The concept of “ovulation”
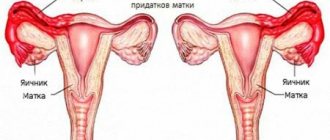
In a normal menstrual cycle, ovulation occurs on days 13-15 from the first day of menstruation. The result of this process is the transportation of an egg ready for fertilization into the fallopian tube. The duration of the ovulatory stage is about one hour, the ability to conceive lasts one day. There is an ovulatory period, during which the release of the female reproductive cell is possible. Physically, a woman does not feel the moment of ovulation; it is only possible to calculate it during a regular cycle. But scientific research has identified the causes of the condition when a woman’s back tightens after ovulation.
What can be done to relieve pain?
There are many ways to eliminate the discomfort that occurs after ovulation. Traditional medicine and traditional therapy offer their own methods, and there are also recommendations that women make on their own.
Herbal medicine
has good effectiveness indicators . Regular use of decoctions of St. John's wort, chamomile or calendula not only has a healing effect, but also makes the natural process of releasing an egg from the follicle less painful.
Methods for diagnosing ovulation
There are several simple methods for determining the presence of ovulation that are available to every woman.
- basal temperature chart is the resting temperature measured during the menstrual cycle with a mercury thermometer in the rectum in the morning of each day immediately after sleeping in bed. A sign of egg release is an increase in temperature during the ovulatory period;
- a cycle of functional tests - a symptom of the “pupil” (opening of the cervical canal under the influence of female sex hormones in the first phase of the menstrual cycle; the study is carried out by examining the internal genital organs in the mirrors), “fern” (crystallization of cervical mucus, which can be observed under a microscope), stretching of vaginal discharge at the maximum concentration of estrogen hormones;
- calendar method - ovulation occurs approximately in the middle of the cycle (with a 28-day cycle - on the 14th, with a 30-day cycle - on the 15th day);
- ultrasound examination of the uterus and its appendages with folliculometry three times per cycle - proliferation, ovulation, secretion phases. A sign of ovulation is the disappearance of the dominant follicle and the appearance of fluid in the pouch of Douglas;
- ovulation tests - first of all, it is necessary to calculate the expected day of rupture of the dominant follicle, add and subtract 2-3 days (for example, with a 28-day cycle, ovulation is expected on the 14th day, following from this, the woman will do tests on the 12th, 13, 14, 15, 16 days). These tests are based on measuring the amount of luteinizing hormone in the urine, the concentration of which increases maximally one day before ovulation.
What pains are not normal?
It is not difficult to distinguish the normal state after ovulation from deviations in the functioning of internal systems. If a woman has formed a cycle , and the symptoms do not change from month to month, then the signs of the release of an egg from the ovary are well known to her. The exception is girls at a young age, whose menstruation occurs with disruptions in the cycle. The younger the body, the more painful the symptoms of the ovulatory period will be.
The following types of pain cannot be normal:
- spasms that restrict movement;
- attacks accompanied by loss of consciousness or vomiting;
- painful spasms that do not stop for a long time;
- the presence of severe bleeding (not to be confused with the characteristic brown discharge).
The concept of “ovulatory syndrome”
Sometimes women after ovulation have lower back pain, they feel discomfort in the ovarian area, engorgement, tenderness of the mammary glands, and discharge from the genital tract. These signs indicate the presence of ovulatory syndrome. This is a condition after a small concentration of blood enters the abdominal cavity after the release of the egg from the dominant follicle. The rupture of the ovarian membrane, the subsequent movement of the reproductive cell through the fallopian tube, is accompanied by pain on the side of ovulation, causing nagging pain in the lower abdomen and lower back. In addition, the level of progestin hormones in the blood increases, creating conditions for the possible implantation of a fertilized egg into the wall of the uterus, which may be the reason for back strain during pregnancy. Progesterone is produced by the so-called corpus luteum (the follicle from which the reproductive cell emerges).
