Menopause, like menopause, is a life pattern for women. In this state, global changes occur in the female body. A decrease in the production of sex hormones is accompanied by characteristic changes . They can be either a common occurrence for this condition or a pathology. This is what fluid forms in the uterus, which can indicate a number of serious diseases.
What symptoms may indicate a problem?
The clinical picture of the deviation depends on the sources of its occurrence. For most women, fluid in the uterus detected on ultrasound is the only sign. The rest of the symptoms depend on the type of pathology:
- gray discharge, nagging pain, slight increase in temperature, painful and difficult urination - with a serozometer;
- tachycardia, discomfort in the lower abdomen - with a lochiometer;
- enlarged, spherical uterus, dull pain, delayed menstruation, increased discharge after exercise - with a hematometer.
Pyometra provokes a sharp pain syndrome and purulent discharge with a greenish tint.
Types of fluid in the uterus
The main types of fluid in the uterus are:
- serozometra - formed against the background of tobacco and alcohol addiction, as a result of medical abortion, cesarean section, physical inactivity, rough sexual contact;
- lochiometra - occurs after childbirth, when the outflow of lochia is disrupted due to the closure of the lumen of the uterine cervix;
- pyometra - abortions and diagnostic curettages can provoke the accumulation of purulent exudate, problems with the tone of the muscle walls of the organ.
The formation of hematometra is associated with the postoperative period.
Causes of watery secretion
The development of the pathological process is provoked by alcoholic drinks, hormonal imbalances, nicotine addiction, unhealthy diet, and disordered sexual intercourse. Fluid in the posterior fornix of the uterus begins to accumulate when the ovulation period begins and fertilization occurs. The presence of blood-tainted water means an ectopic pregnancy. The formation of mucus may indicate endometriosis, adnexitis, salpingitis.
The appearance of fluid in the fallopian tubes indicates a previous miscarriage that resulted in infection of the reproductive organ. Often the disease is provoked by an anatomical obstruction, as a result of which the outflow paths of aqueous secretions are blocked. Mechanical reasons for the appearance of mucus in the uterine cavity:
- adenomyosis;
- narrowing of the uterine cervix, connecting its cavity to the vagina;
- polyps and myomatous nodes.
Doctors distinguish several types of fluid composition; each type of mucus has certain reasons for accumulation in the main reproductive organ. There are the following types of watery secretions (the sources that cause their formation are indicated in parentheses):
- serozometer (rough sex, nicotine abuse, alcohol, cesarean section, abortion, sedentary lifestyle);
- lochiometer (after childbirth, a discharge called “lochia” appears due to the lack of normal outflow due to the closure of the cervical canal);
- pyometra (uterine cavity filled with pus formed after an abortion, miscarriage, curettage, a sharp decrease in the tone of the muscle wall);
- hematometer (observed after surgery, mainly abortion or diagnostic curettage).
Fluid in the uterine cavity provokes hormonal dysfunction, inflammatory and infectious diseases. Treatment tactics are determined after diagnosis.
Fluid in the uterus after childbirth
The deviation refers to uncomplicated pathologies that occur after labor.
Norm
The return of the uterus to its normal state due to childbirth lasts about two months. Pronounced involutional processes occur over 48 hours - the organ decreases in volume to almost standard sizes.
Contraction leads to the release of lochia, the color of which depends on the volume of blood collected in the uterus. Long-term recovery is characterized by a gradual change in the color of the exiting liquid - it becomes lighter every day. There is no reason for concern - the condition relates to physiological processes.
Pathology
The problem occurs when there is an obstacle that prevents the lochia from exiting the organ. The cause of dysfunction is:
- small blood clots;
- pieces of placenta or mucous membrane.
The accumulation of fluid in the uterus is formed due to its slow return to its original state. The secretions are not expelled from the body, but are collected inside the organ.
Treatment of fluid stagnation in the uterus
Therapy is prescribed after a full diagnostic examination and requires the close attention of a doctor. An abnormal process can become a harbinger of developing oncology and require complex treatment. Ignoring the recommendations of a specialist leads to the formation of serious complications.
Operation
Fluid accumulation in the fallopian tubes is treated with surgical correction. The resulting scars are removed during surgery; there is no guarantee for a complete recovery. The prognosis depends on the age of the patient - young women tolerate the intervention more easily. To preserve reproductive function, laparoscopy is used; in older patients, removal of the fallopian tube is recommended.
Physiotherapy
The mild course of the disease allows the use of physiotherapeutic techniques. They help get rid of infectious causes of fluid accumulation in the uterus, causing inflammatory processes. Patients are prescribed courses:
- magnetophoresis;
- electrophoresis;
- balneotherapy, wave therapy;
- laser treatment.
