How is uterine curettage performed for endometriosis?
The most common cause of infertility in women is endometriosis.
There are no obvious clinical manifestations; the symptoms of the disease are similar to other pathologies of the reproductive system, including malignant ones. Cleaning the uterus for endometriosis can reduce the overgrown layer of the endometrium. It is performed only after preliminary drug therapy, if it does not have an effect and the pathology progresses.
After curettage, endometriosis may grow again
Endometriosis is a benign pathological process that affects the genitals and, in some cases, the abdominal organs.
The main cause of the disease is considered to be impaired regulation of immune and hormonal processes.
Endometriosis is a frequently diagnosed pathology in patients of reproductive age.
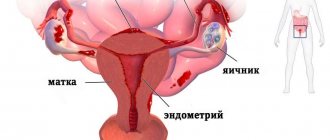
The uterus, as a hollow organ, consists of three layers lining its cavity: endometrium, myometrium and serous membrane.
When is uterine cleaning indicated?
Curettage for endometriosis is performed for the following indications:
- protracted course;
- cyst formation;
- soldering process in pipes;
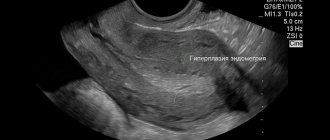
- development of endometrial hyperplasia;
- significant disruption of the menstrual cycle;
- pathological development of the endometrium.
Emergency cleansing is carried out when bleeding occurs in the middle of the cycle, it is profuse, leading to anemia and other complications. Intervention is also necessary if, against the background of hormonal effects using intrauterine releasing systems or contraceptives, there is no improvement in the situation within 6 months.
Indications
Curettage, also called curettage, is considered an absolute indication in the following cases:
- The presence of severe intermenstrual or menstrual bleeding due to a polyp or endometriosis. Also against the background of endometritis and other functional diseases of the uterine cavity. In such a situation, a complete curettage of the entire functional layer is carried out to replace it. The doctor constantly monitors such patients and, if necessary, prescribes additional drug therapy (it must be used with caution, relapses are possible).
- Hyperplasia of the cavity of the uterine structures against the background of endometriosis or polyp. Endometrial growth is not always benign. Hence the probable malignant degeneration. This is a condition when the immune system ceases to control cell division (proliferation) and allows them to spread uncontrollably. Polyps are generally considered precancerous conditions. For small sizes of such neoplasia, it is necessary to resort to curettage.
In the pathological processes under consideration, inflammation often begins. It quickly leads to the formation of special fibrin strands, the so-called synechiae or adhesions. With synechiae, pregnancy is impossible. Hence the need for their radical removal.
Polyps in the uterus and endometriosis do not exhaust the list of indications. It is possible to use this technique in a number of other cases:
- Early abortion.
- Curettage is also used to cleanse the uterine cavity of pathological remains of the fertilized egg during a miscarriage.
- The course of postpartum endometritis (inflammation of the uterine structures).
- In addition to this, there is also diagnostic curettage. It is performed to diagnose endometriosis or polyps in the uterus.
The list of indications is incomplete. It can be expanded at the discretion of the attending physician.
Features of the procedure
The first stage of treatment for pathology is taking hormone-containing drugs that cause medicated menopause. As a result, eggs are not formed and further growth of the endometrium stops.
Curettage of the uterus for endometriosis is done if hormonal therapy does not bring results within six months. Various methods are used. The most popular is laparoscopy - the most non-traumatic type of intervention, during which electrocoagulation or laser is used. This procedure is always performed under anesthesia, as it is very painful.
Surgical curettage is used if heavy bleeding is observed or an infiltrative form of pathology is diagnosed. A total hysterectomy is often performed to remove the ovaries to prevent recurrence of endometriosis.
Preparation
Before the endometrial curettage procedure, preparatory measures are necessary:
- Pelvic ultrasound and other ultrasound diagnostic methods;
- blood test for tumor markers (CA-125);
- hysteroscopy;
- determination of hormonal status.
Also, before cleaning, a woman is recommended to avoid intimacy for at least three days, use neutral baby soap as a cleanser for intimate organs, and avoid vaginal suppositories and douching.
