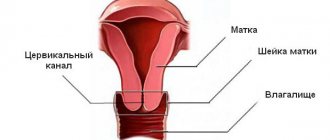
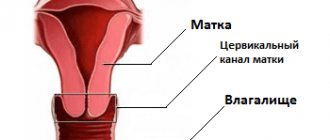
Women's health consists of many aspects. An important place is given to early diagnosis of gynecological diseases and their adequate treatment. But it is not always possible to avoid invasive interventions. And one of these methods is curettage of the cervical canal. Many women, hearing something like this, will be seriously alarmed. But such a diagnostic and treatment procedure is widespread, and there is no reason to think that it can be dangerous. You just need to know when it is performed, how exactly and what should be done after the manipulation. These are the main issues to consider.
Indications
The cervical canal is scraped out in cases where it is necessary to confirm the pathological process in the cervix or eliminate it. Therefore, the range of indications for manipulation is very wide. Conditions that require curettage include the following:
- Polyps.
- Myomas.
- Glandular cystic hyperplasia.
- Pseudo-erosion.
- Adenomyosis.
- Dysplasia.
- Cervical cancer.
- Uterine bleeding (especially during menopause).
In addition, the procedure is also performed after a spontaneous abortion in order to completely clean the uterus and make sure that there are no parts of the fertilized egg. Infertility is also an indication for curettage - in order to determine the obstacle to pregnancy associated with endometrial pathology. Thus, this operation is used as a diagnostic and therapeutic method for various gynecological pathologies. And in order to increase its information content and effectiveness, they can additionally perform cervicoscopy with biopsy.
Cytology
This analysis is one of the most accurate and reliable ways to identify various problems of the female genitourinary system. In addition, it is very simple for a girl or woman, since the procedure is absolutely painless. Unlike the biopsy method, when a piece of tissue is pinched off from the uterus, in this case the doctor takes a sample with a special tool in the form of a brush.
Ways to study samples:
- Cell staining – this method is a Papanicolaou cell staining method. This test is inexpensive and is quite often used in modern gynecology.
- Liquid examination - this research method is more modern and more accurate.
- Cytological examination is a type of examination that is carried out using the Bethesda system. Most accurately helps to recognize and identify cancer and dysplasia.
Contraindications
Taking into account indications for curettage is not all. It is equally important to determine whether the woman has conditions that limit the use of the procedure. Indeed, in some cases it is contraindicated. And this is possible in such cases:
- Inflammation (cervicitis).
- Infectious diseases.
- Normal course of pregnancy.
The last aspect should always be taken into account, because during the expansion of the cervical canal, conditions are created for termination of pregnancy in the early stages (spontaneous abortion). And curettage of the cervical canal, carried out during inflammatory processes, allows the infection to spread to deeper layers and is characterized by further complications.
The procedure for curettage of the cervical canal is performed only if indications and contraindications are carefully taken into account.
Biopsy
Many people put cytology, histology and biopsy on the same level. But this is absolutely not true. Cytology and histology are sciences that study tissues and cells.
Histology is a science that studies tissues, organs and organ systems in the human body. Cytology is a science that studies an organism at the cellular level. That is, this science studies the structure, development and functions of cells. And a biopsy is a method of taking a fragment of the patient’s tissue. For example, histology is carried out through a biopsy, that is, a sample for histology analysis is taken by pinching off a piece of tissue.
Accordingly, biopsy is the procedure itself for taking tissue from the patient, histology and cytology are sciences that study this sample in the future.
Let's take a closer look at what the biopsy itself is. The doctor prescribes a biopsy if there is any suspicion of any abnormalities that require detailed study.
Preparation
In order for the operation to go smoothly and the expected result to be obtained, it is necessary to carry out preliminary preparation. First of all, a woman should undergo a gynecological examination and additional examination:
- General blood and urine tests.
- Blood test for biochemistry: antibodies to infections (herpes, chlamydia, trichomoniasis, syphilis, HIV, hepatitis), coagulogram.
- Smear from the cervical canal (for cytology and microflora).
- Analysis of secretions (bacteriological, PCR).
- Colpocervicoscopy.
- Ultrasound of the pelvis (transvaginal).
- Electrocardiogram.
The research results make it possible to confirm the diagnosis and exclude conditions that are a limiting factor for curettage. For a week, a woman should not take medications that affect the blood coagulation system. On the eve of the procedure, you must refrain from sexual intercourse and use intimate hygiene products (use only water), and immediately on the day of the procedure, come to the doctor on an empty stomach.
How to prepare for surgery
The manipulation is carried out in a hospital, but all preliminary studies are carried out in a antenatal clinic.
Preparation for diagnostic curettage of the uterine cavity includes the following tests and consultations:
- gynecological examination;
- blood test to determine coagulation parameters;
- tests for the diagnosis of viral hepatitis B and C, HIV infection and syphilis;
- electrocardiogram;
- a smear to rule out infection in the vagina.
