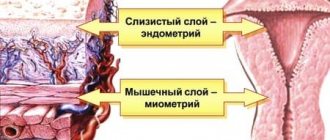
What is the cervical canal
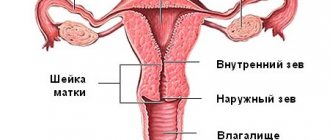
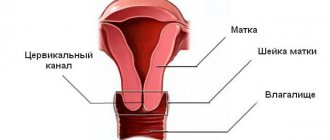
The cervical canal is the canal of the cervix, connecting the vagina and the cavity of this organ. It has two small holes - the internal and external pharynx, the normal diameter of which is 2-3 millimeters. The external pharynx is visible during a standard examination, has a dotted shape if the woman has not given birth, and after childbirth or abortion it becomes slit-like. The layer of mucous membrane covering the cervix is called the endocervix.
Atresia of the cervical canal
A disorder that results in fusion or obstruction of the cervix is called cervical atresia. The disease can be a congenital pathology or acquired as a result of illness or injury. Congenital disorders are cases of abnormal formation and development of internal organs. Acquired atresia in most cases is caused by abortion, cervical cancer, inflammation in the inner and outer layers of the canal tissue.
The cervical canal is closed, what does this mean?
Whether the sperm will pass through to the egg largely depends on the condition of the cervix. When the cervix is completely or partially closed, doctors diagnose stenosis. It can be distinguished by the following symptoms: absence or painful menstruation, infertility, pain during sexual intercourse. A narrow cervical canal and conception are poorly compatible; first you need to eliminate the cause, then carry out bougienage. If you still manage to get pregnant with this disease, there is a high probability of incoordination of labor and subsequent cesarean section.
The cervical canal is dilated, what does this mean?
At any stage of pregnancy, the doctor can report the news that the cervical canal is dilated - what does this mean? This means that the cervix cannot perform its functions of holding the fetus. Enlargement of the cervical canal can be caused by an increased amount of male hormones that soften the cervix, multiple pregnancies, developmental abnormalities and injuries. The following steps can be taken to prevent a possible miscarriage:
- medications are prescribed that strengthen the cervix;
- installation of a special ring, which will be removed only at 37 weeks;
- stitches were placed around the cervix.
Internal os during pregnancy
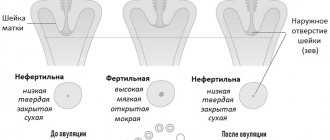
The cervix is a dynamic organ, it changes throughout the entire monthly cycle in a non-pregnant woman, the cervix opens during ovulation and menstruation, and at the beginning of a new cycle the cervix closes and rises. If fertilization occurs, first of all, the appearance and location of the cervix changes: it lengthens and acquires a bluish tint due to increased blood circulation, becoming dense and tight. During the examination, the doctor can accurately determine whether there is a threat of miscarriage; if the cervix is tightly closed, does not allow a finger to pass through, and is also slightly deviated, there is no threat. But if the cervix is partially dilated or loose, hospitalization is necessary to avoid premature birth.
Normally, the length of the cervix changes during the entire period of pregnancy in the following parameters:
- up to 14 weeks pregnancy length is 35-36 mm;
- 10-14 weeks – up to 39 mm;
- 20-24 weeks – 40 mm;
- 25-29 weeks – 42 mm;
- from 30 to 34 weeks it decreases to 37 mm;
- from 35 weeks the length is 29 mm.
A closed internal os of the cervix is important for the correct and safe development of the child, since it:
- promotes retention of the fetus in the uterus until timely birth;
- protects the fetal bladder from infection;
- prevents infection.
During normal functioning of the body, the cervix begins to shorten and expand, and also changes its structure to loose and soft. This allows the fetus to descend in preparation for birth.
If the pregnancy proceeds without complications, the internal os of the cervix should be closed, but there are cases when the os is partially opened, which can cause early miscarriage, infection or premature birth. There may be several reasons why the cervix does not close:
- hormonal changes in the body;
- abortions;
- carrying out conization in the treatment of diseases of the isthmus;
- large fruit, multiple births;
- congenital developmental anomalies.
All this develops isthmic-cervical insufficiency (ICI) - premature expansion of the internal pharynx, due to which the fetus descends into the lower cavity of the uterus, further dilatation and premature birth occur under pressure.
If a pregnant woman experiences symptoms such as heaviness in the lower abdomen; a feeling of fullness in the vagina, heavy discharge, the doctor conducts a gynecological examination using a speculum and prescribes a transvaginal ultrasound, which accurately examines the cervix and determines that the internal os is closed.
Istomico-cervical insufficiency: features of pregnancy and childbirth
In this case, the load on the cervix is greater than in a normal pregnancy, which can also lead to insufficiency. In such conditions, a woman may find out about the diagnosis of ICI during pregnancy when it is already too late.
Pregnancy without complications and pathologies is every woman’s dream. In this case, deficiency begins to develop in the early stages, from about 11 weeks of pregnancy. For example, if the pregnancy is multiple or there is polyhydramnios. The second method of treating ICI during pregnancy is the installation of an unloading pessary, also called a Meyer ring. In cases where a plastic ring is clearly not enough, the following method of treating ICI during pregnancy is chosen: suturing. The internal os of the uterus is narrowed and stitched with non-absorbable threads.
In this regard, a pessary compares favorably with sutures; it can be installed at a later date. If the sutures are not removed at the appropriate time, but due to complications that arise, doctors correct and treat these complications.
Istomico-cervical insufficiency: features of pregnancy and childbirth
Any pathology during pregnancy requires not only timely treatment, but also adherence to one or another regimen. It is very important to get to the maternity hospital in a timely manner, and at the same time be fully armed, that is, at least with your father’s documents: exchange card, policy, passport.
Types and causes of isthmic-cervical insufficiency
ICI is a common cause of miscarriage between 16 and 36 weeks. There are no clinical manifestations of ICI during or outside of pregnancy. Outside of pregnancy, isthmicocervical insufficiency does not threaten anything. When examined in the speculum, a gaping of the external os of the cervix with a prolapsed (protruding) amniotic sac may be detected.