In parallel, the patient is recommended to take multivitamin complexes and medications.
Unconventional methods
Home treatment methods are denied by official medicine - their main effect has not been studied, and there is no guarantee of recovery. Alternative techniques are aimed at improving the functioning of the immune system:
- drinking fresh fruit and vegetable juices - beetroot, celery, sea buckthorn to replenish the lack of vitamins;
- the use of decoctions of medicinal herbs - sage, chamomile, boron uterus, calendula.
Passion for folk methods can worsen the course of the disease and cause allergic reactions. Before use, consultation with your doctor is necessary.
Lifespan
With this pathology, life expectancy is reduced for the fetus during pregnancy. But it all depends on the infected factor. Infection or pus in the case of pregnancy leads to serious consequences.
The cause of fluid accumulation during pregnancy is pathology of the placenta. Which leads to the risk of miscarriage. Sometimes this process is physiological.
During a physiological process, life expectancy does not change. Life expectancy decreases depending on the severity of the lesion. With severe damage, the quality and duration of a woman’s life is reduced.
Causes of fluid accumulation behind the uterus
Regular visits to the gynecologist are not a whim of the doctors themselves. All representatives of the fair sex should visit a doctor several times a year. Often women neglect this instruction and come for examination only when any signs appear. However, one should not lose sight of the fact that some pathologies in the reproductive organs may not appear for a long time. This is how the fluid behind the uterus behaves, the detection of which most often comes as a surprise to the woman.
Normal serozometers in postmenopause
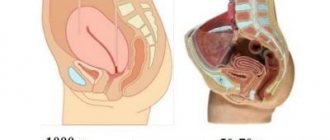
During the postmenopausal period, hormones are produced in minimal volumes, and then their quantity is completely reduced to zero. We are talking about hormones responsible for the reproductive system and fertility of a woman. As a result, the pelvic organs also cease to function normally, gradually decrease in size and seem to fade away. The walls of the uterus, which are smooth muscle tissue during the reproductive period, lose their elasticity during menopause.
Serozometra during menopause is normal and is diagnosed in approximately 40% of women. Therefore, if the cervical canal is not blocked by polyps or any other obstacles, the volume of fluid is small and there are no other complaints, the doctor may not prescribe anything, or simply recommends that the woman regularly attend examinations and be monitored.
Is it possible to cure uterine endometriosis with folk remedies, how effective is it?
When Lactagel vaginal gel is used, you can find out whether there are any contraindications to its use here.
About bakvaginosis in men and women: .
Liquid formations: natural process or pathology?
The presence of free water in the Douglas space is not a disease, but may be a symptom of pathology. Fluid behind the reproductive organ or in the paraovarian areas accumulates in the middle of the menstrual cycle, after the onset of the ovulation process. This is a normal phenomenon and does not require specific treatment. It means the release of the egg from the follicle and the possible occurrence of pregnancy.
Quite often, free fluid behind the uterus is a sign of pathology of a woman’s internal organs. It is extremely difficult to determine the exact volume of such a formation on ultrasound, because it spreads between the reproductive organs. Doctors have developed certain criteria to assess the condition of the fluid in the retrouterine space (the length of the vertical level of the formation is measured):
- accumulation of water up to 10 mm is considered insignificant;
- from 10 mm to 50 mm - moderate stage;
- more than 50 mm - significant.
The volume of water behind the uterus is compared with the woman’s menstrual cycle. If the doctor has suspicions about the cause of the presence of a large amount of water behind the uterus, he may order additional instrumental tests.
Main methods of treatment
Treatment of the disease begins with the evacuation of accumulated fluid if its volume exceeds 5 mm. The operation is mandatory in case of pathological accumulation of watery secretion in the fallopian tubes. Surgery involves removing scar tissue. It is difficult to say how positive the forecast will be. It depends on the age of the patient and the degree of obstruction formed.
If the accumulated fluid is less than 5 mm in volume, the patient is prescribed medication. Conservative therapy consists of the use of drugs that can normalize uterine circulation. Representatives of this group are the following drugs:
Detection of an infectious or inflammatory process involves the use of:
- laser phoresis;
- magnetic therapy;
- electromagnetophoresis.
These treatment methods help get rid of the symptoms of the disease. In the absence of a positive result, if the fluid continues to accumulate, the doctor suggests surgical intervention. If a woman plans to conceive a child in the future, therapy is carried out using endovideosurgical equipment. In other cases, the doctor removes the fallopian tube.
