What is colposcopy in gynecology? This is a widely used gynecological method for diagnosing diseases of the female reproductive system that generate destructive processes within the reproductive organs.
The lack of a complete information base regarding the usefulness and importance of colposcopy causes unnecessary doubts about the importance of the procedure and the occurrence of possible discomfort as a result of its implementation. That is why there is an increasing need to highlight the main aspects of this technique and its significance in gynecology.
Question: Does your stomach hurt after colposcopy?
The site provides reference information for informational purposes only.
Diagnosis and treatment of diseases must be carried out under the supervision of a specialist. All drugs have contraindications. Consultation with a specialist is required! Can abdominal pain occur after colposcopy?
Yes, after colposcopy, normally for several days a woman may experience mild, low-intensity pain in the lower abdomen, which is nagging, aching and dull in nature. Typically, pain after colposcopy is associated with light discharge from the genital tract, which is dark brown or greenish in color. These discharges are normal, do not require special treatment and go away on their own within 3 to 5 days after colposcopy. Usually, abdominal pain after the colposcopy procedure disappears simultaneously with the end of discharge from the genital tract. When a woman has such mild pain within 3 to 5 days after the test, there is no cause for concern, since this is a normal reaction of the body.
However, if the abdominal pain after colposcopy is severe, combined with heavy bleeding or vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor, high fever and chills, then you should immediately call an ambulance. Such severe abdominal pain is associated with complications of colposcopy, which are very rare. But every woman should know in what situation she may need emergency medical care.
Patients who are scheduled for cervical colposcopy worry not only about the procedure itself, but also about what awaits them after the diagnosis. Numerous forums are filled with rumors about various difficulties that await women: after colposcopy, the discharge does not stop, the menstrual cycle has shifted, inflammation has appeared - and many other stories, most of which have no reasonable basis.
This material will help to get an idea of what the patient can expect and what symptoms should cause alarm.
Vulvoscopy
Due to the fact that various lesions of the vagina and vulva, including malignant ones, are becoming more frequent, timely diagnosis of precancerous manifestations is of enormous importance.
One of the methods of widely available examination is vulvoscopy. Vulvoscopy is carried out using a colposcope, which, under high magnification, allows you to examine the surface of the skin and mucous membrane of the vulva, observe changes, and also take samples for histological studies.
In combination with other methods, vulvoscopy allows you to observe the condition of the vulva and vaginal epithelium. All women with suspected vulvar lesions are prescribed vulvoscopy, which is often used with colposcopy, for identification, monitoring and prevention. In this case, material from the vulva area can be obtained through a biopsy for histological examination.
Purpose of colposcopy
The main purpose of colposcopy is to determine the presence of pathological epithelial cells. Colposcopy is performed in the first phase of the menstrual cycle. Before colposcopy, you must not have sex for two days and not use vaginal creams.
Discharge after colposcopy
Gynecologists explain that discharge after colposcopy should not cause alarm, especially in the first 2-3 days. No matter how minimally traumatic this intervention is, it inevitably causes a reaction of the mucous membranes: the glands that produce vaginal and endocervical secretions begin to function in an enhanced mode under any impact, therefore the volume of secretions increases.
Good to know! Even after sexual intercourse, the mucous membranes of the genital tract produce more mucus.
Normally, the discharge after the procedure is watery or mucous, without clots or inclusions, with a neutral or slightly “medicinal” odor. They may contain blood in the form of veins. Such bleeding is observed for no longer than 3 days.
When conducting extended colposcopy with biopsy within a few days after the examination, a different pattern of discharge is observed:
- in 2/3 of patients, a smear may occur, in which bloody transparent discharge with a watery structure predominates - a sign that the mucous membrane was injured during the collection of biopsy material;
- in patients who have undergone the Schiller test, there is some mucous brown discharge - iodine is present in normal discharge from the genital tract, which stained the cervix.
Normally, the described discharge stops after a few days, but when a biopsy is taken and cauterized, the cervical erosion bleeds for a maximum of 5-7 days.
As for pathological bleeding after colposcopy, it cannot be confused with typical discharge, since not blood-stained mucus is released from the genital tract, but full-fledged blood, as with normal menstrual bleeding. If she wets a sanitary pad in less than 2 hours, you should immediately consult a doctor or call an ambulance.
Types of colposcopy
- Simple colposcopy is an examination of tissue using a colposcope without the use of medications. This technique allows you to determine the condition of the mucous membrane, the presence and nature of defects.