Immediately before the procedure, it is necessary to refuse water and food to reduce the likelihood of nausea and vomiting during anesthesia.
Carrying out the procedure
The operation is performed in a hospital on a regular gynecological chair. In most cases, general intravenous anesthesia is used. After complete anesthesia, a vaginal wall dilator is used, which maximizes the lumen and makes the cervix accessible for visualization.
The cervix is supported using a surgical instrument, and a probe with a rounded end is inserted into it. It expands the canal, which is necessary for examining the inner layer of the mucosa with a hysteroscope.
Cleaning is carried out in two stages:
- The surface of the cervical canal is cleared of accumulated mucus. In the second phase of the cycle, the secretion acquires a thick and viscous structure, which can make inspection difficult. Various thinning solutions are used for cleaning. The uterine cavity is treated in the same way.
- Curettage is performed - scraping. The tool for this manipulation resembles a spoon with a thin long handle. A curette is used to clean off the top layer of the uterine mucosa, which is transferred to a prepared sealed container. The tissue will be sent to the laboratory for histological examination.
The whole procedure takes no more than 20 minutes. Additionally, other surgical procedures can be used - dissection of synechiae, fibroids, polyps. The operation is scheduled immediately after the end of the critical days. It is during this period that hypertrophied foci of the mucous membrane are most pronounced.
The procedure is carried out before menstruation and at any period of the cycle only as an emergency in case of heavy bleeding.
Postoperative rehabilitation
To exclude possible complications after surgery, antibacterial drugs are prescribed, and, if necessary, hemostatic agents. Menstruation after curettage begins 20–30 days later. If menstruation after curettage does not occur after this period, a transvaginal ultrasound is performed to determine the cause.
Pathologically scanty or abundant discharge after curettage is a reason for a visit to the doctor. You should also be wary if they acquire an unusual odor, a yellow or green tint, or if there are inclusions of clots.
If no complications arise during cleaning, the woman can return to her normal life after a week. In the first days, pain and bleeding may be observed, the volume of which will gradually decrease. Sexual intercourse after cleansing is prohibited for 10–14 days. Physical activity, the use of intravaginal products and douching, the use of a hot bath, shower, visiting a bathhouse, hypothermia are also not recommended
Recovery after curettage
For several days after the operation, spotting may be observed. Their duration may vary and on average ranges from 3 to 9–10 days.
If there is no discharge, but pain appears in the abdomen, this may indicate that due to spasm of the cervix, hematometra has formed. In this case, you must immediately consult a doctor. The presence of spasm can be confirmed using ultrasound.
To avoid the appearance of hematomas after surgery in the first days after it, you can take No-shpa or its Russian analogue, 1 tablet 2 or 3 times a day.
After the operation, the doctor must prescribe antibiotics, which is necessary to prevent the occurrence of possible inflammatory processes. You should not neglect this appointment after cleaning the uterus.
10 days after the scraping, you need to visit a doctor to get the results of a histological examination of the scraping and discuss their details with your doctor.
It is important to remember that pregnancy after a normally performed procedure can occur within 2-3 weeks, so you should not mistakenly assume that curettage will be a temporary means of contraception.
In this case, complications usually do not occur during childbirth. If the planned pregnancy does not occur within 6–9 months after such an operation, you need to consult a doctor and undergo an examination.
Impaired ability to conceive after cleansing the uterus appears in rare cases, but such cases have been noted in medical practice.
The recovery period usually lasts about 14–15 days and during this time some restrictions should be observed, for example:
Compliance with all instructions during the recovery period allows you to avoid complications. But you should not be afraid of such an operation, since modern equipment and the qualifications of many doctors make it possible to obtain excellent results from such a procedure without harm to health.
Just a few decades ago, curettage often led to problems with conception or complications during childbirth in the future. Today, such operations often help eliminate problems of female infertility and allow a woman to experience the joy of motherhood.
Author: Irina Vaganova, doctor,
especially for Mama66.ru
Possible complications
If the patient approaches the procedure incorrectly or if the patient violates the rules of preparation, complications and consequences may arise:
- infection of the uterine cavity with a further increase in temperature, chills, intoxication, suppuration of tissues;
- rupture of the uterine wall if the surgical instrument is displaced during manipulation;
- inflammation of the uterus due to the accumulation of blood against the background of spasm of the walls;
- light discharge of menstrual blood for 2–5 days.
