High-quality diagnostics and new treatment methods allow 50% of couples with infertility to become parents. Both men and women undergo tests for infertility, and with the help of modern medicine, a way to solve the problem is identified. With the modern level of medicine, anyone can take tests for infertility. Doctors will tell you in detail how much each procedure costs, what tests need to be taken, and will also identify female or male infertility with studies that include: blood and sperm tests, examination by a medical professional, and special procedures.
Infertility – is it worth fighting?
If a married couple has not conceived after a year of regular sexual activity without the use of contraceptives, it is necessary to contact a specialist for examination. This fact in itself does not mean that one of the spouses is infertile; doctors in this case talk about a temporary inability to conceive a child. In most cases, this problem is successfully solved. For this purpose, modern fertility clinics have been created, which practice well-proven methods of treating infertility.
Doctors distinguish between relative and absolute infertility. The first type includes cases in which it is possible to identify and eliminate the causes of disorders in the patient’s body. Absolute infertility refers to irreversible physiological changes in the reproductive system (anomalies in the development of the pelvic organs, traumatic injuries, surgical removal of the gonads).
Infertility is also divided into primary and secondary. In case of primary infertility, there is no history of pregnancy at all, although regular sexual activity occurs without any means or methods of contraception. They speak of a secondary pregnancy if there has been at least one pregnancy (regardless of how it ended: childbirth, abortion, miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy).
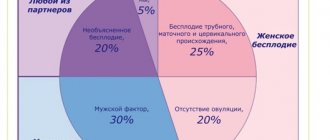
Contrary to popular belief, infertility affects both women and men equally. That is, the quantitative ratio of infertile patients of each sex is approximately the same. The position when one partner places the blame on the other is absolutely wrong. Firstly, it creates strong psychological pressure, which only aggravates the situation. Secondly, a solution to the problem is possible only if the spouses have full mutual support. Thirdly, there are often precedents when treatment is necessary for both partners.
When should you see a doctor?
A woman who wants to get pregnant should also think about visiting a gynecologist if she has the following signs::
- hyperprolactinemia (increased levels of prolactin in the blood, which causes menstrual irregularities);
- a sharp decrease in body weight;
- complete absence of menarche in a woman;
- excess weight;
- the hair in the genital area is located in an abnormal pattern (vertically directed, excessive, insufficient);
- underdevelopment of the mammary glands;
- history of spontaneous miscarriages and miscarriages;
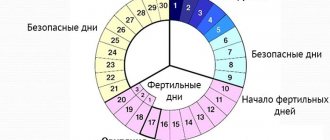
- lack of ovulation.
The above symptoms of infertility are quite common, so it is important to pay attention to them as early as possible.
Symptoms and causes of infertility
First, we need to make a reservation that, due to physiological differences, infertility is divided into male and female. Accordingly, the causes, diagnosis and treatment methods differ.
Female infertility is more multifaceted than male infertility. After all, a woman’s body must not only produce an egg, but also create conditions for conception and the normal course of pregnancy. Any, even minor, malfunction of the female reproductive organs can significantly complicate conception. Among the main causes and signs of infertility in women are:
- problems with ovulation;
- hormonal problems;
- ovarian dysfunction;
- damage to the fallopian tubes, adhesions;
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- hormonal imbalance;
- scars on the lining of the ovaries;
- cervical erosion;
- early menopause;
- disorders in the cervical canal;
- defects in the development and structure of the uterus;
- psychological reasons;
- endometriosis;
- unruptured follicle syndrome.
The most common causes include the following violations.
Obstruction or absence of fallopian tubes
It is in them that the meeting of the egg and sperm occurs, their fusion and the formation of an embryo, which then enters the uterus. Obstruction develops mainly due to the formation of adhesions (sticking together of the walls) of the pipes as a result of their inflammation. Rarely, adhesions can be caused by sterilization, in which the fallopian tubes are ligated or crossed. The absence of a tube may be due to its surgical removal, performed for vital indications (local purulent process, ectopic pregnancy).
Adhesions in the pelvic area
They occur after inflammatory processes, endometriosis, and surgical interventions. The adhesion can envelop the ovary or be localized between it and the tube, making it impossible for the egg to pass through.
Endometriosis
This is the name of a disease in which the mucous membrane of the uterus (endometrium) grows beyond its boundaries. Foci of growth are formed, and adhesions arise between them, interfering with the fertilization process.
Endocrine, also known as hormonal disorder
Endocrine disruption is observed in diseases of the ovaries, thyroid gland, pituitary gland, hypothalamus, adrenal glands, kidneys, and liver. It can be caused by metabolic disorders or severe mental stress or a shock situation.
Psychogenic infertility
Arises as a psychological reaction to not wanting pregnancy. A woman may consciously or unconsciously experience fear of childbirth or possible changes in appearance due to pregnancy. Sometimes the reason is the reluctance to conceive with this particular partner.
Immunological infertility
Occurs when there are antibodies to sperm in the female body, which interferes with the fertilization process. Under the influence of antibodies, sperm become inactive, making it difficult for them to pass through a woman’s body.
Complete examination for infertility... List of tests and tests for infertility for spouses.
