How does a Pap smear differ from a regular smear for oncocytology?
Unlike oncocytological smears, which are done in antenatal clinics, when performing a Papanicolaou smear, a specially selected composition of fixatives and dyes is used, which makes it possible to identify early precancerous diseases of the cervix with the greatest degree of reliability. This technique is standard for developed countries in Europe and America, as it gives the least number of false negative results. When taking smears using the usual method, fixatives are not used, and the set of dyes is extremely simplified.
When taking smears, the Center for Immunology and Reproduction uses glasses and dye sets specially purchased in the USA. After the study, all glasses are stored in perpetual storage in the laboratory, which allows comparison of smears from the same woman over a number of years.
Cytology in gynecology
A cytological smear is taken during a routine gynecological examination. To “obtain” it, you do not need any special training from a gynecologist or any special conditions.
Normally, material is collected once a year, during one of the preventive scheduled examinations, but it can also be taken additionally in the following situations:
- in the presence of inflammatory diseases and suspected urogenital infections;
- when investigating the cause of infertility;
- if there are complaints about menstrual irregularities;
- when planning pregnancy;
- to determine possible changes with long-term use of hormonal contraception.
Cytological studies must be carried out before any gynecological surgical interventions - for example, installation of an intrauterine device, curettage, etc.
What are the causes of abnormal Pap smear results?
When there is an infection such as thrush, trichomonas, chlamydia, or gonococcus, the cells in the cervix become inflamed and appear abnormal. Once the infection is treated, the Pap smear usually returns to normal.
A common cause of abnormal Pap smears is human papillomavirus. The virus may be present in the cervix and may also cause genital warts in the external genital area. There are many types of human papillomavirus, some of which are associated with an increased risk of cervical cancer. Therefore, women who have human papillomavirus may have an increased risk of developing cervical cancer.
Cancer cells are the most modified abnormal cells found in a Pap smear. In preinvasive cancer, only the superficial cells are affected. Invasive cervical cancer means that the disease has spread beyond the surface layer of cells.
Methods for oncocytological examination of the cervix
Doctors distinguish two options for conducting oncocytological studies:
- Leishman method. This method is characterized as simple and is often practiced in public clinics and antenatal clinics;
- The liquid method, which is characterized by greater accuracy and is used in commercial clinics.
Leishman method
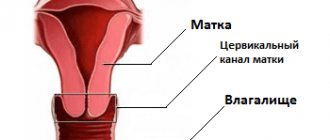
In the first option, the material must be obtained from the transformation zone. In 90% of cases, the problem area becomes squamous and columnar epithelium. The remaining 10% is made up of a cylindrical layer that should cover the cervical canal.
For diagnostic purposes using the Leishman method, the cervical canal and the junction area where the vagina enters the cervix are used as a source of material for analysis. For sampling purposes, an Eyre gynecological spatula and a special brush (Cytobrush) are used.
The doctor installs gynecological speculum without removing mucus from the epithelium. The brush is inserted into the external os of the cervix. Afterwards, the device is turned clockwise, which allows a sufficient amount of material to accumulate, after which the devices are carefully removed from the body.
The traditional smear is transferred to the glass, without drying. The drug contains exfoliated cells of the mucous epithelium, the junction area and the vagina.
Disadvantages of using the Leishman method:
- Uneven distribution of biomaterial;
- Incomplete coloring of the material;
- Quick drying of the prepared material;
- High chance of false negative analysis up to 40%.
It is also possible to use the Papanicolaou test or Pap test. This method is distinguished by a different coloring of the material, but the preparation is also prepared on tables as in the case of the Leishman method.
Liquid cytology of the cervix is the second method, and is an innovative examination of the cytological smear. After obtaining epithelial material and mucus, the smear is placed in a special liquid medium. The fence is placed in a centrifuge and the cells of the cyto-preparation begin to concentrate in one place, forming an even cover under the influence of centrifugal force. This method makes it possible to more accurately establish a diagnosis and check for the presence of pathology.
Liquid analysis of the cervix is used to select effective methods of combating cancer. Advantages of the method:
- Accurate studies of the inner cover of the uterine cervix;
- Improving the quality of material for testing;
- Rapid creation of the drug;
- Using standard methods for staining the drug;
- Possibility of multi-layer smear, creation of several preparations from biomaterial;
- long-term storage of material using a stabilization solution.
Preparatory measures for collecting material
The procedure is carried out in a gynecological chair. For a qualitative analysis, a woman must complete the following points:
- avoiding sexual relations for 2 days before the smear;
- abstaining from using a vaginal suppository and various spermicidal ointments;
- the douching procedure is also prohibited;
- it is necessary to stop taking contraceptive and anti-inflammatory drugs;
- refusal to use tampons.
Taking a smear should be painless and quick. Two hours before the operation you should not urinate. Research is also contraindicated during the active phase of the menstrual cycle, during discharge, itching, and tissue inflammation.
Cytological analysis will make it possible to reliably determine the order of structure of cellular material, the shape and size of cells for diagnosing the state of organ function.
The Leishman method takes 10-14 days of preparation. The liquid method allows you to find out the result in 5-7 days.
Indications for analysis
Women who have become sexually active should undergo testing. The method is also relevant in the presence of pathology in the genitourinary organs. Other reasons for taking a smear may include:
- Pregnancy period;
- Mechanical damage to the internal organs of the pelvis;
- The woman has reached the age of thirty;
- The individual demonstrates a predisposition to cancer;
- Infection with the papilloma virus has been identified (this is a common cause of the development of malignant tumors);
- Disruptions during the menstrual cycle.