Why does the lower back tighten after ovulation? Pain syndrome after ovulation is not always a pathology; it can be explained by the woman’s high sensitivity. In addition to unpleasant sensations, there is also a change in discharge from the cervical canal for the following reasons:
- liquefaction due to the action of a hormone released when the follicle ruptures (until this moment, the mucus was thick and covered the internal uterine os);
- preparation of the reproductive tract for transportation of sperm;
- mucus is secreted in large quantities exclusively in the middle of the ovulatory cycle, thick, viscous;
- Brownish inclusions are normal, bright red inclusions are pathological.
Normal pain is considered if:
- the duration of the pain period is no more than two days;
- moderate intensity is observed;
- inherent simultaneous discomfort in the mammary glands, mucous vaginal discharge typical for this period;
- general weakness, changes in tastes, perception of smells, insomnia, decreased performance, irritability, suspiciousness.
Why does my lower back hurt?
When the follicle ruptures, a small amount of blood enters the peritoneum. This can cause discomfort and nagging pain in the lower back. In place of the follicle, a corpus luteum is formed - a temporary gland. Very often, unpleasant sensations are associated with the occurrence of these processes.
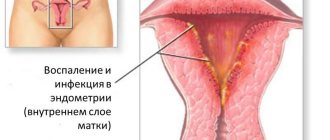
If the egg is fertilized , it tends to attach to the endometrium of the uterus. When this organ is implanted into the body, some vessels in the endometrial layer rupture, which causes aching pain. A week after ovulation, discomfort in the lower back may reappear. This indicates the onset of pregnancy, to the delight of those who planned it. Fertilization is confirmed by the following symptoms:
- Severe nipple sensitivity, breast swelling.
- Minor uterine bleeding, indicating implantation of the egg into the endometrium.
- Nagging pain in the lower back and uterus a week after ovulation.
IMPORTANT : When a follicle ruptures, a woman not only feels pain, but also feels drowsy and lethargic. She loses her appetite and may complain of a headache.
After a couple of days, the unpleasant sensations disappear , but mood swings, drowsiness, and aversion to certain foods and smells occur. Almost all pregnant women are familiar with such symptoms.
The nature of the discomfort
After the ovulation process, nagging pain occurs in the area of the ovaries and lower abdomen. They radiate to the lower back. Not very pleasant sensations can be localized either on the right or on the left side of the abdomen. This is explained by the fact that in each cycle the process of follicle maturation occurs in different ovaries .
This particular area hurts because the nerve endings going to the uterus and appendages are connected to the kidneys , bladder and lower intestine. The pain impulse passes through all innervated structures, so it is not always immediately possible to understand what exactly is the cause of the unpleasant sensations that arise.
IMPORTANT : It is considered normal for pain to persist for two days. As a rule, the intensity of unpleasant symptoms depends on the individual woman. Some people don’t notice anything at all, while others require antispasmodics.
Along with the sensations described above, a woman may be bothered by the following symptoms :
- Periodically appearing pain in the ovary, where the process of formation of the corpus luteum takes place.
- Breast pain, increase in size.
- Vaginal discharge resembling the appearance and structure of a chicken egg white.
Other Possible Causes
can also lead to unpleasant symptoms :
- Hormonal imbalances.
- An inflammatory process in the ovaries caused by chlamydia, ureaplasma, Candida fungus or mycoplasma.
- Consequences of appendix removal - the lower abdomen may hurt after surgery.
- Salpingitis, ovarian cyst, endometriosis.
- Miscarriage - pain and spotting may indicate its onset.
- Osteochondrosis affecting the lumbar spine - pain is especially severe with a sedentary lifestyle.
In such cases, the unpleasant sensations do not go away in a couple of days , in addition, they can increase. Since they have nothing to do with ovulation, pain can occur during any period of the cycle.
A woman has lower back pain after ovulation: causes, factors
Physiologically, a woman may feel pain at the time of ovulation, which continues for some time, and there is a certain explanation for this. A woman experiences lower back pain after ovulation for the following reasons:
- Pregnancy.
