What is the cervical canal and what is its significance?
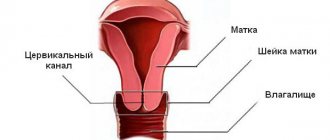
The canal is a through hole that connects the top of the vagina directly to the uterus. It is located inside the cervix.- The length of this channel is about 4 cm.
- Width - about 8 mm, during childbirth - 10 cm.
- It has 2 narrowings: internal and external pharynx.
The external one is usually examined by a gynecologist using medical instruments.
Nulliparous women have a pinpoint pharynx. And those who gave birth have a slit-like pharynx. A smooth, pale pink canal is characteristic of young, healthy women. And during menopause, the mucous membrane is very pale, and almost no secretion is produced.
The main purpose of the canal is to protect against infectious diseases and facilitate the penetration of sperm into the uterus. Blood clots also pass through this channel during menstruation.
At the very beginning and after the end of the menstrual cycle, mucus from the cervical canal has an acidic environment. The mucus from the cervical canal is very viscous and blocks the passage like a plug.
Harmful microorganisms die in this acidic environment. And spermatozoa in such an environment become incapable of fertilization. The level of estrogen can be determined by stretching the mucus; the longer the thread, the more hormones in the body.
Already in the middle of the monthly cycle, estrogen levels increase significantly, and the mucus becomes thin and alkaline. And sperm gain access to the eggs of the uterus.
But after conception, the ovaries produce progesterone, and the mucus in the cervical canal becomes more viscous. A thick mucus plug forms. It protects the fetus from pathogenic bacteria. Before birth, this plug comes out of the canal.
Features of the canal during pregnancy
During pregnancy, the cervical canal undergoes changes associated with the stretching of the cervix and the growth of the fetus, as well as hormonal characteristics. It lengthens to 3-4 cm, forming two borders - the external pharynx and the internal one. The state of the external pharynx at the end of pregnancy is used to judge readiness for childbirth; during pregnancy, the canal should be narrow and both pharynxes should be closed. The tone of the cervical pharynx is an important indicator of health, and it is significantly influenced by microbial contamination.
From the beginning of pregnancy, a thick mucous plug forms inside the canal, which prevents infection from reaching the fetus; its release is a sign that the baby will be born soon.
note
During regular examinations of the condition of the cervix, doctors, in parallel with visual control, also take a culture from the cervical canal for flora; it determines the ratio of microbes in the cervical area to determine whether there is a threat to pregnancy and the fetus.
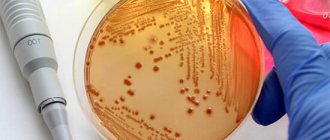
After collecting a sample of material from the cervix, it is placed on nutrient media, grown under ideal conditions for approximately 5-6 days, and the types of microbial colonies are determined.
Why is bacterial culture needed during pregnancy?
A smear from the cervical canal during pregnancy is a mandatory procedure, which is necessarily followed by a culture culture. This helps to detect a particular disease (if any) as soon as possible and promptly treat it. But many mothers are concerned about the question: will such a procedure harm the fetus? Will the doctor cause an infection with gynecological instruments while taking biological material for research?
It’s worth saying right away: this manipulation should not cause any concerns. The doctor takes a sample using disposable plastic instruments that are included in the gynecological kit. You can purchase it at any pharmacy adjacent to the clinic, and not only.
Why is it necessary to perform a culture from the cervical canal during pregnancy? During this period of a woman’s life, the most optimal conditions are created for the reproduction of pathogenic microflora. The immune system of the expectant mother weakens, and hormonal levels change, which often causes the development of inflammatory and infectious processes.
In order to detect pathology in a timely manner, the doctor prescribes the patient a referral for a culture tank from the cervical canal during pregnancy. Over the course of 9 months, developing diseases seriously threaten the child’s health, so the sooner they are detected and treated, the less dangerous the complications will be for the fetus and the mother herself.
A culture tank is the same as a smear, only it is taken not from the walls of the vagina, but from the opening of the cervical canal. This type of test is not preventive; it is prescribed by a doctor due to elevated white blood cells in a regular smear.
An increased number of leukocytes is a sign of an infectious disease occurring in a woman’s body and requiring immediate treatment.
Also, sowing is required when planning a pregnancy, if sexually transmitted diseases are suspected, in case of infertility, or when registering for pregnancy.
The inoculation is taken using a sterile brush and placed in a flask, into which no foreign microorganisms from the external environment should get. After this, the analysis is sent to the laboratory.
There is no need to be afraid of this procedure; it is not painful at all and is safe. This test is also safe for pregnant women.
IMPORTANT! To obtain a reliable test result, you must abstain from sexual intercourse, do not use vaginal contraceptives, douche, or use perfume gels for intimate hygiene for at least 24 hours. If you have taken antibiotics, the test is prescribed no earlier than 2 weeks after you stop taking the medications.
How is a culture taken from the cervical canal?
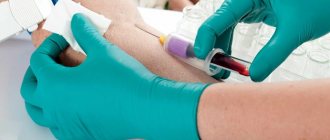
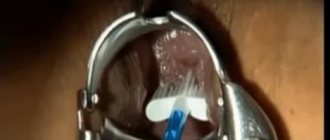
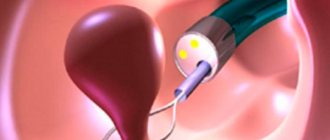
The analysis is carried out by microscopy of the material on days 4-5 of the menstrual cycle. For a smear test, the cervix is exposed using a speculum. Using a sterile swab or brush, collect mucus from the surface of the epithelium, turning it clockwise several times, trying not to damage the membrane.