The most dangerous complication that occurs during cleansing is inflammation of the uterus or its rupture. In this case, the following symptoms arise: a general picture of intoxication of the body, fever, severe abdominal pain.
The course of endometriosis after curettage requires careful medical supervision. The risk of recurrence of the disease cannot be excluded. In this case, repeat cleaning is used. It is recommended to plan conception no earlier than 3–5 months after treatment and subject to normalization of the menstrual cycle.
How to cure endometriosis without curettage
Endometriosis is one of the most common diseases of the reproductive system. During its development, excessive growth of endometrial tissue occurs.
The pathology is dangerous, as it can provoke serious complications, including even infertility. For this reason, women are concerned about the chances of curing endometriosis forever.
To understand this, you need to understand the reasons for the onset of the pathological process and learn about all possible treatment methods.
Signs and symptoms of endometriosis
In some cases, endometriosis is asymptomatic. It is possible to detect pathological changes in the uterus only during an ultrasound examination. Regardless of whether the deep layers of the reproductive organ are affected (adenomyosis) or the endometrium has grown far beyond its limits, the following clinical manifestations may be observed:
- the duration of the menstrual cycle changes;
- spotting a few days before the arrival of the regula and after its completion;
- menstruation with blood clots;
- symptoms of PMS are expressed excessively;
- secretion of secretions mixed with blood outside the period of critical days;
- pain;
- discomfort during intimacy.
The severity of clinical manifestations increases as the disease progresses.
Causes
To this day, scientists have not been able to determine the specific cause of the development of the pathology. There are only theories about the origin of this disease:
- implantation The pathological process begins as a result of the reflux of endometrial cells during the period of regulation or during surgery;
- embryonic. The lesions appear from the tissues of the fetus;
- metaplastic. The peritoneal mesothelium, which undergoes metaplasia, provokes the onset of the disease.
There are also factors that contribute to the onset of the first symptoms of endometriosis:
- damage to organ tissue as a result of abortion, surgery or difficult childbirth;
- heredity;
- early or late appearance of menstruation;
- excessive exposure to ultraviolet rays;
- exposure to stress;
- inflammatory processes of the genitourinary system;
- excessive physical activity;
- hormonal imbalance and disruptions of the endocrine system;
- excess body weight;
- depressed immunity;
- poor environmental situation.
Is endometriosis dangerous?
The endometrium can grow both in the uterine cavity and outside it. In some cases, the pathological process spreads to other organs. The lesions in such a situation are a source of inflammation and provoke the formation of adhesions, which lead to obstruction of the fallopian tubes and severe pain.
Further treatment of endometrial hyperplasia after curettage
Curettage of the uterine cavity if endometrial hyperplasia is suspected is carried out for the following reasons:
- This is the only way to confirm the diagnosis and establish the type of hyperplasia. This makes it possible to choose the most rational treatment.
- Curettage helps to refute or confirm the presence of a malignant process. Almost always, cancer of the uterine body proceeds in the same way as endometrial hyperplasia with the most significant symptom – heavy menstruation. An accurate diagnosis can be made and atypical cells can only be detected by histological examination of the material obtained after curettage.
- In some cases, curettage is the only effective method of stopping uterine bleeding, especially in premenopausal women.
Why and when to do curettage
Curettage of the uterine cavity if endometrial hyperplasia is suspected is a standard procedure that is performed if there are signs of pathology. Its necessity is as follows:
- This is the only way to confirm the diagnosis and establish the type of hyperplasia. This makes it possible to choose the most rational treatment: hormonal therapy or more radical options, including surgery.
- Curettage helps to refute the presence of a malignant process. Almost always, cancer of the uterine body occurs in exactly the same way as endometrial hyperplasia with its most significant symptom - heavy menstruation. An accurate diagnosis can be made and atypical cells can only be detected by histological examination after curettage.
- In some cases, curettage is the only effective method of stopping uterine bleeding, especially in premenopausal women.