Source
You have JavaScript disabled. Some functions may not work. Please enable JavaScript to access all features.
During pregnancy, all the forces of the female body are aimed at protecting the baby and providing him with the most comfortable conditions for full growth and development. Why is the opening of the internal pharynx dangerous during pregnancy, and what is the reason for this in the early stages?
The internal os is the lower part of the uterus. It is this opening that closes the entrance to the uterus, and therefore normally it must be closed before labor begins. From the moment of conception until the birth of the baby, the tightly closed cavity of the internal pharynx protects the future child from possible external infections. This cavity is a kind of barrier that is necessary in order to protect the fetus at the stage of its growth and formation and prevent possible complications.
It is important to understand that the opening of the internal os in the early stages indicates the risks of a possible miscarriage. After all, if this cavity opens too sharply, then the fetus simply will not stay in the uterus.
The reasons why early opening of the internal os of the cervix most often occurs lies in one of the types of uterine pathologies - isthmic-cervical insufficiency. This disease can be either congenital or acquired as a result of hormonal imbalances. The main problem is that the uterus is not developed enough and is very weakened, and therefore the internal os is not closed tightly enough.
Depending on how long the internal pharynx opens, symptoms may vary. If the opening of the internal os of the cervix occurs at the end of the third trimester, then it is accompanied by cramping pain. This indicates that labor has begun, in
Source
Girls, tell me how critical such an opening is, the length of the neck is 29 mm. The doctor with the ultrasound said to go to the hospital, I called an ambulance and they didn’t admit me, they said everything was apparently closed and since there was no labor activity, there was no need to call an ambulance! The attending physician said a week ago that they don’t deal with cervixes, the only option left is to go to the manager tomorrow. But I’m so scared, nothing would happen while I’m running.
While you are running, I don’t think it will happen, but over time it may get worse, since the baby’s weight increases quite quickly, there is not much time to solve the problem. Although the length of the cervix is 29mm. this is not critical, it is critical when it is less than 20mm. Usually in such cases they either stitch up the neck (I don’t know how long this procedure is done) and I also know that they put a ring on it. In any case, this problem can be solved and there is no need to panic. But you need to see a doctor as quickly as possible, that’s a fact.
Thank you, I’ve been depressed for two days, this pregnancy has been so hard for me that I’m afraid of everything. I'M GOING TO THE DOCTOR TOMORROW.
Thank you, I’ve been depressed for two days, this pregnancy has been so hard for me that I’m afraid of everything. I'M GOING TO THE DOCTOR TOMORROW.
Katya, everything will be fine, the main thing is don’t be shy, ask your doctor everything, I think they will definitely help you. In general, it seems to me that in your case this is not critical, everything will work out without special indications. I think first of all you need to stop tormenting yourself, this will not improve your health. If it’s not too much trouble, let me know tomorrow how it went for you.
I might have been calmer if it weren’t for the doctor, I’ve been observing my cervix from the very beginning and it’s getting worse and worse over time, now I’m 22 weeks. And they told me at the maternity hospital that I needed a ring, why haven’t they offered it to you yet? I don’t notice any tone in myself, my stomach doesn’t hurt. So tomorrow we'll go to the
Source
All rights to materials posted on the site are protected by copyright and related rights legislation and cannot be reproduced or used in any way without the written permission of the copyright holder and placing an active link to the main page of the Eva.Ru portal (www.eva.ru) next to with the materials used.
The editors are not responsible for the content of advertising materials. Certificate of registration of mass media El No. FS77-36354 dated May 22, 2009 v.3.4.115
We really need positive examples, girls. History: late miscarriage on the 21st in 2010. Now I'm 18-19 weeks pregnant, I've had stitches since 14 weeks. Today, on ultrasound, the internal pharynx is open by 18 mm, the length of the neck is 12 mm, that is, it is held in place only by the sutures. Urgent hospitalization. Lie. Tomorrow we will put on a pessary. I'm 36, no children
@@@@@@@@@Only calm. legs up and unload the neck. In general, I would recommend sipping red wine to relax. Do you have any tone?
For me it was not so critical: length 35mm, internal opening 14mm. But this was enough to get into the hospital for 21 weeks and study the topic of ICN there. Conclusion: lie down, avoid tone (magnesium is my everything) and progesterone in any form to strengthen the cervix. My throat closed within a couple of days, and I was quickly discharged, and my cervix is still soft and short, but now at 36 weeks it’s no longer scary. Peace of mind to you and lie down, lie down, lie down @@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@
I was lying with stitches in the maternity hospital, I had a roommate - the dilation and length of the neck was 9mm, they didn’t even put a pessary on so as not to touch the neck. Before that it was 8! miscarriages. So I went to bed at 20 weeks, I just lay there all this time, I couldn’t get up or sit, at 31 weeks I gave birth to a wonderful boy, the day after tomorrow he’s already one year old
In the next ward, the girl was also lying dilated from 25 weeks, so at 35 she was put on her feet, since she can already
Based on materials from pregovetro.ru
Bacterial culture from the throat of the cervix during pregnancy
The study of bacteriological culture from the cervical canal is an important criterion for assessing the health of the genital area of a pregnant woman and choosing treatment tactics. The reason for prescribing this study is the presence of an inflammatory process (increased white blood cells in a regular smear). If the inflammatory process affects the cervix, the disease is called cervicitis (or endocervicitis). If left untreated, the pathology often causes miscarriages and premature births.
- The biomaterial is collected with a sterile stick from the cervical canal - the secretion of the glands and desquamated cells (carriers of microflora).
- Before the procedure, you must refrain from any hygienic manipulations; you should not use intimate creams and vaginal suppositories.
- It is also worth excluding sexual relations (one day before the test) and taking antibacterial drugs (at least 1 week before the test).
As a result of bacterial culture analysis, it is possible not only to determine the type of pathogenic pathogen, but also to determine its sensitivity to antibacterial drugs that will be necessary for treatment.
