With brown discharge and lower back pain, the cause of the symptoms can be either a physiological process or one of many diseases. It will be possible to find out what happened only after a full examination. But it is realistic to assume a diagnosis based on other circumstances accompanying these factors.
This shade is a consequence of minor bleeding. There is little liquid and it quickly oxidizes; this is the so-called old blood. Occurs for various reasons in healthy women:
- When taking hormonal drugs or after installing an intrauterine device;
- From minor endocrine disruption;
- Due to diet and exercise;
- Before and after menstruation;
- As a result of stress;
- In case of injury to the vaginal mucosa;
- For colds and general infectious diseases;
- When pregnancy occurs;
- As a sign of ovulation;
- And also as a result of other provoking factors.
Pain in the lower abdomen and lower back in women is often accompanied by discharge. This symptom may indicate the presence of many serious diseases or the threat of miscarriage. To determine the cause of its appearance, you should undergo an examination by a gynecologist. In this article, we will look at the main factors that cause discharge: white, pink, dark brown and bloody.
This is a fungal disease that occurs in women due to decreased immunity. It most often appears during pregnancy, with vitamin deficiency or after taking antibiotics. The key symptom of the disease is white discharge of a cheesy consistency with an unpleasant odor. Aching and nagging pain appears, which affects the lower abdomen, and the genitals begin to itch. General signs of the inflammatory process are fever, chills, headache, and increased sweating. If the disease occurs in a mild form, its symptoms are only discomfort in the abdomen, radiating to the lower back, and white discharge. In some cases, a woman does not see a doctor for years. This leads to the disease becoming chronic and then difficult to treat. The most dangerous consequence of thrush is infertility.
This is a pathological process that consists of the growth in the genital organs of tissue similar in its functional characteristics to the endometrium. With this disease, menstruation is long and very painful, and bleeding during menstruation is very heavy. A common form of the disease is ovarian endometriosis, in which a woman experiences pain in the lumbosacral spine and lower abdomen. Adhesions form in the affected cavity, due to which the discomfort quickly becomes permanent. If left untreated, the disease can develop into a benign or malignant tumor. The main symptom of endometriosis of the uterine body is spotting, bloody or brown discharge, which in its morphology resembles bleeding during menstruation. The most unpleasant form of the disease is retrocervical. A woman experiences constant discomfort, which becomes almost unbearable during sexual intercourse, urination or defecation.
Brown spotting that occurs at the end of the cycle or continues after menstruation is a symptom of endometrial hyperplasia. This is a benign formation that manifests itself in the form of proliferation of the inner layer of the uterus. This pathology is a consequence of hormonal imbalance, metabolic disorder, and is provoked by previous gynecological diseases. Bloody discharge occurs during the intermenstrual period or after a missed period. In adolescence, they are often abundant, which leads to anemia (anemia). The woman feels discomfort in the pelvic area and weakness. The worst consequence of endometrial hyperplasia is infertility. Therefore, if you have regular sexual activity without contraception and there is no long-awaited pregnancy, you should definitely consult a doctor.
Menstrual irregularities, severe pain during menstruation, bloody brown discharge in the intermenstrual period are symptoms of a polyp in the uterus. This is a benign tumor that affects the internal walls and cavity of this important organ. Their cause is hormonal disorders, the most serious consequence is infertility.
Contraceptive methods: intrauterine device or oral medications lead to the appearance of pink marks on underwear. These drugs change the hormonal levels of women. In the first or second month of using hormonal contraceptives, brown discharge may appear. This is considered the norm. However, if they do not disappear even in the third month, there are nagging pains affecting the lower abdomen, there is a good reason to consult a doctor. The product is not suitable for you, and you need to choose another option for protection against unwanted pregnancy.
Pink discharge in the middle of the cycle is a normal phenomenon that most women experience. Their appearance means that the body is ready to accept a fertilized egg, which will lead to pregnancy. The likelihood of getting pregnant on such days is maximum. Pink discharge should alert women only if it has a dirty tint and is accompanied by admixtures of pus. This is a signal about the presence of sexually transmitted infectious diseases. In this case, the symptoms are complemented by unpleasant sensations in the lower abdomen. In some cases, bloody marks on underwear are the result of damage to the vaginal or uterine mucosa. Perhaps you left a wound on delicate tissues while taking a shower.