Hormonal examination: (
LH, FSH, prolactin, estradiol, progesterone, testosterone, 17-OH progesterone, DHEA - sulfate, SHBG transport protein, sex hormone binding protein (SHBG, SHBG), ACAT, androstenedione, androstanediol glucuronide)
Study of the quantitative content of blood hormones. Hormones control the basic processes of the body’s vital activity at all stages of its development from the moment of inception. Using a hormone analysis, you can look at the functional state of the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, mammary glands, adrenal glands, ovaries, identify diseases in the fetus during pregnancy, find out the nature of infertility, and menstrual irregularities.
Tests for infections
: regular smear, PCR for latent infections, TORCH infections (T - toxoplasmosis O - other infections R - rubella (rubella) C - cytomegalovirus infection (cytomegalovirus) H - herpes (herpes simplex virus)).
Assessment of ovarian function and reserve - EFORT - test.
The essence of the extended EFORT test: measuring the physiological response of the ovaries to the introduction of follicle-stimulating hormone. A quick and accurate test of ovarian functional reserve.
Hysterosalpingography
- checking the patency of the fallopian tubes.
Extended hemostasiogram with lupus anticoagulant
. With false complex analysis. The doctor evaluates not so much each specific indicator separately, but rather the whole picture of blood coagulation. Lupus anticoagulant is an inhibitor of the blood anticoagulation system. Being present in the blood, it increases the coagulation activity of the hemostasis system, which adversely affects the process of implantation of the embryo, the course of the entire pregnancy, and the development of the fetus.
Analysis for antibodies (autoimmune antibodies), antibodies to phospholipids.
Autoimmune antibodies are formed when autoimmune disorders develop in the body. Autoimmune reactions are a pathological response of the human immune system to components of the body’s own tissues. They can manifest themselves in the production of antibodies to phospholipids, DNA fragments, thyroid factors, etc. In obstetric and gynecological practice, such disorders are considered within the framework of antiphospholipid syndrome. Autoantibodies cause an increase in blood coagulation, the development of microthrombosis in the placental vessels, implantation disorders, uteroplacental insufficiency, intrauterine growth retardation syndrome, and fetal death.
Immunogram and cytokine profile
. This is a blood test that examines the components of the immune system. It takes into account the number of cells (T and B lymphocytes, macrophages, neutrophils), their percentage and functional activity, as well as the “substances” that these cells produce - immunoglobulins (Ig) classes A, M, G, E, components of the system complement. Sometimes “pathological antibodies” are determined in the immunogram - antinuclear factor, rheumatoid factor, antibodies to phospholipids and others. A special immunological study - cytokine status allows for clinical and laboratory analysis of those regulatory systems that provide management and control over all aspects of the functioning of the immune system. Without performing this section of immunological diagnostics, examination of a patient with suspected and, especially, identified immunodeficiency cannot be considered complete and modern.
Test for antisperm antibodies in blood and cervical mucus
. Antisperm antibodies are found in cervical mucus and blood. Contact of antisperm antibodies with sperm leads to a decrease in their motility, ability to penetrate the mucus of the cervix, negatively affects capacitation (removal of the glycoprotein membrane from the sperm body, without which it is not capable of fertilization) and acrosomal reaction (ultrastructural and biochemical changes on the surface of the head ) sperm, on interaction with the egg.
Homocysteine test
. Homocysteine is a product of the metabolism of methionine, one of the 8 essential amino acids in the body. Normally it does not accumulate. It has a pronounced toxic effect on the cell. Circulating in the blood, it damages blood vessels, thereby increasing blood clotting and the formation of microthrombi in the vessels (one of the causes of miscarriage).
genes of the hemostasis system.
Research in recent years has shown that in patients with recurrent miscarriage, one or more genetic factors for thrombophilia are often detected.
Thrombophilia
is a tendency to develop thrombosis. It may be hereditary or non-hereditary. The presence of thrombophilia is associated with an increased risk of developing pregnancy complications (recurrent miscarriage, placental insufficiency, fetal growth restriction, late toxicosis (preeclampsia)).
Polymorphism of vascular tone genes
. Identification of predisposition to hypertensive conditions, placental function disorders, preeclampsia, myocardial infarction, microcirculation and vascular tone disorders. The block consists of 6 indicators: mutations of the genes of angiotensinogen, angiotensinogen receptor type 1 II, angiotensinogen receptor II type 2, angiotensin converting enzyme, aldosterone synthetase, alpha-adductin.
Laparoscopy
. To exclude endometriosis, accurately check tubal patency, diagnose unexplained infertility - combining diagnosis and treatment. It is better to do it in the first phase of the cycle. General anesthesia.
Causes and signs of infertility in men
In men, infertility is manifested by one single symptom - the inability to conceive. Unlike women, symptoms of male infertility practically do not appear. This fact gave rise to the myth that men suffer from infertility much less often than women. The key factors causing infertility in men are:
- sperm deficiency (impaired sperm motility and viability);
- a sharp decrease in their number;
- complicated movement of sperm along the vas deferens and their release out.
- The causes of male infertility can be:
- varicocele;
- congenital abnormalities of the reproductive system (hypospadias, absence or obstruction of the vas deferens);
- isolated disturbances in seminal fluid;
- infectious and inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system;
- surgical intervention (grooval hernia, hydrocele, bladder surgery, etc.);
- systemic diseases (liver cirrhosis, tuberculosis, diabetes, infectious mumps with complications of orchitis, chronic renal failure);
- sexual and ejaculatory disorders;
- psychogenic factors;
- necrozoospermia;
- obstructive azoospermia;
- endocrine (hormonal) disorders.
