In a healthy state, the cervix has the classic color of the normal mucous membrane - light pink, uniform. Any deviations from the norm most often indicate some kind of pathological process. So, during inflammatory processes or infections, the mucous membrane becomes hyperemic and has a rich red tint. What do the white spots that appear on the cervix mean? It is quite difficult to unambiguously determine the cause of this phenomenon: the symptom may indicate several diverse gynecological pathologies.
Leukoplakia
Doctors call the detected whitish areas leukoplakia. This is not a separate disease, but only a symptom of some disease, in which some areas of the epithelium have become keratinized. The spots themselves do not cause discomfort, which cannot be said about the pathologies that cause them.
A spot on the uterus is fraught with serious danger - there is a risk of developing an oncological disease called squamous cell carcinoma.
Types of leukoplakia:
Flat. This type of leukoplakia is characterized by flat spots of grayish tints. Their size is relatively small. You can only find out about them by inspection. If nothing is done, leukoplakia can gradually worsen until the disease causing it is discovered.
Warty. In this case, the homogeneity of the mucous membrane is disrupted, and bumps appear. In this case, the white spot on the cervix begins to rise above the healthy areas of the epithelium.
As we have already said, the normal state of the mucous membrane does not imply the presence of white keratinized areas. It is very difficult to reliably determine the causes of leukoplakia. Often we are talking about hormonal imbalance when estrogen levels drop.
Simple leukoplakia is not dangerous - such a spot on the cervix cannot develop into an oncological pathology. Often its appearance is preceded by surgery. And at the site of destruction, a keratinized area remains due to improper tissue fusion.
The culprit of warty leukoplakia is the human papillomavirus (HPV), which in some cases can lead to malignant neoplasms.
White spots on the uterus can appear for a variety of common reasons.
Here are the most common ones:
- immunity disorders;
- failure of the endocrine system;
- infectious gynecological diseases;
- mucosal injuries.
The choice of therapy depends on the degree of leukoplakia, as well as the woman’s age. Before offering treatment, the gynecologist conducts a thorough examination.
It includes:
- tests for infections transmitted through sexual contact (PCR method);
- analysis for the presence of HPV in the body;
- extended examination using a colposcope;
- scraping for a cytogram of white areas;
- bacterial culture;
- biopsy if necessary;
- tests to determine the level of sex hormones.
As soon as the cause of the white spot on the cervix is discovered, treatment will begin immediately. The only way to get rid of plaques is through surgery.
There are several of them:
- radio wave coagulation;
- laser therapy;
- cryodestruction;
- conization.
Sometimes cauterization with chemicals is possible.
During pregnancy, any intervention is prohibited. Treatment for other patients begins 5 days after the end of menstrual flow.
Possible causes of a bluish tint
The shape of the cervical region is like a cylinder with a narrow lumen - the cervical canal. It contains a special mucus that protects the gynecological tract from the spread of germs, such as sexually transmitted diseases. But the integrity of the barrier can be compromised with concomitant gynecological diseases, both infectious and hormonal. A number of infectious and inflammatory diseases may be asymptomatic, but the color of the mucous membrane will be changed due to venous congestion.
A regular annual examination by a gynecologist will allow timely diagnosis of changes in color, consistency, and discharge in the presence of inflammation.
The cervix may be bluish for several reasons:
The cervix reflects the state of a woman's reproductive system.
Based on the color of the mucous membrane, consistency, and the presence of discharge, the doctor assumes the presence of a disease and prescribes a series of studies to verify it.
Pregnancy
One of the likely signs of fertilization and normal development of the embryo is a change in the pink color of the mucous membrane to bluish. As a rule, the cervix acquires this shade at 6-8 obstetric weeks of pregnancy.
The reason for this phenomenon is a change in blood supply under the influence of the hormone progesterone, which is otherwise called the pregnancy hormone. In addition to cyanosis, the doctor diagnoses an increase in the size of the uterine body, its softening and increased mobility.