Dark brown discharge may be a sign of an ectopic pregnancy. Its other symptoms are discomfort in the lower back and pelvic area, decreased blood pressure, rapid pulse and dizziness. If you experience these warning signs, you should contact your doctor immediately.
Lebedev Evgeniy Ivanovich
Experience in the industry - more than 10 years
Bleeding in postmenopause
Many years have passed since the last menstruation. Age about 60 years. Menopausal symptoms went away after the female body adapted to the absence of hormones. Don’t even think that blood from the vagina means your period has returned. Bleeding in postmenopause is either a sign of a dangerous disease or a manifestation of atrophic processes in the pelvic organs. First, you need to conduct an examination to rule out oncology, and only then think that vaginal bleeding is a trifle and an accident.
Dangerous secretions
A nagging pain in the abdomen cannot indicate a specific disease; it could be a disease of the reproductive organs, gastrointestinal tract or bladder.
The most common diseases that cause stomach pain and possible discharge:
Inflammation in the reproductive organs - the main symptom is discharge and lower back pain;
- Increased body temperature and bloody mucus indicate infection.
- Blood in the urine indicates diseases of the genitourinary system.
- Gastrointestinal diseases manifest themselves as abdominal pain and possible discharge.
- Appendicitis.
Constant pain and malaise may indicate a chronic disease, the nature of which needs to be clarified. To accurately diagnose a pathology by a doctor, you must definitely find out the color of the secretion, as well as the smell, frequency of discharge and consistency. Often, thanks to this data, the doctor will be able to determine the cause of the disease.
Endometritis
Endometritis is an inflammation of the uterine mucosa. The muscle layer of the organ is often affected. This disease occurs when infectious agents can easily enter the uterus.
The main causes and complications of endometritis:
- Curettage, abortions performed unprofessionally.
- Weakening of the immune system after childbirth.
- Hormonal imbalance.
- Use of oral contraceptives.
- Existing STDs.
- Injuries during childbirth.
- Lack of hygiene, especially during menstruation.
Endometritis (Click to view)
The development of endometritis is noticeable after a few days of infection. Signs of infection include chills, bleeding in women, and a tugging stomach. Vaginal mucus may have a strong odor and may cause pain when urinating.
If acute endometritis is not treated, or the course of therapy is not completed, the disease may become chronic. This complication provokes complications during pregnancy, and cases of premature birth are common. With chronic endometritis, the lower abdomen hurts, bloody discharge acquires green spots due to pus, and the appearance of polyps can be a complication. To diagnose the disease, in addition to collecting an anamnesis, blood is taken for tests and treatment is prescribed in the hospital.
Endometriosis
Currently, endometriosis is one of the most common diseases in gynecology. It represents the formation of benign nodes in the pelvic organs. Women of childbearing age who face high stress loads are most susceptible to the disease.
The main reasons are heredity and hormonal changes in the body, as well as stress, bad habits, and excess weight.
Signs of the disease:
- Pain during bowel movements, sex, urination.
- Prolonged menstruation with large blood loss.
- The appearance of brown discharge and pain in the lower abdomen before and after menstruation.
Often there are no symptoms and the presence of endometriosis is revealed only during a gynecological examination.
The disease is treated both with medication and surgery. Early detection and treatment can avoid surgery. To avoid the appearance of endometriosis, a woman needs to pay attention to her body condition, including monitoring her weight, hormone levels, and nutrition.
Endometrial hyperplasia
Endometrial hyperplasia is a pathology of the uterine mucosa that involves damage to the layers of the endometrium. Women with endocrine disorders living in areas with poor ecology during their childbearing years are most susceptible to the disease.
Endometrial changes are benign, but their presence increases the risk of developing cancer.
Factors contributing to the development of the disease:
- Anorexia.
- Stress.
- Endocrine diseases.
- Liver diseases.
- Menopause.
- Weak immunity.
- Excess weight.
The main sign of hyperplasia is vaginal discharge with blood or bleeding, prolonged menstruation.
Diagnosis is carried out using ultrasound, curettage, and hysteroscopy. Treatment can be medication or surgery.
Ovarian cyst
A cyst is a benign neoplasm that tends to enlarge. Women of the childbearing period who have pathologies of the menstrual cycle are most at risk.