This is how they take a smear from the cervical canal - click to enlarge
The brush is removed and the resulting material is distributed in an even layer on a glass slide, avoiding drying. The glass is placed in an individual bag and sent to the laboratory.
The entire duration of the procedure for collecting material for research is 15 minutes.
If transportation of material is required, then it is carried out only at a temperature not exceeding 20 degrees in a sealed bag - a refrigerator. In laboratory conditions, opportunistic material is placed in an environment favorable for their reproduction.
Each type of bacteria requires individual conditions and time of reproduction. The results at the end of the process are recorded by laboratory staff. The interpretation is carried out by a gynecologist.
Note! Tank culture from a cervical analysis does not reveal the presence of infections such as: herpevirus, ureaplasma, mycoplasma, chlamydia (penetrating into cells and affecting the nucleus). This type of microorganism can be detected by PCR diagnostics (polymerase chain reaction).
Preparing for analysis
The patient needs to be well prepared for vaginal bacterial culture. To do this, you must follow certain rules. Neglecting them can lead to unreliable data, which means that the analysis will have to be repeated.
So how to prepare for a cervical canal test? Follow these guidelines:
- the day before the scheduled procedure, you must stop douching;
- do not use vaginal suppositories, including hormonal contraceptives;
- refuse sexual contacts one day before the study;
- within 48 hours after colposcopy, culture from the urethra in women is not given.
You need to prepare for a gynecological smear. This can prevent false results and misdiagnosis.
Preparation:
- stop taking antibacterial drugs 14 days before the study;
- do not use medications that come into contact with the vagina (creams, ointments, suppositories) 2 days before the test;
- sex with a partner is prohibited 48 hours before taking a smear test;
- do not douche 2 days before the test;
- do not take a bath 24 hours before the test, but a shower is allowed;
- When washing, use special products that do not change the pH. In the morning before the examination, it is generally not recommended to use cleansers - gels, soaps;
- menstruation is a contraindication for testing, at least 3 days must pass after menstruation, then a smear can be done;
- You cannot perform an ultrasound that involves inserting a sensor vaginally, as well as colposcopy 48 hours before the smear;
- Do not go to the toilet to empty your bladder 2 to 3 hours before the smear.
If a woman is taking medications, this information should be conveyed to the attending physician. For example, taking antibacterial agents can distort the results. The specialist decides to cancel medications or postpone the date of the smear test.
Microflora culture requires preparatory measures, then you can be sure that the accuracy of the gynecological examination will increase by 3 to 5 times. But, if the result is unsatisfactory, the doctor will prescribe a smear again. You need to purchase a diaper and replacement shoes in advance. This point requires fulfillment if a woman goes to the clinic. Private organizations provide everything needed.
Stages of implementation:
- Placement on the gynecologist's chair. Usually a smear is taken in the morning. The procedure is performed either in a hospital or in a medical laboratory office.
- To provide access to the organs, a speculum is inserted. If the girl has not yet had a partner, the material is collected from the side of the vagina, then it is impossible to damage the hymen. The size of the mirror depends on the features and age category. For example, for girls they use S, and if the organs are not fully formed - XS. After childbirth, use M or L.
- The specialist collects material from the vagina using a sterile stick. The procedure does not involve pain. Discomfort is possible, but only when the spatula comes into contact with the area of inflammation. Most often, a smear is taken not from 1 point, but from 3 - the vaginal wall, the cervical canal, the opening of the urethra. From each site, material is collected using different sterile instruments.
- Apply the collected material to the glass. The secretion from the vagina must be distributed throughout it. If material was collected from different parts of the genital organs, each of them requires its own glass.
- If the material is delivered to the laboratory after 3 or more hours, the smear must be fixed.
- If the smear is carried out using the Gram method, it must be stained. Methylene blue is used.
- Evaluate the result. The receipt time depends on the specific laboratory and its workload. It can vary from several hours to days. In emergency cases, for example, during surgery, the result is given within a few minutes. In the case of an annual inspection, the period reaches 14 days. Private clinics send results in 1 – 3 days. Cytological examination takes longer - from 7 to 10 days.
Microflora culture in gynecology does not provide for restrictions. You can return to your normal life.
Preparing for the study:
do not have sex the day before tests;
- do not take medications (especially antibiotics) two weeks before the test;
- do not use creams or gels for intimate procedures;
- prepare and refrain from any hygiene procedures before submitting samples;
- do not go to the toilet before submitting samples;
- do not douche or use candles;
- wait a few days if colposcopy was performed;
- Do not take tests during your period, but 7 days after the end.
How to prepare for a cervical smear?
Proper preparation for a painless procedure ensures reliable results. The doctor writes a referral to the patient and talks about the nuances that need to be taken into account before taking the test.
A gynecologist takes tests on a pregnant woman. Sexual contact is avoided for several days before the procedure. Do not take medications or contraceptives.
If a few days before the scheduled date of delivery, vaginal examinations were carried out using a speculum, then it is advisable to postpone the procedure. It is forbidden to do douching, which distorts the vaginal microflora. To maintain hygiene, use regular boiled water without using detergents.
Before visiting the treatment room, wash only in the evening . 1-2 hours before the appointment, refrain from urinating. The procedure does not cause discomfort or pain to the patient.
