Often the cervix is also understood as the cervical canal. In reality, it is located inside the cervix and is part of it. At an appointment with a gynecologist, patients sometimes hear from the doctor that for some reason the cervical canal is closed. Before answering the question of what a closed cervical canal means, it is necessary to consider its structure and functions.
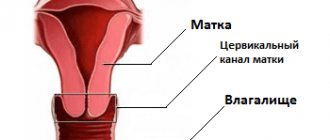
The cervical canal of the cervix connects the uterine cavity to the vagina. It usually has a cylindrical or conical shape. The length is three to four centimeters.
The cervical canal has a lower and an upper part. Its external pharynx opens into the vagina, and its internal pharynx opens directly into the uterus.
This part of the uterine cervix performs several important functions. First of all, the organ cavity is protected from harmful microflora, which can cause inflammatory processes.
The presence of pathogenic microflora in the vagina means that an impressive number of pathogens live on the mucous membrane. It is noteworthy that the uterine cavity normally remains sterile.
The sterility of the uterine cavity is ensured by the cervical canal. It is lined with a special type of epithelium, which contains cylindrical cells of a single layer. The epithelium is characterized by velvety and reddish color. In addition, glands responsible for the production of protective mucus function. This means that the secretion should protect the uterine cavity from infection.
Mucus is heterogeneous on different days of the cycle for certain reasons. At the beginning, as well as at the end of the menstrual cycle, the secretion is quite viscous and has an acidic environment. These conditions cause the death of most microorganisms. Moreover, when sperm penetrate, their motility is lost.
The middle of the cycle is characterized by an increase in the concentration of estrogen in the blood. Thus, the mucus becomes alkaline and somewhat liquid. These conditions contribute to the survival of sperm and further fertilization.
If pregnancy occurs, the level of progesterone in the blood increases. The secretion becomes viscous, eventually forming a plug. This means that this mechanism protects the growing organism from infection.
The discharge of the cervical canal is mucus, which has a different character on certain days of the cycle.
Cervical canal - what is it and what is its function?
The cervical canal (canalis cervicis uteri) is a natural linear space inside the cervix that connects the uterine cavity with the lumen of the vagina. Under normal conditions, it has a spindle-shaped shape due to 2 physiological terminal narrowings. They are called the external and internal pharynx.
The cervical canal is lined with a special cylindrical epithelium, which performs a barrier and secretory function. The mucus produced by its cells contains a large amount of glycoproteins and is essentially a hydrogel with a finely porous structure. Moreover, its consistency, acidity and permeability are not constant, but change depending on the woman’s hormonal background, the day of her cycle and a number of other factors.
The cervical canal performs several functions:
- Barrier
The mucus contained in the lumen of the canal is a natural obstacle to bacteria and viruses, forming a “plug” and thereby preventing ascending infection of the uterine cavity. In addition, the cervical tissues have a local immune system that provides additional protection against most microorganisms. It is represented by immunocompetent cells, the humoral factors and antibodies they produce. It is thanks to the cervix that the uterine cavity maintains its sterility.
- Creation of a selectively acting barrier on the path of spermatozoa
Hormonal levels that change during the ovarian-menstrual cycle affect the acidity and viscosity of cervical mucus, which has a regulatory effect on male germ cells. Before ovulation, the mucus plug liquefies, its pores increase in diameter, the pH becomes alkaline, and the cervical canal opens slightly. All this creates favorable conditions for the penetration of sperm from the vagina into the uterine cavity. And the parietal reverse flow of mucus that occurs during this period is a factor that allows us to “weed out” functionally incomplete male germ cells that are not capable of progressive, targeted movement.
- Removal of menstrual and postpartum discharge from the uterine cavity
The cervix is the natural and only route for the evacuation of blood, rejected endometrium, physiological and pathological secretions. Violation of its patency leads to the accumulation of secretions, progressive expansion of the uterine cavity with the reflux of contents into the fallopian tubes, and provokes an inflammatory process.
- Formation of the birth canal, ensuring the natural expulsion of the fetus, its membranes and separated placenta
This is ensured by the expansion, shortening and centralization of the position of the cervix during contractions in the 1st labor period.
The cervical canal is often considered as a special anatomical formation, paying special attention to it when examining a woman.
What does it mean - the cervical canal is dilated?