- Diseases – cystitis, adnexitis, ovarian cyst, colitis.
- Disorders of menstrual function - algomenorrhea.
- Genital infections – chlamydia, trichomoniasis, gonorrhea, mycoplasmosis.
- Violation of the integrity of the walls of the ovary and fallopian tube.
Pregnancy
The most common reason for lower back pain after ovulation is pregnancy, otherwise it is the period of attachment of the embryo to the wall of the uterus (rupture of blood capillaries). The intensity, as mentioned above, depends on the woman’s pain threshold - the lower the threshold, the longer the pain persists, then disappears and can reappear simultaneously with a delay in menstruation.
In addition to pulling the lower back after ovulation, pregnancy is indicated by:
- sensitivity of the mammary glands, their enlargement;
- blood from the vagina in small concentrations;
- subfebrile body temperature for some time.
Pathological causes
The duration of pain after ovulation for 2 days is considered normal. Some girls experience severe pain, which requires antispasmodics to eliminate, while others experience only minor tingling and pulling sensations in the lumbar region, while others do not notice anything special at all during the ovulation process. Typically, the pain symptom depends on the patient’s sensitivity threshold.
Only a doctor can identify the cause of the ailment; you should not self-medicate
Ovulatory syndrome after ovarian injury
After ovulation, the ovarian area and lower back may be pulled due to injury to the walls of the fallopian tube, ovary, and ligaments. The pain is stabbing and intensifies with any load.
Causes of damage to the uterine appendages:
- heavy loads at work;
- active sexual intercourse;
- lifting objects with heavy weight;
- a favorable factor is stress (causes an increase in hormones, after which tissue density changes).
The main cause of the pathology is determined by ultrasound examination of the uterus and its appendages.
Ovarian cyst and pain after ovulation
A round-shaped benign neoplasm of the ovary is called a cyst. It is a common disease of the female genital area. The cyst is filled with serous fluid.
During the ovulatory menstrual cycle, a follicular cyst appears in the area where the ruptured follicle is located; it can also develop in place of the corpus luteum in the second half of the cycle. Often it does not show itself in any way, but when an inflammatory process occurs, it pulls the ovary and lower back after ovulation. It is imperative to remove the tumors, because they can rupture, causing irritation of the peritoneum (peritonitis), acute abdomen, which requires extensive surgery on the pelvic organs. If pain persists for 3 or more days, you should seek medical help from a gynecologist.
When is a doctor needed?
You need to worry if discomfort in the lower abdominal segment after ovulation is accompanied by:
- significant increase in body temperature;
- purulent, unpleasant-smelling vaginal discharge;
- itching, discomfort, burning in the vagina;
- nausea, vomiting;
- general malaise.
It is also important to sound the alarm in a timely manner if nagging pain in the lower abdomen does not stop for quite a long time, or only gets worse. Under such circumstances, you cannot hesitate to visit the doctor. The gynecologist will find out the reasons why these symptoms appeared and prescribe the necessary therapy.
Note.
Nausea, vomiting, slight increase in body temperature - often such ailments are the first signs of pregnancy. they appear 2-3 weeks after fertilization of the egg. If they occur a few days after the end of the ovulation period, this is no longer a normal phenomenon that should alert you.
Inflammatory processes of the genitourinary system
This is a fairly common cause of back pain after ovulation in women of reproductive age. In this case, microbial factors penetrate into the walls of organs, multiply there, release waste products, decay, which causes discomfort in the lower abdomen (cystitis), in the lumbar region on the side of the pathology (pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis).
Symptoms of urinary system diseases:
- increased body temperature;
- pain when urinating;
- the appearance of dark sediment in the urine;
- blood in urine.
With the development of inflammation of the uterine appendages or uterus, pain spreads to the tailbone, buttocks, and lower back; The nature of the pain is acute, in attacks.
Basal temperature on the 6th and 7th day after ovulation
Let me remind you that the basal chart is valuable for its dynamics, and not for absolute indicators. If it is not possible to compare indicators with previous cycles, you should not wait for an objective assessment of the current results. And of course, there is no need to start measuring now.