Timely diagnosis of the condition of the cervix and its pharynx allows you to take the necessary measures in time and maintain the pregnancy.
My miracle is pregnancy. Diary. 27. Day of birth.
For all 9 months, a baby is growing under your heart, surrounded not only by your love and affection, but also by reliable protection from amniotic membranes and amniotic fluid. The amniotic sac forms a sealed reservoir with a sterile environment, thanks to which the baby is protected from infection. Normally, rupture of the membranes and rupture of amniotic fluid occurs before labor (when the cervix is fully dilated) or directly during labor. If the integrity of the bubble was broken before, this...
39 weeks. Childbirth day - continuation. 16:45. I'm being processed. Damn it, I went nuts. I’m having contractions, but here you go, damn it, sit and answer questions, it’s already a system... they don’t think with their heads at all. They also asked “how are the contractions going now?”, I said, well, yes, they are already such decent contractions!!! And to me: “okay, today you will give birth before 23:00.”
39 weeks. Childbirth day - happy ending! And so I began to feel pressure in my lower back, but I was afraid to call a doctor, because I thought that I was confusing something. But when the pressure began to intensify and put pressure on the butt, the husband promptly ran for a doctor. She came, felt, said that she could already feel the head (with hair), but my dilation was only 8 cm and my neck was torn. And I was already starting to really feel pain. Damn, what a relief it is when it’s already starting to hurt. I didn’t care that my neck was breaking...
Should the internal os be closed during pregnancy?
Even during pregnancy, a woman already begins to worry about her unborn child and his health. But if after the birth of a person you can see for yourself that your child is behaving unusually and take care of his health, then until that moment you have to trust professionals in such matters. Unfortunately, even the most qualified and truly good doctors may not be trained to speak normally with people and clearly explain the results of their research to expectant mothers. If, after being examined by a doctor, you still have questions about what it means when the internal os closes during pregnancy, we will help you figure it out.
The internal os is dense connective tissue between the cervix and the uterus itself, which closes the passage to the organ to foreign substances and prevents the baby from being born prematurely. Based on the definition, we can say that a closed internal os is normal for pregnant women until the prenatal period. So the definition of “closed internal os,” as well as “closed internal os during pregnancy,” does not carry any negative meaning. Instead, it means that your baby is safe, secure, and developing normally inside the womb.
The condition of the internal pharynx can be determined in two ways:
- external examination by a gynecologist;
- diagnostics using an ultrasound machine.
Both of these methods are equivalent and a pregnant woman should alternately undergo both hardware and regular examinations by a doctor throughout her pregnancy. This is necessary to monitor the normality of processes occurring in a woman’s body and the development of the fetus.
An examination by a gynecologist takes place directly in the clinic where the pregnant woman is observed in order to monitor the woman’s readiness to bear a child. It is during an external examination that a doctor can quickly and timely determine deviations from the norm in the condition of a woman’s cervix in order to provide quality medical care if necessary. The examination is carried out in a gynecological chair, and the room must be kept absolutely sterile, and gynecological instruments must be disposable.
The ultrasound examination method is aimed both at determining the intrauterine state of the child and the normality of its development, and at diagnosing the mother’s readiness for childbirth and pregnancy. In this case, the woman lies down on a flat surface, and a special mixture is smeared on her tummy to help carry out the procedure. During the ultrasound, you will be able, just like the doctor, to look at the monitor, which will show the condition of your internal organs. And if such a procedure does not give any pleasure to an ordinary person, then a pregnant woman will be able to admire her unborn child for the first time and even take a photo of him as a souvenir.
What are the benefits of hirudotherapy and how effective is it for infertility? Read here.
Isthmic-cervical insufficiency during pregnancy
Every expectant mother dreams that her pregnancy will proceed easily and calmly and end with the birth of a long-awaited baby. But, unfortunately, this is not always the case. Some disorders in the female body can cause a threat of termination of pregnancy in the first trimester, while others, which is even more sad, in the second or even third. And among such problems, which often become the cause of late spontaneous miscarriages or premature births, is isthmic-cervical insufficiency (ICI).
What is ICN and why is it dangerous?
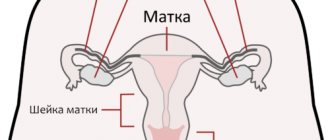
The uterus is a muscular organ that includes the body and cervix. The fetus develops in the body cavity, and the cervix helps hold it and protects it from infection. The cervical canal from the side of the uterine body is limited by the internal pharynx, and from the side of the vagina - by the external pharynx. Normally, during pregnancy, the cervical muscles close into a ring and relax gradually as labor approaches. But sometimes the muscles of the neck weaken earlier than required, and it begins to shorten and open. This condition is called isthmic-cervical insufficiency. It occurs in 1-9% of the total number of pregnant women and in 15-42% of women with recurrent miscarriage. Dilatation of the cervix leads to the descent of the amniotic sac into the lower part of the uterine cavity, as a result of which the membranes of the fetus become infected and open prematurely. Then labor develops, leading to late miscarriage (up to 22 weeks of pregnancy) or premature birth (up to 37 weeks) with the appearance of a premature baby.
Risk factors for ICI
Symptoms and signs of ICN
It is difficult to suspect the development of ICI on your own. In the first trimester of pregnancy, its symptoms are usually absent. In the future, signs characteristic of a threatened miscarriage may appear: a small amount
Source
Hello, Elena Petrovna and girls! Again, I’m creating a post, because I went to the next ultrasound of the cervix and I’m really looking forward to the doctor’s answer, that is, your opinion, Elena Petrovna.
The fourth birth is coming, three babies were born at term, the cervix at the second screening with the third baby was the same length at 22 weeks as it is now at 24 weeks (23 mm), but there was no Y or V shaped expansion of the internal os, at least up to 22 weeks, since no more monitoring was carried out then.
at 20 weeks: the cervix is 28.7 mm long, at the internal pharynx the “V” is figuratively expanded by 8 mm, the length of the closed part is 22.8 mm. The cervical canal is closed. The diameter of the internal pharynx is within normal limits.