Conservative and surgical treatment methods require increasing the body's defenses:
- It is recommended to regularly consume freshly squeezed juices, fruits, and vegetables that contain the necessary vitamins for the female body.
- Therapy using baths with mustard powder is considered effective. The procedure takes 20 minutes.
- Be sure to use a decoction of chamomile, calendula, and boron uterus. Treatment without these decoctions is impossible.
Ovulation process as one of the reasons
Ovulation is a natural process in which water accumulates in the pouch of Douglas. It does not cause serious problems, since a small amount of liquid is formed. The ovulation process occurs as follows:
- follicles are formed first;
- one of the vesicles outstrips the growth of the others, and the formation of an egg occurs in it;
- liquid formation reaches up to 20-25 mm in diameter;
- then the follicle ruptures so that the egg leaves the membrane and begins to move towards the reproductive organ.
In a healthy woman, the ovulation process occurs monthly. When a cell is released from the follicle and travels to the uterus, this is ovulation. There is fluid in the follicle, but it is very small. If the bubble ruptures, water can enter the abdominal cavity. On an ultrasound, the doctor will see a small amount of it, which is normal. The liquid resolves after a few days and does not cause any discomfort to the woman. In addition to ovulation, the formation of water in the retrouterine space can occur for such natural reasons as early puberty, menstruation.
Treatment methods
The treatment tactics are determined by the attending physician based on test results and instrumental diagnostic methods.
In cases where a small amount of fluid is noted and the cervical canal is narrowed slightly, physiotherapeutic methods, vitamin complexes and drugs to stimulate the blood circulation process are prescribed.
If significant changes are present, medications are used or surgery is prescribed.
Drug therapy
In order to dilate the cervix, the gynecologist may prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs that also have an analgesic effect. The most commonly used are Naproxen, Indomethacin, or diclofenac-based products.
When the cause of the disease is an infectious lesion, based on the results of a laboratory test, the doctor selects an antiviral, antifungal or antibacterial drug.
Effective antibiotics for establishing serozocervix are Valprafen, Amoxicillin, Ornidazole or Moxifloxacin.
For the purpose of the regenerating process in the mucous membrane of the uterus and cervical canal, hormonal suppositories are used. They are administered intravaginally and allow you to quickly restore normal microflora and relieve inflammation.
Surgical intervention
In severe cases, when diagnostic results reveal the presence of a large amount of fluid, surgery is prescribed. The procedure can be carried out in two ways
Laparoscopy
To remove accumulated fluid in the abdominal cavity, the specialist performs several punctures. An endoscope equipped with a camera and lighting device is inserted through them.
The procedure is carried out under the control of an ultrasound machine, which allows the operation to be performed accurately.
The advantages of the method are the absence of large scars on the skin and a short rehabilitation period.
Removing fluid through the incision
The technique is used in cases where serozocervix develops against the background of cysts, fibroids and other formations. During the procedure, the specialist has the opportunity to remove not only fluid, but also tumors of various types.
On this topic
- Female reproductive system
Do I need to remove an ovarian cyst if it doesn’t bother me?
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- December 4, 2021
The disadvantages of the method are long-term rehabilitation, the presence of scars and cicatrices.
Regardless of the method used to remove accumulated fluid, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial therapy is carried out after surgery. This reduces the risk of complications and consequences.
Treating the disease using traditional medicine methods is strictly prohibited, as this can lead to aggravation of the disease.
Formation of hemorrhage in the pouch of Douglas
The fluid behind the uterus may be bloody. This kind of education is not the norm. The occurrence of bloody discharge in the pouch of Douglas means the presence of a pathology that can lead to the formation of apoplexy. Causes of hemorrhage:
- vessel rupture;
- the presence of a follicle cyst;
- ovarian cyst or stroma.
After the integrity of the ovarian tissue is broken, water is released into the abdominal cavity. The formation of bloody fluid in the retrouterine space causes pain, weakness, and dizziness. In this case, the woman experiences discharge of a characteristic color - red or dark brown.
Liquid in the space of Douglas may turn into clots. The main reasons for this phenomenon are:
- permanent injuries;
- hard sex;
- lifting weights;
- hyperemia;
- inflammatory process;
- dilated vessels.
Such pathologies cannot be allowed to occur. If a girl knows about the presence of diseases in the female part, then she should visit a gynecologist and be treated to prevent apoplexy and subsequent penetration of fluid into the retrouterine space.
What exactly changes in the uterus occur in early pregnancy?
Enlargement of the uterus is noticeable at 5-6 weeks of pregnancy. At the same time, its shape changes: from pear-shaped it becomes spherical. By the end of the second month of pregnancy, the uterus increases to the size of a goose egg. The following symptom is also very characteristic of early pregnancy: softening of the uterine tissue, especially in the isthmus area. Strong softening of the isthmus provokes increased anterior bending of the uterus, which is also visible during an in-person gynecological examination.