The female genital area is a special mechanism that can be influenced by even the most insignificant external factors. Elementary hypothermia often causes the development of a number of unpleasant and dangerous pathologies. To promptly detect their presence, the gynecologist prescribes a culture tank from the cervical canal.
Such a study is not always carried out, but only under conditions of ineffectiveness of other diagnostic procedures, as well as to confirm a preliminary diagnosis. Why is manipulation needed, and how long do you need to wait for results? Let's try to figure it out.
How is the analysis done?
In the laboratory, the material is transferred from a test tube to a Petri dish, into conditions that are comfortable for it to develop and reproduce. After 3–5 days, the colony of microorganisms grows in quantities sufficient for diagnostic studies. An antibiogram is also immediately performed to determine the sensitivity of bacteria to antibiotics so that the doctor can prescribe effective treatment.
The bacteriological culture indicator is considered positive when the analysis shows the presence of pathogenic microflora. These indicators are divided into 4 degrees according to the speed of growth and development:
- First degree - scanty growth of microorganisms is present only in a humid environment.
- Second degree - microorganisms of the same type on a solid medium show growth of up to 10 colonies.
- Third degree - the number of colonies on a solid medium reaches 100.
- Fourth degree - the number exceeds 100 colonies.
The third and fourth degrees indicate that there is no infection in the body.
Tank culture is the gold standard in identifying infections; it can be used to identify not only acute, but also latent infections. It is able to identify not only pathogens, but also determine their activity and quantity.
This diagnostic method determines the sensitivity of microorganisms to antibiotics.
An antibioticogram is a complete list of antibacterial drugs to which the isolated bacteria are susceptible.
To identify antibiotics to which the detected microorganism will be vulnerable, 2 methods are used:
- diffusion method - test strips soaked in an antibiotic solution are used. The strips are immersed in a nutrient medium with microbes and the changes are observed;
- standard disc method - special discs impregnated with antibacterial drugs are placed in containers seeded with pathogenic microflora; if the growth of microbes stops, then it is sensitive to this antibiotic. To clarify the level of vulnerability, the diameter of the zone of growth arrest is measured.
Preparation for bacterial culture from the cervical canal
Before collecting material, special preparation is required, which will include simple recommendations. Any douching is prohibited the day before collecting the material; also, according to the decision of the gynecologist, any antimicrobial drugs, both local and systemic, will be discontinued. Also, one day before taking samples, intimate intimacy is prohibited, and at least 3-4 days should pass between the ultrasound with a vaginal sensor and the collection of the material. You should not wash yourself before collecting the material, especially with the use of various intimate hygiene products.
Why is bacterial culture needed during pregnancy?
Pregnant women need to take a bacterial test from the cervical canal.
After all, it is in this canal that pathogenic bacteria accumulate, which can harm the fetus.
In order for the pregnancy to proceed without problems and the child to be healthy, it is necessary to detect the infection in time and cure the disease.
But bacterial analysis from the canal is not prescribed to all pregnant women. When registering, women must undergo a general smear test.
And if the content of leukocytes in it is increased, then the doctor prescribes an additional test for culture. A high percentage of leukocytes indicates an inflammatory process. And which bacteria caused the disease can only be determined by analysis from the cervical canal.
Decoding the results of microflora analysis in gynecology
When the analysis is ready, the woman will receive a result form. The analysis form indicates which microorganisms and in what quantity were found in the cervical canal of the subject. If everything is normal, then the analysis will show the absence of fungi and the presence of bifidobacteria and lactobacilli in an amount of at least 107 colonies. It is also considered normal to reproduce E. coli in an amount of no more than 102 and a single number of enterococci.
A smear is considered pathogenic if it contains a large number of enterococci and E. coli, staphylococcus, proteus, yeast, gonococcus, gardnerella, trichomonas, and citrobacter.
Ureaplasmosis, mycoplasmosis and chlamydia invade inside the cell and are not detected by bacteriological culture. To identify these infections, a PCR test is performed.
A cervical smear is done very quickly, but the culture results must wait at least 5 days. After this period of time, the woman is given a form on which the types and number of microorganisms detected are indicated.
Most of the normal flora are various types of lactobacilli. Their content must be 107 and above. The species characteristics do not matter and differ from woman to woman. Normally, as a result of bacterial culture, bacilli of the genus Fusobacterium and Veillonella can be identified. As a result of the analysis, a small amount of Escherichia coli, enterococci, epidermal staphylococcus, bacteroides, prevotella and other rare organisms is allowed.
Pathology is the detection of:
- a large number of enterococci, Escherichia coli, epidermal staphylococcus, bacteroides, etc.;
- Staphylococcus aureus;
- fungi of the genus Candida;
- Gardnerella vaginalis;
- Trichomonas vaginalis (Trichomonas);
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae (gonococci);
- Proteus spp.;
- Citrobacter spp.;
Atypical flora cannot be detected by bacterial culture. Microorganisms of this group are intracellular. To identify them, use a smear for chlamydia using the PCR method. Mycoplasmas and ureaplasmas are also detected by PCR or by inoculating the test material on a special medium.
Opposite the identified microorganism its quantity is indicated. Depending on this parameter, there are 4 degrees of cleanliness of the vagina and cervical canal:
- bacteria grow only in liquid media;
- growth of a certain species up to 10 colonies on a dense medium;
- 10-100 colony forming units on solid medium;
- more than 100 colony-forming units on solid medium.
For pathogenic microorganisms, a spectrum of sensitivity to given antibiotics is established (antibioticogram). It reflects the ability of a particular drug to suppress the growth of a given bacterium. Opposite each drug there are letter symbols S, R, I. S means that the microorganism is sensitive to the effects of this antibiotic, R - that it is resistant, I - that growth is partially inhibited.