At 23-24 weeks: the cervix is 22 mm long, at the internal pharynx the “V” is figuratively expanded by 6 mm, the length of the closed part is 16 mm. The cervical canal is closed, the diameter of the internal os is within normal limits.
What are your recommendations, Elena Petrovna? There are no complaints about my condition. The doctor leading the pregnancy recommends a pessary, I intuitively am against it, I was looking for information and came across your forum. I look forward to your comments! Thank you!
Comments on this post
The only thing that can be recommended to you is vaginal progesterone. However, the diameter of the cervical canal, including the internal os, is allowed up to 10 mm normally. I don’t know how correctly the length of the cervix is measured in your case.
installing a pessary, as I read, is barbaric in relation to the cervix, it’s even worse than climbing with your hands, that’s why I got scared and started looking for information, convinced of my thoughts. In addition, the pessary is applied to the outer part of the cervix, not to the inner os? How will it help in my situation?
Even more interesting:
Sores around the head
Mouth ulcers hiv
Look in this thread Shm 24 mm - I copied links with E.P.’s answers there in the comments. And don’t listen to those who talk about a bad outcome! Everything is in our hands and everything will be x
Source
Possible deviations from the norm and their causes
The cervical canal of the cervix is one of the objects of careful observation by gynecologists when working with pregnant women. This is explained by the fact that not only the birth of a baby depends on his condition, but also the ability to bear a child, because disorders of the cervical canal are often factors that provoke miscarriages and premature births.
The most common pathologies of the canal:
- endocervicitis;
- pathological narrowing of the canal lumen;
- cyst;
- tumor formations;
- isthmic-cervical insufficiency;
- expansion of the internal pharynx, which must be closed.
Endocervix expansion
If the cervical canal is dilated in a patient who is not carrying a baby, then she needs to undergo an examination to identify diseases of the uterine cavity. The reasons for the expansion of the cervical canal are often pathological conditions such as uterine fibroids, endometriosis, cystic ovarian lesions, chronic cervicitis, and adenomyosis. The lumen of the cervix can be enlarged due to the use of hormonal drugs and smoking.
During pregnancy, the natural expansion of the cervical canal occurs before childbirth; it must be open so that the baby can be born. However, if the discovery occurs in the early stages, then there is a danger of miscarriage.
Closed channel
When a doctor determines during diagnosis that the cervical canal is closed, he can assume that the lumen of the cervix is closed. In this case, conceiving a child is almost impossible, since the narrow lumen completely blocks the sperm’s path to the egg.
Canal closure can be either complete or partial. The reasons are:
- operations with curettage of the uterine cavity;
- unprofessional treatment of cervical erosions;
- presence of polyps;
- oncological neoplasms;
- diseases of the mucous membrane of the canal.
Signs of cervical canal infection:
- too little discharge during menstruation;
- pain during menstrual bleeding;
- pain in the groin area;
- heaviness in the vagina;
- pain in the bladder area.
Pathological processes in the female body
The functions of the cervical canal may be disrupted for other reasons. The state of the channel is influenced by both external and internal factors. Common diseases of the cervical canal:
- Inflammatory processes. The mucous membrane of the canal becomes inflamed due to the penetration of sexually transmitted infections, and a disease such as endocervicitis occurs. It can occur under the influence of fungi, viruses or bacterial microorganisms.
- Polyps. These formations are benign, but are often the cause of female infertility. Expectant mothers are sometimes diagnosed with a false decidual polyp. Its appearance is the result of a hormonal deviation from the norm. When the balance of hormones is normalized, such a polyp goes away on its own.
- Cervical tumor formations: fibromyoma, hemangioma, myoma, fibroma. These benign tumors are treated surgically.
Involution of the genital organs
Uterus.
In the postpartum period, postpartum contractions occur, contributing to a significant reduction in the size of the uterus. By the end of the 1st day after birth, if the bladder is emptied, the fundus of the uterus reaches the level of the navel (15-16 cm above the womb). Subsequently, the height of the uterine fundus decreases daily by 2 cm (approximately 1 transverse finger).
The inner wall of the uterus after separation of the placenta and membranes is an extensive wound surface. Epitalization of the inner surface of the uterus is completed by the end of 7-10 days, with the exception of the placental site, where this process ends by the end of 6-8 weeks.
The slow process of reverse development of the uterus is one of the early clinical signs of the pathology of the postpartum period. One of these signs is subinvaluation of the uterus, which can subsequently cause severe purulent-septic inflammatory diseases. An infection in the uterus reduces its contractile activity, thereby causing the spread of the infectious process.
In the first days, lochia (wound secretion of the uterus) has a bright red color, from the 3rd day their color changes and becomes brownish-red with a brown tint, from the 7-8th day due to the abundance of leukocytes they become yellowish-white, finally, from the 10th day - white. The amount of generic secretion by this time is scanty. In general, the amount of lochia in 7 days is about 300 ml.
Cervix.
Involution of the cervix occurs from the inside to more superficial areas. This occurs much less intensely than the involution of the uterine body.
The internal os of the cervix is closed by the 10th day, the external os closes only by the end of the 2nd or 3rd week after birth. However, even after this its original form is not restored. It takes the form of a transverse slit, which indicates a previous birth.
Vagina.
It contracts, shortens, hyperemia disappears, and by the end of the 3rd week it takes on its normal appearance. However, during subsequent births, its lumen becomes wider, and the walls become smoother, the vagina becomes more closed, and the entrance to the vagina remains more open.
Crotch.
If the perineum was not damaged during childbirth, and in case of ruptures it was properly sewn up, it is restored in 10-12 days.
If there is a perineal injury in a postpartum woman, it is necessary to carry out active rehabilitation measures. This need arises due to the fact that, firstly, sites of injury are entry points for infection and can contribute to the occurrence of severe septic complications and, secondly, during secondary wound healing, the anatomy of the muscles and fascia of the perineum is disrupted, and this leads to anomaly development of the genital organs and even disability of women.
The fallopian tubes.
In the postpartum period, hyperemia of the fallopian tubes gradually disappears. The tubes, together with the uterus, descend into the pelvic cavity and by the 10th day they assume their normal horizontal position.
