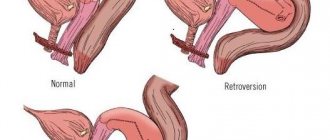
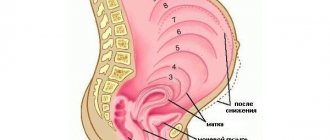
Norms, terms and degrees of maturity
During the course of bearing a child, disruptions occur in the body. Muscle tissue is partially replaced by connective tissue. New collagen fibers begin to form. Unlike the previous ones, they are more flexible and elastic. A small amount is absorbed to form the main substance. You can tell that the cervix is dilating by its appearance. It looks loose, shortened, with a visible canal.
The organ begins to prepare for labor at 32–34 weeks. This is manifested by softness on the outside. The channel remains quite dense. Complete softening of the cervix occurs at 36–38 weeks. The baby enters the pelvis at this stage of pregnancy. Pressure on the reproductive organ increases, forcing it to open.
The process begins with the internal pharynx. The baby moves along the birth canal, which has the shape of a cone with a wide side at the exit. The tissues gradually stretch. For women who give birth repeatedly, the procedure is faster. The canal opens on both sides at the same time; the opening of the cervix is practically not felt during pregnancy.
Immediately before the birth process begins, it becomes exhausted and looks too short. 2 or more fingers will fit inside. However, the action doesn't stop. The limit is considered to be 10–12 cm. This width of the hole is required for the successful exit of the baby’s head. The degree of maturity of the cervix is determined according to the Bishop scale.
There are 3 types:
- immature;
- maturing;
- mature.
The first is characterized by density, length greater than 2 cm, and closedness of the external pharynx. The second corresponds to external softness and internal hardness. Shortening occurs to 1 - 1.5 cm. Half of the path becomes passable. The third type is characterized by softness and the ability to insert 2 fingers.
A couple of hours before the start of labor, cramping pain appears when the cervix dilates. They are not long-lasting, low-intensity, and do not cause structural changes. The normal duration is about 6 hours.
Signs of ICN
It is difficult to consider isthmic-cervical insufficiency in the second trimester of pregnancy. The doctor obtains data from examining the vagina using ultrasound, performing an examination using a speculum. You need to find the problem quickly so that a miscarriage does not occur.
Can you feel the dilatation of the cervix? Yes and no. Some women in labor arrive at the maternity hospital with a 2 cm dilation, feeling nothing. Others experience pain when contracting.
Signs of cervical dilatation in the second trimester:
- bleeding;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- shortening, softening;
- pressure on the vagina;
- on examination the amniotic sac is visible;
- length discrepancy with normal parameters;
- the pharynx is open.
If at least one of these symptoms is detected, immediate treatment is required. Two or more are considered a signal for the woman in labor to be admitted to the clinic. Diarrhea and nausea are also observed when the cervix dilates. Indicates insufficient protrusion of the amniotic sac.
- on top of the internal pharynx;
- on the line of the hole, but invisible to the eye;
- in the canal, visible upon examination;
- moved into the vagina.
What does it feel like when the cervix dilates?
- nagging pain radiating to the thighs;
- feeling of discomfort due to the drooping baby;
- spasms in the vagina.
A gynecologist is able to diagnose ICI having:
- information about previous miscarriages that occurred in the last trimester of pregnancy;
- data on premature termination of pregnancy by labor in the early stages;
- information that conception occurred after IVF;
- results of prolapse of the membranes;
- mirror inspection indicators.
Quite often many signs are absent. Therefore, it is difficult to understand that the cervix is opening. Ultrasound examination is considered the most effective method. The method will promptly indicate the deficiency and also determine why it appeared.
Sometimes women end up in the maternity hospital with an opening of 1 - 2 cm. They are not even aware of the ongoing process. Everything happens unnoticed, and the cervix begins to dilate without contractions. Stretching and tingling are rarely observed.
Causes
Premature dilatation of the cervix in early pregnancy often results in miscarriages. Softening provokes expansion, opening. It is difficult for the fetus to hold on.