Depending on the results, there are 4 degrees of vaginal frequency:
- Normal white blood cell count. Mucus and epithelium in moderate quantities. The degree is not a pathology, it indicates a good immune system and a low likelihood of an inflammatory process.
- Leukocytes in normal quantity. Moderate levels of mucus and epithelium. Beneficial lactobacilli are on a par with yeast and cocci. The condition is normal. But the microflora has already been changed, we can say that the immune system weakens over time. The risk of developing inflammation increases every time.
- Leukocytes are elevated. Cocci and yeasts occupy the main part of the microflora. A large amount of epithelium and mucus. This condition indicates inflammation and requires therapy.
- Too many white blood cells. Pathogenic bacteria are present. Increased content of epithelium and mucus. Severe inflammation, the condition must be treated immediately.
The first stages are the norm. Any gynecological procedures are allowed - curettage, biopsy, etc. Stages 3 and 4 refer to the disorder, and there is a need for treatment. Any gynecological procedures are prohibited.
| Index | Description |
| Gonococci and Trichomonas | Gonococci are the main causative agent of gonorrhea. Upon penetration into the genitals, active reproduction begins. The likelihood of infection increases with contact without contraception. Normal – absence of the indicator Trichomonas provokes the appearance of trichomoniasis. If there is no pathology, then the indicator is not determined |
| Leukocytes | Increased concentration indicates an inflammatory process |
| Epithelium | A high level indicates an inflammatory process, the presence of an infection or a hormonal imbalance. The norm of epithelium is less than 10 |
| Slime | If the amount is minimal ( ) or moderate ( ), there is a disease |
| Key cells | Normally they should be absent |
| Yeast | They are causative agents of thrush. Their number should be minimal. The best option is no yeast |
| Cocci | They should be absent, but a small amount is allowed. Normally no more than 5%. Otherwise, unpleasant symptoms develop – burning, itching, difficulty urinating |
| Dederlein sticks | They are responsible for normal acidity. Thanks to this, sperm penetrate the egg. They also prevent the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria. Normally, rods should be present |
In bacterial culture, the result can be indicated in the form of advantages:
- " " - few;
- "" - in moderation;
- “ ”—great content;
- " " - great amount.
It is advisable that the attending physician decipher the results.
Decoding the culture tank from the cervical canal
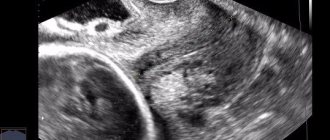
A woman receives the results of a smear 4-6 days after submitting the material. During this period, colonies of bacteria grow. The resulting form indicates all microorganisms that populate the lining of the cervical canal.
In the photo: an example of deciphering the analysis after a smear from the cervical canal - click to enlarge.
The norm is the presence of leukocytes and fungi in moderate quantities, lacto- and bifido-bacteria (107 CFU/mg, which corresponds to 300-400 million/g), creating a protective acidic environment. E. coli normally contains up to 102 enterococci.
An important indicator in decoding is the number of bacteria, indicating the degree of cleanliness of the cervical canal. In a contaminated mucosal environment, there is a minimal number of microorganisms growing in a liquid medium.
This category includes the minimum number of “resistant” bacteria that can develop in a dense environment (no more than 10 colonies). With the development of the inflammatory process, bacteria capable of multiplying in a dense environment (up to 100 colonies) are found in the smear.
On average, prices for delivery of a sowing tank in Russia range from 800 to 1,400 rubles.
- Bacteria are detected using modern automated methods using new technologies. The sensitivity of the pathogen to antibiotics is determined by microbiological analyzers.
- The next stage is the selection of a drug depending on the identified pathogen. The results of the study are given to patients in accordance with standards that help the attending physician to easily navigate the information provided and make the correct conclusion.
Controversy surrounding analysis
Expectant mothers are wary of bacterial testing. After all, the brush is inserted deep into the vagina and a smear is taken from the cervical canal. But taking a smear test cannot lead to a miscarriage.
The study is completely safe, but it is prescribed only when absolutely necessary. When assessing the state of the vaginal microflora, gynecologists use a special concept - the degree of purity.
There are 4 degrees of vaginal smear purity:
- Acidity is normal, lactobacilli predominate, there is no inflammation.
- Acidity is normal, a small number of leukocytes, the number of lactobacilli is reduced, diplococci are present.
- The environment is slightly acidic or alkaline, an increased number of leukocytes, a reduced number of lactobacilli, many coccal organisms.
- The environment is alkaline, a large number of leukocytes, the absence of positive and the presence of a huge number of dangerous microorganisms.
If a vaginal smear indicates problems, and the degree of purity is 3 or 4, then pregnant women are additionally prescribed a culture test from the cervical canal.
A normal culture of a pregnant woman should contain only beneficial microorganisms: lacto and bifido. A small amount of E. coli is allowed. There should be no yeast or bacteria present.
If an increased content of dangerous microorganisms is detected, then treatment is necessary. Therapy in the early stages of pregnancy gives good results.
Norms
Normal analysis indicators include only the presence of beneficial microflora. It consists of bifidobacteria and lactobacilli. They can be present in the analysis in any concentration.
A decrease in indicators in this case is an unfavorable sign, indicating a violation of local immunity.
A normal result allows for the presence of small amounts of E. coli. But its concentration should not exceed 10*2 degrees of colonies. There should be no fungal flora in a normal bacterial culture from the cervical canal.