If a woman has pain in her lower abdomen, this may indicate complications. Often the disease can be accompanied by urinary disorders and constipation. If the cyst puts pressure on the intestines or bladder, pain often occurs in the left groin.
Ovarian cysts (Click to view)
The main causes are thyroid diseases, surgical interventions, and abortions.
Diagnosis is carried out using examination, ultrasound, laparoscopy, MRI, and anamnesis. Treatment depends on age, stage of development of the disease, symptoms. It is treated with conservative and surgical methods.
Main reasons
It is possible that the problem is benign, but it is better to first rule out the following malignant causes:
- The second pathogenetic variant of endometrial cancer;
- Cervical canal carcinoma;
- Malignant formation of the vagina;
- Tumor of the vulva;
- Ovarian neoplasms that produce female hormones;
- Chorionepithelioma.
According to statistics, oncological causes of postmenopausal bleeding are detected on average in 30% of women. The most common benign problems are:
- Atrophic thinning of the uterine mucosa (small vessels easily rupture when blood pressure rises);
- Senile (age-related) colpitis associated with a lack of estrogen hormones;
- Endometrial hyperplasia or uterine polyp (in postmenopause, these diseases are a precancerous condition).
Let it be atrophy or age-related disorders: until oncological causes are excluded, postmenopausal bleeding is considered an alarming signal for women's health.
Causes of uterine bleeding
Let us consider the causes of dysfunctional uterine bleeding depending on the woman’s age, since at different periods of a woman’s life, the risk factors for the development of bleeding are different.
Uterine bleeding at the age of 12-18 years
During this period, uterine bleeding appears in almost 20% of all gynecological pathologies in girls, this is due to a violation of the formation of hormonal regulation for a number of reasons:
- Provoking factors are mental or physical trauma
- Hypovitaminosis, malnutrition
- Disorders of the adrenal cortex and thyroid gland
- Various serious childhood infectious diseases also affect the appearance of signs of uterine bleeding in girls of puberty - influenza, chronic tonsillitis, chickenpox, measles (see symptoms of measles in adults), mumps, whooping cough (signs of whooping cough in a child), etc.
- If a girl was born to a mother during a complicated pregnancy and pathological birth.
- Rarely, there are cases when the cause of bleeding is a bleeding disorder or tuberculosis of the female genital organs.
Causes of uterine bleeding in women of reproductive age
During childbearing age, this pathology among all gynecological diseases accounts for only 5% of cases. As a rule, uterine bleeding is accompanied by ovarian dysfunction, the causes of which are a number of provoking factors:
- Stressful situations, chronic mental stress, overwork
- Occupational hazards, living in cities with developed chemical and metallurgical industries
- Changing of the climate
- Various inflammatory and infectious diseases of the female reproductive system, which lead to thickening of the ovarian capsule, and also reduce the sensitivity of their tissues to gonadotropins, as well as: Chronic endometritis, endometriosis of the uterus
- Myoma
- Polyps and malignant neoplasms of the cervix and uterus itself
- Ovarian tumors
Uterine bleeding during menopause
This is the most common pathology occurring in premenopausal women - 15% among all gynecological diseases in this age category. This is explained by a natural decrease in gonadotropins secreted by the pituitary gland, therefore, during menopause, the release of hormones occurs irregularly, disrupting the cycle of ovulation, development of the corpus luteum, and folliculogenesis. Uterine bleeding especially often accompanies menopausal syndrome - in 30% of cases, when the signs of menopause in women are significantly pronounced and intense. With progesterone deficiency characteristic of the menopausal period, hyperestrogenism and endometrial proliferation develop.
If a woman aged 45-55 years experiences uterine bleeding, other pathologies that can cause it should be excluded, so the woman should undergo hysteroscopy twice - both before and after diagnostic curettage. The most common causes of uterine bleeding in this case are:
- Endometriosis
- Uterine fibroids
- Uterine polyps
- Rarely - ovarian tumors are hormonally active
Common causes of uterine bleeding
- Thyroid dysfunction - diseases such as hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism increase the risk of symptoms of uterine bleeding.
- Hormonal imbalance. This is the most common cause of uterine bleeding in young girls and women over 45 years of age. With normal hormonal levels, when the balance between progesterone and estrogen is optimal, blood loss during menstruation is usually minimal. When this imbalance is disturbed, uterine bleeding occurs.
