Infertility according to the ICD is coded by a special alphanumeric code, which patients repeatedly see in medical documentation and have no idea about its meaning. It seems much easier to write the name of the disease than to search for the required code in a huge list of pathologies. After all, the register includes as many as 3 volumes! In fact, a unified classification makes it possible to redistribute financial resources at the state level and optimize the work of medical and scientific centers depending on the information received.
What is secondary infertility
Women who have previously been pregnant face difficulty conceiving. To establish a diagnosis, it does not matter whether the pregnancy ended in childbirth or not. Secondary involves difficulty in conceiving when a couple has a baby, but it is not possible to get pregnant or carry a subsequent one. Often a woman and a man have children from other partners, but conceiving together is not possible.
There is an international classification of diseases according to the 10th revision (ICD-10). Secondary infertility ICD 10 is information about a disease associated with the problem of conceiving a child. Secondary infertility ICD-10 implies a specific code that tells the specialist about the cause of the underlying ailment (from No. 97.1 to No. 97.9).
Causes
The causes of the disease are considered to be the age of the future parents, health, sperm motility in the man, the lifestyle of the spouses, their compatibility and the presence of infectious or other diseases.
In men
Secondary infertility in a man means difficulty conceiving a second and subsequent child. The main reasons are availability. Fertility is affected by prostatitis, urethritis, and epididymitis. If a man has undergone surgery on the scrotum, after surgery there is a high probability of complications, and as a result - problems with conception.
Whatever the cause of a man’s disease, only a qualified specialist can diagnose it. In 95% of cases, with timely consultation with a doctor, positive dynamics can be achieved.
Common factors of the disease in men are also:
- genital injuries;
- endocrine disorders/diseases;
- chemotherapy;
- taking hormonal medications;
- drinking alcohol, drugs, smoking;
- taking anabolic steroids (for building muscle mass);
- frequent visits to the bathhouse and/or sauna;
- eating disorders;
- chronic stress.
Among women
Secondary infertility in women occurs due to age. Many ladies give birth to their first child when they are young. The subsequent pregnancy is carefully planned, by which time the woman is well over 30.
Giving birth at this age is the norm today, but it should be understood that fertility declines at this age, which means it is much more difficult to conceive a baby. According to statistics, a quarter of all women after 35 years are diagnosed with secondary infertility (ICD-10 code).
There are also gynecological diseases. Often, difficulty in conceiving arises due to previous abortions. It happens that a woman does not have any obvious reasons, but pregnancy does not happen. In this case, it is necessary to exclude biological incompatibility with the partner.
The lifestyle followed by a girl planning a pregnancy is of great importance.
Causes of secondary infertility in women:
- ectopic pregnancy and miscarriages;
- polycystic ovary syndrome and uterine fibroids;
- complicated childbirth;
- external genital endometriosis;
- early menopause;
- bad habits;
- poor nutrition;
- emotional overload.
A common cause as well. Due to their instability, the menstrual cycle is disrupted, and catching ovulation, if it occurs, is much more difficult.
Symptomatic manifestations
This disease is a consequence of pathologies that are extremely difficult to notice. In women, symptoms are expressed more clearly than in men.
Among women
It is possible to notice signs of secondary infertility in most cases during a gynecological examination or during an examination.
The symptoms that a woman will certainly notice are:
- sore vagina;
- disorders;
- increased/decreased body weight;
- chronic diseases.
In men
A man may be completely unaware of the presence of diseases that lead to further difficulties with conception. Usually there are simply no symptoms. He can lead an active sex life, feel completely healthy, but not be able to conceive. As a rule, a man finds out about this after a long period of time, when his partner has undergone a full examination and is convinced that she is healthy. That is why experts recommend not to waste time and get both partners examined at once.
Methods of influence
There are quite a few methods of influencing the problem. Specialists use both medical and surgical methods. It all depends on the underlying disease.
Traditional treatment
Drug treatment of secondary infertility involves taking medications that are prescribed exclusively by a specialist.