In the first trimester of pregnancy, the uterus is small and still located in the pelvis. In this case, a woman, especially a primigravida, experiences only a slight increase in abdominal circumference. In the early stages of pregnancy, when the fertilized egg is implanted, a woman may experience scanty bleeding. This may be due to the fact that small pieces of the uterine lining may be shed during implantation. In this case, the woman either does not feel pain, or it is insignificant. This does not bode well, but it is worth informing your doctor, if only because the cause of the discharge cannot be determined without the help of a specialist, and bloody discharge in the early stages of pregnancy may indicate an incipient miscarriage.
In addition, early pregnancy is characterized by mild cramps, soreness, or a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen. Many women in the first or second week of pregnancy notice periodic tingling in the uterus. This is due to stretching of the ligaments of the enlarging uterus.
Early in pregnancy, the uterus may be in a state called hypertonicity (contractions that in some cases can lead to spontaneous abortion). Women describe their sensations with this condition as “heavy uterus”, “stony uterus”, “pains like menstruation”, etc. Hypertonicity of the uterus is not a disease, it is a sign of trouble in a woman’s body, a signal that needs to be responded to urgently, otherwise trouble will not be avoided. There can be many reasons for its occurrence. These include hormonal disorders, the presence of inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs, and the consequences of previously performed artificial terminations of pregnancy. In addition, hypertonicity can signal certain anomalies and malformations of the uterus, and tumor processes. Increased uterine tone must be eliminated, because, as we have already said, in the early stages it can cause the death of the fertilized egg, non-developing pregnancy and spontaneous termination of pregnancy.
Another cause of spotting in the early stages is cervical erosion. After all, now there is increased blood flow to the uterus, and the mucous membrane (which is damaged in this disease and is a kind of wound) begins to bleed. With cervical erosion in pregnant women, blood from the genital tract appears after sexual intercourse or for no apparent reason at all; such bleeding is not accompanied by pain, is insignificant and quickly stops spontaneously. If necessary, the doctor will prescribe a local treatment that does not pose a threat to the fetus, and after birth he will propose a treatment regimen for this disease.
Other conditions for the formation of pathology
The formation of water in the Douglas space is often the cause of some pathological process occurring in the internal reproductive organs of a woman. Doctors identify many diseases that can lead to fluid accumulation. These include the following pathologies:
- inflammatory process in the surface layer of the endometrium (endometritis);
- inflammation in the kidneys, liver, heart failure lead to the formation of ascites, as a result of which free fluid flows into the pelvic organs;
- benign formations characterized by limited growth of the endometrium in the form of a tubercle on a thin stalk;
- an infectious disease accompanied by unilateral or bilateral inflammation of the fallopian tubes (salpingitis);
- adnexitis (inflammation of the ovaries and fallopian tubes);
- oophoritis.
The formation of fluid in the pouch of Douglas may indicate the presence of an ectopic pregnancy, in which a pregnancy test will show a positive result. In addition, this phenomenon causes endometriosis, the appearance of endometrioid cysts on the ovaries, and a condition after an abortion. If you find an accumulation of fluid behind the uterus on an ultrasound, you should not panic. A competent doctor will prescribe appropriate treatment, consult the patient and give recommendations on tactics for the woman’s further actions.
Diagnostics
The specialist prescribes a number of laboratory and instrumental research methods to the woman in order to establish an accurate diagnosis and determine the method of therapy.
First of all, a gynecological examination is carried out, based on the results of which a preliminary diagnosis is established. During the procedure, a smear from the vaginal mucosa is necessarily taken for microflora.
Colposcopy
The examination is carried out using a colposcope. This is a special device that allows you to enlarge the tissues of the cervical canal and study their structure.
The procedure is painless, but some discomfort may occur. Colposcopy allows the gynecologist to obtain basic information about the disease.
Biopsy
It is prescribed for the purpose of taking cervical tissue for the purpose of cytological examination.
The methods allow you to confirm or refute the presence of a malignant neoplasm.
Ultrasound
Transvaginal ultrasound allows the specialist to obtain an accurate picture of the disease and determine the extent of the inflammatory process.
Ultrasound reveals the presence of changes in the tissues of the cervical canal and cervix.
Laboratory research
The woman also needs to have her blood and urine tested. Laboratory tests can determine the presence of tumor markers, hormone levels, and the presence of sexually transmitted diseases.
An accurate diagnosis cannot be established without test results.