The most reliable sign of pregnancy is a blood test for hCG, which will show a positive result even before the next menstruation is missed.
Infectious and inflammatory processes
The causes of a cyanotic cervix may lie in an active infectious process occurring in the tissues of the cervical canal, the integumentary epithelium of the cervix, and the uterine cavity. Infections such as chlamydia, urea and mycoplasmosis, herpes simplex viruses, diseases caused by opportunistic flora can cause venous congestion of the lower gynecological tract.
The reason for the change in the color of the cervix from pink to bluish are pronounced infectious processes - endometritis, cervicitis, as well as inflammation of all parts - the ovaries, tubes and uterine cavity.
The vaginal mucosa also becomes bluish.
Factors contributing to the development of inflammatory processes:
- decreased resistance;
- genetic predisposition;
- moderate to severe anemia;
- chronic diseases of the genitourinary system;
- sedentary lifestyle, unhealthy diet;
- hormonal therapy with corticosteroids and oral contraceptives;
- intrauterine contraception.
Warning signs regarding hidden diseases of the genital organs are infertility, menstrual irregularities, periodic aching pain, spotting and acyclic bleeding, and pathological discharge.
Tumors and uterine prolapse
Changes in hormonal levels in a woman’s body can cause the growth of fibroids, which are localized both in the body of the uterus and in the cervical region. The growth of a benign tumor leads to impaired blood circulation in the cervix. Obstruction of the outflow of venous blood leads to a change in the color of the mucous membrane from pink to bluish.
The reasons for the bluish tint of the cervical region with growing fibroids are excessive production of estrogen or disruption of the perception of this hormone by the uterine receptors.
Conditions such as elongation (lengthening and drooping) of the cervix and its prolapse cause the bluish color of the mucous membrane. Signs of the disease include the sensation of a foreign body in the vagina, pain during sexual intercourse, and discomfort.
A bluish color of the cervix can accompany a health and life-threatening condition - cancer.
A malignant tumor completely changes the anatomy of the organ, causing a change in color.
In addition to tumors, the cervical region can acquire a blue color due to endometriosis. The cause of the bluish tint in this case is endometriotic lesions.
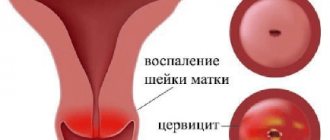
Cervicitis
If you have been diagnosed with cervicitis and during an examination white spots are found on the uterus, the doctor will explain what it is. This pathology means that the cervical canal has become inflamed due to a sexually transmitted infection.
Symptoms of cervicitis are:
- pain in the lower abdomen is predominantly nagging or dull;
- vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor;
- pain during sex;
- painful urination.
A spot on the cervix will indicate that the area of infection has not healed properly. It is very important to start therapy on time using antibiotics and other drugs prescribed by your doctor. It is important that both partners are treated at once.
Characteristics of background processes
Even in teenage girls, the gynecologist can see displacement of the columnar epithelium during examination. After colposcopy, it becomes clear that it is bright red in color. However, it is impossible to paint it with Lugol's solution. This condition is often called pseudoerosion or ectopia. It can be congenital or acquired. But these are not yet precancerous conditions of the cervix, so such erosions do not require treatment. You just need to monitor them regularly.
Cyst
A cyst may form in the cervical canal or in the area of the vagina that is closer to the cervix. Visually, it is similar to protruding white spots on the uterus, since it consists of glandular epithelial cells filled with liquid contents. There can be several cysts at once.
If the size of the tumor exceeds 2 centimeters, then the symptoms will be quite pronounced. Fortunately, this happens very rarely. Still, let's take a look at them:
- discharge of various types is brown, bloody, bloody;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- unpleasant discomfort during sexual intercourse.