Additional reasons include: alcohol and nicotine abuse, exposure to radiation, and scrotal injury. Working in difficult and harmful professional conditions, for example, at too high or low temperatures, or in a toxic environment, has a negative impact on reproductive function. Separately, there are factors that can provoke a decrease in sperm count: stress, poor nutrition (lack of proteins and vitamins in the diet), chronic lack of sleep.
Classification of sperm pathologies
Regardless of what exactly caused infertility in a man, its mechanism can always be determined using a spermogram. The following sperm pathologies are distinguished:
- Azoospermia – sperm (ejaculate) does not contain sperm. It is divided into secretory and obstructive forms. In the secretory form, the testicles do not produce sperm; in the obstructive form, ejaculation is impaired due to obstruction of the vas deferens.
- Oligozoospermia – low number of sperm in the ejaculate (normally no less than 15 million/ml).
- Oligospermia – small sperm volume (norm – at least 1.5 ml).
- Anejaculation is the complete absence of sperm.
- Asthenozoospermia – sperm are not motile enough.
- Necrospermia - the ejaculate does not contain living sperm.
- Teratozoospermia is a disorder of the structure of sperm.
Infertility of unknown origin
Occurs in patients of both sexes. This is the name for a situation when, after a thorough diagnosis of the spouses, no causes of infertility are found. According to doctors, the couple is absolutely healthy, but conception does not occur. This diagnosis is explained by the fact that modern diagnostics are still not able to identify absolutely all the causes of pathology of the human reproductive system. Often, instead of an unclear genesis, another cause is mistakenly determined, and accordingly, measures to eliminate it do not bring the desired result.
Sometimes the cause of infertility of unknown origin is determined by the incompatibility of partners at the biological or immunological level. This is confirmed by situations where spouses were unable to conceive for many years, and after a divorce, each of them soon had children in new families.
Mary77
Firstly, in order to start taking some action, time must pass. For a young couple who is sexually active, this time is 6 months of active (at least 3-4 times a week) unprotected sexual relations. If sexual life is less active, then about a year should pass. In any case, in medicine it is customary to diagnose “infertility” only after a year of unsuccessful attempts.
QUOTE• The normal monthly fertility rate is 30%.• The monthly pregnancy rate for couples with unexplained infertility (UI) is 1.5-3%.• Within 3 years, 60% of couples diagnosed with UI for less than 3 years will achieve pregnancy without treatment.• When a diagnosis of NB persists for more than 3 years, the likelihood of pregnancy decreases by 24% each subsequent year.• A definitive diagnosis of NB requires the use of IVF technologies.
It is still advisable to start contacting doctors after 6 months of trying, as this allows you, first of all, to save time and get closer to the birth of the desired child.
So what will you have to go through? What examinations will need to be done under the watchful supervision of the attending physician?
The first complex includes partly what needs to be done before planning begins (even if all this has been done, the results are already outdated and will have to be repeated):
1. General examination by a gynecologist, examination of the cervix in the speculum, two-handed examination. History (when did you get sick, what cycle, when was your last period, etc.).
2. Testing for latent infections (TORCH complex), namely culture for ureaplasma, mycoplasma; antibodies to chlamydia, herpes virus, human papilloma virus, cytomegalovirus, toxoplasmosis, rubella virus (if you have not been sick before or have not been vaccinated, then you need to get vaccinated).
3. Vaginal smear for gonococcus and flora.
4. PAP test or Papa-Nicolau test for oncocytology of the cervix (not mandatory, has nothing to do with infertility, but useful for the prevention of cervical cancer).
5. Ultrasound of the pelvis with a transvaginal sensor three times:
-immediately after menstruation;
- periovulatory period (presumed ovulation);
-peak of the second phase (if the cycle is 28 days, then on days 20-23).
6. Hormones (etradiol, progesterone, FSH, LH, 17-OP, testosterone, dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), 17-ketosteroids, prolactin) twice or three times. Each laboratory has its own standards - they depend on the methods for determining hormones.
-at the beginning of the cycle 3-8 days;
- in the middle of the cycle;
-at the end of the cycle 21-25 days
(if there are deviations, endocrine infertility is suspected).
QUOTE 1) Follicular phase (on days 3-8 of MC) - mandatory: Prolactin; FSH/LH, Estradiol, Testosterone, DHEA, 17-OP, 17-KS; - additionally: Progesterone, TTT, total T3 and T4, free T3 and T4 2) Ovulation (on the 13-15th day of MC with a 28-day cycle, it is better to determine by the increase in basal temperature or ultrasound monitoring data): - mandatory: LH, Estradiol; - additionally: FSH, Prolactin, Testosterone, DHEA. 3) Luteal phase (on days 20-23 of the MC with a 28-day cycle): - mandatory: FSH, Progesterone; - additionally: LH, Prolactin, Testosterone, Estradiol.
Additional methods for assessing hormonal levels:
Sometimes determining the basal level of pituitary and ovarian hormones is not enough, since even the normal level of a particular hormone does not always provide the processes necessary for conception. Then other functional diagnostic tests come to the rescue:
· Endometrial biopsy is the most accurate method (in various variants - aspiration curettage, aspiration biopsy, scraping). Biopsy in nulliparous women should be performed only under strict indications due to its invasiveness. The degree of secretory transformation of the endometrium under the influence of progesterone is mainly assessed.