The doctor prescribes hormonal, antiviral, immunological, antibacterial drugs or antibiotics - depends on the true cause of infertility. Treatment of secondary infertility in women involves the use of traditional methods:
- psychotherapy;
- drug treatment;
- hormone therapy;
- laparoscopy;
The first is the patient’s mood, his ridding of negative memories. It is important to make a woman or man forget about difficulties with conception, believe in their strength and a positive outcome.
Hormonal therapy involves stimulating egg maturation. This method is used if a woman is diagnosed with endocrine infertility.
Laparoscopy is performed on a woman with polycystic ovary syndrome or tubal obstruction.
The indication for in vitro fertilization is obstruction of the fallopian tubes or infertility of unknown origin. During the procedure, an egg is removed from the female body and artificially fertilized. Then they are placed for development in an incubator where special conditions are created. They are then transferred to the uterus.
Treatment with folk remedies
With secondary infertility, the couple turns to traditional medicine recipes. So, if a man has low-quality sperm, it is recommended to take mumiyo. 0.2 gr. You should mix it with freshly squeezed carrot or sea buckthorn juice. Take at 1:20 am in the morning on an empty stomach. It is advisable to use this remedy in a course of 25-28 days, then a month break.
Among the folk remedies, knotweed is effective. It can be purchased at any pharmacy and taken as an infusion. It is extremely simple to prepare; you need to mix the knotweed with boiling water in the proportion of 1 cup of herb per 1 liter of water.
An excellent solution would be field wormwood. This plant is very beneficial for women's health. To prepare a decoction, you need to pour 200 ml of hot water into a tablespoon of dry herbs. Leave for three hours, then bring to a boil and strain. Drink the decoction two to three times a day, ½ cup.
Recipe: pour a tablespoon of herb with a glass of boiling water, place the container in a dark, warm place or wrap it in a towel and leave for two hours. It is recommended to use several times a day.
An excellent remedy is Adam's root: pour 2 teaspoons of the plant with hot water. Leave for two to three hours, then drink 4 times a day.
ICD code 10 male infertility
Male infertility should be treated strictly by pathogenetic methods.
Male infertility caused by hypogonadotropic hypogonadism
- Gonadotropins are prescribed:
- Chorionic gonadotrapine intramuscularly 1000-3000 units once every 5 days, 2 years
- +
- (after 3 months from the start of therapy)
- Menotropins intramuscularly 75-150 IU 3 times a week.
The dose of hCG is selected strictly individually, under the control of testosterone levels in the blood, which, during therapy, should always be within normal limits (13-33 nmol/l).
To stimulate spermatogenesis, menotropins (menopausal gonadotropin) are added no earlier than 3 months after the administration of hCG. Combination therapy with gonadotropins is carried out for at least two years.
Evaluation of effectiveness in relation to spermatogenesis is carried out no later than 6 months from the start of combination therapy with gonadotropins.
Male infertility due to other reasons
For infectious lesions of the genital organs, antibiotic therapy is indicated, which is prescribed taking into account the sensitivity of the microflora.
- In the case of the immunological form of the pathology, it is possible to carry out immunosuppressive therapy with GCS
- For varicocele and obstructive form of the disease, surgical intervention is necessary.
- Most often, when treating this condition, errors occur due to the incorrect choice of medication.
- In treatment, especially idiopathic treatment, many methods of drug treatment that do not have rational pathophysiological prerequisites – the so-called “empirical therapy” – still continue to be used (often for quite a long time, simultaneously or sequentially).
- When evaluating appropriate therapeutic approaches, it is necessary to adhere to the principles of evidence-based medicine, which requires controlled studies.
- Unreasonable appointments include:
Evaluation of treatment effectiveness
Evaluation of the effectiveness of treatment is carried out no earlier than 3 months from the start of treatment based on spermogram analysis. The maximum duration of treatment should not be more than three years; If infertility persists for three years, the use of artificial insemination is necessary.
Complications and side effects of treatment
In rare cases, enlargement of the mammary glands, fluid and electrolyte retention, and the appearance of acne vulgaris are possible, which disappear after treatment.