- Diseases of the circulatory system. With a decrease in platelet levels, as well as with other blood diseases, bleeding is also possible in women.
- Uterine fibroids. Particularly severe bleeding occurs in women with internal uterine fibroids, when the only option is surgery.
- Adenomyosis. This disease is characterized by fusion of the inner and muscular layers of the uterus; menstruation with adenomyosis becomes painful, prolonged and abundant, since the menstrual area expands significantly.
- Polyps. These are benign formations that often occur in women of childbearing age. If their number or size is significant, their removal is indicated, since they are the cause of uterine bleeding and painful menstruation.
- Ectopic pregnancy, miscarriage, premature placental abruption . These complications during pregnancy have recently become quite common among women. If there is any bleeding during pregnancy, a woman should immediately call an ambulance, since bleeding can threaten the life of not only the baby, but also the expectant mother.
- Malignant neoplasms of the genital organs. This is the most serious cause of possible bleeding, and regardless of the location of the tumor - uterus, cervix, ovaries, with any bleeding, a woman should first of all exclude cancer, since in our time the oncological intensity increases every year, and no longer has clear age boundaries , oncology occurs both in very young women and in women during menopause.
- Breakthrough uterine bleeding. This reason is directly related to the use of intrauterine contraceptives - spirals or the use of hormonal contraceptives. The risk of bleeding especially increases after simultaneous use of both contraceptives and anticoagulants (aspirin). Breakthrough bleeding may be minor when starting to use hormonal contraceptives as an adaptation to the drug. In these cases, the dosage should be reconsidered or the drug discontinued; if this does not help, then another cause of uterine bleeding should be sought. Blood loss also occurs due to damage to the uterus by the intrauterine device, and it should be removed as quickly as possible.
If something unusual happens during menstruation, in the middle of the cycle, during pregnancy or premenopause, at the slightest suspicion of starting bleeding, a woman should immediately contact her gynecologist for consultation, examination and establishment of the true cause of uterine bleeding, since only knowing the exact diagnosis, adequate and timely treatment can begin.
For emergency symptomatic treatment of uterine bleeding, experts recommend the following hemostatic drugs: etamzilate, vikasol, dicinone, aminocaproic acid, calcium preparations.
Bleeding in postmenopause: scope of examination
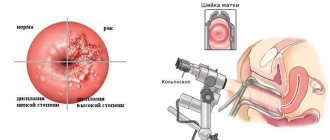
The first thing to do is consult a gynecologist. Some pathology can be detected during a standard examination. In particular, cancer of the vulva and cervix can be detected by visual examination and by taking smears from the cervix, vagina and vulva. The following mandatory examination methods are used:
- Smear for oncocytology;
- Transvaginal ultrasound examination;
- Colposcopy;
- Taking an aspirate from the uterine cavity;
- Hysteroscopy;
- Targeted tissue biopsy performed during endoscopic examination.
The worst option for a woman is to decide that postmenopausal bleeding is the return of her periods. Calm yourself with these thoughts and conjectures. Don't say anything to anyone. Refuse to visit the doctor. And wait for everything to return to normal on its own.
Any postmenopausal bleeding is dangerous. Primarily due to the high risk of uterine cancer or cervical carcinoma. You can’t sit at home and “wait for weather by the sea.” You shouldn’t assume that “maybe it will go away on its own.” After consulting a doctor, it is necessary to conduct a full examination (first of all, using an ultrasound to assess the thickness of the endometrium) to identify the cause of the appearance of blood from the vagina.
Source of the article: https://parashistay.ru/krovotechenie-v-postmenopauze-prichiny-i-obsledovanie.html
What types of endometriosis are there?
Endometriosis of the uterine body
One type of disease is uterine endometriosis, which affects the walls of the organ. Endometriosis of this localization is also called adenomyosis. The epithelium grows into the muscular layer of the uterus, sometimes endometrial cells penetrate all the way to the serous membrane. This type of disease is characterized by increased blood loss during menstruation, the development of anemia, and a significant increase in pain in the lower abdomen during menstruation. Often, endometriosis of the uterus causes miscarriage or the development of infertility.