The appearance of Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella, enterococci, streptococci in the analysis is an indication for mandatory treatment. In this case, doctors also determine the reason that caused the appearance of these pathogenic microbes in the cervical canal.
If the level of these microbes in the analysis is increased, then this not only can pose a threat to the development of pathologies of the female genital organs, but can also lead to the development of pneumonia or other diseases of the internal organs in an infected woman.
Cervical canal fusion
Overgrowth of the cervical canal can be congenital or acquired. Overgrowth (atresia) of the cervical canal leads to partial or complete closure of the walls of the opening and prevents the passage of menstrual blood.
- infectious diseases suffered in childhood (diphtheria, mumps);
- poor quality scraping;
- damage by cancer;
- traumatic birth;
- abortion injuries;
- damage by endocervicitis;
- cauterization of the cervical canal;
- advanced inflammatory processes of the internal genital organs;
- elderly age.
Primary atresia is diagnosed during the first menstruation without finding a way out; menstrual blood accumulates in the uterus and stretches it, the girl feels a general deterioration in health and if she does not consult a doctor in time, the blood further spreads through the fallopian tubes and can cause purulent inflammation.
Acquired (secondary) atresia is diagnosed when a woman consults a doctor about infertility. Stagnant blood clogs the tubes, and the egg does not have the opportunity to enter the uterine cavity. The diagnosis can be established using ultrasound, hysterosalpingoscopy, MRI, and sounding. This pathology is treated by bougienage of the cervical canal.
The bougienage operation is performed in a hospital and takes about 30 minutes. If the infection is complete, then the manipulation is performed under general anesthesia, and if not significant, then under local anesthesia. After the operation, if general anesthesia was used, the patient is discharged for home treatment the next day, and with local anesthesia, the patient is released on the day of the operation. The duration of home treatment lasts 10 days, wound healing drugs and anti-inflammatory suppositories are prescribed.
Indicators are normal
Based on the results of the study, it can be determined whether the indicator is within the normal range.
| Indicators | Age category (years) | ||||
| 1 – 5 | 6 – 10 | 11 – 15 | 16 – 17 | Sexually active teenagers | |
| Leukocytes | 0 – 2 | 3 – 5 | 5 – 7 | Less than 10 | |
| Slime | 1 – 2 | ||||
| Epithelium | 1 – 3 | 4 – 6 | 5 – 6 | Less than 10 | |
| Flora | Kokkovaya | Mixed | Rod | ||
The indicators of a woman of reproductive or menopausal age depend on the location of the material collection.
| Indicator name | Vagina (V) | Cervical canal (C) | Urethra (U) | What causes the quantity to change? |
| Leukocytes | To 10 | Up to 30 | Up to 5 | Inflammatory process |
| Epithelium (flat) | From 5 to 10 | |||
| Gonococci | None | Gonorrhea | ||
| Trichomonas | Trichomoniasis | |||
| Key cells | Pathology | |||
| Yeast | Infection | |||
| Microflora | Gram-positive rods of Dederlein | Absent | Presence of pathology | |
| Slime | Moderate | No | Presence of infection | |
The level of the expectant mother changes, the smear is performed 3 times. An increased level of lactobacilli indicates the patient's normal condition. During pregnancy, the mucus content increases. The allowed number of epithelium is no higher than 15, leukocytes - 10.
Norms of indicators in the analysis of microflora in a woman:
- epithelium – 15;
- leukocytes, vagina, urethra – up to 10, cervix – 30;
- Dederlein sticks;
- mucus in small quantities.
If yeast, cocci, and trichomonas are present in large quantities, the woman has a pathology. It is necessary to consult a gynecologist. Taking a microflora test helps evaluate the functioning of the genital organs, which is why the procedure is used in gynecology.
The study is carried out to determine the infection and inflammatory process. As a preventive measure, it is necessary to pay attention to an annual examination by a gynecologist. If you detect deviations in the early stages and begin timely treatment, you can quickly get rid of the disorders.
The canal is populated by various microorganisms; it cannot be completely sterile. Lysozyme contained in the secretion of the canal has an antimicrobial effect.
Beneficial bacteria must be present in the cervix. But just one harmful bacteria, for example, staphylococcus, indicates an infection and the need for treatment.
The composition of the microflora depends on:
- on the age of the woman;
- presence of infection;
- hormonal levels;
- taking antibiotics;
- various pathologies.
The analysis provides data on the microorganisms inhabiting the cervix. A normal indicator should not contain any fungi or bacteria.
However, there must be beneficial bifidobacteria and lactobacilli, but not less than 10.7. Indicators of E. coli – 10.2 enterococci. Leukocytes are normal up to 30. Flat epithelium – 5-10. There should be a moderate amount of mucus.
Pathological is a condition in which a large number of E. coli, gonococci, yeast fungi, staphylococci, and trichomonas are found. This analysis is not able to detect chlamydia and ureaplasma.
The gynecologist interprets the results obtained from the laboratory. The analysis shows the name of the microorganisms inhabiting the cervix, as well as one of the 4 levels of cleanliness of the canal.
There are 4 levels of channel purity:
- Microorganisms show little growth. They are present in liquid media, but not in solid media.
- Bacteria of one type show growth of up to 10 colonies on a hard surface.
- The number of bacteria is up to 100 colonies on a solid medium.
- The number of different colonies is more than 100.
The first two degrees indicate contamination of the canal, and the third and fourth degrees indicate inflammatory processes.