· Study of the distensibility of cervical mucus, assessment of the dilation of the external os of the cervix (“pupil symptom”), assessment of crystallization of saliva or cervical mucus (“fern symptom”) during the periovulatory period. The degree of mucus stretching can be assessed by the patient independently. Mini-microscopes are also now available for sale, with the help of which the “fern leaf” is assessed.
· Estimation of basal temperature (BT).
7. Examination by an andrologist or urologist, donation of sperm for spermogram analysis (for the husband, if the sperm is bad, a diagnosis of male infertility is made, further examination and treatment is carried out by a urologist-andrologist).
A little more about the standards for spermogram, the criteria of the World Health Organization (WHO).
QUOTE Number of sperm - 20 million/ml or more (if less - oligospermia) Actively motile - 25% or more (if less - asthenozoospermia) Morphology - 50% normal sperm or more (if less - teratozoospermia) Agglutination - should not be Volume ejaculate - 2 ml or more Acidity - from 7.2 to 7.8 pH Leukocytes - less than 1 million/ml (if more - pyospermia)
If there are no sperm in the semen, it is called azoospermia. If there is no ejaculate at all - aspermia.
Further, there are differences in the survey depending on the results of the first set of studies:
1. If the cycle is regular, hormones are normal, all tests of the first complex are normal, then the following is done:
· Postcoital test (after sexual intercourse, a few hours later, cervical mucus is taken, and if the sperm there are alive and moving, then the test is considered positive; if the sperm are dead, the test is negative, based on which a diagnosis of immunological infertility is made (artificial insemination is recommended).
· If the postcoital test is positive, hysterosalpingography (HSG) is performed. It is performed on the 6-7th day of the cycle, a contrast agent is injected into the uterus, an image or ultrasound (USGHA) is taken, which shows whether the substance has passed through the tubes into the abdominal cavity or not. If both tubes are obstructed, a diagnosis of tuboperitoneal infertility is made (IVF is recommended).
· If the tubes are passable and the postcoital test is positive, then diagnostic operations such as hysteroscopy, fertiloscopy or laparoscopy are performed. Using hysteroscopy, you can see pathologies of the uterus and endometrium. With the help of fertiloscopy and laparoscopy, it is possible to diagnose tubal patency, adhesions, and inflammatory processes. And with the help of laparoscopy, various deficiencies can also be surgically eliminated.
2. If the cycle is NOT regular and/or there are any abnormalities in hormones.
· If prolactin levels are normal, tests for thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) are additionally prescribed, which can suppress ovulation and disrupt the cycle (if TSH levels are elevated, hyperthyroidism is diagnosed and treated, and ovulation then normalizes)
· If prolactin levels are elevated, a skull x-ray or CT scan is done to look for a pituitary tumor. (If there is no pathology on the X-ray, then a diagnosis of functional hyperprolactinemia is made and treated with Parlodel, bromocretin or Dostinex.
· If the level of testosterone, 17-OP, 17-CS or DHEA is increased, do a test with dexamethasone, if when taking dexamethasone the level of these hormones decreases by 75%, then the source of the increase in androgens is the adrenal gland (diagnosis - adrenal hyperandrogenism, treated with dexamethasone or metipred) . If the decrease occurs by only 25%, then a diagnosis of polycystic ovarian disease is made (treated by ovulation stimulation or ovarian resection). If there is no reduction in androgens while taking dexamethasone, a CT scan is done to look for an adrenal tumor.
· If the level of estradiol is low, estrogen drugs progynova, divigel, estrogel, microfollin are prescribed.
· If progesterone levels are low, utrozhestan, duphaston, and progesterone injections are prescribed.
If none of the studies carried out confirmed any abnormalities, or all identified abnormalities were eliminated, but pregnancy did not occur within 6 months after this, then in-depth diagnostics are carried out in the following areas:
1. By immunological factors (exclusion of immunological infertility)
· Determination of antisperm antibodies using the immunoenzyme method in the blood of both spouses (in men, also in the sperm itself).
· MAR test. A test that determines the percentage of sperm associated with antibodies (direct MAR test). The test is an internationally recognized standard for diagnosing immunological infertility. The test has high specificity, but not always high sensitivity.
· Tests can also be done: a) Immunobead test, which is an analogue of the MAR test and b) latex agglutination test - essentially determine the same thing as the previous ones.
· Tests for the diagnosis of immune status and hemostasis (exclusion of infertility associated with the non-survival of the embryo, as well as miscarriage) - Study of venous blood for lupus anticoagulant (LA)
—Hemostasiogram
— Immunogram — Blood test for antiphospholipid antibodies.
It is treated comprehensively, Wobenzym, then blood thinning drugs - fraxiparin, aspirin, etc. plus dexamethasone or metipred.
2. By genetic factors (excluding genetic infertility)
· For a woman: — Karyotype study and determination of the frequency of spontaneous chromosomal aberrations. —In case of stopping the development of the embryo (frozen pregnancy), a cytogenetic study of the fetus.
· For men: — Karyotype study and determination of the frequency of spontaneous chromosomal aberrations. —Study of microdeletions of the AZF locus on the Y chromosome. Allows us to identify one of the most common genetic causes of male infertility. —Study of the most common mutations in the cystic fibrosis gene. More than 50% of men with congenital absence of the vas deferens have mutations in the cystic fibrosis gene. Identification of such genetic disorders in a man will allow an adequate program to solve the problem of infertility and the doctor to adjust a set of measures for pregnancy management to prevent the birth of a child with cystic fibrosis (cystic fibrosis).