Women with bad habits should also undergo analysis.
What is done if the Pap smear is abnormal?
The plan of action depends on the degree of cellular changes described by the cytologist. If the changes are associated with inflammation, the smear is usually repeated several months later. If necessary, appropriate treatment can be prescribed. Smears that show low-grade abnormalities may be repeated after a few months, or your doctor may order a colposcopy. High degree deviations are always an indication for colposcopy. Patients with abnormal smears are usually advised to use condoms and spermicidal gels or abstain from sexual intercourse until the examination is completed.
Oncocytological analysis of cervical smear
Decoding the analysis for oncocytology of the cervix occurs when cytological analyzes are divided into 5 types:
- Absolute norm. In this case, the epithelium fully corresponds to the proper structure;
- There is an indicator of the inflammatory process that changes the structure of the cell;
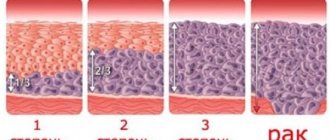
- Dysplasia of 1-3 degrees was revealed. In this case, individual cells exhibit atypical characteristics. In this option, the woman must undergo additional testing such as a biopsy and colposcopy of the problem area;
- The smear revealed individual cells with signs of abnormalities in a malignant form;
- The drug contains a significant number of malignant cells; the presence of a tumor is an accurate analysis.
What is colposcopy?
A colposcope is an instrument, much like a microscope, that allows the doctor to examine the external genital area (vulva), vagina, and cervix under magnification, so that areas of change can be more easily detected. The patient is placed on a gynecological chair and a gynecological speculum is inserted into the vagina. The doctor lubricates the cervix with special solutions, which make it easier to see cellular abnormalities. The colposcope itself does not touch the patient. Colposcopy is not performed during menstruation. 24 hours before colposcopy, the patient should not douche, use vaginal gels, ointments or tampons, because this may affect the accuracy of the study.
Why is the analysis taken?
Cytology tests are taken not only in gynecology. Such studies must be carried out if there is a suspicion of the development of malignant processes in absolutely all areas of medicine.
Tests are carried out in the following cases:
- to confirm the diagnosis;
- when monitoring during treatment of the disease;
- during a preventive examination;
- during surgery;
- during dynamic observation.
In gynecology, the result of a smear is analyzed - material can be taken from the uterine cavity, the outer or inner surface of the cervix.
In other areas of medicine, all biological fluids are examined:
- urine;
- sputum;
- prostate juice;
- discharge from the mammary glands;
- flushes during endoscopic examinations;
- joint fluid;
- scrapings from ulcerative or wound surfaces;
- punctates.
Tissue prints that are removed during histology are also sent for examination.
In addition to its main purpose - accurately determining the presence of a malignant formation or its absence - the nature of the ongoing process is revealed, and a conclusion is made about the development of inflammation. At the same time, the nature of the pathogenic flora is accurately revealed.
The nature of the lesion is established - inflammatory, proliferative or precancerous, and the stage of the oncological process.
Based on the results of the cytology smear analysis, when deciphering it, you can choose the necessary treatment method and determine whether surgical intervention is required. Tumors of different structures respond differently to treatment depending on their origin and degree of atypia.
What to do if the biopsy indicates abnormalities?
Medical recommendations will depend on the histological report.
At the Center for Immunology and Reproduction, the doctor may prescribe periodic monitoring, frequent Pap smears, colposcopy or laser therapy. In this case, the changed cells are removed using a laser beam. The Center recommends that every woman undergo an annual medical examination.
More details about the program You can take this and other tests in the CIR laboratory Find out the cost of the analysis
Oncocytology of the cervix is not normal
In this variant, the morphological norm of tissue elements is reduced. This may indicate the presence of various diseases, ranging from vaginosis. Also, the doctor can observe if the cell has damaged its internal structure in the area of the cytoplasm and nucleus. In more severe cases, a precancerous stage or cancer may be diagnosed.
In the case of intraepithelial cervical neoplasia and other negative conditions. Such diseases are designated by the symbol HPV. In the case of 1st degree dysplasia, CIN I is used, in the second stage, CIN II, and in the case of a malignant tumor, grade 3 dysplasia is used, which is designated CIN III.
Decoding the analysis of a smear from the cervical canal has a system of notations that will help decipher the individual result, confirming the generally accepted point of view.
Table of values
| CBO | No visible changes in the analysis. The sample material from the cervix shows during analysis that the leukocytes have moved away from the norm. This condition can be caused by: exocervitis, vaginosis or leukocytosis |
| Koilocytes | Presence of papilloma virus |
| Leukoplakia | Presence of hyperkeratosis (altered cells not related to cancer) |
| Proliferation | Accelerated division of tissue cells is observed, which indicates an inflammatory process up to an advanced stage |
| Metaplasia | Replacement of cells with another type of cellular structure. In some cases it is normal |
| Leukocyte infiltration | Means excess white blood cells |
The role of cytology becomes the reason to submit on time and consists in identifying various diseases and neoplasms. Suffering from various diseases in the pelvic area is always dangerous for the reproductive system, especially if a woman is going to bear a child. Prevention of various types of pathologies depends on the woman’s vigilance and systematic examination in the gynecologist’s office. To accurately confirm the diagnosis, it is necessary to periodically conduct an oncocytology test.
Video: analysis for oncocytology of HPV and pap tests
Analysis for oncocytology of HPV Pap test
Video: what is a smear for oncocytology. How to properly take a smear for oncocytology?
Smear for oncocytology. How to properly take a smear for oncocytology?
Video: liquid oncocytology
Oncocytology liquid