And the reasons for the increased number of bacteria in the cervix are decreased immunity, hormonal imbalances, taking antibiotics, hereditary diseases, poor hygiene, infection during sexual intercourse, infection due to medical procedures.
Tank culture for the presence of bacteria can also determine sensitivity to various antibiotics. Bacteria whose sensitivity needs to be determined are placed in a dish with a nutrient medium. Discs soaked in antibiotics are placed on the surface of the medium.
This antibiotic penetrates the environment and affects the growth of microorganisms. The bowl should stand for some time at room temperature, and then it is placed in a thermostat for several hours.
After the required amount of time has passed, the diameter of the growth inhibition zone is measured and the suppression of bacterial growth is assessed:
- the absence of growth inhibition indicates bacterial resistance to the drug;
- zone diameter up to 1.5 cm – weak reaction, low effectiveness of the product;
- zone diameter from 1.5 to 2.5 cm – moderate sensitivity;
- diameter greater than 2.5 cm – hypersensitivity to antibiotics.
It is important to determine sensitivity to antibiotics, because in different women, bacteria react differently to certain medications. You cannot prescribe medications based only on textbook recommendations. It is necessary to find out which antibiotic can cope with the disease.
Interpretation of culture results
The number of bacterial colonies inoculated may vary. When more than 100 colonies of pathogenic microbes are detected in the culture, clinical acute inflammation is diagnosed . The development of this can occur both against the background of poor hygiene, and during infection with dangerous and infectious diseases that are transmitted through intimate intimacy.
The degree of infection (cleanliness of the cervix) and canal will be determined.
- The first degree is the optimal ratio of microbes - some useful, no pathogenic.
- At the second degree of purity, less than 10 CFU per ml of material or growth of a similar amount on a solid medium is determined.
- The third degree of purity is a dangerous state. From 10 to 100 CFU are detected, this result is a reason for immediate treatment in order to suppress the inflammation and prevent it from spreading to the baby.
- The fourth degree of purity is a difficult situation; it is an acute inflammatory infection with more than 100 CFU in the material.
It is important to treat this condition with local or even systemic drugs . The choice of drugs is determined by general data and culture results for sensitivity to antibiotics.
Alena Paretskaya, doctor, medical columnist
11 total today
( 60 votes, average: 4.33 out of 5)
Diagnosis of protozoal infections
Tests, scrapings for enterobiasis in a child: what they show, the norm
Related Posts
Thickening of the cervical canal
In a woman of reproductive age, the opening of the cervical canal is 7–8 mm wide, which is enough for the removal of menstrual blood and for the penetration of sperm into the uterus.
During the reproductive period, expansion of the pharynx occurs in the middle of the cycle, which is absolutely normal and is associated with approaching ovulation.
With age, a woman’s body undergoes various changes, and the reproductive system also becomes different due to changes in hormonal levels. You need to monitor your health during menopause even more carefully than before. During this period, various diseases, including deadly ones, may appear.
During the examination, some women find that the opening of the canal is greatly expanded, which is a sign of some gynecological disease that needs to be urgently diagnosed and treated.
The cervical canal plays a huge role in the functionality of a woman’s internal reproductive system. This organ takes an important part in the process of childbirth and is of great importance for carrying a pregnancy.
To prevent the appearance of abnormalities in the cervical canal, it is imperative to undergo routine examinations with a gynecologist. Never self-medicate if any ailment occurs!
In addition to attentiveness and accuracy to the patient’s health on the part of doctors. Every woman should take her health seriously. If a woman leads a healthy lifestyle, attends antenatal clinics on time, does not have bad habits, and does not have a promiscuous sex life, her risk of developing inflammatory diseases is much lower.
Smear culture during pregnancy: purpose of the study, norms and deviations
The female body during pregnancy is predisposed to various diseases, since the immune system is too weakened. The bright prospects of bearing and giving birth to a healthy baby can collapse due to the appearance of infection, bacteria of various origins. In this regard, doctors prescribe a huge number of tests, one of which is culture.
What is tank smear culture
Bacteriological culture is an analysis to determine the provoking factor and how sensitive it is to a particular drug.
This research method is widely used in medicine.
Almost any liquid biological material can become a substance for study. Collection from the genitals is preferable.
Based on the results, correct and successful treatment can be prescribed.
Objectives of the study
In the female reproductive system, the balance of the acidic environment plays an important role. It consists of protective microbes that prevent infections from entering.
Under the influence of negative factors, pathogenic bacteria multiply to huge numbers and exceed the indicators. A chain reaction of inflammation occurs.
A smear culture during pregnancy is prescribed to identify harmful bacteria. The doctor takes a smear from the genital mucosa, since then the most accurate results are obtained.
Bacteria are placed in a comfortable environment for them to develop and examined under a microscope.
Bacteriological culture plays a huge role in the detection of infectious diseases. Research methods may differ, but the goal is the same: to obtain indications and identify pathogens without foreign impurities.
Indications for analysis
What is the sowing tank used for? Biological material from pregnant women can be examined routinely at scheduled times at the discretion of the gynecologist. The fence is made from the cervical canal.
Also prescribed according to some indicators:
- when a woman plans to become a mother in the near future;
- with inflammation of the female genital organs and
- microflora disorders;
- if the results of the previous smear are questionable;
- in cases where the uterus is constantly susceptible to infection.
The various visible manifestations of infectious diseases are also taken into account. For example, unpleasant vaginal discharge, itching, burning, irritation.