The structure of the endometrium is normal
Curettage is performed if the following indications are present:
- in cases of uterine bleeding;
- if a woman complains of constant heavy periods with clots;
- if there is a suspicion of hyperplasia and polyps that appeared after an ultrasound examination on the 3-7th day of the cycle;
- to monitor the treatment of hyperplasia.
And here is more information about when abdominal surgery is necessary for uterine fibroids.
Contraindications
Any curettage, be it diagnostic or therapeutic, is a surgical intervention. Therefore, it has a number of contraindications. Among them:
- Severe respiratory failure. Usually we are talking about 2-3 degrees of the disease state.
- Heart failure in the decompensation phase. It is necessary to compensate for the condition and only then resort to therapy or diagnostic methods.
- Coronary heart disease in any phase.
- Hypertonic disease. Also hypertension of unspecified origin. Strictly speaking, it is not a contraindication. It is enough to resort to the correct anesthesia.
- Inflammatory diseases of the genital tract. Including colpitis (vaginitis), endometritis, salpingoophoritis and other pathological processes.
- Kidney disorders. Renal failure in the decompensation phase.
- Any inflammatory process in the body, confirmed by a general blood test.
- Mental disorders. As a rule, we are talking about psychosis (psychotic symptoms often make a person inadequate).
- Perforation of the uterine wall. A condition in which a perforated defect of the uterine structures develops. This is an urgent indication for urgent surgical intervention.
- Urethritis, cystitis, pyelonephritis. In other words, inflammatory processes in the urinary system.
- Oncology in progress. In remission, surgery can be resorted to.
The list of contraindications is relative. After correction of the underlying condition, curettage can be performed.
Methodology
Curettage of the uterine cavity can be performed as an emergency or planned. In the latter case, a minimal examination is necessary (blood and urine tests, blood group and Rh factor, ECG, examination by a therapist, smears for vaginal flora).
Curettage can be performed in a hospital setting in the presence of an anesthesiologist who administers medications intravenously that have an analgesic effect. The woman falls asleep without feeling pain. At this time, the gynecologist performs curettage with a special set of instruments. The steps are as follows:
- The vagina and cervix are treated with an antiseptic solution.
- The cervix is grasped with special instruments.
- With a set of expanders, the cervical canal is slightly enlarged for subsequent unhindered passage of instruments.
- Using curettes of different sizes, the doctor scrapes out all the walls of the uterus one by one, trying to completely remove the functional layer of the endometrium. This has a unique healing effect, and for some time after the procedure the woman will note that her periods are not so heavy. However, without adequate hormonal treatment, symptoms are sure to return.
Methodology of the procedure
A woman comes for uterine curettage on an empty stomach, after complete emptying of the intestines and bladder. They prefer to schedule the operation three to four days before menstrual bleeding, when the cervical canal becomes wider and the mucous membrane will be easier to reject. The manipulation is performed under sterile operating room conditions. At first, everything happens as during a regular gynecological examination, then the patient falls asleep and does not experience sensations.
After treating the vagina with antiseptics, the doctor fixes the cervix and expands it with instruments of increasing diameter. This is followed by diagnostic and separate curettage: at the first stage, the membrane of the cervical canal is separated with a curette and collected separately, at the second stage, the scraped endometrium is collected. If there are no complications, 3-4 hours after the procedure the patient is released from the clinic to go home.
Treatment after curettage of endometrial hyperplasia
Immediately after curettage, drug therapy is prescribed, which should prevent complications after the procedure. This includes:
- hemostatic drugs: “Etamzilat”, “Tranexam”, “Vikasol”;
- painkillers: Analgin, Ibuprofen, Ketorolac and others;
- antibiotics to prevent infectious complications;
- if necessary, oxytocin may be prescribed to improve uterine contractility.
As soon as the result of the histological examination is ready, the doctor prescribes further treatment. In most cases, it includes various hormonal drugs:
- Oral contraceptives for uncomplicated hyperplasia in young girls. Prescribed according to the standard contraceptive regimen, one tablet daily at a fixed time. “Midiana”, “Dimia”, “Janine”, “Klayra”, “Regulon”, “Diane” and others are often prescribed.