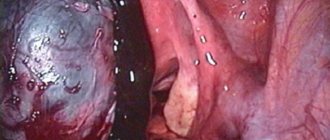
The cyst is easy to detect during an examination by a gynecologist, carried out on the chair, and the ultrasound diagnostic method allows you to study the features of the neoplasm in more detail. A colposcope also helps to carefully examine the white spots on the uterus - what they are and how to treat them. Thus, leukoplakia does not change its color when interacting with iodine. The epithelium surrounding the cysts turns brown.
Alternative medicine
Some are starting to look for alternative methods. The most popular are douching with a diluted infusion of calendula (1 tsp in ¼ glass of water), eucalyptus (1 tsp diluted in a glass of water), tampons with sea buckthorn oil or mummy.
But these are not all the options for how the cervix can be treated with folk remedies. Some healers recommend brewing St. John's wort for douching at the rate of 1 tbsp. l. for a half-liter jar of boiling water. The herb must be boiled for about 10 minutes and infused for at least half an hour.
If you decide to refuse qualified help and are treated with the indicated methods, then regularly visit a gynecologist in order to monitor the condition of the cervix. This is the only way to see the deterioration in time and try to correct the situation.
Papillomatosis
Papillomas are benign tumors formed from altered epithelium due to HPV infection. The virus is transmitted through sexual contact, during medical interventions with non-sterile instruments, and also from mother to baby during childbirth.
The affected area in this pathology is not classified as leukoplakia, although the tips of the tumors are white, so they look like a white spot on the uterus. HPV does not immediately begin to attack, but only when the immune defense weakens.
Papillomas may have sharp ends or may be flat. In the case of recent neoplasms, when the vaginal biocenosis is disrupted and the immune system is suppressed, malignant degeneration is possible.
As papillomas develop, they sometimes form a growth, which is a white spot on the cervix.
Papillomatosis has a number of symptoms:
- unpleasant odor of vaginal discharge;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- itching and burning of the vaginal area;
- bloody contact discharge;
- discomfort in the lower abdomen.
If you notice these symptoms, contact your gynecologist.
If during the examination he sees white spots on the uterus, then further examination will allow him to differentiate leukoplakia and papillomatosis. When the diagnosis is in favor of HPV, treatment is selected based on the following factors:
- woman's age;
- type of HPV;
- results of cytological examination;
- appearance of papillomas;
- state of the immune system.
If necessary, tumors are removed. To suppress HPV, special drugs with antiviral activity are used. Additionally, the patient is prescribed a multivitamin complex. Getting rid of HPV is very difficult, sometimes even impossible, but taking the virus under control is possible.
Causes
An interesting feature of this condition is that it can be both a sign of a serious pathological process and a normal symptom in certain non-pathological conditions. For example, this is normal during pregnancy. For this reason, all reasons that can cause such changes in blood circulation can be divided into pathological and non-pathological. For non-pathological processes, treatment is not required; for pathological processes, in most cases, it is necessary. What reasons can cause cyanosis of this organ?
Pregnancy
Very often, the gynecologist makes the first assumption about the presence of pregnancy based on such a symptom as a cyanotic cervix. This is considered one of the main diagnostic signs of pregnancy during a standard examination by a gynecologist. After this phenomenon is detected, the patient is prescribed ultrasound examinations and pregnancy tests to confirm this condition.
Why does this symptom appear during pregnancy? It is directly related to the action of the hormone progesterone. Moreover, it is present at all stages of pregnancy, since in the early stages progesterone is produced by the corpus luteum in the ovaries, and in later stages by the placenta.
Infections and inflammation
Pathological processes of this nature cause a fairly strong disturbance of blood circulation in the mucous membrane, as a result of which it changes its color and cyanosis of the cervix occurs. It is quite easy to diagnose such a process. Firstly, it is accompanied by characteristic symptoms, such as pain, menstrual irregularities, uncharacteristic discharge, etc. Secondly, you can take a smear from the vagina and/or uterus, which will show the presence of pathology.
The most common conditions that cause cyanosis are:
- Endometritis;
- Cervicitis;
- Inflammation of the tubes/ovaries/uterine cavity.