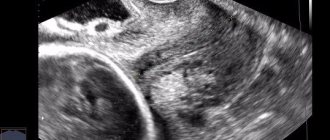
Normally, in an adult nulliparous woman with sufficiently developed genitals, the length of the cervical canal is on average 3.5-4.5 cm, and the diameter at the widest part does not exceed 8 mm. Its external pharynx has a round shape and a diameter of 5-6 mm. And after childbirth, it naturally takes on a slit-like shape with several radiating traces of tissue tears along the edges and no longer closes so tightly.
The permissible width of the lumen of the cervical canal outside the process of labor is up to 8 mm. An increase in diameter above this indicator is the basis for diagnosing enlargement (dilatation). This is complemented by shortening of the cervix, which is sometimes used as an independent criterion.
A closed cervical canal is the norm during pregnancy until the onset of labor. Its expansion exceeding the average statistical size is spoken of in several cases:
- there is an expansion of the internal pharynx up to 2 mm or more already at the end of the first trimester of gestation, with a normal diameter of the remaining parts of the cervical canal;
- the cervical canal is slit-like expanded in the upper third, and there is often a significant increase in the number of cervical glands;
- there is a funnel-shaped deformation of the internal os; when performing a 3D ultrasound and sufficient specialist skills, it is often possible to record prolapse of the membranes;
- expansion of the canal along its entire length, with a simultaneous decrease in the length of the cervix and its softening.
The mucus plug has come off: when is the due date?
As labor approaches, the cervix becomes more elastic and soft, allowing it to open. During this process, there is a release of the mucus plug, which the canal walls can no longer hold.
A mucus plug forms in absolutely all pregnant women; this process begins from the moment of conception. It prevents infection from entering the uterus, protecting the fetus.
The period of removal of the plug does not depend on whether the woman gave birth or not. In a multiparous pregnant woman, the mucus may drain 1 to 2 weeks before giving birth, and with the same probability, immediately before the onset of labor, with amniotic fluid, the release of which is a more accurate harbinger of the imminent birth of the baby.
The conclusion is that there is no need to worry about the plug coming out if the contractions have not yet begun and the water has not broken. The release of mucus is only a signal that the cervix has begun to open, but it is necessary to inform the doctor about this.
If the plug has come out and the cervix is closed, then there is no need to worry. In this case, it is recommended to refrain from taking a bath and sexual contact to eliminate the possibility of bacteria entering. When you definitely notice that the mucus has already come out, this means that the opening of the canal will soon occur, it is already ready for labor, and you need to prepare for a trip to the maternity hospital.
Usually, women begin to prepare for childbirth with the onset of contractions, or the breaking of water, and if the cervical plug comes out, there is no need to panic.
Video: what is a mucus plug and how to understand that it has come off?
What is a mucus plug and how to understand that it has come off
Diagnostics
Confirmation of the presence of dilation during a routine basic gynecological examination is usually not possible, except in cases of gaping of the external os. Reliable diagnosis requires intravital imaging techniques, and ultrasound is usually sufficient. In this case, preference is given to a vaginal sensor, although it is also possible to use a conventional transabdominal one. Measuring the cervix during an ultrasound is called cervicometry.
A more accurate imaging method is MRI of the pelvic organs. Of course, this technique is not used for the primary diagnosis of cervical pathology. MRI is performed at the second stage of examining the patient to reliably determine the nature of her changes.
Smear analysis during dilation of the cervical canal is an additional diagnostic method that allows you to confirm the presence of an inflammatory process and determine its nature. To exclude STDs as the cause of cervicitis, a serological blood test is performed for major infections.
Preparation for the operation
To reduce the risk of complications, a woman needs to undergo a series of preparatory examinations. They are needed not only to confirm the diagnosis, but also to establish the general state of health. The set of diagnostic measures includes:
- general blood analysis;
- blood chemistry;
- test to detect sexually transmitted infections;
- test for HIV, syphilis, hepatitis B and C;
- blood clotting test;
- colposcopy;
- microscopy of vaginal and cervical smears;
- electrocardiogram;
- fluorogram;
- probing;
- bacterial culture from the vagina;
- Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs.
The woman should visit an anesthesiologist. On the day of the operation, drinking water and food is prohibited. The prohibition is due to the fact that nausea and vomiting may occur during intravenous anesthesia. The cost of the procedure differs in many clinics. When choosing a medical center, you need to take into account its reputation and the qualifications of its doctors.
Why is this dangerous?
If the cervical canal is dilated in the absence of pregnancy, this does not pose an immediate danger to the woman’s life. But such dilatation is a symptom of various pathological processes in the cervix or body of the uterus, which requires adequate diagnosis and timely, comprehensive treatment.