When prescribing a procedure, you must inform your doctor about the medications you are constantly taking. If they may affect blood clotting parameters, they may need to be stopped a few days before surgery.
Women with severe general diseases, such as epilepsy, severe arrhythmias, infective endocarditis, insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, are recommended to visit a specialized specialist (neurologist, cardiologist, endocrinologist, etc.) to adjust their therapy.
During the last 2 days before the operation, you should abstain from sexual contact, douching, and do not use vaginal suppositories or creams. In the evening before the intervention, you can have a light dinner, and from midnight do not take food and, if possible, water. The perineal area must be shaved, take a bath or shower, and thoroughly wash the genitals. In most cases, an enema is not prescribed.
Carrying out
The procedure is most often performed in the second phase of the menstrual cycle to minimize the risk of bleeding. The woman sits on a gynecological chair. Before carrying out any manipulations, the doctor treats the vagina and cervix with antiseptic solutions (sanitation). Then you need to give local anesthesia. And only after this the gynecologist begins the procedure itself.
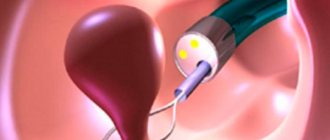
The cervical canal is gradually opened with the help of special dilators of different diameters. Then a metal instrument is inserted into it - a sharp curette, similar to a spoon. It is used to carefully scrape out the superficial (functional) layer of the columnar epithelium, while the basal layer remains intact. If necessary, a cervicoscopy is performed before this, and if an obvious pathological focus is identified, a piece of tissue is taken by biopsy. The resulting material is placed in separate plastic containers for further histological examination.
The presence of endometrial pathology is a situation in which separate diagnostic curettage is performed. That is, first they “clean” the uterine cavity, and then the cervical canal. These tissues are analyzed separately. The procedure itself lasts about 40 minutes. And the results of the histological examination will be received no earlier than in 10 days.
Only a qualified and experienced specialist can scrape the cervical canal. Although this procedure is simple, it requires compliance with all the rules.
results
To preserve all the cells of the resulting sample, it is stored in a special solution until it reaches the laboratory. Before starting the study, the scraping is colored and placed in a paraffin composition until it hardens completely. After this, the tissue sample is cut into very thin pieces and carefully examined under a microscope.
The results of the histological analysis are given to the patient personally. But to decipher the medical terms, she needs to visit her gynecologist again.
Consequences
If curettage of the cervical canal has already been performed, then the woman remains in the ward of the gynecological department for several more hours under the supervision of the attending physician. Then she is sent home, warned about the course of the postoperative period. Normally, over the next few days there may be bloody or bloody discharge from the genital tract. This is a normal reaction of the mucous membrane to damage. If the patient notices that there is pain in the lower abdomen, severe bleeding or a rise in body temperature, then she definitely needs to contact the doctor who performed the procedure. After all, we are talking about the emergence of complications.
But in addition to the inflammatory process and bleeding, other adverse consequences for a woman are likely in a later period:
- Adhesions and scars.
- Cervical insufficiency.
- Myomatous nodes.
- Endometriosis.
But such conditions are extremely rare and cannot be considered a reason to refuse a procedure, the value of which far outweighs the potential risk. If the operation is carried out without technical violations, by qualified personnel and with appropriate equipment, then there is no need to fear complications. And in order to quickly recover after scraping, you should adhere to the following simple rules:
- Refrain from sexual intercourse.
- Avoid thermal procedures (bath, sauna).
- Avoid swimming in the pool and taking a bath.
- Follow hygiene recommendations.
- Avoid physical activity.
- Do not take blood thinning medications (antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants).
When curettage was carried out for diagnostic purposes, it makes it possible to establish the correct diagnosis, and therefore to plan further therapeutic measures. A medical procedure makes it possible to remove pathological tissue inside the cervical canal and, in most cases, save the patient from the disease. But for everything to go smoothly, you should follow all the doctor’s recommendations: both before and after the operation.
Histology analysis
So, let's figure out how the concepts of histology, cytology and biopsy differ. Histology analysis is taken through a biopsy. That is, a small piece of tissue is taken. Most often, this procedure is done under local anesthesia, but it is possible not to use it. In this case, the sensations will be more unpleasant, but tolerable.
Basic tissue sampling methods:
- Radio wave - the main advantage of this method in gynecology is that it is bloodless, but there are also cases when after the procedure the patient experiences vaginal discharge.
- Conization - this type of sample collection is characterized by cutting off a cone-shaped piece of tissue. It can be used not only to collect tissue, but also to remove the affected area.
- Pinching is a method during which a piece of material is pinched off from the patient using special biopsy forceps.