- Color colposcopy. Research using special color filters can be used for a detailed study of vascular architecture (for this purpose, a green filter is used that absorbs red radiation).
- Chromocolposcopy is the treatment of the epithelium with dyes such as hematoxylin, acridine, methylene blue, uranine, etc. This technique is based on the different ability of tissues to stain. for example, when methylene blue reacts to squamous epithelium, the latter is stained blue, the epithelium of oncological formations becomes bright blue, and the columnar epithelium does not stain at all.
- Colpomicroscopy is a method that allows you to examine tissues under multiple magnification (up to 160–280 times), therefore this method in its diagnostic significance is equal to intravital histological examination. After all, this technique allows a specialist to evaluate even the intracellular structures of the upper layers of the epithelium. The method is as informative as possible, but requires special training of a specialist (fundamental knowledge of a pathologist is required).
- Extended colposcopy is a technique using tests that can evaluate the reaction of tissue when exposed to certain substances.
- colposcopy with an acetic test (3% acetic acid) - under the influence of this acid, protein denaturation occurs, temporary tissue swelling appears, and blood vessels contract. The action begins 30–40 seconds after applying the solution and lasts for 3–4 minutes. The reaction of blood vessels to acetic acid is of great diagnostic significance: the wall of normal vessels should decrease in diameter; the walls of pathological vessels (during oncological processes) are not capable of contraction.
- test with iodine solution (Schieler) - under the influence of iodine, the squamous epithelium, which is rich in glycogen, becomes brown. The pathological tissue remains unstained. This test is very easy to use and makes it possible to determine the boundaries of the pathological area.
- test with trichlortetrazole - allows you to detect the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase, as the main marker of cancer.
- Hanse test - with adrenaline (vessels normally react to adrenaline by decreasing their diameter, pathological vessels of neoplasms are not capable of narrowing).
Can colposcopy cause burning and itching?
As a result of a standard examination, burning and itching are not a sign of normality, especially if atypical discharge is present: yellowish or greenish in color, with an unpleasant sour, fishy or putrid odor. However, most often such consequences are observed after an extensive examination, during which Lugol's solution was used. This reagent may irritate the delicate mucous membranes of the genital tract and external genitalia after removal from the vagina, causing an unpleasant itching sensation.
When is it necessary to consult a doctor:
- burning and itching does not stop for more than a week;
- discomfort is accompanied by redness and swelling of the external genitalia;
- abundant cloudy or white discharge with an unpleasant odor appears;
- There is acute pain when urinating.
A vaginal smear for microflora will help to find out the cause of the listed symptoms. Based on the test results, the doctor will prescribe therapy.
The essence of colposcopy in gynecology
Colposcopy is the examination of the cervix by scaling it using specialized equipment - a colposcope. The duration of the procedure is half an hour, so you should not worry about its lengthy nature.
Colposcopy is divided into simple and advanced types of implementation. Simple colposcopy helps to identify defects of the reproductive organ being studied, its shape and parameters. The second type is considered more effective in terms of information content.
To identify the results, Lugol's solution or iodine is used. As a result of its application, a characteristic change in the color parameter of the marked area occurs, which indicates the normal state of the area under study. Otherwise, the examination revealed the presence of affected tissue. To improve the visual effect of the results obtained, light filters are widely used.
If pathological symptoms are detected during diagnosis, a biopsy procedure is performed. This surgical intervention is characterized by relative safety and absence of pain. There may be mild discomfort, but it is quite tolerable. In the absence of a vaginal biopsy, local anesthesia is used.
The effect of colposcopy on menstruation
When carrying out diagnostics, this method does not affect the sex glands (ovaries), which are responsible for the regularity of menstruation, therefore, after the procedure, hormonal imbalances leading to a delay or early appearance of menstrual bleeding are excluded. However, some patients experience that their cycle shifts. There are reasons for these phenomena, and they are worth considering in more detail.
Can colposcopy provoke menstruation?
Gynecologists unanimously claim that colposcopy is not able to provoke menstruation. In most cases, bleeding that occurs on the first day after the procedure is a consequence of additional manipulations performed as part of the examination:
- taking a biopsy;
- “cauterization” of erosion;
- conization of the cervix.
If the wound surface is treated poorly with coagulators or the result of such manipulations may be bleeding. In intensity and pain, it is very similar to normal menstruation. This type of bleeding is not normal and requires treatment.
Can menstruation be late?