After conception has occurred, normal BT will be consistently high, approximately 0.3–0.5 degrees more than the average value of phase I. This is a common manifestation of the work of the hormone that supports pregnancy - progesterone.
Basal temperature at 7 DPO is consistently high - the test should be done at 12 DPO
Note(!) Embryo attachment can be asymptomatic (even painless) and without any changes in the graph. In this case, the test should be done as standard at 12 - 14 DPO, or better later, from the first day of the delay, but only if BT remains elevated .
In what cases should the test be done before day X?
The next day after implantation retraction, you can do a test if there was no retraction, but at some point the BT became even higher and more stable (in comparison with the same phase II) by about 0.2-0.3 degrees. This phenomenon is called the third phase on the BT chart.
Basal temperature chart: from the 7th day after ovulation, BT began to increase in relation to phase 2
All of the listed signs and characteristic symptoms can be assessed later than the 7th DPO. If they occur, you can do a test the next morning.
If a very, very pale line appears - a ghost, it is better to quietly postpone your joy until the day after tomorrow and repeat the test (in case there is a reagent). During a real pregnancy, the hCG level doubles every two days and the second line will certainly become a little brighter.
If the test is negative, don't be upset. This happens when the hormone has not yet entered the urine. Repeat testing every other day or donate blood for total hCG - it is the most accurate.
Observe your condition, but not anxiously and with constant worry, but calmly, with a joyful and happy expression, as if the pregnancy has already been confirmed.
If this time there is no result, but there is definitely ovulation, another reason for the absence of a child is possible. This material describes in detail the reasons for the absence of pregnancy and the steps that should definitely be taken.
To everyone planning a successful pregnancy and healthy babies!
Source of the article: https://ovuliaciya.ru/ovulyaciya-i-cikl/7-den-posle-ovulyacii-priznaki-i-oshhushheniya-pri-uspeshnom-zachatii
Bowel problems and ovulatory syndrome
Modern girls and women, when pain appears, do not go to the doctor, but relieve it on their own with medications, which makes a big mistake, because this can distort the main picture of the disease, which affects the diagnosis and treatment of the pathological condition. If you feel lower back pain a week after ovulation, you can suspect the presence of an intestinal pathology - colitis.
The age of women is up to 36 years. The reason for the increased pain a week after ovulation is the dulling of the symptoms of colitis during the ovulatory period due to the influence of female hormones.
STD
If the lower abdomen feels tight after ovulation, or purulent or mucous discharge with an unpleasant odor appears, this may be evidence of the development of sexually transmitted diseases - chlamydia, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis. The symptoms of these diseases are very similar to each other, so it is quite problematic to independently understand the causes of the illness. But if a woman feels pain in the lower abdomen or lower back for several days after ovulation, and the pain does not go away, but, on the contrary, intensifies, she should consult a doctor immediately.
Malignant processes of the reproductive system
Women of reproductive age are vulnerable to genital cancer. According to statistics, if after ovulation there is pain in the lower abdomen and lower back for 15 days or more, cancer is diagnosed in one woman out of 10,000.
The main signs of a malignant process of the genital area:
- Copious vaginal discharge.
- Blood and mucus from the cervical canal.
- Changes in body temperature for no apparent reason.
- A sharp decrease in body weight.
- General weakness, headaches.
- Depressive states, neuroses.
- Loss of performance.
Every woman needs to remember that cancer in the initial stages does not manifest itself in any way, therefore it is necessary to undergo a medical examination at least once a year by a gynecologist, take all the required tests, smears, and check the mammary glands.
When and in what cases should you consult a doctor?
Ovulation is a normal process and therefore does not require medical supervision. But the following symptoms should cause concern:
- The occurrence of bleeding.
- Acute pain localized in the lower abdomen, which does not allow the woman to straighten up.
- Increased body temperature.
- Prolonged absence of the urge to urinate.
- The appearance of edema.
- Significant deterioration in health.