There are 2 types of ICN:
What a particular woman will have will be determined by the reasons that formed her. Organic is also called traumatic because it is caused by injury. The cervix loses its elasticity and becomes scarred.
- abortions;
- miscarriages;
- cervical injuries;
- treatment of polyps, erosion;
- scraping.
Scar tissue cannot stretch. It is made up of connective fibers. They are characterized by increased rigidity. The ability to contractility is lost. As a result, the baby is not held inside. The ICN appears.
- changes in hormones;
- polyhydramnios;
- pathologies of the reproductive organ;
- imbalance of tissues.
A large amount of androgen produced or a small amount of progesterone leads to hormone disruption. The consequence is detected at the 11th week of pregnancy. The cervix weakens and opens.
Large accumulation of water is also considered a serious cause. This phenomenon is observed during multiple pregnancies. The load on the reproductive organ increases, and insufficiency occurs.
These reasons contribute to varying degrees of softening. The uterus prepares for childbirth ahead of time and becomes pliable. As the baby grows, the ability to stay inside decreases. Functional failure affects women who have problems with the functioning of the ovaries. Congenital ICI is also sometimes present.
Each woman experiences this disease individually. Instead of one reason, it can be caused by two or more. In any case, it is difficult for the child to hold on, he heads towards the exit. As it goes down, the pressure increases. Low position leads to infection. As a result, a miscarriage or premature labor occurs.
Soft cervix in early pregnancy
Conceiving a child leads not only to changes in the uterus, but also in the organ considered here. The neck will change its color to a bluish tint. This metamorphosis is due to the emerging, more complex network of blood vessels and glands necessary to nourish not only the pregnant woman, but also the new life that has arisen.
The level of tissue density undergoes changes: before fertilization they are softened, but after a special position occurs, the cervix needs to be dense again, thus carrying out a kind of clogging. It should help keep the embryo in the bowels of the uterus. Another function of the object of the article is a barrier that prevents pathogenic flora and infectious strains from penetrating into the uterus.
During this period, a mucus plug begins to form in the object of interest to us, serving as another barrier to threats from the outside. There may be a discharge that resembles a cream and does not have a pathogenic odor. Shades can range from clear, pink hues to reddish and in some cases brown hues. You can safely forget about such symptoms after the 3-4th week of the special situation.
If in the future, in the early stages of a special situation, an undesirable diagnosis is recorded, it is better to begin taking measures to resolve the problem. Since the cervix does not return to its original state after a certain time, clear signs of a threat appear, namely spontaneous abortion. An expectant mother who is in the same position will have to face the emerging threat of miscarriage.
Such clinical pictures can arise in parallel with a number of pathological metamorphoses. A common reason for the appearance of such an undesirable condition of the organ is decreased muscle tone of the tissue. Various factors lead to this pathology. An example of the pathology of the development of the uterus is a hormonal imbalance and injury to the organ due to previous childbirth or abortion.
Treatment
The doctor determines the exact causes of the deficiency, then recommends a course of therapy. For functional symptoms, hormonal medications are often prescribed. They restore hormone levels in 1–2 weeks. After the situation improves, treatment does not stop.
How to check the cervix before childbirth:
- manual inspection;
- ultrasound diagnostics.
It is necessary to observe bed rest when all signs of opening of the cervix before childbirth are observed in a woman in the early stages of bearing a child. The gynecologist recommends complete calm. Any load should be limited.
Conservative treatment methods involve the use of a Meyer ring. The product is made of plastic. Goal: To control the baby's pressure on the cervix. The manipulation is suitable for women in labor with a small opening at a gestational age of 28 weeks or more. Thanks to it, the baby's weight is evenly distributed. This method is used as an auxiliary method.
At an earlier stage, in the absence of infectious diseases, surgical intervention is prescribed. The goal is to place sutures on the cervix so that dilation does not occur until after birth. No discomfort is felt during surgery. Anesthesia is administered in advance. The suture material is removed before labor begins, when the amniotic sac is opened.