Errors and unreasonable assignments
- gonadotropin therapy for the normogonadotropic form of the pathology;
- androgen therapy in the absence of androgen deficiency. Testosterone and its derivatives suppress the pituitary secretion of gonadotropins, thereby leading to inhibition of spermatogenesis. Azoospermia has been observed in a large percentage of patients receiving androgens;
- the use of selective estrogen receptor modulators (clomiphene, tamoxifen), which are drugs with a potential carcinogenic effect in the idiopathic form of the pathology;
- use of aromatase inhibitors. (testolactone), kallikrein, pentaxifylline, which are ineffective for this pathology;
- the use of dopamine receptor agonists (bromocriptine) in the idiopathic form of the pathology (effective only for infertility caused by hyperprolactinemia);
- the use of somatotropin, which leads to an increase in the volume of ejaculate, causes prostate hypertrophy, but does not affect the number and motility of sperm;
- the use of herbal medicines, the effectiveness of which has not been proven for this pathology.
Forecast
There are many reasons for difficulty conceiving, and the complexity of treatment depends on how serious it is. On average, it takes a year or more for women to become infertile.
However, even with the most positive result after treatment, you need to wait at least three months, or even six months, to start trying to conceive. Often the course of therapy is repeated more than once.
The International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision of Diseases, is a generally accepted structure that codes specific diseases and their types. ICD-10 consists of three volumes: 1 - main classification, 2 - instructions for use for users, 3 - alphabetical index to the classification.
This classification is intended more for doctors than for patients. For infertility, the ICD 10 code helps the doctor find out the diagnosis when he comes to examine the patient, without conducting a diagnosis or collecting an anamnesis.
Among women
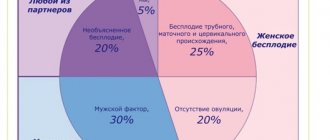
Infertility is a condition that affects approximately 1 in 10 couples. This diagnosis is given to couples who have been unsuccessful in trying to conceive for 1 year. In approximately 50%, the absence of a child is associated with female factors.
The most common causes of female infertility:
- problems with ovulation;
- damage to the fallopian tubes;
- age (as it increases, a woman’s fertility tends to decrease);
- problems with the implantation of the egg into the lining of the uterus.
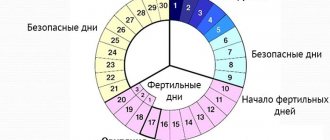
Infertility according to ICD-10, associated with lack of ovulation, has code N97.0. This type of inability to conceive a child can be associated with hormonal imbalance, bulimia, anorexia, benign formations and cysts on the ovaries, excess weight, problems with the thyroid gland, constant stress, alcohol and drug abuse. Also, lack of ovulation can be caused by extremely short menstrual cycles.
According to ICD-10, female infertility of tubal or uterine origin has codes N97.1 and N97.2. These types of inability for a woman to conceive can be caused by one of the following factors:
- inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs;
- endometriosis or fibroid formation;
- adhesions in the pelvis;
- chronic pathologies;
- previous ectopic (ectopic) pregnancy;
- birth defect.
The drug DES, which is given to women to prevent miscarriage or premature birth, can cause fertility problems in the unborn child.
Female infertility with ICD-10 code N97.3 means problems with mucus from the cervical canal. Abnormal cervical mucus can also cause prolonged failure to become pregnant. It prevents sperm from reaching the egg or makes it difficult for them to penetrate.
Infertility associated with male factors (N97.4), other forms (N 97.8) and an unspecified type (N97.9) are also distinguished. If infertility is primary, according to ICD-10 the patient will have code N97. It means that a woman who is sexually active has never been pregnant. If infertility is secondary, according to ICD-10 a code is assigned indicating the cause of the disease (from N97.1 to N97.9).
Diagnostics
In the first volume of the International Classification of Diseases I indicate the examination methods necessary to determine the cause of infertility. To evaluate a woman's reproductive system, doctors use the following tests:
- blood analysis;
- examination of the breast and pelvic area using ultrasound;
- a sample of cervical mucus to determine the presence or absence of ovulation;
- laparoscopy to detect adhesions or scar tissue, view the condition of the pelvic organs.
An X-ray examination is also performed, used in combination with dye. This makes it easier for doctors to determine whether there is an obstacle to sperm penetration in the fallopian tubes.
Infertility according to ICD
Infertility according to the ICD is coded by a special alphanumeric code, which patients repeatedly see in medical documentation and have no idea about its meaning.