Accumulation of fluid in the uterus and behind the body of the organ
Fluid in the uterus or outside its borders means the accumulation of secretion of a liquid consistency of various etiologies. The presence of pathology is determined by ultrasound diagnostics. It is noteworthy that echo signs of free fluid do not always manifest themselves in a clinical picture. Detection of free fluid behind or inside the uterus can only indicate the presence of certain gynecological pathologies. Thus, “fluid in the uterus” or “fluid behind the uterine body” are not separate diagnoses.
After detecting free fluid, it is advisable to conduct an examination to determine the causes of the pathological condition. In some cases, the presence of free contents indicates severe pathologies of the uterus. Sometimes free fluid is associated with harmless physiological processes.
Causes
The reason for the formation of fluid in the uterus is the activity of the glandular structures of the mucous membrane. They produce serous fluid in small quantities. With the development of the inflammatory process, the glands are activated, which, by producing fluid, try to wash away the infection and prevent damage to deeper layers. The mechanism of development of the inflammatory process involves an increase in the amount of fluid, and then its suppuration when an infection occurs.
The source of bloody contents in the uterus can be blood vessels if they are damaged. A significant amount of blood is observed after curettage and childbirth.
The accumulation of fluid in the uterus is sometimes caused by the glandular structures of the cervical canal. With the active production of mucus due to the inflammatory process, an accumulation of fluid may appear in the uterine cavity.
It is noteworthy that fluid accumulates in the body of the uterus when an obstruction occurs along the outflow path. Among the reasons for the accumulation of uterine fluid of a mechanical nature are:
- myomatous nodes in the immediate vicinity of the cervical canal;
- fibroids of significant size, which deforms the uterine cavity;
- polyps of the uterus and cervical canal;
- narrowing of the cervical canal;
- abnormal development of the genital organs;
- adenomyosis and endometriosis.
Fluid may appear behind the uterus, as well as in the tube area. Inflammation leads to changes in blood supply and lymphatic drainage in the pipes. As a result, serous fluid begins to accumulate, causing the development of hydrosalpinx. The tube is stretched and deformed, which leads to a breakthrough into the uterine cavity. If purulent contents accumulate in the tube, pyosalpinx develops. This pathology is dangerous due to the development of purulent inflammation in the uterine body.
Fluid in the uterus can accumulate during an ectopic pregnancy. Fluid behind the uterus may be a sign of an inflammatory process with accompanying symptoms. Often, the accumulation of fluid behind the uterine cavity indicates ovulation has occurred.
The following unfavorable factors contribute to the accumulation of fluid in the uterus:
- bad habits that weaken the immune system and cause hormonal imbalance;
- injury to cervical tissue, in particular the cervical canal, uterine cavity during diagnostic and therapeutic manipulations, which leads to adhesions and scar deformation;
- abortions, which greatly increase the risk of pathology;
- lack of a monogamous lifestyle and the use of barrier methods of contraception, which causes sexually transmitted infections;
- cycle disruption, which is based on hormonal imbalance and improper functioning of the organs of the reproductive system;
- HRT during menopause and the accompanying inflammatory process leading to tissue changes;
- atresia of the internal os in menopause and postmenopause.
Secretion in the uterine body during pregnancy indicates a possible pathology. In early pregnancy, the appearance of free contents in the uterine cavity may indicate an ectopic pregnancy. The presence of blood means the placenta has been rejected.
After childbirth and caesarean section
Lochiometra is considered a complication of the early postpartum period. After childbirth, a gradually healing wound surface remains in the uterine cavity. Thus, tissue regeneration and involution occur, implying the return of the organ’s size to normal.
The processes of involution are most active in the first two days. During uterine contractions, lochia is released, which means postpartum discharge. At first there is quite a lot of bloody discharge. After six weeks, the discharge becomes light and scanty.
Transparent mucus from female organs: what does it mean, photo
Every woman needs to be attentive to her health, because... it is an integral part of a fulfilling life. This is especially true for the female genital organs.
The nature of the discharge is one of the indicators of physiological or pathological processes.
Causes of mucus secretion in women
Normally, women secrete clear mucus from the vagina, but it must have certain characteristics:
- no specific odor.
- quantity – no more than 5 ml per day.
- asymptomatic mucus production - absence of elevated body temperature, pain and discomfort in the lower abdomen, itching, burning and redness.
- Color may vary slightly depending on various factors from white transparent to pinkish. Periodic creamy discharge is also considered normal if it does not cause discomfort to the woman and does not cause pain.