Both types of treatment for the disease involve the prescription of antibacterial drugs. They are needed to exclude birth and prevent an infectious process. To enhance effectiveness, antispasmodics are prescribed. Reduce hypertension with tocolytic agents. Hormonal medications are prescribed if an opening is observed due to a malfunction of the endocrine system.
Instrumental diagnostics
Now it is quite problematic to imagine a doctor who does not have methods for modern diagnostics, carried out through innovative medical technological solutions.
Instrumental diagnostics used in this situation may mean:
- Hysterosalpingography. The X-ray diagnostic technique includes the use of contrast agents. The technique allows you to assess the condition of the organs of the woman’s reproductive system.
- Magnetic resonance imaging of organs in the pelvic area, which is an advanced examination method characterized by a minimal level of radiation exposure.
- Ultrasound studies. Echo graphic study.
- Endometrial aspiration biopsy, which involves examining tissue samples taken under a microscope.
- Puncture of the uterine space through the posterior vaginal fornix.
- Scraping.
- Endoscopy, hysteroscopy or colposcopy is an examination technique that includes the use of optical solutions equipped with a lighting device.
Stimulation of dilatation during labor
With a mature cervix, labor begins at 38 weeks and ends with the birth of a baby. Sometimes doctors stimulate the process. Indications are premature, late labor. The onset can be spontaneous, weakly occurring, with an unexpected stop.
How to open the uterus before childbirth:
- by administering medications;
- use amniotomy;
- manually.
The obstetrician notes the weakness of the process, stimulates it, if the reproductive organ stops contracting, contractions are not enough to fully open. The doctor uses medications when 12 hours have passed after the water has broken, and the birth process has not begun. Such stimulation is carried out carefully under the supervision of medical staff. The absence of an allergic reaction to drugs is checked prematurely.
Signs of the need to stimulate uterine dilatation during labor:
- hypertension;
- gestosis;
- early release of water;
- stretchiness;
- weak contractions, complete absence;
- the reproductive organ does not open;
- heart failure;
- placental abruption;
- late toxicosis.
The obstetrician, based on the health status of the mother in labor, makes a decision on stimulation. If symptoms of premature cervical dilatation appear during pregnancy in the third trimester, the doctor will recommend that the woman in labor go to the clinic for a couple of weeks. Medical staff will monitor the condition of the woman and baby. If necessary, uses the surgical method.
The method of amniotomy is widely known. The idea is to pierce the bubble. The main indication for manipulation is suddenly stopped dilatation, which has already occurred by 2 cm. Piercing will speed up labor. The amniotic fluid will recede and the pressure on the pelvic bones will decrease. The method is considered safe and absolutely painless.
Another method of stimulation is to manually dilate the cervix. Special tools are often used - reamers. A prominent representative is an inflatable balloon filled with liquid. He acts on the neck, achieving an opening. When using the method, there is a danger of the bubble bursting. Therefore, it is carried out in case of emergency.
Straightening the cervix before childbirth occurs on the eve of the process. If during the examination the gynecologist discovers that this has not happened, the procedure is performed manually. Sometimes accompanied by severe pain. Manipulation is necessary to facilitate the child's exit.
Signs of dilatation begin unnoticed in many cases. Then a nagging pain sensation appears, the mucous membrane and blood plug come away. The main indicator of approaching labor is uterine contractions. If such symptoms become apparent in the middle of pregnancy, tell your gynecologist. There was a threat of premature birth of the baby.
A baby growing in the mother's womb requires good support. It is created by the cervix, on which the fetus rests during its intrauterine development. Pathologies of this organ can lead to various pregnancy anomalies.
What does this mean?
For normal intrauterine development, it is very important that the cervix is sufficiently firm and dense. It must also be in a closed state. This is very important, especially in the early stages of pregnancy. A softened cervix can lead to the threat of spontaneous abortion.
For many women, the tone of this organ changes significantly closer to childbirth. This reaction is completely physiological. Typically, this condition develops closer to 37-39 weeks of pregnancy. A soft cervix at this time is necessary for the baby to move well through the birth canal during birth.