It seems much easier to write the name of the disease than to search for the required code in a huge list of pathologies.
After all, the register includes as many as 3 volumes! In fact, a unified classification makes it possible to redistribute financial resources at the state level and optimize the work of medical and scientific centers depending on the information received.
What is ICD
The International Classification of Diseases is a worldwide standardized document - a list of pathologies that simplifies the collection of data on the causes of morbidity and mortality in the population. Thanks to a common way of encoding information for most states, it is easier for statisticians and epidemiologists to navigate changes in basic health indicators.
Important. The register allows you to organize the work of medical institutions in cities, manage the healthcare system in the country as a whole, and determine priority tasks for the most important research in the world.
Classification of diseases according to ICD-10
Since 1994, the version of the tenth revision, or ICD-10 for short, has been in force everywhere. Today, a new 11th version of the code is being developed, which should be released in a couple of years.
In the structure of the document, 22 groups of diseases are encrypted under Latin letters. Female infertility according to the ICD is listed under the general code N97. This pathology is characterized as the patient’s inability to conceive a child during regular sexual activity without contraception.
Female infertility according to ICD
In the international classification, the lack of conception is divided into subgroups that caused the pathology.
The disease is encrypted as follows:
- N97.0 ovulation disorders (hormonal imbalance, anovulation, endocrine changes, toxic effects);
- N97.1 tubal factors (inflammatory changes, adhesions, previous ectopic pregnancy);
- N97.2 pathologies of the uterus (structural anomalies, implantation defects);
- N97.3 cervical causes;
- N97.4 disorders associated with male factors (immunological incompatibility);
- N97.8 other types (endometriosis, fibroids);
- N97.9 unknown cause.
Primary infertility according to ICD-10 allows you to numerically express the number of couples who, with regular sexual activity, have never conceived. In women, there is underdevelopment of the structure of the genital organs, abnormal location of the uterus, and serious hormonal disorders, leading to a persistent lack of ovulation.
Secondary infertility code according to ICD-10 quantitatively reflects patients who have a history of pregnancy, regardless of the outcome: childbirth, miscarriage, abortion, ectopic location of the embryo. Typically, the occurrence of infertility is associated with frequent interventions in the uterine cavity, inflammatory diseases, the occurrence of tumors, bad habits, and metabolic disorders.
Male infertility according to ICD
Representatives of the stronger sex have infertility code ICD-N46. The code implies a violation of the quality of a man’s sperm, pathologies associated with ejaculation. The trigger for the inability to conceive a child is: inflammation, varicose veins of the genital apparatus, structural anomalies of the reproductive organs.
Necessity of application
The use of unified coding allows us to clarify the main health problems and combine efforts in the fight against the most common causes of mortality and morbidity.
In men
Male infertility in ICD-10 is a subclass of the department “Diseases of the male genital organs”; this problem is assigned code N46. Male infertility usually occurs due to poor sperm, insufficient sperm count or ejaculation problems. Sperm is considered bad if the life of the male reproductive cells is too short. Deviations from the norm are caused by one of the following factors:
- inflammation processes in the genital organs;
- varicose veins in the scrotum;
- abnormally developed testicles.
There are a huge number of different syndromes that can lead to the inability to conceive a child naturally. Male infertility in ICD-10 is divided into three parts: 1 - male infertility, 2 - infertile marriage, 3 - different syndromes.
In the last section, infertility problems are noted, only ICD-10 codes were not included in separate articles or considered within the framework of the corresponding disease. These include problems with conception in men.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of male infertility is made through a thorough history and physical examination of the patient. A man needs a semen analysis to determine quantity and quality, a blood test to detect infections or hormonal problems, and urethral swabs. You will also need to undergo a physical examination of the penis, scrotum and prostate gland.
Infertility according to ICD-10 also has treatment regimens. Treatment of the problem occurs using traditional methods, which include:
- taking medications to increase sperm production;
- use of antibacterial medications for the treatment of infectious pathologies;
- taking hormones to improve hormonal imbalances.
Unfortunately, infertility cannot be prevented, especially when the problem is related to genetics or disease. However, reducing alcohol abuse, smoking and maintaining a healthy lifestyle reduce the likelihood of infertility in men.