Enlargement of the cervical canal during pregnancy is clearly a pathological sign. It may be a manifestation of:
- Threatened spontaneous abortion in early pregnancy. At the same time, in addition to the expansion of the cervical canal on ultrasound, there are signs of pathological hypertonicity of the uterus. Incipient detachment of the ovum with a retrochorial hematoma can also be detected, while maintaining the viability of the embryo.
- Isthmic-cervical insufficiency, which is diagnosed from the 2nd trimmeter of pregnancy. Additional diagnostic ultrasound signs of this condition are a funnel-shaped expansion of the internal os, a decrease in the length of the cervix at less than 20 weeks to 3 cm, a decrease in the ratio of the length of the cervix to its diameter (at the level of the internal os) to less than 1.5. Isthmic-cervical insufficiency is the cause of recurrent miscarriage.
- Abortion in progress or incomplete spontaneous abortion (in early pregnancy), premature birth (after 26 weeks of gestation).
Therefore, if dilation of the cervical canal is diagnosed during pregnancy, the doctor needs to decide on treatment tactics as soon as possible and assess the advisability of urgent hospitalization of the patient.
Treatment
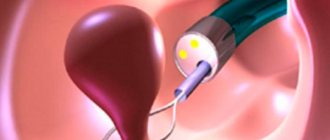
If we talk about effective treatment of a true polyp of the cervical canal, then it can only be surgical. First, the doctor observes the pathogenic growth, and if the polyp continues to grow rapidly, he prescribes surgery under local anesthesia. Polypectomy involves the final removal of this benign neoplasm, after which additional histological examination is required.
If inflammation in the cervical canal predominates, then intensive therapy is usually medicinal, that is, aimed at normalizing the condition of the mucous membrane. The choice of medications is made on an individual basis, and depends on the form of the disease, the stage of the pathological process and the characteristics of the affected organism. The success of such treatment is guaranteed in 90% of all clinical pictures. If complications predominate, doctors suggest more radical methods.
One way or another, all lesions in the cervical canal must be diagnosed in a timely manner, otherwise complications in the woman’s reproductive system are unlikely to be avoided. A timely response to the alarming symptoms of one’s own body allows one to make a correct diagnosis in a relatively short time and medically return the patient to her former health.
Main causes of pathology
Why is the cervical canal enlarged? There are many reasons for this condition:
- Threat of miscarriage.
- Polyp of the cervical canal.
- Cystic lesion of the cervix (the so-called Nabotov cyst), usually with anechoic contents. These can also be multiple small cysts up to 1 mm in diameter.
- Other benign tumor-like formations of the cervix. Possible fibroids, sarcomas, hemangiomas, leiomyomas.
- High-grade adenocarcinoma of the cervix.
- “Born” fibroid or endometrial polyp.
- Endometriosis, adenomyosis.
- Acute or chronic cervicitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal), including those developing as a result of STDs.
- Tumors of the uterine body of significant size, leading to stretching of the internal os.
In women of reproductive age, dilation up to 12 mm or more can be observed for some time after a completed spontaneous or medical abortion, during the recovery period after childbirth, after therapeutic and diagnostic interventions with cervical dilation.
In menopause, dilation may be due to progressive atrophy of uterine tissue against the background of severe estrogen deficiency. In this case, the cervical canal is usually dilated unevenly, and there may be concomitant prolapse of the vaginal vault and uterus. And as the process of age-related involution of the reproductive system progresses in the postmenopausal period, dilatation is replaced by narrowing to 3 mm or less, and subsequent atresia (fusion).
The most common diseases
Unfortunately, the female reproductive system is often susceptible to various diseases. Many of them are not dangerous and can be treated with medication. Others have to be treated surgically.
The cervical canal is no exception; it can have both congenital and acquired pathologies.
Congenital diseases are:
- Atresia of the cervical canal is a congenital pathology that implies obstruction of the canal. Which can lead to death in advanced cases. But this happens very rarely. With atresia, the canal between the uterus and vagina is completely blocked. Main symptoms: no menstruation, no vaginal discharge. It can only be treated with surgery.
- D two-channel reproductive system . Very rare. It implies a congenital pathology in which two cervical canals are formed, connected to one uterus. It can only be corrected surgically. If everything is done correctly, reproductive functions will be restored. The probability of a developing pregnancy without pathologies is very high.