Ovaries.
In the postpartum period, the regression of the corpus luteum in the ovaries ends and the maturation of follicles begins.
For non-breastfeeding mothers, menstruation usually resumes within 6-8 weeks after birth, with ovulation occurring at 2-4 weeks postpartum.
In nursing mothers, ovulation can occur after the 10th week of the postpartum period. In this regard, breastfeeding mothers should be aware that the period of contraception due to lactation lasts only 8-9 weeks, after which the ovulatory menstrual cycle may resume and pregnancy may occur.
Abdominal wall.
The condition of the abdominal wall is gradually restored by the end of the 6th week. Sometimes some separation of the rectus abdominis muscles remains, progressing during subsequent births. Purple pregnancy scars on the surface of the skin gradually fade and remain in the form of whitish wrinkled stripes.
Mammary gland.
The function of the mammary glands after childbirth reaches its highest development. In the first days (up to 3 days) of the postpartum period, colostrum is released from the nipples. Colostrum is a thick yellowish liquid. Colostrum contains, in addition to a large amount of protein and minerals, factors that neutralize some viruses and inhibit the growth of E. coli, as well as macrophages, lymphocytes, lactofferin, and lysozyme. On the 3-4th day, the mammary glands begin to produce transitional milk, and at the end of the first month - mature milk. The main components of milk (proteins, lactose, water, fat, minerals, vitamins, amino acids, immunoglobulins) affect the entire body of the newborn, especially his gastrointestinal tract. It has been proven that children fed with breast milk get sick less often than children fed artificially. Human milk contains T- and B-lymphocytes, which perform a protective function.
Metabolism.
In the first weeks of the postpartum period, metabolism is increased, and then becomes normal. The main exchange becomes normal at 3-4 weeks after birth.
Respiratory system.
Due to the lowering of the diaphragm, lung capacity increases. The respiratory rate decreases to 14-16 per minute.
The cardiovascular system.
The heart takes its normal position due to the lowering of the diaphragm. A functional systolic murmur is often observed, which gradually disappears. Under the influence of external stimuli, there is greater lability of the pulse, and there is a tendency to bradycardia (60-68 beats/min). Blood pressure may be slightly low in the first days, but then reaches normal levels.
Morphological composition of blood.
The composition of the blood has some features: in the first days after birth, the number of red blood cells decreases slightly, the number of leukocytes remains elevated. These changes soon disappear, and the picture becomes normal.
Urinary system.
Diuresis is normal or slightly increased in the first days of the postpartum period. Bladder function is often impaired. The postpartum woman does not feel the urge or has difficulty urinating.
Digestive organs.
Typically, the digestive system functions normally. Sometimes there is intestinal atony, manifested by constipation.
Management of the postpartum period
2 hours after birth, the postpartum woman is transferred to the postpartum ward on a gurney with the newborn. Before transferring a postpartum woman to the postpartum ward, it is necessary to: assess the condition of the postpartum woman (clarify complaints, assess the color of the skin, visible mucous membranes, measure blood pressure, pulse and measure body temperature); through the anterior abdominal wall, determine the condition of the uterus, its consistency, configuration, sensitivity during palpation; determine the amount and nature of discharge from the genital tract. Place a bedpan under the mother's pelvis and offer to empty the bladder. If there is no urination, release urine with a catheter; toilet the external genitalia with a disinfectant solution according to the generally accepted scheme; in the birth history, note the general condition of the mother, body temperature, pulse, blood pressure, condition of the uterus, the amount and nature of vaginal discharge.
Shortened cervix and slightly open internal os
Today I was in the hospital, I am a day patient, 2 weeks ago I had a small spot. 2 weeks ago they did an ultrasound - the cervix is 34 mm, the internal os is closed, now they did an ultrasound - the cervix is 28 mm, the internal os is slightly open by 4 mm, the cervix itself is closed. My stomach doesn’t hurt, I don’t feel any tone, but the doctor won’t be there until tomorrow morning. Duration 15-16 weeks. Girls, who had something similar? What they were doing?
My cervix is now 47mm, and my dilation is already 1 finger, well, about 1-1.5 cm. But this provoked contractions. The first signs began at 15-16 weeks, and at 25 I was again admitted for conservation and also had contractions. Be careful, no stress, more rest, try not to get nervous. And she was treated with genipralol 1t 3 times a day with veropamine. Droppers with magnesium, and magnesium B6 tablets 2t 2 times a day. But it’s better to discuss everything with a doctor
Thank you, of course I'll see the doctor tomorrow, I'm just scared :'(
Galko, I was scared then, but now the best way to calm down and not stress yourself out ahead of time may still work out. Lie down and rest
Galyuny, yes, I definitely need to see a doctor tomorrow, I think it might be worth staying in the hospital, getting some IV drips, in general, when I was in bed, a lot of girls with a similar situation were there, some even had their necks stitched up... Today it’s better not to overexert yourself and sit less! It’s better to lie down and go to the hospital in the morning for a consultation
At 24 weeks I had a cervix of 23 mm, although the internal os was closed! Made it to 41 weeks!! In your case, I think they will offer to put a ring (pessary). Do not worry everything will be alright.
When I was in the hospital, one girl had the same thing; at first they wanted to put a ring on her, but after therapy, it lengthened and everything was fine. She lay there for 10 days and was given injections, the term was 19 weeks, now she is doing well and will soon give birth.
Hello. At 32 weeks, on palpation, my shm was 1.5-2 cm, shortened and soft, and the cervical canal was missing 1 finger, and according to ultrasound, the shm was 3.1 and the internal pharynx was closed, or rather it was 4, just like yours, but at my time this was acceptable. Contact a good specialist. I know that treatment can help and they put rings in, but if they put a ring in, there shouldn’t be any tone, if there is tone, then you need to remove it and then put the ring in. Everything will be fine! The main thing is to believe in it!