There are two main types of male and female infertility - primary infertility and secondary.
Primary infertility is a condition in which a woman cannot become pregnant without previously having such a condition. Secondary is a type of infertility in which it is impossible to get pregnant again.
Short description
Male infertility is the inability of a man to fertilize due to disorders of spermatogenesis, erection or ejaculation. 1 ml of ejaculate normally contains about 60 million sperm. In the female genital tract they retain the ability to fertilize for up to 6 days. About 200 of them reach the funnel of the fallopian tube, where the sperm meets the egg. Spermatozoa that do not participate in fertilization are removed from the female genital tract or digested by phagocytes. When considering the problem of infertility as a whole, various disorders in men are classified as related to male and coital factors.
Female primary infertility – what is it?
Primary infertility according to ICD 10 is divided into several forms, each of which differs in its course and manifestations.
From a medical point of view, this diagnosis means the inability to conceive a child due to congenital or acquired pathologies of the reproductive system.
Similar pathologies are:
- Uterine fibroids;
- Cyst;
- Cervical erosion;
- Gynecological diseases of various etiologies.
There is another pathology that affects the inability to get pregnant - ovarian diseases. Due to their malfunction, the egg does not mature and, accordingly, conception does not occur. This condition may be accompanied by absence of menstruation or heavy and prolonged menstrual flow.
A diagnosis of primary infertility according to ICD 10 may mean the presence of consequences of abortion or other methods of terminating a previous pregnancy. After an artificial or natural abortion, a woman’s hormonal levels are disrupted, which is an obstacle to the successful conception of a child.
Primary infertility according to ICD can be explained by the consequences of gynecological diseases, as well as injuries to the internal organs of the reproductive system. A woman can receive such injuries during an abortion.
Adhesions in the fallopian tubes are also a cause of lack of pregnancy. Since the path of advancement of the egg is closed, its fertilization does not occur.
Additional facts
Primary infertility is the impossibility of pregnancy associated with congenital pathology of the female body or acquired before the onset of sexual activity. The concepts of “infertility” and “childlessness” should be differentiated: in the first case we are talking about complete infertility (the absence of pregnancies in any form - uterine and ectopic), in the second - about the inability of a woman to carry a pregnancy to term and complete it with the birth of a viable fetus (this category includes cases of ectopic pregnancy, spontaneous miscarriages, stillbirths, etc.). According to researchers in 2010, in the world 1.5% of women aged 20 to 44 years suffer from primary infertility, and in Russia – 1.9% of women in the same age range. It is believed that primary disorders of reproductive function in women occur 1.5-2 times more often than secondary ones.
Main causes of pathology
Primary and secondary infertility have similar causes, so for these two forms of pathology the following list is applicable:
- The lack of ovulation may be due to hormonal imbalance. In this condition, a woman is alarmed by irregular menstrual cycles and heavy bleeding. Treatment of pathology is medication;
- Loss of quality characteristics of the egg can occur as a woman ages. For example, at the age of 40, female reproductive cells become abnormal. The problem of conception can be solved with the help of a donor egg and surrogacy;
- Primary infertility is a diagnosis that can be made based on endometriosis. A characteristic sign of this disease is the pathological growth of the endometrium outside the uterus. This condition is accompanied by severe menstrual pain. Elimination of the pathology is possible surgically.
- Obstruction of the fallopian tubes can occur due to inflammation or an STD;
- Due to polycystic ovary syndrome, the functioning of the hormonal system is disrupted, as a result of which the menstrual cycle and ovulation are delayed. Polycystic ovary syndrome may be accompanied by weight gain. Hair also grows quickly and skin problems appear. To treat this condition, medications are prescribed to stimulate ovulation.