This pathology can have extremely negative consequences . Experienced obstetricians and gynecologists know how to distinguish a hard cervix from a soft one.
They regularly conduct such research during the entire period of pregnancy. It is necessary especially if a woman has any diseases of the cervical canal or there are concomitant diseases of the reproductive system.
Complications
Any pathology entails disruptions in the functioning of the patient’s body. Complications may be as follows.
- As noted repeatedly above, a miscarriage may occur.
- Doctors may diagnose infertility for similar reasons.
- These complications turn out to be enough for women dreaming of motherhood to think about it and turn to obstetricians and gynecologists.
Why does it appear?
Doctors identify several causative factors that lead to the development of this condition during pregnancy. The most common option is the development of hormonal disorders, which are associated with the different effects of numerous hormones formed during this specific period in the female body.
experience cervical softening The risk of developing this pathology increases significantly if the expectant mother had any problems with the cervical canal or cervix during the previous pregnancy of her first child.
Softness of the cervix before the start of menstruation
Women's bodies are unique in that they are designed for such an important task for humanity as releasing an egg. The egg must be ready for fertilization, gestation of an embryo and the birth of a still small, but potential member of society in the future.
This mission requires the women to train monthly. With each menstrual cycle, the female body has to go through a cyclical path. If the path does not end with ovulation or subsequent pregnancy, the woman will have to face menstruation, which is a discharge of an already “rotten product.” The mucous membrane of the reproductive system is also renewed, preparing the body for the next cycle.
During the stages of the cycle, the density of the placement of the cervix, the uterus itself and other factors change.
The softness of the cervix can be one of the main signals of the observed menstruation. This fact is accompanied by lifting of the segment and its partial opening.
This feature simplifies sperm invasion and subsequent fertilization. If a woman fails to become pregnant, the discharge is recorded. During this period, women may experience much larger cervical discharge.
When fertilization of the eggs does not occur, the uterus and its cervix descend, and the canal begins to expand, which is why softening is observed. This change in the physiological nature of the cervix allows for the unhindered flow of blood released during menstruation.
This is how a woman’s body is able to regulate the process of conceiving a child, or, conversely, in the event of outdated “material” being released.
How is the treatment carried out?
If during a gynecological examination the doctor determines the presence of signs of a softened cervix, then he will definitely recommend that the expectant mother monitor her daily routine. In this case, all physical activity and heavy lifting are necessarily excluded.
A woman should spend more time in bed and rest . For mild violations, doctors will allow the expectant mother to take short walks in the fresh air. They will be useful not only for her, but also for her baby.
Any psycho-emotional stress is excluded. It is strictly forbidden for the expectant mother to worry and be nervous, especially over trifles. This can worsen her well-being and also significantly harm the baby.
If, against the background of severe softening of the cervix, a woman exhibits clinical signs of hypertonicity, then the obstetrician-gynecologist may suggest that she be hospitalized in the hospital. This forced measure will help preserve the life and health of the baby, and will also reduce the likelihood of premature birth.
To eliminate moderate uterine hypertonicity, medications that have an antispasmodic effect are also suitable. “No-spa” is a good remedy for relieving spasms from the smooth muscle muscles of the female genital organs.
In a hospital setting, the woman will receive a range of necessary treatment. Medicines can be prescribed in different ways. Most often they are used parenterally through injections and intravenous drips. Such therapy helps to achieve a good therapeutic result in a shorter time.
To compensate for hormonal imbalances that have arisen, doctors may recommend that the expectant mother use various hormonal medications. One such remedy is Utrozhestan . It is usually prescribed in suppositories. This remedy is prescribed for a complex treatment. When prescribing such hormonal therapy, the doctor must monitor it by conducting regular examinations.
For many women, the soft neck may also shorten. Typically, this condition is registered in pregnant women at 20-28 weeks of pregnancy. In some cases, this pathology may occur later - by 30 weeks.