Mucus production begins at puberty and continues throughout life. The discharge contains microorganisms that live in the vagina, mucus from the cervical canal, lymph, and dead epithelial cells. However, the nature of mucus and its absence are influenced by various external and internal factors:
- Period of the monthly cycle - the menstrual cycle is divided into two phases: follicular and luteal. Between them, the process of follicle rupture occurs, which is called ovulation. During these periods, hormone levels change, which leads to an increase or decrease in mucus secretion.
In the first half of the cycle, the discharge is small, liquid and does not stretch. This phase is controlled by the hormone estrogen, the concentration of which invariably increases until ovulation.
During ovulation, the discharge becomes thick and viscous, and the cervical mucus is stretchable. This is the so-called fetal mucus, which is intended for the free movement of sperm to the egg.
In the case of fertilization, the life of sperm is maintained for up to 3-5 days precisely thanks to the fetal mucus.
Sometimes a pink tint of discharge may appear due to rupture of the follicle.
After ovulation, progesterone production begins to increase and before menstruation, mucus in scanty quantities acquires a sour odor and creamy consistency. Immediately after menstruation, there may be no discharge at all for 2-3 days.
- Menopause - during menopause, the amount of estrogen in women's bodies decreases, which means mucus is secreted in smaller quantities, resulting in vaginal dryness.
- Pregnancy - When a woman is pregnant, many questions cause anxiety. The same applies to vaginal discharge, which changes hormonally over the course of 9 months.
Pregnancy usually occurs on the days of ovulation, when the mucus is sticky, viscous and in larger quantities than on other days. This creates favorable conditions for the survival and transportation of male seed.
After conception, copious mucous discharge may initially be white or pink as a result of the attachment of the fertilized egg to the wall of the uterus, and then become transparent. In the second trimester, less mucus is produced.
Before childbirth, discharge in the form of a mucus plug indicates the imminent onset of labor. Premature breaking of water is also accompanied by very thin, watery secretions, which requires immediate medical attention.
- Postpartum – Blood and mucus that is released after childbirth is normal. Every day there are fewer of them and after about a month the discharge disappears or remains transparent without any blood.
- Breastfeeding - breastfeeding is regulated by the hormone prolactin, under the influence of which the level of estrogen decreases somewhat and the mucous discharge becomes scanty.
- Sexual arousal - during sexual intercourse, due to improved blood circulation and blood flow into the pelvis, stimulation of the glands of the woman’s genital organs, lubricant (vaginal mucus) begins to be produced abundantly.
This mucus is sticky, odorless, acts as a natural lubricant and reduces friction during sexual intercourse. Lubricant continues to be released for several hours after sex. An admixture of blood in the discharge may indicate the presence of cervical erosion, which is bleeding, which requires consultation with a gynecologist.
- Stress - exposure to stress, chronic fatigue and excessive physical or mental stress cause significant disruptions, including at the hormonal level. Therefore, after stress, women note not only a decrease in discharge, dryness in the vagina, but sometimes a complete absence of menstruation.
- Taking hormonal medications - oral contraceptives and other hormonal medications reduce the production of mucus in the vagina. White discharge of a uniform consistency and odorless may appear. In the middle of the cycle, a pinkish tint of mucus is allowed, which is called menstrual-like bleeding.
- Age - newborn girls may experience slight discharge from the genital tract. This is due to the influence of maternal hormones received by the baby through breast milk. This symptom does not require treatment and goes away on its own after a few days. In girls under 10-12 years of age, there is no mucous discharge, because an active surge of hormones occurs during puberty. The early appearance of vaginal mucus indicates a disease and requires examination by doctors.
What diseases cause discharge (photos of this discharge)
Various types of microbes (saprophytes) constantly live in the genital tract in small quantities and do not cause harm. They prevent the excessive proliferation of foreign microorganisms and thus perform a protective function.
Mucus from the female genital tract serves as a barrier to infectious agents and blocks the occurrence of inflammation. Sudden changes in the color, uniformity and odor of the discharge are unacceptable, because this indicates an existing disease.
A change in the acidic environment in the vagina leads to excessive proliferation of Candida yeast .
This situation is possible with frequent changes of sexual partners, hypothermia, decreased immunity, and exacerbation of other chronic diseases.
As a result, normally contained fungi begin to multiply rapidly, leading to
thrush .
This disease causes cheesy white discharge, itching and burning in the vagina. When other bacteria grow excessively, bacterial vaginosis . It is also characterized by white discharge, but of a foamy nature and with a specific smell of rotten fish.
The most well-known sexually transmitted infections - trichomoniasis, chlamydia and gonorrhea - can have different clinical courses. In such cases, women consult a doctor when they notice a viscous, creamy discharge from the vagina.