Since 19 weeks I have had 2.3.-2. 5 and the internal os was opened... they didn’t do anything, I myself lay down more, didn’t lift anything heavy... now I’m 34 weeks, sm 2.0 in the same internal os. It was also scary, I drank magnesium to make my stomach softer. And now there’s a general lull in everything, I’m probably so healed that I won’t give birth in time...
Galko, here they either observe you and prescribe you a protective regimen and sexual rest, or until 19-20 weeks they put stitches on the cervix, then they are removed shortly before birth, and at a later date an obstetric pessary is placed. It all depends on your condition.
The girl was lying with me, she had a ring inserted at your due date, because... There was a premature birth at 25 weeks. And a miscarriage at 16 weeks... Now on bed rest.
I'm 25-26 weeks pregnant. The length of the cervix today is 2.6 mm, the internal os is funnel-shaped, cerv. the channel is expanded to 2.7 mm. What is the best thing to do in this case? During my first pregnancy I was stitched up at 22-23 weeks, removed at 38 and gave birth at 39 weeks. And now I don’t want to stitch myself up. I read here about an obstetric pessary and I would like to know how long you need to stay in the hospital after it is installed. I wouldn’t want to leave my son without his mother for a long time.
Based on materials from www.my-bt.ru
Norms for the condition of the cervix at different stages of pregnancy
In the early stages of pregnancy and up to the 37th week of the process (individual options for the development of the situation are possible with a difference of several days), the internal os should remain closed. This state of affairs ensures a stable and safe state of the child inside the womb. If, during early pregnancy, the internal os is open, there is a danger of miscarriage, since normally the cervix should open only immediately before birth for the baby to be released into the world conveniently.
After the 37th week of pregnancy, when all the organs and systems of the child are almost completely ready for independent life support, the cervix should normally begin to shorten and open slightly. For the prenatal state, the characteristic length of the cervix is less than one centimeter, and the patency in the area of the internal os should be large enough to accommodate two fingers. If these parameters are met, childbirth will certainly be easy and without complications. If the cervix does not open quickly enough, and the internal os has too dense a consistency, surgical intervention is possible to facilitate the process of the baby’s release.
Methods for correcting deviations in the state of the internal pharynx
There are two gynecological problems associated with the internal os that may bother an expectant woman:
- the internal os is open during early pregnancy;
- the pharynx does not begin to open even at a later stage (more than 37 weeks).
A woman who is at risk of premature birth associated with a slightly open pharynx during early pregnancy, when the fetus has not yet fully formed, should be regularly observed by a gynecologist and follow all his instructions. In especially severe cases, a pregnant woman must be immediately hospitalized and must remain in the hospital until a successful birth. In most cases, doctors successfully resolve this problem.
Find out why Vibrocil drops are dangerous during pregnancy.
What are the chances of pregnancy after hysteroscopy, read here.
If during childbirth the cervix does not smooth out and the passage for the baby is closed, then natural childbirth becomes impossible. In this case, the woman will have to undergo a caesarean section to remove the baby from the womb.
When a woman expecting a child receives examination results with the note: “the internal os is closed,” this means that the pregnancy process is proceeding absolutely normally and the fetus is completely safe in the womb. Otherwise, the doctor will immediately inform you of any problems that have arisen, and together you will find ways to solve them.
Based on materials from moeditya.com
During pregnancy, all the forces of the female body are aimed at protecting the baby and providing him with the most comfortable conditions for full growth and development. Why is the opening of the internal pharynx dangerous during pregnancy, and what is the reason for this in the early stages?
Opening of the internal os in the early stages The internal os is the lower part of the uterus. It is this opening that closes the entrance to the uterus, and therefore normally it must be closed before labor begins. From the moment of conception until the birth of the baby, the tightly closed cavity of the internal pharynx protects the future child from possible external infections. This cavity is a kind of barrier that is necessary in order to protect the fetus at the stage of its growth and formation and prevent possible complications.
It is important to understand that the opening of the internal os in the early stages indicates the risks of a possible miscarriage. After all, if this cavity opens too sharply, then the fetus simply will not stay in the uterus.
The reasons why early opening of the internal os of the cervix most often occurs lies in one of the types of uterine pathologies - isthmic-cervical insufficiency. This disease can be either congenital or acquired as a result of hormonal imbalances. The main problem is that the uterus is not developed enough and is very weakened, and therefore the internal os is not closed tightly enough.
Opening of the internal os during pregnancy: symptoms Depending on the period at which the internal os opens, symptoms may vary. If the opening of the internal os of the cervix occurs at the end of the third trimester, then it is accompanied by cramping pain. This indicates that labor has begun, and in the future this cavity will only expand.
Opening of the internal pharynx with ICI If the opening of the internal pharynx occurs with ICI - isthmic-cervical insufficiency, then it is accompanied by severe pain in the vaginal area. However, the danger is that sometimes the cavity opens almost asymptomatically, and therefore the risk of a possible miscarriage increases many times over. Sometimes, especially when the placenta is poorly attached or is dilated in the early stages, the internal os is sutured to ensure the safety of the fetus.
Thus, opening of the internal pharynx during pregnancy is a harbinger of imminent labor if it occurs shortly before the expected date of birth of the baby, and is also accompanied by cramping pain. But in the early stages this happens due to the fact that the uterus is not developed enough. There is a possibility of miscarriage and the woman must undergo mandatory examination in a hospital.
HCG for hydatidiform mole Hydatidiform mole is a serious disorder during pregnancy, as a result of which the fetus receives exclusively male chromosomes. This anomaly leads. The degree of maturity of the lungs in the fetus One of the indicators that determines how ready the child is for birth is the degree of maturity of the lungs in the fetus, which differs significantly in different environments. Smoothed cervix Throughout pregnancy, a woman’s body gradually changes. The main changes take place in the uterus, which changes shape, size, etc.
