment.
You will also have to: take vitamins, walk in the fresh air, play sports, avoid nervous shock and stress.
In gynecology, antibacterial treatment is required for many pathologies. However, we must not forget that with such therapy some consequences may occur. That is why it is advisable not to choose antibiotics yourself, but to entrust this to your doctor.
It would be appropriate to understand which gynecological antibiotics are used during pregnancy. After all, inflammatory processes during this period befall women quite often.
Inflammation of the fallopian tubes and ovaries during pregnancy
Carrying a child is a contraindication to the use of tetracyclines, since such drugs easily overcome the barrier of the placenta and accumulate in the tissues of the embryo or developed fetus. Because of this, problems may arise during the formation of the child's skeleton.
During pregnancy, a number of macrolides are also contraindicated; for example, clinical studies have proven that Clarithromycin is harmful to a woman’s body. The patient will receive less harm from the influence of macrolides when treated with drugs such as Josamycin, Spiramycin, and Erythromycin.
If the inflammation of the appendages is severe and the woman is pregnant, she may be prescribed Azithromycin.
Any fluoroquinolones are not prescribed at all when carrying a child.
Storage conditions
Any medications should be stored
in a dark place out of reach of children. The instructions for use for each product additionally indicate the storage temperature - some of them should be placed in the refrigerator. In most cases, to prevent spoilage of drugs, they should be placed in a place whose temperature does not exceed 25 degrees.
If the storage conditions are not met, it is undesirable to use the product. It can cause harm to the body or, on the contrary, have no effect. The expiration date must also be taken into account - after it expires, the medication should be thrown away.
Contraindications to the use of antibiotics
If an overdose of antibiotics occurs, the side effects are more pronounced. Treatment in this case requires symptomatic treatment.
In case of an overdose of macrolide drugs, changes in heart rhythm, stool disturbances, and nausea occur, but such symptoms are usually minor and do not threaten the patient’s life.
The same applies to fluoroquinolones. Side effects can be eliminated at home on your own.
Epilepsy attacks during drug overdose are very rare. However, exceeding the amount of antibiotic can negatively affect the condition of the joints, heart and liver.
We list contraindications by group of antibiotics.
Tetracyclines: renal failure, hypersensitivity to the composition, patient age under eight years, lactation, leukopenia, pregnancy.
Macrolides: breastfeeding and pregnancy.
Secondary quinolones: deficiency of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, allergy to drug components, breastfeeding, childhood, pregnancy.