Types of proteinuria
Under some circumstances, a pregnant woman may have enough protein in her urine to be detected. The reason for this may be hypothermia, heavy physical or mental stress, or eating large amounts of meat. But its quantity will still not be as large as during inflammation, and the protein will disappear quite quickly after the action that provoked such a quantity ends.
If, however, there is still a suspicion of inflammation, then it is very important to promptly identify why protein appears in the urine, the consequences of which can have a very negative impact on both the condition of the body of the expectant mother herself and the development of her unborn baby.
Proteinuria during pregnancy can occur:
- Due to the occurrence of various types of urinary tract diseases. This may be an inflammatory process in the renal pelvis, bladder, ureter or urethra. At the same time, the quantitative amount of protein does not increase very significantly from the norm.
- Due to increased breakdown of tissue protein, which occurs with burns, tumors, frostbite, hemolytic disease (decomposition or gluing of red blood cells). In this case, the protein level is also not significantly increased.
- Due to the appearance of an inflammatory process in the kidney tissues. The cause may be pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, nephrosis in the kidneys, even minor effects on the kidneys of infectious factors or toxic substances, as well as damage to the blood vessels of the kidneys (nephropathy of pregnancy). At the same time, the quantitative level of protein in the urine is very high.
There are also cases when leukocytes and protein are detected together in the urine. It all depends on the quantitative number of protein and leukocytes in the urine. If their number is not increased or increased, but insignificantly, this can only indicate that the pregnant woman, as mentioned above, may have had stress, hypothermia or slight physical activity, and also that she probably did not comply with the test before taking the test. all hygiene rules. But if the quantitative number is still too high, this is the first signal that an inflammatory process in the genitourinary system has nevertheless formed and needs to be urgently eliminated.
Daily urine output
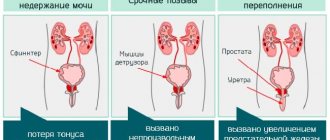
In a healthy middle-aged person, daily diuresis is 1.5-2 liters. For a woman, it is considered normal when the body removes up to 80% of the fluid received. About 2/3 is excreted during the day, and the remainder at night.
In pregnant women, the body adapts to the needs of the fetus, but diuresis should remain at the same levels as before this period. The volume of urine excreted by the body per day is affected by:
- surrounding air temperature, humidity;
- illnesses accompanied by fever;
- physical activity.
The minimum threshold for the normal volume of urine excreted is 0.5 l. Due to pregnancy, the body retains some of the fluid consumed. This is preceded by an increase in progesterone levels. The acceptable amount of excess fluid in a pregnant woman’s body is considered to be 1.5-2.7 liters. It is believed that there is no health hazard.
To restore normal water balance, pregnant women should enrich their diet with foods that have diuretic properties. These are watermelons, melons, buckwheat, berries and a little coffee.
Disturbances in diuresis during pregnancy can be detected by the volume of urine, the ratio of daytime to nighttime amounts, and the biochemical and physical parameters of the urine sample may change.
Deviations are classified as follows:
- oliguria – less than 0.5 l is excreted;
- polyuria – more than 2 liters are secreted;
- nocturia – nocturnal volume predominates;
- anuria – less than 0.05 l is excreted.
A situation where more fluid is excreted than the body received is considered negative. This risks dehydration. Impaired diuresis is accompanied by changes in the chemical composition of the biomaterial - the concentration of active substances changes, which leads to variations in the density and osmolarity of urine. In addition to classification by volume, diuresis is distinguished:
- water – polyuria due to decreased osmolarity;
- osmotic – polyuria against the background of increased osmolarity;
- antidiuresis - oliguria with increased osmolarity.
Pyelonephritis
This is an inflammatory process in the renal pelvis, which is caused by various microorganisms, such as gram-negative ecterobacteria, Escherichia coli, Proteus, Enterococcus, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Candida type fungi, which multiply due to the problematic outflow of urine in the urinary tract and the formation of infectious focus in the body. The source of infection is very often a purulent-inflammatory process, for example, skin furunculosis, carious teeth, gallbladder infection, sexually transmitted infection or respiratory tract infection.
Inflammation of the kidneys in a pregnant woman is most often caused by the growing uterus, which with its volume puts pressure on the internal organs, including the kidneys, as a result of which the passage of urine through the ureters is difficult. Also, the occurrence and exacerbation of pyelonephritis is observed due to hormonal changes that occur in the body of a pregnant woman during the entire prenatal period.
Treatment of pyelonephritis is usually carried out in a hospital. The doctor prescribes a course of antibiotics, uroantiseptics, ureteral catheterization, positional therapy, detoxification therapy and physical therapy. For general strengthening of the body, the doctor prescribes vitamins without fail.
Collection of urine for analysis
Pharmacy chains offer containers for collecting urine, but if this is not possible, a glass jar of about 2 liters with a tight lid will do. The container needs to be sterilized.