Aug 07 2014 09:36 | Katerina in Pregnancy
Group: Participants Messages: 16 Registration: 23.5 User No.: 58 077
Quote(Horli #064; 23.5, 17#58;09)
Hi#33; I have a similar situation, although so far (ugh, ugh, ugh) there is no disclosure#33; At 20 weeks I went for a scheduled ultrasound, and there the doctor was dumbfounded: the cervix is short, the closed part is 11mm. They put him in the hospital. There is nothing to sew up, they put a ring on it. She stayed there for a week and was only allowed out for a walk for 1 hour a day. I went out 2 times. A week later the situation is worse - the closed part is 5 mm, the internal pharynx is 16 mm. After another week, the closed part is 2mm, the pharynx is 22mm. Gloom#33; Well, I started crying. I felt sorry for the baby and myself. They sent me home because... The hospital can't hold it for long. Bed rest, no psychos, at least. no walk. Lie. Once a week, take tests and ultrasound check of the cervix. I have been in bed since April 28th, at home since May 14th. sad and scary#33;#33;#33; In pon och ultrasound. The waters can break at any time. First pregnancy, wildly desired, tortured. I lie there, trying to believe in the best, only the good.
I didn’t have any symptoms either, nothing hurt.
Horli, good luck to you too, stay strong #33;
User Diary Group: Users Messages: 2,597 Registration: 18.3 From: Germany User No.: 26,959
Quote(Lulu1974 #064; 23.5, 10#58;52)
Thank you for your support. I’ve been lying upside down for three days. They also say that this happens if a male child does this.
Our child is not male, but nevertheless we also faced the same problem. At 30 weeks they said that the neck was short 24 mm, at 32 weeks - the neck was 22 mm and opened to the finger. But before that there was pain. as if my period is about to start, and now it hurts at times. Basically, I have been on so-called bed rest since 17 weeks due to low placentation and frequent bleeding because of this. I used to at least go for a walk. It seems like I still have a little bit left, I firmly believe that I will carry it to term and give birth on time. Pregnancy like Horli
the first and long-awaited one.
We all have strength and patience#33; Everything will be fine
May there always be sunshine.
User Diary Group: Users Messages: 1,052 Registration: 21.1 User No.: 46,203
Quote(Malyusya #064; 23.5, 19#58;35)
Our child is not male, but nevertheless we also faced the same problem. At 30 weeks they said that the neck was short 24 mm, at 32 weeks - the neck was 22 mm and opened to the finger. But before that there was pain. as if my period is about to start, and now it hurts at times. Basically, I have been on so-called bed rest since 17 weeks due to low placentation and frequent bleeding because of this. I used to at least go for a walk. It seems like I still have a little bit left, I firmly believe that I will carry it to term and give birth on time. Pregnancy like Horli
the first and long-awaited one.
We all have strength and patience#33; Everything will be fine
I, too, am now in the maternity hospital being preserved, my cervix is 15 mm, the head has already dropped much down, it can be felt during examination. But. I also hope to carry the baby to term and give birth on time, which is what I wish for everyone
How to close the cervix
When the cervix is shortened and partial dilatation is observed, doctors carry out procedures to help close the pharynx. There are several methods to:
- therapeutic;
- conservative;
- surgical.
Medication method
Therapy consists of taking hormonal drugs based on progesterone, which help stabilize the condition and possible closure of the cervical canal. Such drugs include Duphaston, Utrozhestan. Two weeks after prescribing the drug, it is necessary to diagnose the cervical canal to determine the effectiveness of this method; if all is well, the drug is prescribed for long-term use.
Conservative method
It can be used as an aid to drug therapy if ICI progresses or independently.
This method includes the installation of a gynecological ring - a pessary. An oval ring is placed on the cervix so that it rests against the walls of the vagina. This will remove the main load from the internal pharynx.
This method allows you to close the cervix and:
- carried out at any stage of pregnancy;
- does not require the use of anesthesia and hospital observation;
- used for multiple pregnancies.
The ring is used only at the early stage of ICI, when the cervical canal is completely closed.
An obstetric pessary is a foreign body in a woman’s body, so it is important to carry out preventive cleaning of the ring itself and sanitization of the vagina in order to avoid the development of vaginal dysbiosis. There are contraindications for installing a pessary:
There are contraindications for installing a pessary:
- partial opening of the internal pharynx;
- non-developing pregnancy;
- protrusion of the membranes through the internal os;
- the presence of infectious and inflammatory sexual diseases;
- periodic bleeding.
The ring is removed at 37–38 weeks of pregnancy or at the beginning of labor.
Surgical method
It consists of suturing the cervix and thereby compressing the cervical canal. This method is used if there is a real threat of miscarriage and other methods are not effective.
This operation is performed in the early stages of pregnancy and no later than 28 weeks.
It is important that the amniotic membranes are not broken and do not prolapse into the cervix, otherwise infection is possible
Contraindications for suturing:
- there are infectious diseases of the genitourinary system;
- placenta previa;
- pathologies of fetal development;
- severe maternal illness.
Before the procedure, it is necessary to carry out therapy aimed at reducing the tone of the uterus, as well as an ultrasound examination that will determine the condition of the fetus and the location of the placenta. Since suturing is a surgical procedure using anesthesia, inpatient preparation before surgery and observation after surgery are required. It is necessary to undergo a weekly examination by a doctor and periodically sanitize the vagina. Since the suture can provoke increased uterine tone, the use of drugs such as Ginipral and Magnesia and the antispasmodic Papaverine is recommended. Sutures are removed at 38 weeks in the gynecologist's office. This procedure will allow the fetus to descend for further delivery.
Closing the internal pharynx in this way can lead to complications:
- thread cutting through muscle tissue due to stress;
- intrauterine infection;
- bleeding;
- hypertonicity of the uterus.
Ultrasound after childbirth
Ultrasound examination is carried out 2-3 days after birth. This is the easiest way to detect problems in the process of uterine involution. Ultrasound can show the following pathological conditions:
- Deviation of organ sizes from the norm. Too large a size of the uterus indicates problems with its reverse contraction.
- Postpartum endometritis. Ultrasound waves help to see a decrease in the tone of the uterus, expansion of its cavity or accumulation of gases. In this case, the woman requires urgent treatment.
- Postpartum bleeding. According to the results of the examination, the remains of placental tissue or fetal membranes may be clearly visible.
After appropriate therapy, ultrasound examination is repeated to assess its effectiveness.