Infertility diagnostics, examinations and tests
As with any other disorder, high-quality diagnosis of male and female infertility is the key to successful treatment. It is extremely important that the procedure for diagnosing infertility is carried out on both partners. First, you need to do blood tests for hormones, tests to detect infections, and an ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
Examinations for infertility in women
The following methods are used to diagnose infertility in women:
- A gynecological examination under ultrasound control is the first stage of examining a woman, allowing her to assess the size and establish the structural features of the uterus and ovaries, identify ovarian cysts, fibroids and other pathologies of the pelvic organs.
- Hysteroscopy is an examination used to more accurately examine the uterine cavity, making it possible to detect abnormalities that were not diagnosed during a routine examination and ultrasound.
- Hysterosalpingography is a method designed to determine the patency of the fallopian tubes; it is based on the introduction of a contrast agent into the uterus, after which a series of images is taken.
- A blood test for hormones is carried out to determine the function of the ovaries and endocrine system.
- Laparoscopy is both a diagnostic and therapeutic procedure. During laparoscopy, the doctor has the opportunity to see an enlarged, clear image of the pelvic organs on the screen. If the causes of infertility are discovered, the specialist can eliminate them directly during the procedure: remove ovarian cysts, adhesions, and foci of endometriosis.
- Basal temperature chart - compiled by the patient independently over 2-3 menstrual cycles, used to assess ovulation.
- Ultrasound monitoring of the process of follicle maturation and ovulation is prescribed at the discretion of the doctor as an additional examination.
Diagnosis of infertility in men
Just like a woman, a man must undergo general clinical tests, do a blood test for hormones, and undergo examinations aimed at detecting infection. An ultrasound of the scrotum and prostate gland is prescribed, during which they are examined visually.
In the process of diagnosing male infertility, the main point is to determine the fertility of sperm, that is, the ability to fertilize. The key analysis at this stage will be a spermogram. This is a complete detailed analysis of sperm, which examines its physical parameters, chemical and cellular composition. The examination allows you to find out the following characteristics:
- sperm concentration (must be more than 15 million per 1 ml);
- their mobility (over 40%);
- the number of normal forms of sperm (at least 4%);
- viability (more than 58%);
- ejaculate volume (1.5 ml or more);
- total number of sperm (39 million or more).
In addition to these indicators, be sure to pay attention to the color of the sperm, color, smell, acidity, and white blood cell content. The spermogram also determines the presence or absence of antisperm antibodies produced during the immunological form of infertility - MAR test.
To take a spermogram, the patient must adhere to several medical requirements. For two weeks before the test, you should not drink alcohol, take antibiotics, or visit a sauna or bathhouse. You need to abstain from sexual intercourse for 4-7 days.
Often, simultaneously with a spermogram, an analysis of sperm maturity (SVA test) is performed. The test determines the binding of sperm to hyaluronic acid, an important component of the environment surrounding the egg. This parameter is extremely important for fertilization. A mature sperm usually connects with hyaluronic acid with special receptors, while an immature one is not able to connect. Normally, sperm maturity should be 60% or higher, otherwise conception through natural means is impossible.
As an additional examination, the doctor may prescribe a testicular biopsy, which allows you to find out the presence of sperm and the condition of the tissues. This procedure can also be used for therapeutic purposes.
Features of visiting a doctor
If a married couple dreams of having a child, they should visit a fertility specialist together. There are several nuances of preparing for the visit:
- abstain from sexual intercourse for 1-2 days;
- a woman should not douche or use tampons 2-3 days before the appointment;
- The time of the visit should not coincide with menstruation;
- you need to observe personal hygiene measures (take a shower, put on fresh underwear);
- take medical histories and results of previous tests and examinations;
- a woman needs to be prepared for an examination in a gynecological chair.
The doctor of both spouses will be interested in past diseases (including those that are sexually transmitted), possible operations in the pelvic area, the use of additional lubricants and contraceptives during sexual intercourse, the frequency and duration of sexual intercourse; current health. The doctor will ask the woman about the duration of the menstrual cycle, the nature of the discharge during menstruation (if any, you need to take a menstruation calendar to the appointment), the presence of painful sensations before and during menstruation, as well as about previous pregnancies, miscarriages, abortions.
The questions asked during the first and subsequent appointments must be answered frankly and in detail. They will help establish a diagnosis, even if we are talking about problems in the digestive tract, changes in weight, discomfort during sex. An experienced doctor knows how to use any information for therapeutic purposes.
The following factors indicate the need for tests for infertility:
- the man is unable to ejaculate;
- the woman has an irregular menstrual cycle or does not ovulate;
- if the spouses are over 35 years old.
Which doctors treat infertility?
The field of medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of infertility is called reproductive medicine. Treatment of men is carried out by andrologists, women – by gynecologists. Also involved in the treatment process are:
- embryologists – determine the fertilization method
- endocrinologists – study hormonal levels;
- hematologists – study blood counts;
- immunologists - I find out immune factors;
- ultrasound diagnostic doctors;
- geneticists - perform early diagnosis of chromosomal disorders.
One of the key factors for successful treatment will always be the qualifications of the attending physician. A true professional does not stop his education throughout his entire work experience, follows new techniques, and strives to use new technologies. Pregnancy and the birth of a child is a responsible step, so you should not skimp on the services of competent doctors. The specialists of JSC “Medicine” have dedicated themselves to the fight against infertility and have already helped many families find family happiness.