- Gestagens . Preference is given to this group when treating older women, as well as young women who do not need reliable protection (since they do not protect against pregnancy). These include Duphaston, Utrozhestan, Norkolut and others. The Mirena IUD can also be used. It provides both a contraceptive effect and has a reservoir that maintains a certain level of hormones in the body, sufficient for a therapeutic effect.
If previous drugs are ineffective, stronger, and also more expensive, gonadotropic hormone agonists may be prescribed. They suppress ovarian function at the level of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus. These are “Buserelin”, “Diferelin”, “Zoladex” and others.
Watch this video about the treatment of endometrial hyperplasia after curettage:
The essence of the surgical operation
Uterine curettage is a surgical procedure to partially or completely remove endometrial tissue and all contents inside the cavity. The technique involves performing the procedure blindly - the doctor does not see what is happening inside the uterus during all the manipulations. It is advisable to complement the operation with a hysteroscopic examination, but even in this case, a specialist will only be able to assess the intrauterine situation before and after the procedure. Important and significant disadvantages of the operation include:
- high level of trauma (damage to the mucous membrane of varying degrees of severity always occurs);
- high risk of complications (bleeding, inflammation, uterine perforation);
- painful procedure (intravenous anesthesia is a prerequisite);
- unpredictability of long-term outcomes (chronic endometritis, infection in the tubes and ovaries, provoking the formation of leiomyoma or endometriosis, uterine or tubal infertility).
The following operation options are possible:
- zug biopsy (minimal scraping from the uterus for histological examination of endometrial tissue);
- complete curettage of the uterus during an unwanted pregnancy or after an incomplete miscarriage;
- targeted scraping after hysteroscopy;
- separate diagnostic scraping from the endocervix and uterus to identify intrauterine pathology.
For each type of surgical intervention there are indications and contraindications. It is important to strictly follow the doctor’s advice at all stages of preparation and conduct of the operation.
If cleaning is unsuccessful
Curettage in itself is not carried out for therapeutic purposes, more often for diagnostic purposes. Therefore, talking about successful and not very successful attempts is not entirely correct. If, after curettage and subsequent treatment, hyperplasia recurs again, that is, the treatment did not bring results, it is necessary to consider other options for solving the problem. For example, it is also possible to carry out:
- endometrial ablation: cauterization during hysteroscopy of the entire inner surface of the uterus;
- uterus removal . It is offered to the patient when atypical cells are detected in the histology results, as well as when hyperplasia and other diseases are combined, for example, uterine fibroids, adenomyosis, ovarian cysts.
Consequences of curettage for endometrial hyperplasia
Curettage is a standard diagnostic procedure; in most cases it proceeds smoothly and without any complications. Moreover, immediately after its implementation, medications are prescribed to prevent any undesirable consequences.
Immediately after curettage, a woman may feel the following:
- Nagging pain in the lower abdomen, which is caused by contraction of the uterus.
- Bloody discharge, which usually gradually decreases and disappears within a week.
- Immediately after curettage, weakness and dizziness are allowed, which are caused by anesthesia and the procedure itself.
The following symptoms should alert you and cause you to contact a doctor or any medical personnel nearby:
- increasing pain in the lower abdomen;
- progressive weakness up to loss of consciousness;
- discharge with an unpleasant odor;
- increased body temperature;
- copious discharge.
The most common complications after curettage include perforation of the uterine cavity with a curette (often requiring subsequent surgical treatment), retention of clots inside (hematometra), and inflammation (endometritis).
And here is more about the consequences of hysteroscopy when removing an endometrial polyp.
Curettage is a standard procedure for suspected endometrial hyperplasia. It is performed in a hospital setting under anesthesia. After the procedure, all material obtained from the uterine cavity is sent for histological examination, which helps to subsequently select the most appropriate treatment. As a rule, the procedure goes quickly and is not accompanied by complications, but if you have complaints, it is better to consult a doctor.
Complications after surgery
After curettage, some complications may occur, but they are rare. These include:
To avoid complications, you must trust the operation only to a qualified doctor who will do everything not only correctly, but also carefully.
Curettage for endometriosis
Among diseases affecting women of reproductive age, doctors identify endometriosis. This pathology often occurs latently, causing various dysfunctions of internal organs. The most serious complication is the development of infertility.