A delay in menstruation is possible, but the reason for its occurrence may have nothing to do with the procedure. Most often, a delay in menstruation is a consequence of stress, because most women are afraid of the procedure and also worry about its results. Pregnancy occurring in the middle of the cycle can also provoke disruption of the menstrual cycle.
Important! If menstruation is delayed by 7 days or more, it is first recommended to take a pregnancy test, and only then make an appointment with a gynecologist with complaints about the delay.
DISCHARGE IN THE FORM OF BLEEDING
The appearance of bleeding after colposcopy indicates one thing: a complication has arisen. This complication is often provoked by a specialist who, during the examination, damaged the walls of blood vessels or injured the cervix. If, after completing the study, a woman detects blood discharge from the vagina, then it is necessary to contact the doctor again and inform him about the problem, which should not exist. If the specialist who conducted the examination refuses to help, then you need to contact the manager or the head physician.
The appearance of short-term bleeding is allowed only if therapeutic actions were carried out simultaneously with the diagnosis. It is important to remember that such discharge should not be abundant, which can lead to blood loss and cause deterioration in health.
Bleeding from the vagina can be provoked by electrocoagulation or cauterization of erosion. In this case, the woman is faced with the appearance of pain in the lower abdomen, which has an aching and pulling character, like before menstruation. If bleeding occurs due to medical intervention, then the doctor needs to warn the patient about this. Electrocoagulation involves cauterizing the area where erosion begins to develop.
After detection of erosion and coagulation, the woman needs to remain under the constant supervision of a doctor. To stop bleeding, vaginal tamponade is performed. A woman should remain in the hospital until heavy bleeding from the vagina continues.
It is necessary to consult a doctor again in the following situations:
- 1. If vaginal discharge is abnormal.
- 2. The occurrence of nagging pain in the lower abdomen that lasts more than a day.
- 3. Increased body temperature, general malaise and weakness.
It should be noted that complications after completion of colposcopy are very rare. If this happens, the woman should receive emergency care to prevent serious blood loss and progression of the pathological condition. Only the help of a qualified specialist will avoid unpleasant consequences and complications. Therefore, if you find bleeding, do not hesitate to inform your doctor about it. Liquid vaginal discharge is not dangerous, so it is allowed to last up to 5 days. Trying to stop bleeding at home is prohibited, as the consequences may shorten your life.
The colposcopy procedure is not mandatory, but if women do not undergo such an examination, the risk of developing pathologies increases. The technique is a simple and quick procedure, the duration of which does not exceed 20 minutes. The study makes it possible to timely identify the initial stage of cervical cancer and begin its timely treatment. Women who are familiar with the procedure know that it is absolutely painless and safe. This is confirmed by reviews from women, which are often only positive. Exceptions are cases when, after a colposcopic examination, women experienced discharge. What kind of discharge is this and why this happens, we will find out in this material.
Are there any restrictions after colposcopy?
After the procedure, the patient will learn from the gynecologist about what is possible and what is not possible after colposcopy. Until complete recovery and cessation of discharge, it is recommended to use sanitary pads. They should be changed after every trip to the toilet. To avoid complications, it is important to maintain intimate hygiene, wash yourself at least 2 times a day with warm water and soap.
To reduce discomfort, you can use NSAIDs or antispasmodics. It is important to remember that this should be done under the supervision of a doctor.
The standard list of prohibited actions includes the following restrictions:
- being in conditions with elevated temperatures - baths, saunas, beaches, open sunny places;
- water procedures - it is not advisable to visit the pool after colposcopy, take a bath, or swim in open water until complete recovery (at least a week);
- hygienic procedures - douching should not be done after colposcopy of the cervix for 7-10 days, and you should not use hygienic tampons;
- Sexual life - for 10 days after colposcopy you cannot even have protected sex.
Also, after colposcopy, you should not do cupping massage on the lumbar region, ride a bicycle or lift weights. All these activities cause blood flow to the pelvic organs and can cause bleeding.
After the procedure
Indications for a colposcopic examination are determined by the attending specialist.
So the question of when and for what symptoms a colposcopy can be done should be answered by a gynecologist at an appointment. Colposcopic examination is a procedure necessary to examine the cervix, as well as the vagina and surface of the vulva. The examination is carried out using a colposcope. The excellent multi-magnification ability of this microscope allows the gynecologist to examine the uterus more closely.