To eliminate such symptoms, the doctor may recommend that his patient install a special device called an obstetric pessary . In appearance it resembles a regular ring. It is inserted into the cervix and fixed there. This fixation helps secure the fetus and reduces the likelihood of premature birth.
The expectant mother should not be afraid of this procedure if her doctor recommended it. The installation of a pessary does not cause any pain or significant discomfort. The duration of the procedure is usually 25-35 minutes. Doctors will remove the pessary 1-2 weeks before giving birth. This procedure is usually performed in a maternity hospital.
If a soft cervix is one of the manifestations of isthmic-cervical insufficiency, then suturing may be required . This procedure also often causes real panic among expectant mothers.
No need to worry! In this case, stitches are not applied for life, but only until childbirth. This manipulation is forced. Otherwise, there is a high risk of losing the baby or getting a premature birth.
Doctors most often apply sutures for isthmic-cervical insufficiency at 24-26 weeks of pregnancy. These periods are not constant and may vary depending on the initial condition of the expectant mother.
Before carrying out this procedure, the doctor must conduct a thorough extended examination of the genital tract. It is very important that the stitches be applied by an experienced and qualified doctor who has sufficient clinical experience in such work.
Obstetrician-gynecologist V. G. Khorun will talk about isthmic-cervical insufficiency during pregnancy in the next video.
For every expectant mother, the pregnancy period is stressful for the body: hormonal levels change, health worsens, and mental instability appears. All these factors indicate that a woman should pay a lot of attention to the issue of preparing for childbirth. The question of how to soften the cervix immediately before childbirth often worries women. Therefore, we will learn from the material below how to do this and in what cases this procedure is performed.
Soft uterus upon examination, what does this mean?
After hearing the diagnosis, many wonder if the cervix is soft, what does it mean? A healthy woman has a firm neck with a smooth surface and a pale pink color.
At the end of pregnancy, the cervix prepares for delivery and gradually softens.
But such a course of events can start much earlier than the physiological period; in such situations, the soft cervix is treated.
A soft cervix is its natural state during the period of ovulation and some time after fertilization. After one to two weeks it becomes hard again. This creates suitable conditions for the fetus to develop normally. If the pregnancy is proceeding correctly, then the next time a soft cervix is noted is already in the last weeks before childbirth.
Causes
As for the reasons, softening may be the result of pathological changes or be a normal phenomenon.
Pathological changes
Factors leading to changes in the consistency of the cervical region may be the following:
- The use of medications without a doctor's prescription during pregnancy (papaverine, no-spa), which are often used to relieve nagging pain, but have a relaxing effect on the cervix.
- Pathological birth, which was accompanied by deep tears and injuries, resulting in stitches.
- Isthmic-cervical insufficiency is a pathological condition in which the cervical section of the uterus shortens and softens prematurely. This syndrome can be caused by both mechanical and hormonal causes. Mechanical causes imply defects in the structure of the organ: the content of muscle and connective tissue is not proportional in favor of the latter. As a result, the cervix cannot withstand the pressure of the growing fetus. The causes of this condition are congenital defects in the structure of the organ. Hormonal factors that lead to ICI are an increase in the production of male sex hormones in the body of a pregnant woman. 17-OH-progesterone and DHEA sulfate increase. With this cause of ICI, labor may begin prematurely and urgently at 17 or more weeks of gestation. Mechanical causes often trigger labor at 30 weeks or more.
- Inflammatory processes in the female genital area – endocervicitis. As a result, the likelihood of infertility also increases.
- Neoplasms.
- Congenital anomalies of the structure of the internal genital organs.
- Multiple artificial abortions.
Ovulation period
Under the influence of a number of hormones that regulate a woman’s menstrual cycle, the cervix changes its consistency, the width of the cervical canal and the nature of the discharge. The main hormone that has a significant effect on the hardness or softness of cervical tissue is estradiol.
Normally, by the middle of the cycle, its level in the blood increases to its maximum, reaching a peak at the moment of rupture of the follicle - the period of ovulation. The egg passes through the fallopian tube, where it can hypothetically meet a sperm.