With gonorrhea - with a greenish or yellow tint, with nagging pain in the lower abdomen and painful urination. Chlamydia is characterized by a yellow or dark gray sticky discharge.
Bloody, copious discharge signals a disease in the overlying genital organs - the uterus and ovaries. Endometritis, cervicitis, endometriosis , benign and malignant neoplasms are possible diseases in which scarlet, dark red or brown blood is noted in the mucus discharged from the vagina.
Vaginal discharge, which is accompanied by symptoms such as itching, burning, redness of the genitals, occurs with increased sensitivity to hygiene products, latex (barrier contraceptive material), dyes and flavors in condoms, spermicides and other substances.
Which doctor should I contact and when?
To diagnose and treat diseases of the female genital organs, you should contact a gynecologist. A dermatovenerologist also specializes in the treatment of genital infections if there is damage to the skin and vaginal mucosa.
If there is discharge or other symptoms that raise questions or suspicions in a woman, it is necessary to consult a specialist. Self-prescription of medications is fraught with complications and deterioration of health.
At any period of the monthly cycle, with the exception of menstrual days, you can undergo the necessary examinations and tests. Based on the diagnostic results, the doctor will prescribe treatment.
What to do, what examinations to undergo and how to treat
Diagnosis begins with a consultation with a gynecologist. The doctor determines visually when examining in the mirrors the presence of changes in the vagina.
This may be redness, swelling, white discharge or mixed with blood, creamy discharge with a yellow, green tint, the smell and its quantity are assessed.
From the list of tests, a genital tract smear and flora culture are usually taken to confirm the infectious process and identify the pathogen.
In a blood test using PCR, ELISA, and RIF methods, antibodies to the pathogen are detected. This serves as an additional source in making a diagnosis.
Ultrasound of the uterus and appendages is a very informative method and is usually performed on the 5th day of the menstrual cycle and during the period of ovulation (12-14 days). In the case of sexually transmitted infections, this examination is auxiliary and shows the degree of involvement of the pelvic organs in the process.
Treatment.
Treatment of vaginal discharge depends on the diagnosis, stage and symptoms of the disease.
For candidiasis, antifungal drugs ( Nystatin,
Levorin)
, after taking which the curdled white discharge stops and the microflora is restored. Evidence that the disease has been cured is repeated negative results of a genital tract smear.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eVrvZdiVuXo
For infectious processes, antiseptics, antibiotics in the form of tablets, injections or topical preparations such as suppositories and ointments are prescribed.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are widely used as pain relievers.
After drug control of the infectious agent, the creamy discharge becomes liquid and transparent, and other symptoms gradually disappear.
Hormonal medications are taken by women who have been diagnosed with changes in blood tests for female sex hormones. Taking these medications usually lasts several months.
Prevention and recommendations
There are basic recommendations that it is advisable to follow for preventive purposes to maintain the health of the genital organs:
- the use of barrier methods of contraception when frequently changing sexual partners to prevent infection with sexually transmitted infections;
- observing the rules of intimate hygiene prevents the proliferation of microorganisms and allows you to notice pathological discharge in time;
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle to strengthen the immune system, protect against hypothermia and increase stress resistance;
- regular visits (every 6 months) to a gynecologist in order to be fully examined and treated in a timely manner;
- reasonable use of medications, especially antibiotics and hormonal agents. Only after consultation with a specialist should you begin treatment without prescribing medications yourself;
- giving up bad habits, which invariably affect the reproductive system, preserves the health and reproductive function of the female organs.
The secretion of mucus is a physiological process in the female body. Its consistency changes depending on the action of various factors. Most often this is a clear discharge without color or odor or extraneous symptoms. If additional changes occur in the discharge, you should seek help from specialists.
Source: https://tvojajbolit.ru/ginekologiya/prozrachnaya-sliz-iz-zhenskih-organov-chto-eto-znachit-foto/
Symptoms and diagnosis
Gynecologists emphasize that there are no special signs indicating the presence of fluid in the uterus and behind it. Often the symptoms are due to the cause of the pathological condition. Often, the accumulation of fluid within the uterine body is detected accidentally during an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs.
The clinical picture is determined by the nature of the contents. If there is free fluid in the uterus, a woman may experience the following symptoms.
- Increase in the size of the uterine body. This feature is typical for a significant amount of content. Pathology can be detected by ultrasound examination and palpation during a gynecological examination on a chair.
- Pain syndrome. Usually the pain is nagging or aching in nature. Their occurrence is associated with compression of nerve endings. Sometimes pain is associated with an inflammatory process.