How often can a colposcopy be done? According to certain medical indications. Let us remind you that an examination with a colposcope is carried out by a doctor only if there is an indication for the procedure. These include:
- diagnosis of cervical cancer, including during pregnancy;
- diagnosis of cancer of the vulva, vagina;
- precancerous condition of the vagina, vulva or cervix;
- detection of formations on the uterus in pregnant women;
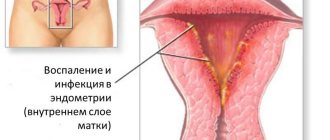
- inflammatory processes in the cervix;
- the presence of warts on the genitals;
- fungal infections on the vaginal mucosa;
- monitoring changes in affected areas;
- for cervical erosion, colcoscopy is also performed.
If a potential patient is thinking about the question of which day of the cycle a colposcopy is performed, it should be noted that the optimal time for an examination is the first three days after the end of menstruation. In some cases, colposcopy can be performed on other days of the cycle, which is usually warned about by the attending physician.
It is worth noting that conducting a colposcopic examination in pregnant women is one of the mandatory procedures. The fact is that various kinds of pathological changes in the cervix are diagnosed in a large number of female representatives.
Very often observed pathologies are a consequence of decreased immunity. During pregnancy, they can progress and develop.
This, in turn, will negatively affect the health of the expectant mother and her child. A contraindication to performing extended colposcopy is only intolerance to acetic acid or iodine by the patient’s body in some cases.
Quite often, after a colposcopic examination, slight vaginal bleeding may be observed, there may also be a delay in menstruation after colposcopy, and some patients have a stomach ache after colposcopy.
In these cases, you should use sanitary pads for several days. The discharge is associated with the treatment of the cervical mucosa with special solutions that are used during extended colposcopy.
The examination is carried out by a gynecologist in a special treatment room with a colposcope. This is a special system on a tripod with illumination and the ability to additionally magnify the image with lenses up to 15-40 times.
The device is placed at a distance of approximately 20-25 cm from the cervical area. All areas of the cervix are examined by rotating special screws on a microscope.
Colposcopy is performed before two-handed examination and other procedures in the gynecologist's chair, but in this case, the discharge is first removed from the surface of the cervix.
During the research process, it is possible to conduct a targeted biopsy of particularly suspicious areas and establish an accurate diagnosis.
Colposcopy is a painless procedure, although it may cause some discomfort when processing reagents or taking a biopsy.
Colposcopy is performed outside of menstruation, preferably immediately after or before menstruation.
On the eve of the study, you should stop having sexual intercourse, using lubricants and douching.
Before the procedure, you can take paracetamol to facilitate the examination process.
On average, the examination takes 20 minutes, before which you need to undress from the waist down and lie down on a gynecological chair.
The doctor will conduct a visual examination of the vagina and cervix by inserting speculum into the vagina. The speculum will remain in the vagina during the procedure. During the process, the walls and cervix will be irrigated with saline to prevent the mucus from drying out.
After a general examination of the cervix with a microscope, it is treated with acetic acid - this can be unpleasant and may resemble a burning sensation. In a couple of minutes, inspection and further processing with Lugol with glycerin will begin.
If a biopsy is necessary, the doctor will take a piece of tissue no larger than 2-3 mm with a special tool; this may cause short-term discomfort. If necessary, the doctor will also perform curettage of the cervical canal, which gives a pulling discomfort due to cervical spasm.
After colposcopy, it is necessary to wear panty liners for about 3 days; there may be slight spotting bleeding due to damage to blood vessels. There may be liquid discharge that is dark or green in color and odorless, but this is acceptable.
After colposcopy, sexual intercourse, douching and the use of tampons, vaginal preparations and intimate hygiene products are prohibited for 5 days.
Can the procedure cause negative consequences?
Various complications after colposcopy, if the doctor’s recommendations are followed, are extremely rare. The most common consequences of the procedure:
- exacerbation of thrush after colposcopy;
- inflammation of the cervix;
- reactive or allergic cystitis.
The main reasons for the occurrence of such complications are associated with poor personal hygiene and early onset of sexual relations after diagnosis.
A complication such as bleeding occurs due to overheating of the body, heavy lifting or rough sex. In extremely rare cases, bleeding occurs due to the death of the fertilized egg (early miscarriage). This usually happens if the procedure was done while planning a pregnancy, and a biopsy was required to make a diagnosis. The incidence of complications associated with medical error, infection or gross trauma to the cervix is less than 1%.