When collecting urine according to a schedule, thoroughly wash the genitals before each time. The first, morning process is carried out in the toilet. Further, according to the schedule, strictly all portions are collected in a container. The final collection takes place at a time similar to the first collection.
The container should be stored in a cool, dark place (bottom of the refrigerator). At the same time, you need to keep records that record the volume of fluid consumed per day.
Glomerulonephritis
This is a bilateral inflammation of the kidneys, predominantly affecting the glomeruli of the kidneys (small vessels). With this disease, the basic functions of the kidneys are disrupted: the formation of urine and the removal of toxic and unnecessary substances from the body. The incidence of glomerulonephritis among pregnant women is about 5-7%.
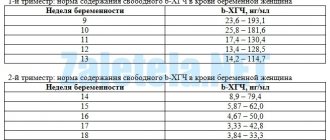
The causes of this disease are most often: chronic tonsillitis, meningococcus, pneumococcus, staphylococcus, viridans streptococcus, hepatitis B virus, salmonella, viruses of acute respiratory diseases. In pregnant women with glomerulonephritis, proteinuria is observed from 0.036 g/l to 30 g/l. Sometimes, especially in the second half of pregnancy, when acute glomerulonephritis appears, it can initially be mistaken for gestosis, since its symptoms are similar: severe swelling of the entire body and high blood pressure. But, as a rule, test results clarify the situation.
Treatment of glomerulonephritis during pregnancy is carried out exclusively under the supervision of doctors and includes: taking a course of antibiotics allowed during pregnancy, treating edema and hypertension, and maintaining kidney function until they are completely restored.
Diagnosis of gestosis:
- body weight control;
- general and biochemical blood tests;
- daily diuresis;
- blood pressure measurement;
- general and biochemical urine tests;
- blood clotting test;
- kidney examination;
- fundus examination;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys, Doppler ultrasound, consultation with a therapist, nephrologist, ophthalmologist and neurologist.
Treatment:
- use of drugs that lower blood pressure;
- intravenous therapy using drugs to improve blood circulation;
- a diet with limited salt and liquid (no more than 1 liter per day, including soups and fruits);
- prevention of placental insufficiency;
- taking sedatives and diuretic decoctions.
Indications for early delivery (caesarean section):
- severe forms of gestosis with no effect from treatment within 2-3 hours;
- nephropathy of moderate severity with no effect of treatment within 7-10 days;
- intrauterine growth retardation;
- preeclampsia and eclampsia, their complications.
Prevention of the development of gestosis should be carried out in pregnant women at risk for this disease, starting from the second trimester of pregnancy. The risk group includes women with obesity, hypertension, pathologies of the kidneys and other internal organs, and endocrine disorders.
It is necessary to understand that the development of such a serious disease as gestosis is easier to prevent than to treat, so follow the recommendations of your obstetrician-gynecologist for the sake of your own health and the health of your unborn baby.
Nephropathy
This is one of the manifestations of late toxicosis, which is based on dystrophic damage to the renal capillaries, which is usually accompanied by the development of severe nephrotic syndrome, eclampsia or arterial hypertension. This disease is observed in 2-3% of pregnant women.
Nephropathy in pregnant women is more often observed in the first trimester, in young women giving birth (under 20 years of age) and in women over 35 years of age. This is accompanied by proteinuria, severe edema, shortness of breath, hypertension and oliguria (decreased daily urine output). This disease is directly related to pregnancy, the appearance of which is promoted by heart disease, toxoplasmosis, obesity, and diabetes. Nephropathy is also caused by excessive hormonal influence of the placenta and sensitization of the body by placental protein.
Treatment of nephropathy is carried out only in a hospital with bed rest under the supervision of doctors. All drug treatment is aimed exclusively at eliminating the main manifestations of the disease. Sedatives and drugs that increase diuresis are also prescribed.
Also, after protein is detected in the urine during pregnancy and the disease is established, the pregnant woman is temporarily prescribed a diet, which includes limiting table salt to 1.5-2 g per day and liquid. The amount of proteins, carbohydrates and fats remains unchanged, but everything smoked and fried is excluded from the diet. For severe edema, fruit days (1.6 kg apples and 100 g sugar) and cottage cheese-sugar days (450 g cottage cheese and 150 g sugar) are recommended.
Carrying out analysis
The collected liquid must be delivered to laboratory technicians in a minimum period of time. You can mix the biomaterial, make a note of the daily volume obtained, then pour out 100 ml and take it to the laboratory assistants.
Specialists determine the reaction of the environment, the density of the liquid, the concentration of glucose, protein, as well as urobilin and ketone bodies. The liquid sediment is studied to obtain maximum data on the operation and condition of the urinary system.
When deviations in daily diuresis are identified, the reasons are determined. Late toxicosis becomes the most common, as well as kidney pathologies, endocrine diseases, cardiovascular system disorders, and electrolyte disorders. Each case requires separate diagnostic tactics. Considering that some conditions cast doubt on the ability to bear a fetus, you need to consult a doctor in time and carry out treatment when necessary.