For many gynecological pathologies, curettage is used as a method of diagnosis and treatment. Patients with endometriosis often wonder whether uterine cleaning is necessary for endometriosis.
Endometriosis is a pathological process that involves the growth of the uterine endometrium beyond its anatomical boundaries. In endometriosis, endometrial cells, for an unknown reason, spread to surrounding tissues, forming lesions that function as a full-fledged endometrium.
It is noteworthy that the mechanism of development of endometriosis is similar to the progression of a malignant tumor. Endometrial cells are also distinguished by their aggressiveness and the ability to metastasize, like malignant elements. Endometrioid cells, like cancer cells, can penetrate into surrounding tissues along with the blood and lymph flow.
The development of the disease is characterized by endometrial ectopia. This means that the inner layer of the uterus appears in an area that is unusual for it.
The body of the uterus is heterogeneous in its structure and consists of three layers:
- external or peritoneum,
- middle muscular or myometrium,
- internal or endometrium.
With endometriosis, cells from the endometrium, which is the inner layer of the uterus, can grow in the ovaries, tubes, intestines, lungs and other organs. Depending on where the peculiar islands of pathological cells are located, two types of endometriosis are distinguished:
Genital endometriosis means damage to the organs of the reproductive system, while extragenital endometriosis means damage to the intestines, bladder, and lungs. Endometrioid cells, if the disease develops, can be diagnosed in almost any organ.
The most common form is considered to be adenomyosis or internal uterine endometriosis, which involves damage to the myometrium. With this type of endometriosis, curettage is used quite often.
Indications for surgery
The list of main indications for surgical treatment includes:
- combined course with uterine fibroids;
- massive blood loss, causing the development of anemia;
- detection of polyps or hyperplasia;
- ovarian cysts.
There are several options for surgical elimination of pathology, the most radical is removal of the uterus. This technique is used extremely rarely, because the woman loses her reproductive function. The method is used if there is a risk of the presence of malignant cells. It is possible to undergo surgery to remove the uterus after menopause.
It should be noted that removal of the uterus is a blow to the female body, but if the ovaries are not affected during the operation, hormonal levels can be adjusted through the use of specific medications. They are prescribed to prevent menopause. A woman can be sexually active, her partner will not notice any changes, and there may be a slight decrease in libido.
How much the intervention will cost and in which clinic it is best to have it done, you need to check with your doctor. The price of the operation varies significantly depending on the location of the lesions and the method used. Laparoscopy is considered the most expensive. After the operation there are no scars, only small scars remain from punctures on the abdomen, as in the photo.
Endometriotic lesion: dynamics and consequences
The pathology of endometriosis is especially dangerous for the female body due to the fact that it leads not only to infertility, but also to a functional disorder of a whole range of organs, which become the focus of the development of pathology. For example, endometriosis, in addition to the uterine cavity itself, develops in organs and systems such as the ovaries, uterine appendages, gastrointestinal tract, and peritoneum.
In general, there are genital and extragenital forms of the disease. The extragenital type of disease develops outside the reproductive system. In some particularly advanced cases of pathology, it may be characterized by mixed localization.
Diagnosis of the disease is possible only with the help of a special study, and its symptoms are often completely absent. Endometriosis can manifest itself as painful symptoms typical of menstruation, spotting, weakness and anemia.
One of the characteristic symptoms, as well as a consequence of the pathology, is the inability to get pregnant, which can lead to chronic infertility. To prevent this manifestation, uterine cleansing is used for endometriosis. The operation consists of removing foci of the disease with subsequent restoration of the vital functions of the affected organs.
Causes and symptoms
The etiology and pathogenesis of any form of endometriosis is poorly understood. Endometriosis is considered one of the most mysterious diseases of the female reproductive system. It has been established that the basis of the pathological process of adenomyosis and other types of genital type of disease is the retrograde reflux of menstrual blood. As a result, endometrial cells penetrate into neighboring organs and tissues.
However, for endometrial cells to grow in a foreign environment, certain conditions must be met. Endometriosis cannot develop in the presence of a normally functioning immune system. In addition, the disease often reveals hormonal disorders, manifested in increased production of estrogen and prolactin by the body.