Colposcopy is a modern standard gynecological procedure for examining a woman's vagina, cervix and vulva. To carry it out, the gynecologist uses a colposcope with a special lighting and optical system. Such a procedure is usually recommended if the doctor discovers a pathological condition of the cervix, vagina during a routine examination, or a cytological smear is abnormal.
However, there are cases when cancer can be suspected colposcopically in the absence of patient complaints, and if cytology and visual examination of the cervix are normal. That is, colposcopic signs appear much earlier than cytological, and, moreover, visual ones. This is a very valuable method to detect cancer at a very early stage and cure it. This procedure should be included in the mandatory examination of all women registered at the antenatal clinic (fibroids, endometriosis, etc.).
Ideally, colposcopy should be performed at least once a year on absolutely all women. Abroad, this procedure is performed on women annually, but a cytology smear is taken every 5 years (colposcopy is cheaper).
During a colposcopy, your doctor may find any growths and take a biopsy for a thorough laboratory diagnosis of abnormal cells. Before primary colposcopy, most women are worried because they have insufficient information about the essence of this procedure and the results of such diagnostics.
What are the indications for the procedure?
Colposcopy is a modern diagnostic that makes it possible to identify a number of pathologies in the field of gynecology, and therefore has an impressive list of indications.
Only a doctor prescribes an examination for certain indications.
If the cytology smear is negative or genital warts are detected, the doctor prescribes colposcopy. Patients with certain symptoms may also be referred for examination:
- with the appearance of vaginal itching and uncharacteristic discharge;
- if a woman suffers from prolonged pain in the lower abdomen;
- in case of vaginal bleeding that is not menstrual;
- with bloody discharge and pain during sex.
The purpose of such a diagnosis?
Very often, precisely with cervical erosion, colposcopy is an important diagnostic procedure. It is used to promptly diagnose and promptly treat diseases of the female genital organs such as:
- Genital warts, papillomas
- Cervical cancer
- Precancerous conditions of the vulva, vagina, cervical tissue
- Cervicitis - inflammation of the cervix
- Cancer of the vagina or vulva
- Cervical polyps
Therefore, the indication for the procedure is any deviation from the norm during examination or smear analysis, and there are no contraindications for its implementation, except for the period of menstruation. Based on the diagnostic results, the doctor prescribes appropriate treatment.
How is vulvoscopy performed?
The beginning of the procedure is not much different from a regular gynecological examination. The patient is asked to remove clothes below the waist and sit on the gynecological chair. Further examination is carried out in several stages:
- Examination of the genital organs at low (8x) magnification using a calcoscope.
- Examination of tissues using medical solutions of iodine and acetic acid.
- If necessary, a histological examination of epithelial tissue is prescribed if lesions are detected.
Preparation for cervical colposcopy
As a rule, it is recommended to carry out the procedure after the end of menstruation in the first 2-4 days. If an examination is scheduled and the woman begins to have menstrual flow, the procedure should be rescheduled. To prepare for cervical colposcopy you should:
- 2 days before colposcopy you should abstain from sexual intercourse
- The same applies to the use of various suppositories, sprays, vaginal tablets, if the doctor did not recommend using anything specifically.
- Do not use intimate hygiene products, but wash your genitals only with water.
- You cannot do douching yourself a few days before colposcopy, especially since douching itself is not a safe method of treatment (see All about douching - harm or benefit, how to do douching).
- No painkillers are required before colposcopy - this is an absolutely painless examination, the same as before an examination by a gynecologist, speculums are simply inserted, and the cervix is examined under magnification, nothing touches it.
How is colposcopy performed?
The colposcopic picture can be influenced and distorted for the worse by factors such as mucus and palpation of the uterus and appendages, therefore:
- The doctor removes the mucus from the cervix and treats it with vinegar and Lugol, always with a cotton swab and not a gauze swab.
- Colposcopy is done before palpation of the uterus and appendages (the same applies to the exclusion of sexual intercourse the day before).
Colposcopy can be extended or simple.
Simple colposcopy - when the examination is performed immediately after removal of discharge from the surface of the cervix.
Indications
Video colposcopy is performed if the following diseases are suspected:
- malignant and benign formations of the uterus or vaginal cavity: oncology, polyps, papillomas, condylomas, cysts;
- pathologies of mucous surfaces: dysplasia, leukoplakia, cervicitis, erythroplakia, erosion;
- endometriosis of the cervix and/or retrocervical space;
- hyperplasia of the uterine cavity and/or cervical canal.
Video colposcopy is also performed to monitor postpartum or postoperative ruptures or scars.