In order for sperm to freely penetrate into the uterine cavity, the cervix must become soft and the cervical canal wide.
The time for the release of the egg from the follicle and the softening of the cervix during the average menstrual cycle occurs on days 12–15. If the length of the cycle is not 28–32 days, but 33–45, then the cervix becomes soft on days 17–30.
Course of pregnancy
Often, a soft cervix is observed during pregnancy earlier than expected. This reaction of the body is considered natural only from the 36th week of gestation.
But often ignoring this fact leads to irreparable consequences.
If such a reaction is observed during the formation and growth of the embryo, when pressure is placed on the lower part of the uterus, a course of treatment should be undertaken and this often happens in a hospital setting.
If the muscle tone of the uterus is too strong, then the cervix may open, and this is always accompanied by its softening and shortening.
Such a reaction can be recorded from 20 to 30 weeks, occasionally in the first trimester. In a normal state, softening is noted already before childbirth.
First week after conception
The change in cervical density in the early stages is due to the formation of a more complex network of blood vessels that are responsible for feeding the uterus and baby in the womb. In addition, the corpus luteum of the ovaries does not yet produce progesterone strongly enough, a hormone that ensures the density of the cervical region.
Over time, during a healthy pregnancy, the cervix becomes dense in consistency and also long. The cervical canal closes, and the mucous contents protect the amniotic membranes from the penetration of microorganisms. Sometimes an obstetrician-gynecologist during an examination determines a soft cervix during early pregnancy.
This is a reason to prescribe progesterone drugs.
The period before delivery
A soft cervix before childbirth is considered to confirm the readiness of the female body for childbearing. It is at this point that the organ is no longer able to hold the mucus plug and becomes more susceptible to expulsion of the fetus. At this stage, the cervix is soft, short and opens gradually.
Often, women notice stretching in the lumbar region and the gradual removal of the mucus plug. Such processes, as a rule, are observed from the end of the 37th week, but can also begin at the 39th week.
If the cervical region does not dilate sufficiently, and labor has already begun, then additional stimulation is required.
Softening occurs due to a cascade of reactions that occur at the time of delivery. This process is very complex and begins in advance, covering changes both at the level of the fetoplacental system and at the level of the brain.
Not everyone's neck becomes soft in due time. Often its softening and shortening occurs either too early or does not occur at all. Ultrasound and palpation are used to monitor the cervix.
The gynecologist regularly examines the woman before childbirth, determining her readiness, and takes appropriate measures if any deviations are detected.
Symptoms
Source: https://venyvarikoz.ru/mjagkaja-matka-pri-osmotre-chto-jeto-znachit/
How to soften the cervix before childbirth?
During pregnancy, a pregnant woman's reproductive organ (uterus) undergoes some changes. And if at the beginning of pregnancy the neck of this organ is tightly compressed, then closer to childbirth it shortens, and just before delivery its tissues become softer and more elastic.
The process of softening the cervix occurs under the influence of the hormone prostaglandin, which actively begins to be released just before childbirth. As a result of softening, the cervical pharynx loses its elasticity, and the mucous plug quickly comes off.
For each woman, the period of preparation for childbirth passes at a different speed. It is known from medical practice that it can begin between 35 and 42 weeks.
How to prepare the cervix for childbirth if it is not ripe?
Only a doctor can determine whether the cervix is ready for delivery. During the examination, the gynecologist takes a closer look at its location, hardness, degree of smoothness and patency of the cervical canal. Based on these indicators, it is assessed whether a pregnant woman has an immature cervix, an insufficiently mature or mature cervix.
Routine examinations of the uterus begin at 38 weeks of pregnancy.
If upon first examination the uterus does not show a normal level of maturity, there is no need to worry. Each woman’s body has its own characteristics, and cervical dilatation can occur even during the period of delivery.
In cases where labor dynamics are not observed, the doctor may resort to methods to accelerate the labor process.