Taking an anamnesis is the first stage of diagnosing infertility
Consulting a gynecologist is very important at the beginning of an examination for infertility. It allows the doctor to assess the overall picture of the problem and identify possible causes of infertility.
When assessing the gynecological health of the patient, the doctor asks her about the following points:
- Symptoms that concern you (general health, duration of absence of pregnancy, pain “before” and “during” menstruation, sudden weight loss or weight gain, discharge from the breast and vagina).
- Family history (presence of gynecological pathologies in the mother, relatives, age, Rh factor and health of the husband, bad habits).
- Medical history (surgical interventions, infections that the woman had previously suffered from, injuries, gynecological and other diseases).
- Menstrual function (age of first menarche, regularity, duration, pain of menstruation, amount of discharge).
- Sexual function (onset of sexual activity, methods of contraception used, regularity of sexual intercourse, number of marriages and partners, libido level, presence of orgasm, discomfort during sex).
- Fertility (number of pregnancies and living children, spontaneous and induced abortions, course of previous pregnancies, complications during childbirth).
- Results of examinations and treatments that were carried out previously.
Treatment methods for male and female infertility
Infertility treatment tactics are determined by a fertility specialist based on the patient’s medical history and the results of a comprehensive diagnosis. Treatment methods are divided into traditional (medicinal, surgical) and assisted reproductive technologies (ART). It should be understood that in the process of treating even one of the partners, the second partner also takes a direct part. Therefore, the methods of treating female and male infertility described below are relevant for both spouses.
Get tested for infertility
So, you decided to take tests for infertility and received the results. Test results are valuable information that helps doctors prescribe adequate treatment for an infertile couple or recommend effective methods of artificial insemination.
If you want to undergo an examination, but do not know where to get tested and start infertility treatment, contact the clinic of Professor V.M. Zdanovsky. Our medical centers have our own modern laboratory. It allows you to do all the necessary research at the highest level in a short time. We never prescribe unnecessary tests; we employ honest specialists who are responsible for each of their patients.
source
Treatment of female infertility
The treatment method is determined by the cause of the pathology. Drug treatment is used:
- for endocrine infertility, it is based on taking medications containing hormones (urinary or recombinant gonadotropins, Clomid);
- infertility caused by infectious diseases (antibiotic therapy: metrogil, metronidazole, ofloxacin, ciprofloxacin and other drugs);
- immunological infertility (antihistamines and corticosteroids are prescribed).
Surgical treatment methods are effective for pathologies of the fallopian tubes and uterus. We are talking about minimally invasive operations that cause minimal harm to the patient. They are carried out in a hospital setting, but the rehabilitation period is short – 3-5 days. Surgical methods include laparoscopy and hysteroscopy.
Do not forget about such an important factor as the psychological state. According to statistics, about 30% of infertility problems are caused by psychological factors affecting the patient - stress, shock, etc. Psychologists and psychotherapists successfully combat this problem.
How is diagnostic hysteroscopy performed?
Diagnostic hysteroscopy can be used even in the absence of any changes visible on ultrasound. Thus, this study is carried out in the case of ineffective IVF programs with the transfer of good quality embryos and with difficulties in the process of embryo transfer in the past. Identifying the cause of such a difficulty and possibly eliminating it significantly increases the chances of IVF success.
If there is no need for significant manipulations in the uterine cavity, the examination (so-called office historoscopy) can be performed on an outpatient basis without anesthesia.
Modern office hysteroscopes are not inferior in quality of visualization to their “larger” counterparts, and in experienced hands the need for hysteroscopy under anesthesia is minimized, since most diagnostic interventions can be performed using a small-diameter hysteroscope.
Assisted reproductive technologies in women
If traditional treatment methods are ineffective, then ART is resorted to. There are many reproductive technologies:
- planned sexual intercourse;
- artificial intrauterine insemination;
- in vitro fertilization (IVF);
- oocyte donation;
- sperm injection into the egg (ICSI);
- surrogacy.
Intrauterine insemination is based on the introduction of sperm into the uterus artificially, using a catheter. Then everything happens naturally: sperm move towards the egg through the fallopian tubes and fertilization occurs. A prerequisite is the integrity of the fallopian tubes. Insemination is possible with both the partner’s sperm and the donor’s sperm. The method is effective in case of reduced fertility of the spouse (low number or absence of sperm, their weak mobility), as well as if a single healthy woman desires pregnancy.
In vitro fertilization (IVF) involves fertilizing an egg in a laboratory, obtaining embryos and transferring them to the uterus - this is a standard technology. It is possible to carry out IVF using a donor egg or donor sperm. The IVF method consists of several stages, quite extended over time. This is a complex but effective technique, it is performed by experienced reproductologists.
Functional tests
An examination for infertility also necessarily includes functional tests, which provide information about the nature of ovulation, the level of female hormones, and the presence of antisperm bodies.
The following are used:
- Cervical index. This study reflects the quality of cervical mucus, expressed in a scoring system. It assesses the level of estrogen saturation in the female body.
- Basal temperature. A curve is constructed based on daily measurements of the temperature in the anus. Its analysis gives a picture of the monthly cycle, confirms the presence or absence of ovulation and ovarian activity.
- Postcoital test. It is performed to study in more detail the activity of sperm in the mucus on the cervix.