- Pathological vaginal discharge. When the uterine cavity is partially opened, liquid contents seep into the vagina. If the discharge is serous, it is light and watery. Pus refers to the appearance of a thick yellow-green discharge with an odor. Signs of intoxication often appear. Discharge may increase with physical activity and sexual intercourse.
- Cycle disruption. The fluid causes disruption of the processes of rejection of the functional layer of the endometrium. There may also be a delay in menstruation. Sometimes there is an accumulation of blood in the uterine cavity. If hematometra is observed, menstruation is scanty or absent altogether.
The accumulation of lochia has a specific clinical picture. Signs appear in the first week of the postpartum period. The amount of bleeding is sharply reduced. Thus, lochia accumulates, stretching the cavity and causing pain and fever. During the examination, an enlarged painful organ is determined.
The presence of free fluid during an ultrasound examination can be determined by the following signs:
- increase in organ size;
- deformation of the outer contour;
- irregular cavity shape;
- change in the shape of the cervical canal cavity;
- heterogeneity of lochia due to the presence of fragments of the membrane, clotted blood;
- in some cases, ultrasound determines the cause of lochia, for example, polyposis or myomatous nodes;
- in the presence of adenomyosis, foci or heterotopias are visualized.
To identify concomitant inflammation and hormonal disorders, additional diagnostic methods are required. To study the structure of the endometrium, curettage is performed.
In the early stages of pregnancy, the presence of free fluid in the uterus may indicate an ectopic pregnancy. In this case, it is important to perform a dynamic ultrasound, as well as donate blood for hCG every 2 days. The increase in hCG during an ectopic pregnancy may be insufficient. However, there are cases of normal amounts of hCG in ectopic pregnancies.
Sometimes an ectopic pregnancy is not accompanied by a clinical picture for a long time. You can suspect the occurrence of an ectopic pregnancy based on the following signs:
- liquid free contents in the body in the absence of a fertilized egg;
- presence of delayed menstruation;
- positive pregnancy test;
- the emergence of subjective sensations of pregnancy;
- spotting discharge.
Free liquid contents in the organ cavity during menopause often indicate hyperplasia. It is known that in old age, excessive growth of the endometrium is a factor in the development of a malignant tumor.
Is this the norm?
According to numerous gynecologists, only the complete absence of any type of fluid in the area of the uterus and fallopian tubes can be considered normal. However, you should not immediately fall into despair if during the examination it was possible to determine the presence of fluid, since this symptom itself cannot be considered a bad indicator. In order for a gynecologist to be able to accurately diagnose the presence of an inflammatory process in the pelvic area (weight in the area of the uterus or behind it is one of the main signs of pathology), the total volume of fluid should be taken into account, as well as the day of the menstrual cycle. If the fluid in the uterine area is in small volumes, then this phenomenon is not considered a pathology.
In some cases, the presence of a small amount of fluid behind the uterus can be a good sign that a woman has ovulated. This means that the woman should soon become a mother. However, in all other cases you need to be wary; the presence in the uterine area most likely indicates various serious diseases, among which are:
1 Polyps;
2 Endometriosis;
3 Ectopic pregnancy (in this situation there will also be bloody impurities in the fluid);
4 Inflammatory process in acute or chronic form, including in the ovarian area (salpingitis, adnexitis).
As you can see, there are indeed reasons for concern. In addition, after surgery (caesarean section, post-abortion period, laparoscopy), certain deviations also occur. In such a situation, it makes sense to talk about the presence of a pathological process in a woman. If there is a possibility of diseases, then it is necessary to prescribe a puncture - a sample of the existing fluid, which is located behind or directly in the uterine cavity itself. It is recommended to carry out this procedure using laparoscopy.
It is also necessary to know that in some women, fluid accumulation is observed not only in the uterus, but also in the area of the tubes. In this case, it is recommended to prescribe urgent treatment, because if a large amount of fluid accumulates, there is a possibility of pipe rupture. In this case, their contents will spill into the abdominal cavity, peritonitis may occur, which without urgent surgical outcome will cause death.
In addition, it should be noted that even if there is a small amount of fluid accumulated in the uterine area, there is a possibility that the woman has a cancerous tumor. It is for this reason that if the doctor finds fluid in or behind the uterus, this symptom should under no circumstances be ignored; be sure to follow the doctor’s instructions. If we talk about the presence of a malignant tumor, then against its background the woman should also develop other symptoms, thanks to which the gynecologist can assume the presence of cancer. Such symptoms may include the following:
1 The presence of pain in the lower abdomen, which may be accompanied by a feeling of cold;
2 Vaginal discharge that has a foul odor;
3 The presence of unpleasant sensations, feelings of discomfort, painful manifestations are possible during sex.