Diagnostics
Patients who complain about the absence of pregnancies are examined according to an expanded scheme. At the first visit to the gynecologist, clinical and anamnestic data are clarified and an examination is performed. The general and gynecological anamnesis, the nature of menstrual function, and how long unsuccessful attempts to conceive have been noted are determined. An objective examination includes determining height, weight, BMI; assessment of hair growth and condition of the mammary glands; performing a rectal or bimanual examination. Already at this stage, sexual infantilism and anomalies in the structure of the genitals can be suspected or identified. The second stage of examination of women with primary infertility is carried out using laboratory and instrumental techniques. Functional diagnostic tests (colpocytology, examination of cervical mucus, analysis of the basal temperature chart) help assess the nature of the menstrual cycle. In addition, to study the functional state of the reproductive system, it is advisable to examine the hormonal status, the most important indicators of which are the levels of prolactin, gonadotropins (FSH and LH), estradiol, testosterone, cortisol, thyroid hormones (TSH, T3, T4), etc. It is advisable for all patients to examine a smear on the flora, according to indications, conduct a bacteriological study of discharge from the genital tract, PCR and ELISA. The information value of ultrasound of the pelvic organs can hardly be overestimated in the diagnosis of structural defects, post-inflammatory changes, and space-occupying formations of the uterus and ovaries. Folliculometry is used to track folliculogenesis and ovulation. In the diagnosis of primary uterine and tubal infertility, the role of ultrasound examination and hysterosalpingography is invaluable. Endovideosurgical examination (laparoscopy) is usually performed at the final stage of diagnosis. To establish the causes of infertility, it may be necessary to perform an ultrasound of the thyroid gland, Rg of the sella turcica, examination of the fundus, determination of visual fields, consultation with an endocrinologist, ophthalmologist, and genetics. In order to exclude the male factor of primary infertility, simultaneous examination of the sexual partner (spermogram, ultrasound of the scrotum, assessment of androgen status) is recommended. A postcoital test suggests the immunological nature of primary infertility.
Primary infertility - diagnosis for men
As stated earlier, this pathology can be diagnosed not only in women, but also in men. The reasons for its development will be the following:
- Urinary tract infection. During inflammation, antisperm antibodies are produced. The inflammatory process can be caused by pathogenic fungi, bacteria and viruses. The effectiveness of treatment depends on finding the source of the problem;
- Venous dilatation of the vas deferens or, in other words, varicocele. Primary or secondary infertility can be diagnosed due to overheating of the testicles, as well as due to an autoimmune reaction;
- Genetic abnormalities that affect the possibility of a surrogate mother carrying a child. Since the risk of transmitting diseases by heredity is high, it is recommended to use donor biomaterials for IVF;
- Male infertility can be explained by frequent illnesses, in particular, tuberculosis, bronchial asthma, diabetes mellitus, liver cirrhosis, gastrointestinal and pancreatic diseases. Hormonal disorders are also important;
- Bad habits are one of the main causes of male infertility, these include addiction to alcohol, smoking and drug use;
- Regular contact with chemical compounds, work in poor environmental conditions;
- Frequent stress, constant fatigue and poor nutrition - all this affects the production of male sex hormones.
Prevention of tubo-peritoneal infertility
Preventive measures include timely detection and complete treatment of diseases of the genital organs of an infectious and inflammatory nature. The dangers of sexually transmitted diseases are constantly discussed. Therefore, it is necessary to use condoms to protect against infections. It is recommended to exclude casual sexual relations. Try to plan your pregnancy, do not allow it to be artificially terminated. Be literate in sexual relations, adhere to the rules of intimate hygiene. Visit your gynecologist not only as needed, but also for prevention twice a year.
Effective treatment
Depending on the primary infertility according to the ICD, the most effective treatment will be selected. In modern medicine there are several methods that give good results, these are:
- Therapeutic treatment using medications, as well as chemotherapy and radiation therapy;
- Surgical intervention, for example, removal of hernias, correction and elimination of scrotal injury, etc.;
- IVF – this method of infertility treatment is safe and particularly effective.
What pathology diagnostic methods are applicable?
In order to make an accurate diagnosis, the patient must undergo a comprehensive examination. This is also necessary to identify the cause of primary infertility. The complex of diagnostic measures includes tests, as well as instrumental and laboratory studies.
Based on the test results obtained and the information collected about the patient’s life, the doctor draws conclusions regarding the diagnosis. If primary infertility is confirmed, then appropriate treatment is prescribed based on the cause of the identified pathology.
Thanks to modern medicine, this diagnosis is not a death sentence for childless couples. Depending on the situation, you can always find the right solution.