Treatment of male infertility
When treating the secretory form of male infertility, if possible, they strive to eliminate the cause - varicocele, hydrocele, mumps, elimination of an unfavorable factor. After eliminating the cause, a course of therapy is carried out aimed at improving the spermatogenic function of the testicles - drug therapy comes into play. The course includes taking medications that stimulate blood supply to the scrotum, vitamin therapy, good nutrition and adherence to the regimen. Sometimes stimulating hormone therapy is required. Treatment of this form is a long and painstaking process, but not hopeless, so the patient should be patient.
Treatment of obstructive infertility in men is based on performing different types of biopsies - surgical extraction of mature sperm from the testicle and its appendages. For this purpose, special testicular biopsy techniques have been developed: using puncture (testicular tissue - TESA, appendage tissue - PESA) and small incisions (TESE and MESE, respectively). The rehabilitation period after a biopsy is 10-12 days, during which physical activity, sexual intercourse, and increased physical activity are contraindicated.
Special gynecological examination for suspected infertility
It is carried out using gynecological mirrors on a chair.
During the procedure, the doctor assesses the condition and degree of development of the genital organs (internal and external), the type of pubic hair, the appearance of discharge and its nature. The presence of abnormalities in the structure of the genital organs can be a symptom of infantilism and other congenital anomalies of the reproductive system. Excessive male pattern hair indicates hormonal problems. Discharge is a sign of an inflammatory or other pathological process in the vagina, which requires additional tests to identify the causative agent.
Cost of initial appointment and examinations
You need to understand that the total price of the initial appointment and examinations is formed as the diagnosis progresses. For some patients, a few tests are enough to determine the cause of the disease, while others may need additional examinations. Sometimes diagnosis takes a fairly long period, but the result - pregnancy - is worth the effort and money. You can get an approximate picture of the cost by reading the table of prices for services. But the best decision would be to make an appointment at JSC “Medicine” (academician Roitberg’s clinic), where, during a conversation with qualified doctors, the most accurate total cost will be determined.
Happy stories
Oksana
Dec 23 2020
I would like to express my gratitude to the MOON AND BACK to Diana Omarovna, Margarita Beniaminovna, Mikhail Yuryevich for our son, whose birth we are almost
Read the story
Natalia
29 Nov. 2020
I am 40, my husband is 49. We have a male factor, which makes it very difficult to get pregnant: most embryos stop on the 5th day of development. Except
Read the story
Elena
13 Nov. 2020
Our Moscow holidays were spent at the Fertimed clinic to fulfill our deepest desires. After endless attempts to get pregnant with...
Read the story
Marina
Oct 11 2020
It is impossible to express in words all the gratitude to our wizard - Torchinov Aslanbek Ruslanovich!!! Thanks to him, our baby was born on March 29, 2020.
Read the story
Irina
12 2020
I would like to express my deep gratitude to all the employees of this center for their professionalism. I would like to say a special HUGE THANK YOU to our doctor
Read the story
Orlova Olga Aleksandrovna and Chemodurov Dmitry Leonidovich
24 Jul. 2020
We would like to express our deep gratitude to all the doctors at this clinic! Thanks to you, we have two wonderful children growing up in our family - Zakhar (24.0
Read the story
Oksana
29 Jun 2020
Hello! We have an unusual story. My husband and I had our first children born in EB. Because We always wanted a very large family, so we decided not to stop..
Read the story
Evgeniya
May 16, 2020
My children are already 11 and 8 years old, but I periodically remember you with gratitude, dear Fertimed. Especially Anna Anatolyevna, Diana Omarovna, Margar
Read the story
Irina
17 Apr 2020
We owe our happy story to Anna Anatolyevna Smirnova! Thanks to her professionalism, our son was born. Anna Anatolyevna - they will notice
Read the story
Nikolai and Ekaterina
19 Feb 2020
Dear FertiMed, my wife and I want to sincerely thank the wonderful doctor, smart woman and great professional - Anna Anatolyevna Smirnova and sk
Read the story
Maria
10 Dec. 2019
Two years of unsuccessfully visiting doctors with my husband. We were advised to contact Zhordanidze Diana Omarovna in Fertimed. Wonderful doctor! Rezul
Read the story
Alipat
Oct 21 2019
Thanks to you, your clinic and Anna Anatolyevna Smirnova, I came to my cherished dream after 7 years of wandering from one doctor to another. Thankfully, I found out about
Read the story
Natalia
09 Oct 2019
I'll write a story too. 7 years of infertility, 3 IVF attempts. Out of desperation, I go and ask for a referral for laparoscopy. And in the intensive care unit I got into a conversation with a woman. TO
Read the story
Natalia
20 Feb 2019
Hello. I want to express my deep gratitude to your center. I got the impression of a close-knit team focused on results. Were treated by
Read the story
Andrey and Alexandra
14 Feb 2019
Many thanks from our entire large family to all the employees of the center for your work, for the smile on your face and faith in a positive result! Mihai
Read the story
Valentina
15 Jan 2019
My husband and I’s path to the happiness of being parents began in 2012 after the sounds of Mendelssohn’s wedding march died down. Like everyone else, we thought
Read the story
Catherine
May 16, 2019
After marriage, I couldn’t get pregnant at the age of 22; it turned out to be problems with the fallopian tubes. When I found out that I could never have anything on my own
Read the story
Olga
02 Mar 2019
I would like to express my deep gratitude to the FertiMed clinic, and especially to doctor Aslanbek Ruslanovich, for his good, caring attitude, and also for his
Read the story
Irina
23 Jun 2018
I would like to express my deep gratitude to the wonderful doctor of the FertiMed clinic, Aslanbek Ruslanovich Torchinov, for our long-awaited son. On hold
Read the story
Yuri
May 15, 2018
It will probably be an unusual review, since this is a review from a new father, and in general, I don’t really understand how I can express ours to you,
Read the story
Catherine
15 Dec. 2017
We first turned to FertiMed back in 2010, after 3 years of visiting doctors and undergoing all sorts of exotic tests. Unfortunately, the first
Read the story
Catherine
25 Sep. 2017
I got married at 22, my husband was 23, I never thought that there might be problems with conception, it turned out after I had appendicitis in childhood.