Using this diagnostic method, you can determine why the menstrual cycle is delayed.
For pregnant women, the test is prescribed if a genitourinary infection is suspected, or for the purpose of its prevention.
The development of pathogenic infectious parasites in the uterus cannot be ignored. This can lead to miscarriage or infection of the fetus.
How the research is carried out
Tank seeding from the cervical canal during pregnancy is carried out quite often. With normal gestation, this occurs at 30 weeks.
If there are specific complaints or there have been previous miscarriages, infection of the fetus in the womb, and so on, a smear is given as prescribed by a doctor.
The collection of material is carried out by a midwife or nurse from the antenatal clinic.
In this case, preparation for tank sowing includes:
- exclusion of water hygiene procedures;
- you cannot douche and use antiseptics;
- do not insert suppositories or other medications;
- if during planning the procedure coincides with menstruation, then a smear cannot be taken; it is taken 2 days after the complete end of menstruation;
- tank analysis is not taken immediately after colposcopy;
- Any treatment that includes antibiotics or drugs interferes with reliable results.
The patient is positioned on a gynecological chair. The health care provider inserts a speculum into the vagina and then uses a sterile probe with a small loop to take a swab.
The procedure is absolutely painless and safe for the child.
What does the results show?
The female genital organs have many microorganisms in their flora. Some of them do not pose a danger, and some are not the norm for beneficial gestation.
Normal tests should show the presence of: lactobacilli, bifidobacteria. Other microorganisms that are inherent in the intestines should not be detected, except in a single quantity.
If the culture shows a large accumulation of them, this indicates that the genitourinary system is inflamed.
Norms
The following indicators are considered normal results:
- in the cervical canal no more than 30 units of leukocytes;
- in the vagina 3 times less;
- up to 5 units should be in the urethra;
- squamous epithelium can range from 5 to 10 units.
Harmful bacteria that depress the body must be completely absent.
What do deviations mean?
The results do not always show normal values. Poor culture during pregnancy is not uncommon.
Depending on the identified pathology, possible treatment options are considered.
The absence of squamous epithelium indicates a decrease in estrogen; an excess of these components indicates inflammation.
Yeast-like fungi indicate characteristic diseases, for example staphylococcus in the cervical canal in pregnant women.
Abundant mucous discharge also indicates inflammatory processes.
In connection with the detection of any deviations from the norms, additional procedures are prescribed. A pregnant woman undergoes tests to examine vaginal discharge.
First of all, they consider options for harmful bacteria acquired through sexual contact.
Treatment is prescribed based on the timing of pregnancy.
The preferred treatment option during this period is topical remedies without antibiotics. Medicines should not adversely affect the fetus.
In the second trimester, more radical methods are allowed, but in case of urgent need.
Important! There are infections that do not manifest their existence openly in the body. That is, they develop in a latent form and affect the development of the child while in the womb. Therefore, even without any apparent reason, it is advisable to take this test.
Degrees of quality and growth of bacteria
There are microorganisms that live without actively manifesting themselves. At the time of immune and hormonal disorders, they are activated and begin to actively multiply. Each of the parasites finds its own habitat, where it is more comfortable. That is why one or another flora is used for analysis.
The results of the readings are based on the possibility of rapid development of harmful microorganisms.
The following options are possible:
- first degree. This is when there is a slight growth of bacteria and only relative to its environment;
- the next step is about a dozen colonies in another solid medium;
- at the third stage there is an increase to 100 colonies;
- in the last stage, more than 100 colonies of the same type are observed.
The primary two degrees of proliferation of microorganisms indicate clogging in the microflora, and the latter show inflammation.
These changes do not exclude the possibility of development associated with the interesting position of a woman during which hormonal changes occur, immunity decreases, and medications are used.
The entry of an infection into the body and its rapid reproduction can bring not only physical discomfort to the expectant mother in the form of itching, burning and discharge. For this reason, miscarriages, infections of the child during passage through the birth canal, and many other troubles occur.
To ensure a successful pregnancy, take care of your health in advance.
Daria Andreevna, neonatologist
Especially for the site kakrodit.ru
: bacterial smear culture during pregnancy
Source: https://kakrodit.ru/bakposev-mazka/
Is there a difference between tank culture and smear cytology?
Sowing tank is a scraping from the cervical canal for microflora. It can only detect fungi and bacteria.
And cytology shows changes in epithelial cells. She studies precancerous and cancerous conditions of the cervix.
Along with the analysis for bacteria, you can take samples for cytology. But the subject of tank culture research is only bacteria.
Changes in the canal cells are determined using a biopsy. Malignant abnormalities in individual cells do not yet indicate cancer.
In oncology, a large number of cells have negative changes. Colposcopy provides more detailed information about the cells of the cervical canal.
The importance of the analysis is that it helps identify not only the bacteria that caused the disease, but also determines antibiotics that can cope with the disease.
The patient not only needs to undergo tests, but also undergo the course of treatment prescribed by the doctor. Only in this case can she become healthy again.
How to correctly perform the procedure
So that you understand how safe this procedure is, I will tell you how a smear is taken and what is subsequently done with the material. So, only a sterile brush is used for the procedure. It is sent to the cervical canal, where glands and cells with microorganisms collect.
This procedure is somewhat unpleasant for a woman, but generally safe and not painful. The next stage is related to the direct study of the material. As soon as the specialist has taken the analysis, the contents of the brush are placed in a glass beaker, where the necessary conditions have already been created for the development of microorganisms.