Contraindications
There are no direct contraindications to video colposcopy, but in most cases, gynecologists avoid performing this type of examination during menstruation or in the presence of an acute inflammatory process in the vagina.
A conditional contraindication for colposcopy is the integrity of the hymen (hymen). In this case, the research is technically possible, but it is not resorted to unless absolutely necessary.
What can the results of cervical colposcopy mean?
If the doctor finds changed areas during extended colposcopy, then in some cases a biopsy is taken. In case of cervical erosion (ectopia), the affected area is not stained with Lugol; this only proves the presence of ectopia and a biopsy is not indicated. But if:
- pathologically altered vessels are visible (tortuous, intermittent, comma-shaped, etc.)
- punctation - these are dotted inclusions in an area not stained by Lugol
- mosaic is in the form of a quadrangle in various shapes, again on an unpainted area
- whitish areas without changes - leukoplakia
then a biopsy is required.
Even if changes are detected, the doctor will not be able to make a diagnosis based on appearance alone; everything will depend on laboratory data after 2 weeks. When a histological analysis reveals tissue changes, then additional examinations and therapy will be required based on the results of the analysis.
Survey results
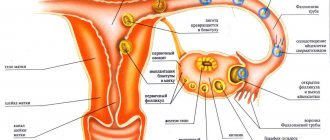
The key task of colposcopy is to identify foci of epithelial cell degeneration. Such cellular structures can develop into diseases that pose a threat to the patient’s life. This is the most accurate and fastest, completely safe way to identify internal pathologies. Normally, the cervix is pink and has a smooth, even, shiny surface without the slightest sign of change. The shape of the external pharynx is round or slit-like, the cervix is conical, not hypertrophied. The border between columnar and squamous epithelium is clear.
Atypical changes during colposcopy include: an abnormal vascular pattern, the presence of reddish spots or iodine-negative areas. The discovered benign transformations are most often ectopia, erosion, formations that appeared during colpitis, diathermocoagulation. Precancerous conditions are defined as an atypical epithelial surface of different widths, while the mucous membrane has pronounced keratinization. In the case of intraepithelial cancer, vascular atypia is observed, in microcarcinoma - heterogeneity of the relief, chaotic arrangement of blood vessels.
You can have a standard or extended colposcopy inexpensively at a self-supporting clinic on Yunosheskaya. The medical institution offers an expanded range of gynecological services.
What should not be done after colposcopy and biopsy?
If there was a colposcopy without a biopsy, then you can do whatever you want.
And if the colposcopy was with a biopsy, then after the procedure it is possible:
- after a biopsy, a woman may have nagging pain in the lower abdomen for 4-10 days
- scanty greenish or brown discharge appears (see Brown discharge in the middle of the cycle). Don't panic, these are normal variants.
To avoid complications after colposcopy with biopsy, you should follow some rules within 2 weeks:
- Avoid sexual intercourse
- You cannot douche, use tampons, and only use pads
- You should not drink medications that contain acetylsalicylic acid.
- Limit any heavy physical activity or exercise
- You cannot visit the bathhouse, sauna, avoid taking a bath, you should only take a shower
Colposcopy during pregnancy and biopsy
Pregnancy is not a contraindication for colposcopy. Because it is a painless and safe method. Colposcopy has only one contraindication - menstruation.
But it’s better not to do a biopsy, because:
- This can cause bleeding, miscarriage, and premature birth, especially in situations where placenta previa is detected.
- And not only for this reason, but also because of possible false-positive results of pathological changes in the cervix under the influence of hormones during pregnancy.
- In addition, treatment, if anything, is still not possible until the woman gives birth (an exception may be cervical cancer, and even then advanced).
Therefore, most often, doctors do not perform a cervical biopsy during pregnancy and postpone the procedure until after childbirth. Colposcopy without a biopsy during pregnancy is safe and even if changes in the cervix are detected, already 6 weeks after the birth of the child it will be possible to repeat the colposcopy and perform the necessary biopsy.
What is colposcopy
This method allows you to identify the very initial tissue defects that cannot be seen without a colposcope (small erosions, atypical vessels, microtumors), early diagnosis of precancerous conditions is possible, so colposcopy has become widespread in the practical work of gynecologists and oncologists.
This research method allows:
- identify the localization of the pathological process;
- determine the nature of tissue damage;
- assess the need for a biopsy of the altered tissue area;
- identify the most suitable site for biopsy (if necessary);
- determine the optimal method of treating this pathology;
- evaluate the quality of treatment.