Read the story
Elena
May 23, 2017
My husband and I dreamed of having a child for 6 years. I have an adult daughter (20 years old) from my first marriage; my husband had no children. Passed several attempts at Eco in p.
Read the story
Elena
21 Feb 2017
My husband and I wanted more than anything to become parents, but time passed, wandering around to different doctors led to nothing, constant tests and treatment
Read the story
Nina and Peter
27 Sep. 2017
My husband looked at his spermogram as if it were a death sentence - not a single sperm count. And the reason is unclear. There was only one hope - for TEZU. It was explained to us that
Read the story
Faith
18 Jul 2016
I was ready to do anything to have a baby. By the age of 32, I had already undergone five operations on my ovaries and only one tiny piece remained from them. Nasty
Read the story
Maria
27 Jun 2016
I had two ectopics and no chance of having my baby. The irony was that my closest
Read the story
Valentina and Mikhail
Oct 14 2016
My husband and I flew from Kamchatka. They really wanted a second child. FertiMed was recommended by friends. They say that small and thin women like me have
Read the story
Sophia
27 Jul 2016
At FertiMed, at first they didn’t believe that I had 43 IVF attempts. There was clearly distrust and sympathy in the eyes of the staff - they say the woman went crazy.
Read the story
Alya
30 Sep. 2016
When I left my husband, with whom we had three children, no one, of course, could understand this, and no one wanted to. And even more no one could understand what m
Read the story
Valentina and Victor
01 Nov 2016
Our Dasha is growing up, at 1 year and 9 months she is a very smart girl, learning the alphabet on her own tablet (a real one, not a toy one)
Read the story
Christina
05 Apr 2016
I was 45 when I was ready for IVF. At the first meeting, the doctor at FertiMed said: there is no chance of having a child with my own eggs. At first there were sh
Read the story
Yana
13 2016
I am 29 years younger than my husband. He has three adult children, but I really wanted my child and ours together. Over the past few years, my husband has been very
Read the story
Anna
01 Mar 2016
I'm a happy mom! 5 years of standing with a birch tree, measuring basal temperature, tracking ovulation, hysteroscopy, laparoscopy (for my husband too), clostil
Read the story
Tests for infertility in women in our clinic are carried out as quickly as possible and are accompanied by the necessary consultations with specialists. Once the cause is identified, based on the test results obtained, a diagnosis is made and treatment is prescribed.
The examination has been completed. What to do next?
It is important to understand that if a diagnosis of infertility is established, pregnancy is possible. True, to achieve it, the help of an IVF clinic is required. Depending on the situation, treatment is prescribed (including using surgical techniques) or it is recommended to resort to assisted reproductive technologies.
Modern high-tech methods make it possible for even couples with severe forms of infertility to conceive a child. In this case, diagnostics should be carried out as quickly as possible in reproductive clinics with modern laboratories - for example, at ICLINIC. This will allow you to get reliable examination results and not waste time on visits to different medical institutions and waiting in line to see different doctors.
The desired “stripe” test for infertility is an achievable goal when contacting truly competent specialists. ICLINIC is a reproductive clinic focused on achieving the best possible results for all forms of infertility. Diagnosis and treatment are carried out by experienced, highly qualified specialists, focusing on modern WHO recommendations and using proven innovative technologies. More than 5 thousand children have already been born to previously infertile couples with the help of ICLINIC doctors.
A complete and reliable diagnosis of infertility is the most important step on the path to pregnancy.
What can lead to infertility in women?
The most common causes of female infertility:
- Any condition leading to obstruction of the fallopian tubes. Their lumen is most often closed by adhesions. And the cause of inflammation is often infections, including sexually transmitted diseases. This also includes the absence of fallopian tubes after operations or due to the individual anatomical characteristics of the woman.
- Persistent imbalance of sex hormones (so-called endocrine infertility), which is an obstacle to the successful maturation of the egg and timely ovulation. This can also be the reason for miscarriage after implantation of the fertilized egg.
- Dysfunction at the level of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus - special neuroendocrine formations in the brain. They are responsible for the production of hormones that regulate the functioning of all endocrine glands, including the ovaries.
- Hyperprolactinemia (increased prolactin levels), which inhibits the process of egg maturation and ovulation.
- Hyperandrogenemia – increased androgen levels. The body of a healthy woman also produces these male hormones, but in very small quantities. And their excessive secretion leads to disruption of the ovaries.
- Endometriosis. Critical for conception can be either damage to the body of the uterus or involvement of the appendages.
- Various changes in the uterus: tumors, adhesions, deformations, insufficient development, etc.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome.
- Immunological incompatibility.
In addition, sometimes an examination for infertility does not reliably reveal any abnormalities. In this case they speak of an inexplicable form.