George N. Papanicolaou – Father of Cytology
The content of the article
Cytology would never have arisen if not for one Greek doctor who one day decided to check whether... guinea pigs had their menstrual periods. The doctor who discovered this remarkable diagnostic method was George N. Papanicolaou, who later became a professor at Cornell Medical Center in New York and director of the Papanicolaou Cancer Research Institute in Miami.
The future scientist was born in 1883 on the Greek island of Euboea. Since childhood, Papanicolaou has been interested in natural sciences. In 1899 he began his medical studies at the University of Athens. However, he dreamed of studying natural science in Germany, which was categorically opposed by his father, who wanted his son to become a military doctor. It was this fact that became decisive in the fate of the student.
Inspired by Hertwig, a zoologist from Munich, the student became interested in the question of sex determination in embryos. He managed to get a job as an assistant in the pathology department of a New York hospital. There he planned to learn the secret of the origin of sex by practicing on experimental animals.
At the time, it was widely believed that guinea pigs did not menstruate. However, during Pap research, he discovered that this was not the case. Guinea pigs have menstruation, but it is short-lived and barely noticeable. At the same time, he discovered cyclically changing cells in the vaginal mucus of animals. The Greek doctor wondered if this could be related to processes occurring in the uterus and ovaries, and whether such cells exist in women.
So, George N. Papanicolaou, a man who had never shown much interest in gynecology (at least at first), made the first smears from a woman's vagina, of course not knowing what discovery he had made.
The doctor began his research on his wife, and later received permission to take several smears from patients in one of the maternity hospitals in New York. Several months later, after making countless swabs, he noticed cancer cells in a sample from a young and seemingly completely healthy woman.
Cervical cancer cells
The doctor shared his discovery with the medical community. A group of gynecologists began to conduct tests using all methods available at that time, but they were unable to confirm the results obtained by Papanicolaou. However, the Greek doctor was sure that he was not mistaken. And later the woman actually experienced cancerous changes in the cervix.
Today we know that cervical cancer can take years to develop before it becomes visible.
Causes of increased leukocytes in a smear
A high level of leukocytes in a smear most often indicates the development of an infectious disease
There are many reasons for an increase in the number of white blood cells. Among them, there are also physiological reasons - pregnancy or premenstrual condition. Basically, deviations from the norm are caused by the following infectious diseases (STIs):
- Gonorrhea
- Syphilis
- Chlamydia
- Mycoplasmosis
- Tuberculosis of the genital organs
- Granuloma inguinale
The cause of the deviation is viral infections - HIV, papillomaviruses, herpes, cytomegaloviruses. There are protozoal and fungal infections - trichomoniasis, candidiasis and actinomycetes. A strong increase in white cells may also indicate cancer.
In addition to PPIs, the cause of deviations from the norm can be diseases such as dysbiosis, colpitis, cevitis, endometritis, adnexitis, urethritis. As a rule, all these diseases have pronounced symptoms, but some pathogens can remain dormant and wait for the body’s immunity to fail. In this case, nothing bothers the woman.
Deviation from the norm can be caused by hormonal imbalance - pregnancy, menopause, puberty of a girl, miscarriage or abortion, as well as endocrine diseases.
Often the indicators are overestimated due to a decrease in local immunity. A woman constantly washes herself deeply, thereby disturbing the healthy microflora of the vagina. Leads a promiscuous sex life and does not take care of personal hygiene.
The cause may also be self-medication, uncontrolled use of antibiotics and douching. A deviation from the norm may be an allergic reaction to various vaginal creams, lubricants or contraceptives that are inserted into the vagina before sexual intercourse.
Useful video - Smears in gynecology:
Read: What vaginal discharge is considered normal: color, smell and consistency
Hypothermia or, conversely, overheating can also cause infection. Doctors often pay attention to mechanical damage caused by constant wearing of thongs. Such underwear can provoke inflammation of the reproductive system.
Accurate diagnosis of the disease is possible with additional tests. The doctor will determine the cause of the inflammation and prescribe treatment.
What is cytology
Cytology is an absolutely safe, painless test that takes very little time. The test is taken in the gynecological office during a routine visit.
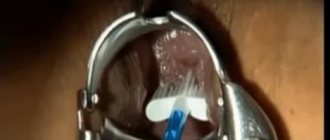
First, the patient sits on a chair. Then the doctor inserts a speculum and uses a special brush to remove cervical epithelial cells. The material thus obtained is placed on a glass slide, stained and viewed under a microscope.
Cytological examination of cervical epithelial cells
How often should you take a smear for cytological analysis?