Histology analysis can answer the following questions:
- The most important of them is whether there are malignant formations or cancer cells in the body. Histology analysis can warn or help diagnose cancer in a timely manner.
- The second is to find out the causes of infertility.
- Also, a biopsy test will help determine the general condition of the patient’s genitourinary system.
How long does a histology analysis take? This question will be answered by the clinic or laboratory where you are doing the analysis. But on average, you will receive the results of a histology analysis within 6-10 days from the moment the tissue is taken.
Can the histology test results be incorrect? There is a very low chance that the histology test will be incorrect. This type of diagnosis is one of the most accurate and reliable. But sometimes doctors admit that the result is incorrect; this happens extremely rarely. After all, if the technology for taking a tissue sample and the further algorithm of actions were followed, then the probability of error is equal to zero.
Recovery period after cleaning the cervical canal
After surgery, the patient usually experiences heavy bleeding for several hours, which is completely normal - this is how the uterus gets rid of particles of the endometrium affected during the procedure. Later, the discharge becomes less abundant and lasts about seven to fourteen days. If bleeding does not occur after the manipulation, this is an alarming symptom indicating the presence of a pathological condition such as accumulation of blood in the uterine cavity (hematometer). You should immediately notify your doctor about this to prevent harmful health consequences.
For fourteen days after gynecological cleansing, you should refrain from intimacy, washing the vagina with solutions of medicinal substances (douching), severe physical overload, and being in a sauna or bathhouse.
If you experience severe pain in the lower abdomen, bleeding that lasts for several hours, the patient develops a fever, feels dizzy, or loses consciousness, you must immediately seek emergency medical help.
In cases where no side effects are observed, on the tenth to fourteenth days after the cleansing, the woman needs to come to see a gynecologist. In order to find out what condition the uterus is in, it is possible to prescribe a transvaginal ultrasound examination.
About the procedure
- the cervix and vagina are disinfected;
- then expanders and mirrors are inserted;
- while the nurse holds the mirrors;
- the doctor makes smooth movements, collecting material for research.
A socket is a gynecological instrument that consists of a loop with a cutting surface and circular sides. The instrument is widely used in gynecology for scraping the uterus, but there is one significant drawback - an unreliable grip.
The scraping is carried out using a curette; the gynecologist collects material from the walls of the uterus, carefully scraping off the top layer. The doctor makes delicate movements with the handle, approaching the bottom of the organ.
When the procedure is completed, the doctor removes the speculum, removes the dilators and treats the cervix with an antiseptic.
The procedure is performed under general anesthesia and lasts 30 minutes.
What is uterine scraping and why is it performed?
This is a histological study that is used when it is difficult to make a diagnosis.
Tissue is collected from the uterus using the scraping method. The resulting epithelial cells are sent for research, which can be carried out in 2 ways.
Why a study may be prescribed:
- To determine the condition of the uterine mucosa (epithelial cells).
- To determine the nature of the tumor formation.
- In principle, the procedure has one goal - to collect material for analysis, followed by study and diagnosis.
If we talk specifically about the procedure called uterine scraping, it is not much different from the abortion procedure familiar to many women.
Collection of material from the uterine cavity is carried out if the presence of endometriotic changes, cancer cells, cystic formations and endometrial polyps is suspected.
The procedure is carried out using several methods; there is an urgent and planned scraping from the uterine cavity.
With the urgent method, it is possible to obtain information a few minutes after collecting the material. This method has its own characteristics and is considered relatively inaccurate. But in emergency cases, a procedure performed in this way may be required by a surgeon for several reasons.
- determine the nature (quality) of the tumor;
- verify the presence or absence of pathogenic cells in the material;
- diagnose cancer at an early stage;
- check the effectiveness of the treatment.
A uterine scraping is different from other diagnostic tests because it is done in a slightly different way. The thing is that the procedure does not involve cutting tissue, but rather scraping (collecting) biological material.
Scraping of the endometrium of the uterus is carried out not only for the purpose of diagnostic procedures. But also as part of therapy for the treatment of endometriosis.
This type of therapy can slow down the development of endometriosis, cope with unpleasant symptoms and improve the patient’s condition. In such a situation, biological material is not sent for analysis, only if necessary.
In the epithelium, the doctor can detect cancer cells that indicate the development or presence of cancer in a woman.
Scraping is done not only from the uterine cavity, but also from the cervical canal (cervix). For the purpose of diagnosing tumor formations of the cervix.
Service cost
| Name of institution: | Procedure price: |
| Pact clinic | from 5500 rub. |
| Tsar's Clinic | from 2500 rub. |
| Eden Clinic | from 3500 rub. |
The price depends not only on the method of conducting the study, but also on the anesthesia that will be given to the patient. When contacting a medical institution, this fact should be taken into account. And also some centers do not perform scrapings without prior consultation with a specialist.