If the mother’s condition after the birth of the child is normal, an ultrasound scan is scheduled on the third day and is performed using the transabdominal method. If there is a suspicion of problems with the cervix, the doctor may prescribe a transvaginal diagnosis. If a uterine rupture is suspected, an ultrasound is performed 2 hours after birth. On the same day, a study can be carried out on women who gave birth by caesarean section.
After discharge from the maternity hospital, an ultrasound scan is recommended one month after birth. Women who were at risk or had complications should have a repeat procedure 5 days after discharge. It is very important to take time and visit a gynecologist in order to prevent possible complications and take timely measures. If an ultrasound examination shows that the uterus is contracting normally, a preventive ultrasound examination is prescribed after another 6 months.
Cervical erosion during pregnancy
Often a normal pregnancy is unexpectedly complicated by a disease such as cervical erosion. It is possible, of course, that it was there even before pregnancy, but there is a risk that erosion formed during it.
What is cervical erosion
Cervical erosion is a very common disease that occurs at any age. Erosion itself is a defect that occurs on the mucous membrane due to various external influences. For example, after an injury, inflammation, hormonal imbalance, oral contraceptives, etc. Often erosion is a consequence of infectious diseases such as gonorrhea, chlamydia, ureplasmosis, trichomoniasis, etc. Erosion is often a consequence of difficult pregnancy and childbirth, excess weight, and even improper douching.
What is noteworthy is that approximately 70% of women have experienced a disease such as cervical erosion.
Erosion can be true or pseudo (the second name is ectopia). True erosion is a very rare disease, so concepts are often substituted and ordinary ectopia is passed off as erosion. Basically, “erosion” means slight redness on the cervix, but true erosion is much more serious.
Signs of cervical erosion during pregnancy
- Erosion can be detected during a routine examination by a gynecologist in the chair. In order for the diagnosis to be accurate, the doctor will take a scraping. Recently, women who are not pregnant are being referred for a colposcopic examination - it will allow a careful examination of the vagina and walls of the cervix.
- But even before going to the doctor, a woman may feel that something is not right with her body. Signs of erosion are:
- discharge - mixed with blood, especially abundant after sexual intercourse, douching or other mechanical impact on the cervix;
- pain - during sexual intercourse.
But these symptoms are rare. If erosion is just beginning, then it may not manifest itself at all for a long time, and the disease will proceed without symptoms.
Treatment of cervical erosion during pregnancy
Today, experts do not advise young women who have not yet given birth to cauterize erosion, since after such a procedure a scar will form that will interfere with the dilation of the cervix during childbirth. Due to the scar, the cervix can tear and generally cause severe pain when dilated.
Non-pregnant women are advised to undergo laser coagulation - this is a safe and reliable modern method, which in all cases has proven itself to be positive. But still, doctors do not treat cervical erosion during pregnancy. Experts are sure that this is best done after childbirth.
Only if the extent of damage to the cervix causes alarm or its pathological changes are noticeable to the naked eye, then attempts are possible to revive the position and condition - in this case, treatment is selected individually.
Erosion does not affect the baby in any way, just as it does not have any effect on the pregnancy itself.
It will be necessary to cure the disease after your baby is born. By the way, sometimes cervical erosion after pregnancy can go away on its own - without treatment. But you shouldn’t hope for hope; be sure to consult a specialist.
What problems may arise after childbirth
If the uterus decreases in size slowly after childbirth, this indicates hypotension or atony.
In some cases, lochia or parts of the placenta may remain in the uterus. This condition cannot be ignored, so the woman undergoes cleaning - mechanical removal of pathological residues. The problem is usually detected by ultrasound.
A woman may notice increased uterine bleeding, which occurs for various reasons. The release of a large amount of blood is observed both with poor contraction of the uterus and with an infectious process.
One of the common complications is cervical erosion. If the process is not accompanied by infection, doctors recommend continuing dynamic monitoring, since the structure of the cervix can recover after some time. To exclude pathogenic microorganisms, a smear is taken from the cervix, and colposcopy is performed to confirm tissue eversion.
Erosion is often asymptomatic, so a few weeks after giving birth, a woman needs to come for a routine examination so that the doctor can identify the disorder.
In some cases, after childbirth, a complication such as uterine prolapse occurs. It is caused by weakness of the ligamentous-muscular system and is typical for women who have given birth many times.
If lochia continues to be discharged 6 weeks after giving birth, this is not considered normal and the woman should consult a doctor. Early disappearance of lochia can also be a pathology. This condition can occur when there is retention of secretions in the uterine cavity, uterine atony, or blockage of the cervical canal. If its secretion is released, an infection begins to develop in it.
With rapid labor or a large fetus, cervical ruptures are possible, which necessitates the need for sutures.
Endometritis after childbirth occurs when an infection enters the uterine cavity. Symptoms appear a few days after birth. Most often, a woman’s temperature rises, chills, nausea, and increased pulse and heart rate occur. At the same time, she feels severe pain in the lower abdomen, which radiates to the lumbar region. The color and smell of the discharge becomes pathological.
Causes
The uterine sphincter keeps the uterus in good shape, and during the period of bearing a child, it controls that dilatation does not occur before the due time. With ICN, the process is disrupted.
The main reason is cervical injury.
- with a history of abortions or fetal-destroying operations;
- having internal breaks;
- those who have undergone surgical delivery using obstetric forceps or in a breech presentation;
- after surgery on the cervix.
These procedures disrupt muscle fibers, reducing overall tone.
ICI also occurs when the structure of a woman’s reproductive organs is abnormal. Congenital isthmic-cervical insufficiency is rare and can be diagnosed even in a non-pregnant patient; in this case, cervical dilatation is observed at ovulation of more than 0.8 cm.
Other reasons:
- with an increased content of male hormones in the body (hyperandrogenism);
- polyhydramnios – there is additional pressure on the cervical canal and it cannot cope;
- large fruit;
- in patients over the age of 30, the risk of ICI increases;
- conception using IVF;
- observed in patients who engage in heavy physical work during pregnancy.