Here the laboratory technician is faced with an important task - not to allow microorganisms to die, otherwise he will not be able to determine which ones are present in the woman’s body. And the flora analysis will be done in vain.
To multiply parasites, the flask is placed in a thermostat; the temperature here is always 37 degrees. The next step is to transfer the contents of the flask to another nutrient medium and place it again in a thermostat for several days. Here the process of reproduction of fungi and bacteria is already in full swing.
When the number of parasites increases to a volume that can be examined, the laboratory technician performs the following actions:
- determines the types of microorganisms present in the material;
- calculates the number of units within species;
- Conducts antibiotic tests.
Now that you know what the analysis shows, you need to understand how important it is for the health of the mother and child. How many days does the analysis take? About five, the doctor will tell you more precisely.
What is microflora in gynecology and its functions in the body
Microflora are microorganisms that are found in the vagina. It is not naturally sterile. There is constant competition between bacteria for food and habitat. Normally, a woman should have more lactobacilli, which protect the body from the action of pathogenic bacteria.
Some species have the ability to produce hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), which additionally prevents negative microflora from growing and multiplying. And also, in a woman’s vagina, bifidobacteria are predominantly found - they provide an acidic reaction in the secretion.
Studies indicate that with dysbacteriosis, vaginal lactobacilli can produce no more than 25% H2O2. Normally, this figure should not be lower than 90%. In addition to lactobacteria and bifidobacteria, there are various microorganisms in the vagina. With dysbacteriosis, the level of lactobacilli decreases, and the acidity of the vagina decreases.
This is fraught with the following consequences:
- decreased immunity;
- increased likelihood of illness;
- irritation of the labia.
If treatment is not timely, the condition may progress to infertility. This is why normal vaginal microflora is so important.
How and under what conditions does microflora appear?
The normal microflora of the vagina consists of several types of bacteria - more than 300. It can change. Changes in microflora indicators are allowed not only due to the presence of diseases.
It depends on the following points:
- phase of the menstrual cycle;
- hormonal background;
- age category;
- method of contraception;
- sexual activity;
- compliance with hygiene rules.
For example, during menstruation, the phases may fluctuate. In the first days of the cycle, the pH reaches 5 - 6. This occurs due to a decrease in the number of lactobacilli. When menstruation ends, normal levels (3.8 - 4.5) are restored.
Indications for microflora research
Culture analysis in gynecology is carried out exclusively when indicated, but from time to time it can also be performed for preventive purposes. Indications for performing such a test may include:
- pregnancy planning;
- the presence of inflammatory processes in the cervix;
- infectious diseases of the genital organs;
- detection of pathogenic flora in a smear from the cervical canal;
- increased level of leukocytes in an ordinary smear;
- frequent relapses of chronic inflammatory or infectious gynecological pathologies.
A tank seeding from the vagina involves placing representatives of pathogenic microflora in a certain nutrient medium. It is different for each type of bacteria or fungus, as is the time required for germination. After this process is completed, the laboratory worker counts the number of bacterial colonies (cells), then records the data obtained on a special form. The results are interpreted by a gynecologist.
Microflora culture in gynecology helps to assess the condition of a woman’s genital organs.
The procedure is prescribed in the following cases:
- The presence of vaginal secretions. It can be copious and usually has an unpleasant odor.
- The occurrence of painful sensations during sexual intercourse with a partner.
- As a preparatory measure for artificial (in vitro) fertilization.
- To monitor the health of the expectant mother. The analysis is performed before and during pregnancy. In the latter case, the procedure is carried out once per trimester.
- Presence of pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen. Moreover, the symptom should not be associated with the cycle, because pain is allowed to occur before menstruation.
- Deviation from normal bladder emptying. That is, a woman often wants to go to the toilet, little urine is released, and incontinence appears.
- Before this, the doctor prescribed medications from the group of antibiotics and it is necessary to determine the composition of the microflora after therapy.
The procedure is performed if various gynecological diseases are suspected:
- vaginitis;
- thrush;
- trichomoniasis;
- gonorrhea.
In addition to the above reasons, the procedure must be performed during an annual examination. This way you can prevent various diseases in gynecology or detect them at an early stage. Typically, an analysis of vaginal microflora is prescribed by a gynecologist. And he must also decipher the results.
What is a tank culture from the cervical canal
The procedure involves taking a sample of biological material from the walls of the vagina for further clinical examination. It is performed if there is a suspicion of infectious diseases of the genital organs in women. The goal is to determine exactly what type of pathogenic microflora caused the ailments and alarming symptoms in patients.
What is a cervical canal scraping? Using a cotton swab or a special sterile gynecological instrument, the doctor carefully removes the material for examination. The stick is placed in a special flask, which prevents foreign microorganisms from attaching to the sample taken.
Sometimes a gynecologist can place a smear on a sterile glass, which is then sent to a laboratory for testing. After the analysis, the doctor confirms or denies the presence of a bacterial or fungal infection, and can also judge what could have caused the patient’s illness.
What does tank seeding show?
It is very important to understand what a smear on a culture tank shows. This will help you understand the features of decrypting the received data. So, when performing an analysis you can find:
- enterococci;
- Escherichia coli;
- leukocyte cells;
- epithelial cells;
- chlamydia;
- Trichomonas;
- various fungi;
- gonococci;
- mucous impurities, etc.
Fact. Cervical canal culture is one of the most informative and important clinical procedures, with the help of which pathologies that are extremely dangerous to a woman’s health are detected. Based on the data obtained, the results are deciphered and a strategy for further treatment of the current disease is developed.