If no infectious agents are detected as a result of a smear, then the doctor begins to look for other reasons why a blue cervix could occur.
Tumors
The condition can develop in the presence of any neoplasms. The most pronounced cyanosis accompanies cervical cancer, since the oncological process completely changes the anatomy of the organ, including its circulatory system. For this reason, the doctor often takes tissue for a biopsy for this diagnosis - the samples are examined for the presence of atypical cancer cells.
But not only malignant tumors can cause such changes. For example, myomas and fibroids are sometimes also accompanied by the same symptom as endometriosis. Although these conditions have nothing to do with oncology, they are also associated with active tissue proliferation, and therefore affect the circulatory system in the organ.
Organ prolapse
Another fairly serious condition is significant prolapse and prolapse of the uterus. It is due to the fact that the tone of the pelvic floor muscles weakens for one reason or another, the ligaments that fix the organ stretch and lose elasticity, and under the influence of gravity the organ falls down. First, it puts pressure on the vaginal vault, and then, together with the cervix, may fall into it altogether. After this, the organ may even fall out through the genital opening.
It is clear that in this condition the blood circulation of the organ is disrupted, and this is what causes cyanosis.
This condition is quite easy to diagnose, since its signs are obvious. But prolapse in the early stages is more difficult to diagnose, since at first no characteristic symptoms are observed.
Dysplasia
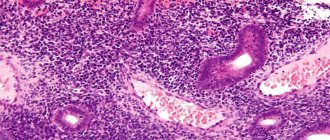
Dysplasia is characterized by changes in the epithelium - excessive growth of its tissues. The disease is considered a precancerous condition. At the initial stage, the pathology can be easily eliminated. Upon examination, the doctor will find flat white spots on the uterus - its cervix, and the mucous membrane will consist of reddened areas.
Dysplasia does not manifest itself in any way. Sometimes spotting and discomfort may occur during sex. This is why it is very difficult to detect dysplasia in a timely manner.
If a woman regularly visits a gynecologist, then she has every chance of not developing a pathology. Dysplasia usually affects women of childbearing age, even during pregnancy. To prevent the altered epithelium and white spot on the cervix from turning into a terrible diagnosis, it is necessary to start therapy on time.
Causes
The squamous epithelium of the cervix consists of four layers. When the lower basal layer is affected by the papilloma virus, the uppermost layer, the superficial one, completely changes, becoming atypical. White spots on the uterus in this area are precisely warty leukoplakia caused by HPV.
The following factors can provoke this problem:
- reduced local immunity;
- bad habits - alcohol, smoking, drugs;
- chronic pathologies of the pelvic organs;
- hormonal disorders;
- specific genital tract infections;
- injuries;
- heredity.
Very rarely, dysplasia disappears on its own, but this is also possible.
Disease Prevention
The following rules will help prevent the development and spread of infectious processes:
- Regular preventive examinations with a gynecologist.
- Timely treatment of various inflammatory processes localized in the pelvic organs.
- An unscheduled visit to the doctor if changes in well-being are detected.
- Related examination and treatment of the sexual partner.
- Using condoms to protect against unwanted pregnancy, avoiding taking COCs and IUDs.
- Elimination of physical inactivity.
- Compliance with the rules of a healthy diet, additional intake of vitamin and mineral complexes in the autumn-spring period.
Most often, the cervix becomes blue during pregnancy, so the discovery of such a change during a gynecological examination is not a cause for concern, but this does not always happen. In some cases, cyanosis of the vagina and cervix signals the development of dangerous changes in the girl’s body and indicates pathological progress. The diagnostic process should begin immediately after identifying the problem.
An interesting feature of this condition is that it can be both a sign of a serious pathological process and a normal symptom in certain non-pathological conditions. For example, this is normal during pregnancy. For this reason, all reasons that can cause such changes in blood circulation can be divided into pathological and non-pathological. For non-pathological processes, treatment is not required; for pathological processes, in most cases, it is necessary. What reasons can cause cyanosis of this organ?