Treatment depends on the extent of organ damage by the disease. It may be limited to the prescription of hormonal medications. At an advanced stage, surgical intervention and surgical removal or cauterization of foci of endometrial growth are indicated.
Cervical endometriosis
With cervical endometriosis, endometrial cells grow in the thickness of the cervix and on its surface. It may be caused by previous treatment of the cervix and surgery on the cervix. Such operations should not be prescribed during the premenstrual period. With this arrangement of areas of endometriosis, the main manifestations will be spotting during the period between menstruation (usually 7-10 days before its onset), and spotting after sexual intercourse.
Treatment includes hormonal therapy and coagulation of areas of endometriosis using special devices.
Ovarian endometriosis
With ovarian endometriosis, the organ is affected by endometrioid cysts. In this case, first of all, the particular danger lies in the depletion of the follicle reserve. When suffering from ovarian endometriosis, reproductive function suffers and the ovulation process is disrupted. This type of infertility is practically incurable, so if you experience sharp, stabbing pain felt in the lower abdomen, you should urgently consult a doctor. Pain may occur during sexual intercourse or immediately after it. For diagnosis, ultrasound is used, which is performed several times during the menstrual cycle.
Metrorrhagia in postmenopause. Postmenopausal problems: treatment
Metrorrhagia in postmenopause is bloody discharge from the uterine cavity that is irregular and independent of the menstrual cycle. The reason for the appearance of such discharge may be a state of severe stress, physical or mental stress, the consequences of intoxication of the body or disruption of the endocrine system.
To make a diagnosis, an examination of the vagina, cervix, urinary tract and rectum is performed. During an external examination, pathological changes are detected or excluded, such as polyps, tumors, injuries, foreign bodies. The next step is to exclude causes associated with intrauterine and ovarian pathology. Such uterine bleeding can occur when hormonal and non-hormonal drugs are prescribed or taken incorrectly.
The laboratory takes clinical and biochemical blood tests, ultrasound of the pelvic organs, and takes blood to determine hormone levels. If the presence of tumors is suspected, a tumor marker test is performed.
Bleeding and shock in gynecological pathologies
If a cyst ruptures, ovarian apoplexy or ectopic pregnancy, bleeding may occur as a result of rupture of blood vessels in the genital area. In this case, blood pours into the abdominal cavity, invisible to the eye, which forms life-threatening internal bleeding. Against this background, uterine bleeding is possible at the same time, which will not always occur (with an ectopic pregnancy). Typically, such bleeding is light, scanty and prolonged, and is associated with changes in the level of sex hormones.
Against the background of internal bleeding, a woman may experience shock, which is typically characterized by sudden paleness of the skin with loss of consciousness, decreased blood pressure and increased heart rate. The condition is progressively worsening and emergency care is required.
When severe and prolonged pain occurs in the area of the right or left side, which is acute and continuous, or cramping, accompanied by fever and sweating, nausea or vomiting, and the condition and consciousness progressively worsen, you should immediately call an ambulance. In such a condition, the hours are counting; the woman needs competent medical care, including surgery, and in some cases, a transfusion of blood substitutes or red blood cells in order to save her life. Doctors carry out a full range of measures to not only save a woman’s life, but also to preserve reproductive functions as much as possible.
Metrorrhagia during postmenopause
Metrorrhagia in postmenopause can be characterized both cyclically and acyclically. The causes of such bleeding may be age-related changes in the vaginal endometrium or more serious diseases, so self-medication is unacceptable.
Metrorrhagia in postmenopause is expressed by such clinical manifestations as prolonged uterine bleeding, lasting 7 days or more. They often occur after a missed period, are irregular and can cause anemia.
Metrorrhagia, causes
Before prescribing treatment, it is necessary to accurately determine the cause of uterine bleeding. For this purpose, a number of laboratory tests are carried out to help identify the disease, the consequence of which is metrorrhagia. In some cases, this may be due to an overdose of drugs with high estrogen content.
In this case, it is recommended to stop using the drug, replacing it with another, or completely abandon such therapy. Sometimes the appearance of uterine bleeding during the postmenopausal period is caused by the occurrence of cancer of the body and cervix.
If anovulation is observed, then curettage is performed from the body of the uterus for diagnostic purposes and to achieve a therapeutic effect. Immediately after curettage, a hormone therapy complex is prescribed. If such treatment is not effective and bleeding occurs again, the doctor will prescribe surgical removal of the uterus.