Gynecologists have proposed many theories regarding the mechanism of development of endometriosis.
- With abnormal development of the genital organs, the disease can be diagnosed in girls 11-12 years old. This is caused by the laying of endometrial cells in various tissues due to intrauterine disorders.
- It is assumed that the cells of some organs have the ability to transform into elements similar to the endometrium. In this situation, as with congenital malformations, there is no retrograde reflux of menstrual blood.
- Various surgical manipulations and curettage, accompanied by damage to the inner layer of the uterus, can cause the penetration of endometrial cells into neighboring tissues.
Symptoms of the pathology depend on the location of the lesions. Among the signs characteristic of most types of endometriosis are:
- chronic pain in the lower abdomen and back, which tends to intensify during menstruation and intimacy;
- spotting that accompanies the beginning and end of menstruation;
- cycle disorders;
- increase in the amount of menstrual flow;
- acyclic bleeding;
- infertility due to the formation of ovarian cysts, adhesions.
Pain is the main symptom that helps suggest endometriosis. The mechanism of pain development is due to the fact that endometrial cells in the lesions undergo the same changes by day of the cycle as normal endometrium.
During menstruation, bleeding from pathological areas is noted. Unlike the properly positioned inner layer of the uterus, bloody discharge cannot be eliminated from the body. Irritation of the lesions, inflammation and pain occurs. Over time, the inflammatory process ends with the formation of connective tissue strands - adhesions.
In the initial stages, the pathology can occur without pronounced symptoms, which contributes to late diagnosis and treatment of endometriosis. As a result, disorders associated with the functioning of internal organs develop. Extensive adhesions and growths of the endometrium can lead to infertility.
Curettage of the uterus for endometriosis: indications for use
Curettage is a fairly simple but painful surgical procedure, so it is performed under anesthesia. In most cases, general anesthesia is used, and sometimes local or spinal anesthesia is used.
The doctor determines which anesthetic is given in a particular situation, taking into account the specific clinical picture of the disease.
If the uterus is sufficiently dilated (for example, after childbirth), then anesthesia is not used.
This operation is used to treat the genital type of endometriosis, if the effectiveness of conservative treatment is insufficient, or there is a risk of more complex pathological changes in the body. The optimal time for surgical intervention: 2-3 days before menstruation.
In case of endometriosis, cleaning is carried out mainly by the endoscopic method, by introducing a special instrument into the vaginal cavity to excise and cauterize the lesions.
Curettage is used for endometriosis if there are the following indications:
- prolonged uterine bleeding, subsequently which develops anemic manifestations;
- increased pain;
- infertility;
- endometriotic cyst developing in the ovaries;
- infiltrative pathological forms;
- combined pathology.
As an alternative method of surgical intervention, laparoscopy (cleaning performed with a laser) is used. It allows you to remove even the most complex foci of endometriotic lesions.
The main goal of surgery for endometriosis is to preserve the possibility of childbearing. It is this factor that determines the effectiveness of the curettage operation. It is worth noting that this type of surgical intervention in some cases makes it possible to exclude amputation of the uterus and appendages, which leads not only to the loss of reproductive function, but also to significant disruptions in the hormonal background of the woman’s body, and other related disorders. After curettage, the body recovers quite quickly, and within a few weeks it is ready for fertilization.
Coagulation
Many patients, having heard the word coagulation from a doctor, are interested in what it is. Coagulation is the cauterization of foci of endometriosis. The procedure is carried out using a laser, liquid nitrogen or a hot loop, under the control of laparoscopy. Cauterization is less traumatic, and subsequently the adhesive process is not activated.
Laser coagulation is performed under general anesthesia. Before the procedure, a diet that does not cause bloating is prescribed. Five days before the operation, you should start taking activated charcoal, and before the procedure, a cleansing enema is performed.
After surgery for endometriosis, the recovery period is quite short. You are allowed to get out of bed after just a few hours, and discharge is possible after 1 to 3 days. Sexual rest continues for a month.
At the end of hormonal treatment after coagulation, you can plan a pregnancy. Laser coagulation is performed only by a highly qualified doctor, which avoids complications in the form of scars (which can become an obstacle to the development of pregnancy), injury to organs and blood vessels.