The process of preparing the immature cervix before childbirth at 40 weeks, in order to stimulate labor, can only be caused if there are a number of compelling factors, such as:
- Hormone imbalance. Lack of estrogen slows down the process of softening cervical tissue.
- The presence of scars from operations and ruptures. Scars are considered a mechanical obstacle to tissue softening.
- Post-term pregnancy.
- The muscles of the female organ do not have sufficient elasticity. This factor may vary from person to person.
The softening of the tissues of the cervix of the female reproductive organ can be strongly influenced by the nervous background of the pregnant woman. The last prenatal periods of bearing a baby should be characterized by a calm readiness for childbirth. The presence of panic attacks in a woman can cause inhibition of natural processes in the body.
As a rule, doctors do not prepare a woman for artificial childbirth. The doctor cannot always understand why the cervix cannot ripen in due time. However, in medical practice there are certain indications that give permission to accelerate the birth process:
- manifestation of concomitant pathology during delivery, obliging immediate delivery;
- pregnancy is at 42 weeks;
- manifestation of uncontrolled gestosis;
- the fetus develops with a delay;
- there is Rh factor incompatibility between the mother and the child;
- there is a threat to the child’s health;
- the presence of injuries to the cervix received during previous births.
A contraindication to the use of methods of artificially stimulating uterine dilatation is planned and unplanned cesarean section.
Diagnostics
The phenomenon in question can be diagnosed during preventive examinations by gynecologists, during examinations regarding the registration of women with a special situation, or at the stages of monitoring the course of pregnancy. That’s why an obstetrician-gynecologist diagnoses the cervix and identifies this phenomenon.
Soon they may be scheduled for another examination if there is a suspicion of the presence of any of the diseases, the symptom of which becomes the central topic of the article.
The stages of the examination include:
Anamnesis.
Studying complaints if any.
Examination by a specialist using a gynecological chair, which is carried out after the end of menstruation. If there is a suspicion of a special situation, this stage of the examination is carried out only for serious medical indications, so as not to disrupt the development of the unborn child.
Before the start of menstruation, a woman can independently check the condition of her cervix.
But this procedure is done with the obligatory observance of all hygiene rules. Not every woman is capable of weighing such a situation. In this case, it is better to entrust the examination to specialists in this matter.
Research in the laboratory includes:
- Urine analysis of general and biochemical type.
- Blood tests are similar to urine tests.
- Study of secretions.
- Histological studies “if necessary”.
- An examination that always includes the use of modern medical solutions.
- Differential type diagnostics.
- Analyzes
Patients who present with certain problems are prescribed general and biochemical blood and urine tests.
If necessary, studies may be prescribed:
- Blood to determine group and Rh factor.
- Bacteriological and bacterioscopic analysis of vaginal discharge, which is necessary to answer the question about the presence of infections.
- Hormonal level of the pituitary-gonadotropic system.
- Pap test, which means a smear from the vagina. Sample examinations are carried out in a laboratory using a microscope. If uncharacteristic cells are present, the patient is referred for additional examinations.
- If necessary, a biopsy is performed. The goal is to test for the presence of human papillomavirus. The collected swab is sent for polymerase chain reaction (PCR). If the virus is recognizable, its type is determined.
- Immunohistochemistry with tumor markers - this study is prescribed only when malignant pathologies are suspected.
Why does the cervix soften shortly before labor occurs?
The cervix, which has been tightly compressed and hard throughout pregnancy, must soften before natural birth. This is necessary for the birth process to take place successfully. Softening and opening, the cervix allows the fetus to pass through, which must successfully overcome the birth canal and come out. There is no need to worry if the cervix is slow to open. She may behave this way because, out of inertia, she does not want to give up the protective function that she has successfully performed for 9 months.
The gynecologist will quickly be able to understand that the cervix has softened at the next examination. The woman herself cannot always guess that her cervix has softened, since specific signs are usually not observed.
But sometimes it happens that the cervix is in no hurry to soften before childbirth. Therefore, below we will tell you how you can soften it.