Uterine bleeding during menopause can also be caused by the appearance of polyps, inflammation in the endometrium of the uterus, hormonally active neoplasms in the ovaries, hyperplasia, hyperthecosis, and tecomatosis.
Forum Wisdom: Women's Health
Blood during sexual intercourse
Stomach hurts like menstruation.
Menstruation twice a month
How to delay your period by 3-4 days?
Severe stomach pain during menstruation
Pimple or bump on the inner labia
If you have your uterus removed
Water leaks from vagina
Are pieces of meat during menstruation an egg or a miscarriage?
The labia minora are very large
How to get rid of vaginal odor
Chunks of vaginal mucus between periods
don't hesitate, go to the doctor or call him
In this section, only neutral information is published in topics and comments. Topics and comments containing advice, recommendations, promotion of alternative methods of treatment or other actions will be closed.
anything can happen. And it’s not a fact that the doctor will guess the reason. Good luck, control yourself.
This happened to me, but I never found out why. It went away on its own.
I saw a doctor only after 4 months, nothing criminal was discovered.
I’ll get some chamomile now. Bye now.
Go and get an ultrasound of the pelvic organs at any private clinic in your city. If you live according to Moscow time, then there is a chance to do it today.
I had the same problem. I took a pregnancy test beforehand, and it was positive. I went to the doctor, an ultrasound did not reveal any pregnancy in the uterus, everything was fine in the tubes too, there were not even indirect signs, if we assume an early ectopic when it is not yet detected on an ultrasound. I didn’t have time to take the HCG test, since there were holidays for 5 days, I decided to take it after them.
After I didn’t pass, I first took another test. It's negative. So I sit and think, what was that?
PS A similar situation happened 5 years ago. The doctors shrug their shoulders, there is some kind of glitch.
By the way, the doctor diagnosed me with “ovarian dysfunction.” He prescribed vitamin E and sent me home. So don't worry, it might actually be a glitch.
Did your religion not allow you to call an ambulance? Bleeding and pain are no joke.
This happened to me, but I never found out why. It went away on its own.
I saw a doctor only after 4 months, nothing criminal was discovered.
many things cannot be detected by a simple examination, so you need to fly to the doctor at the time of the attack.
I had this happen - the spiral fell out.
It happened to me - I have endometriosis, I had a cyst - they cut it out, and it came back. In any case, YOU NEED TO SEE A DOCTOR. and not in 3-4 months, but SOON! An ultrasound now may not show anything; it MUST be done 5-6 days after the start of the cycle (count from the first day of normal menstruation). I wish you, author, HEALTH and GOD’S HELP! May everything be fine with you! maybe she was just carrying a heavy bag. Don't be afraid of doctors! you just need to go to a GOOD doctor. If God forbid you have any problems, then let the doctor determine them NOW. The sooner treatment begins, the better! God help you.
This is a hormonal imbalance. Happens sometimes. do not panic.
Diagnostics
For timely diagnosis of metrorrhagia, the following is used:
- Collecting anamnesis of the patient’s lifestyle and previous diseases.
- Clinical examination on a gynecological chair.
- Blood tests for hemoglobin level, clinical, biochemistry, coagulation, hormones.
- Analysis of cervical smears and endometrial biopsy.
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
- Treatment of metrorrhagia
Treatment of metrorrhagia depends on the pathology. If glandular fibrous polyps are detected, they are removed under hysteroscopy control. If after this a relapse occurs and a suspicion of cancer arises, removal of the uterus and appendages is prescribed. But on an individual basis, it may be recommended to use a course of oxyprogesterone intramuscularly for a period of up to 4 years.
This treatment is carried out under strict control with regular collection of scrapings of the endometrium of the uterus. If it is not effective and relapses still occur, then the only solution to this problem is to remove the uterus and appendages.
If chronic inflammatory processes are detected, which are the cause of uterine bleeding, intrauterine administration of a mixture of dimexide, deoxyribonuclease, ribonuclease, chymotrypsin, lidase, hydrocortisone and isotonic sodium chloride solution is prescribed. The proportions are determined by the doctor.
Uterine bleeding: causes and treatment
Uterine bleeding is profuse abnormal blood discharge from the uterus. In medicine, they are usually called dysfunctional, since they are the most striking evidence of hormonal disorders in women.