There are no clear recommendations regarding how often Pap smears should be performed. Most gynecologists believe that it is better to have smears once a year, starting from the age of 18-20. In turn, a number of gynecologists recommend cytology every 3 years for all women aged 25 to 59 years. In some countries, doctors say that the test can be done even once every 5 years, provided that the previous cytological analysis and HPV test were good.
Cytological examination is carried out even for women who have not yet had sexual intercourse. This is important, for example, in the case of hereditary oncology. Yes, most cases of cervical cancer are caused by the human papillomavirus, which we mainly contract through sexual contact, so the risk of this cancer in a virgin is small, but it cannot be excluded. Therefore, the doctor should not refuse cytology to a patient - in a virgin, this can only be done with a smaller mirror.
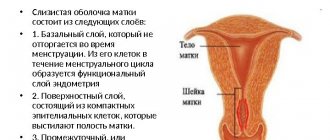
Vaginal and cervical smear
A general smear (bacterioscopy) makes it possible to determine the degree of sterility of the vagina. It can be used to detect thrush, cervicitis, vaginitis, vaginosis, as well as more serious infections that cause trichomoniasis and gonorrhea.
Various microorganisms, gram-positive or gram-negative, are capable of staining under the influence of substances. Under a microscope, a laboratory doctor counts the number of leukocytes and bacteria colored microorganisms. An important indicator is the shape of the bacteria and their size. A big problem for the female body are gram-negative microorganisms, which are the least sensitive to antibiotics.
Sometimes a gelatin-based nutrient medium is required to confirm the presence of pathogenic flora. The biomaterial is placed for reproduction and after some time (about two weeks) a more accurate result can be obtained; this method is called bacterial seeding. When testing for chlamydia, it takes at least 15 days to get confirmation.
Tank culture is used to determine the further treatment plan. As the microflora matures, it is tested for sensitivity to various drugs in order to provide targeted treatment. Experts examine unstained smears to detect active Trichomonas.
How is a smear taken for microscopy?
An analysis to determine genitourinary infections should be taken in the middle of the cycle to avoid red blood cells getting into the smear. Using a special brush, material is collected from the walls of the vagina, cervix and cervical area.
Before the test, you should refrain from douching and using antibacterial suppositories. In addition, 1-2 days before taking the test you should avoid sexual intercourse. 2-3 hours before the procedure, it is forbidden to urinate so as not to disturb the composition of the microflora.
What is the importance of early cancer cytology?
Cytological analysis can detect precancerous and neoplastic conditions of the cervix at a very early stage of development, before the patient develops any symptoms.
Cytology is also used to detect other changes in the cervix, including inflammation and erosions. In addition, a smear test will show the presence of human papillomavirus (HPV), which is a major factor in the development of cervical cancer, although its type can only be determined using a genetic test.
Liquid cytology is a modern diagnostic option
A new method of screening for cervical cancer is the so-called liquid-based cytology. The analysis differs from the traditional one in that the material is collected on a special liquid basis, and is not transferred or smeared onto the glass.
Liquid cytology
Liquid-based cytology has been proven to be more sensitive and accurate than classical cytology. First of all, the method allows you to obtain more cells of better quality for microscopic analysis. In addition, the collected material can be immediately used for other tests, such as HPV genetic testing or CINtec PLUS cytology.
Interpretation of cytology results
In the laboratory, the smear is assessed for the presence of non-epithelial cells - red blood cells, lymphocytes, inflammatory cells, necrotic cells and cytoplasmic debris. Pap smear results in European clinics are assessed according to the Bethesda system.
According to this classification, the cytological picture can be considered as:
- Normal is the norm.
- LSIL (low grade squamous intraepithelial lesion) - low grade intraepithelial dysplastic changes - equivalent to CIN I.
- HSIL (High Grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesion) – High grade intraepithelial dysplastic changes – equivalent to CIN II and CIN III.
Remember that only a gynecologist can interpret the results. But does an abnormal Pap test always mean cervical cancer? No! This result may also be due to inflammation or fungal infection.
To summarize, cytology is a key element in cancer prevention. The examination can detect precancerous and neoplastic conditions of the cervix at a very early stage of development. Although a Pap test is usually recommended every 3 years, most doctors recommend that women have it done once a year.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Preparation for the procedure
In approximately ten cases out of a hundred, the results of the cytology test are incorrect, which may be due to non-compliance with the rules of preparation for the procedure. In order to get the most reliable result, two days before the upcoming procedure you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- abstain from sexual intercourse;
- do not douche;
- do not use vaginal suppositories, intimate creams and lubricants, tampons soaked in medications;
- give up alcohol and smoking.
The woman should be informed that she should not overdo it with hygiene procedures (washing), as this changes the natural microflora of the vagina. In this case, the test results will be deliberately false.
A prerequisite for manipulation is a full bladder. Therefore, two or three hours before this you should refrain from urinating.