- Dyspnea.
- Nausea, vomiting.
The doctor will prescribe a thorough examination, which will determine the cause of the problem in the body. If you ignore such symptoms , this can lead to serious consequences, for example, the inability to conceive in the future.
The presence of a high temperature may indicate inflammation of the ovaries, intense pain in the lumbar region may indicate kidney disease, etc. When severe pain bothers a woman during other phases of the cycle, most likely she has an inflammatory disease of the genital organs.
IMPORTANT : To make the pain after ovulation less intense, you need to eat right during this period, avoid stressful situations, and avoid coffee and alcohol.
A woman needs to be especially attentive to her health . A slight nagging pain after ovulation is normal if it does not cause too much discomfort. When discomfort increases and is accompanied by other symptoms that cause concern, it is better not to wait and consult a doctor immediately.
Appendicitis after egg release
This acute surgical disease of the appendiceal process requires immediate surgical intervention. The main symptom of this pathology is pain in the area of the projection of the organ - the right iliac part. It must be remembered that the right uterine appendages are still there. Therefore, if after ovulation the stomach and lower back are tight, it is necessary to carry out a differential diagnosis of appendicitis with ovulatory syndrome. During the inflammatory process of the appendix, a woman takes a characteristic position in bed - on her left side with her legs bent and pulled up to her stomach (“fetal position”). If an acute abdomen is suspected, analgesics are contraindicated.
To distinguish the signs of ovulatory syndrome from other diseases that may cause lower back pain after ovulation, girls are advised to keep their menstrual cycle calendar, measure basal temperature, and examine cervical mucus. At the first symptoms of a pathological process, immediately consult a doctor and do not self-medicate, as you may miss a serious disease, which will lead to the development of complications. It is necessary to remember that the lower back may be sore for a week after ovulation due to illness, and in case of ovulatory syndrome – for two or three days.
Main causes of pain
Interestingly, severe pain can occur not only in the middle of the menstrual cycle.
Often pulls the lower back at the end of the cycle. There are several main causes of pain:
- decrease in estrogen;
- increase in progesterone levels;
- a significant increase in the amount of prostaglandins;
- various negative processes in the uterus;
- multiple increase in thyroid activity;
- use of intrauterine contraceptives.
Changes in estrogen levels are the most common cause of pain. The characteristics of the uterus and the sensitivity of a woman are largely determined by hormonal levels. A significant increase in estrogen levels can often be observed in women over 37 years of age. After this age, menstrual flow begins to be especially painful.
Altered hormonal levels may also have an effect on this. As a result, a woman may develop signs of the following painful conditions - algodismenorrhea and PMS. If you often experience lower back pain or cramping pain, there is a serious risk of algomenorrhea. The woman begins to feel severe pain, accompanied by weakness and dizziness. Sometimes severe nausea is possible.
When treating such conditions, the following measures are used:
- use of antispasmodics or analgesics;
- non-drug methods of influence;
- use of prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors;
- the use of combined agents that affect hormone levels;
- compliance with the most rational regime during the day;
- taking sedatives and vitamins.
Increased levels of prostaglandins can also lead to severe pain. They lead to various violations of the natural harmony of sex hormones. Not only pain in the lower abdomen occurs, but also pain in the back during menstruation. Prostaglandins are represented by specific substances that are produced by uterine tissue. If they predominate, intense contractions of the uterus may begin, which leads to pain. Associated symptoms include headaches and nausea, vomiting and chills, as well as tachycardia.
The thyroid gland is the main regulator of hormone production in the human body. Due to her excessive activity during menstruation, a woman may experience not only severe pain, but also experience insomnia. Pathological processes occurring in the uterine cavity may appear. These include various infectious diseases, endometriosis, and fibroids.
Intrauterine contraception can cause pain during ovulation. The occurrence of unpleasant sensations may indicate not only the presence of a foreign body, but also the activation of prostaglandin synthesis. If you experience pain in the abdomen or lower back when an intrauterine device is installed, it is better not to use it.