- during puberty or juvenile age (12-18 years);
- reproductive age (18-45 years);
- period of decline of ovarian function (menopause - 45-55 years).
The development of this pathology is due to a number of reasons that determine several types of uterine bleeding: dysfunctional, organic and those caused by systemic diseases (diseases of the kidneys, liver, blood, thyroid gland).
Dysfunctional uterine bleeding is characterized by excessively heavy and prolonged discharge caused by disruption of the hormonal regulation of the menstrual cycle. In turn, they are divided into ovulatory and anovulatory.
Ovulatory uterine bleeding is characterized by the persistence of ovulation, as well as shortening or lengthening the interval between menstruation. This condition occurs most often against the background of inflammatory diseases of the genital organs or adhesions in the pelvis. Often before and after menstruation, as well as in the middle of the menstrual cycle, spotting is observed. Since ovulatory bleeding occurs most often in women of childbearing age, it is accompanied by miscarriage and infertility.
Anovulatory uterine bleeding is characterized by the absence of ovulation, which, over a long period of existence, can lead to the development of hyperplasia, fibroids, endometriosis and even endometrial cancer. This pathology most often occurs in premenopause (premenopause).
Organic uterine bleeding is accompanied by diseases such as endometrial polyp, uterine fibroids, endometriosis, inflammatory diseases of the uterus and appendages, cancer of the uterine body or cervix. This type of disease is chronic and is characterized by bleeding of varying intensity and duration on any day of the menstrual cycle.
What else to do
If staphylococcus joins the inflammatory process, an alcohol solution of chlorophyllipt is added to this mixture. This is a long-term therapy, the course of which lasts more than 1 thousand procedures. The prognosis of treatment depends on the nature of the inflammatory process. Metrorrhagia in postmenopause is treated by eliminating anovulatory dysfunction, eliminating metabolic and endocrine disorders, and using hormonal contraception.
In addition to treating the cause of uterine bleeding, the patient is prescribed complete rest, bed rest, cold is applied to the lower abdomen, preferably an elevated position of the pelvis 25-30 cm above the level of the body position. Thus, you can alleviate the condition and reduce blood loss.
Uterine bleeding during menopause can be significantly reduced by using herbal remedies that can reduce or stop bleeding, but it should be remembered that these are only auxiliary methods of control and cannot be used as the main treatment. Improvement in the condition after herbal medicine is observed after 2-3 weeks. Before use, you must carefully study the composition, contraindications and side effects.
If there is a white discharge and a tummy tug
Such secretion without additional unpleasant symptoms usually does not pose any danger. This is the so-called leucorrhoea, which should be present as vaginal secretion of every healthy woman. If copious mucus is accompanied by other discomfort, you should consult a doctor for further examination.
White, copious discharge with a cheesy consistency is usually a sign of thrush. At the same time, the smell of discharge from thrush has an unpleasant sour note, and additional symptoms include itching, burning, irritation and swelling in the vagina.
Physiology and pathology of the postmenopausal period
Postmenopause is the period of a woman’s life after the cessation of menstruation. The status of menopause can be diagnosed based on tests of estradiol levels (less than 30 pg/l) and an increase in FSH of more than 40 IU/l in the blood serum. The average age of menopause is 51 years. Due to a decrease in estrogen levels, this age period accounts for the largest number of cancers of the genital organs.
Changes in the functioning of the ovaries and adrenal glands begin even before menopause. A decrease in the level of progesterone, estrogen and estrone leads to many disorders in the body. On the one hand, this is a normal physiological process, and on the other, it can cause significant damage to a woman’s health. About 70% of women are susceptible to such diseases associated with disruption of normal ovarian activity.
How to independently determine uterine bleeding - symptoms of blood loss
- At any age, a characteristic symptom of bleeding in a woman is prolonged heavy discharge, lasting more than a week with signs of anemia, confirmed by a blood test and the following symptoms: Weakness, increased fatigue
- Dizziness, headaches
- Pale skin
- Hypotension - low blood pressure
Menopause symptoms and their treatment
Elderly women are more often susceptible to urogenital disorders 2-5 years from the beginning of the postmenopausal period. Under the influence of a decrease in estrogen levels, symptoms of diseases such as atrophic vaginitis, dyspareunia, decreased lubrication function and pistourethritis, pollakiuria, and urinary incontinence occur. During this period, genital prolapse may also appear.