Pregnancy
Very often, the gynecologist makes the first assumption about the presence of pregnancy based on such a symptom as a cyanotic cervix. This is considered one of the main diagnostic signs of pregnancy during a standard examination by a gynecologist. After this phenomenon is detected, the patient is prescribed ultrasound examinations and pregnancy tests to confirm this condition.
Why does this symptom appear during pregnancy? It is directly related to the action of the hormone progesterone. Moreover, it is present at all stages of pregnancy, since in the early stages progesterone is produced by the corpus luteum in the ovaries, and in later stages by the placenta.
Infections and inflammation
Pathological processes of this nature cause a fairly strong disturbance of blood circulation in the mucous membrane, as a result of which it changes its color and cyanosis of the cervix occurs. It is quite easy to diagnose such a process. Firstly, it is accompanied by characteristic symptoms, such as pain, menstrual irregularities, uncharacteristic discharge, etc. Secondly, you can take a smear from the vagina and/or uterus, which will show the presence of pathology.
The most common conditions that cause cyanosis are:
- Endometritis;
- Cervicitis;
- Inflammation of the tubes/ovaries/uterine cavity.
If no infectious agents are detected as a result of a smear, then the doctor begins to look for other reasons why a blue cervix could occur.
Tumors
The condition can develop in the presence of any neoplasms. The most pronounced cyanosis accompanies cervical cancer, since the oncological process completely changes the anatomy of the organ, including its circulatory system. For this reason, the doctor often takes tissue for a biopsy for this diagnosis - the samples are examined for the presence of atypical cancer cells.
But not only malignant tumors can cause such changes. For example, myomas and fibroids are sometimes also accompanied by the same symptom as endometriosis. Although these conditions have nothing to do with oncology, they are also associated with active tissue proliferation, and therefore affect the circulatory system in the organ.
Organ prolapse
Another fairly serious condition is significant prolapse and prolapse of the uterus. It is due to the fact that the tone of the pelvic floor muscles weakens for one reason or another, the ligaments that fix the organ stretch and lose elasticity, and under the influence of gravity the organ falls down. First, it puts pressure on the vaginal vault, and then, together with the cervix, may fall into it altogether. After this, the organ may even fall out through the genital opening.
It is clear that in this condition the blood circulation of the organ is disrupted, and this is what causes cyanosis.
This condition is quite easy to diagnose, since its signs are obvious. But prolapse in the early stages is more difficult to diagnose, since at first no characteristic symptoms are observed.
Treatment
Naturally, everything depends on the pathology, which is evidenced by the resulting white spots on the uterus. This is what the doctor deals with first and foremost. Be sure to restore the vaginal microflora using probiotics and vitamin therapy. Thanks to these measures, the epithelium will recover faster. It is important to assess the woman’s general condition, as well as her predisposition to cancer.
If surgical intervention is necessary, the immune picture is corrected before surgery. Depending on the affected area, a method of removing atypical tissue is selected to capture both the spot on the uterus and the surrounding epithelium. The specialist’s task is to return the cervix to a normal healthy state.
Complications
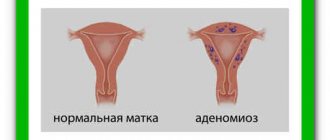
Retrocervical endometriosis, left unattended, can lead to the development of complications requiring longer and more complex treatment. Neglect may result in:
- development of infertility;
- anemia (with prolonged and heavy bleeding);
- adhesions of the pelvic organs (the most common localization is the area of the uterosacral ligaments);
- malignant neoplasm.
Cervical endometriosis is a rare pathology characterized by the formation of endometrial foci outside the uterus. Timely identification of the process and treatment allows the pathology to be eliminated in the short term without harm to the woman’s health. However, advanced disease can lead to unwanted complications. To avoid the development of pathology, periodic visits to the gynecologist are necessary (at least once a year, and the recommended rate is every 6 months). A routine examination can detect most disorders of the reproductive system.