Due to the occurrence of estrogen deficiency, the number of cardiovascular diseases caused by atherosclerosis increases. Preventative measures such as exercise and a healthy, nutritious diet can help combat such symptoms. Diseases of this nature are treated as prescribed and under the close supervision of a doctor.
Older women face problems with unwanted facial hair. The solution may be depilation and hormone replacement therapy.
Loss of skin elasticity leads to sagging breasts, facial contours and body contours. Massage courses, sports, healthy eating, skin care products and hormonal therapy courses will come to the rescue.
Another of the most serious consequences of postmenopause is osteoporosis, which makes bones brittle and thins the skeletal structure. In addition to hormone replacement therapy, a diet high in calcium and magnesium, sunbathing and exercise are prescribed.
The walls of the vagina atrophy, become thinner, and itching appears. This problem must be combated with the help of estrogen creams and the use of artificial lubricants. A good measure would be to continue sexual activity.
The increased risk of arthritis is reduced by regular exercise, taking mild painkillers, and using ointments for joints. Severe pain can only be treated under the supervision of a specialist.
Postmenopause is often accompanied by infectious diseases of the urinary tract and enuresis. Infections are “killed” by antibiotics. Enuresis is treated with hormonal therapy in combination with strengthening the pelvic muscles and a diet high in dietary fiber.
Why does the lower abdomen and lower back hurt in women during menstruation?
Why does your stomach hurt and lower back bother you during your period? This question is often asked by women at an appointment with a gynecologist and will be answered below.
During the menstrual period, many women say that their back and lower abdomen hurt, and the reasons for such negative symptoms may be the following:
- First of all, the lower abdomen and lower back can hurt due to hormonal imbalance - an increase in the hormone can provoke painful sensations.
- Contraction of the uterus is also one of the reasons why the lower back and lower abdomen hurt when menstruation occurs. Contraction of the uterus is provoked by an increase in the level of the hormone prostaglandin - depending on the level of increase, the uterus will contract less or more, provoking pain of varying intensity.
- Diseases that affect a woman’s genitourinary system are pathologies of the reproductive system that worsen during menstruation and cause pain during menstruation. More often, such symptoms are characteristic of the course of uterine fibrosis and endometriosis, inflammation, and so on.
- Deficiency of macro and microelements in the body - magnesium and calcium, which provoke painful sensations during menstruation.
- Genetic predisposition - if a grandmother or mother experienced painful periods during menstruation, then most likely both daughters and granddaughters will inherit this feature of the physiological process.
- Negative factors are stressful situations and impaired blood flow in the pelvic area, poor nutrition and enormous physical activity, heavy lifting. There can be many unfavorable factors - in each case, all circumstances are considered individually.
- A woman’s use of intrauterine contraceptive devices and other contraceptives. They can provoke heavy, intense bleeding, and menstruation may last longer than usual, accompanied by severe pain.
- Violation of water-salt balance. Another reason for painful menstruation is when a woman’s genitourinary system swells due to pathological stagnation of fluid in the pelvic area. This provokes pain in the lumbar back and lower abdomen.
In any case, the reasons that can provoke these types of pain can be both physiological and pathological, which indicate the course of a certain negative process, a disease in the woman’s body. You should not practice self-medication, diagnose yourself - if the pain is too intense and lasts more than 3 days, you should see a doctor and undergo an examination by a gynecologist.
As you can see, if the stomach and lower back hurt during menstruation, the phenomenon can be triggered by various reasons, ranging from a cold to oncology. In order to diagnose the problem in a timely manner and accurately make a diagnosis and begin treatment, it is worth knowing in which cases it is necessary to visit a doctor without fail.
If your body gives the following signals, you should definitely visit a gynecologist:
- Intense and long-lasting pain in the lower back and abdomen, which occurs every menstruation.
- During menstruation, body temperature rises unreasonably, chills and general weakness manifest themselves negatively.
- If taking painkillers does not help relieve pain and any discharge from the genital organs has an uncharacteristic color, consistency, and is marked by an unpleasant odor.
- The process of urination causes discomfort - a burning sensation, pain, and an incompletely emptied bladder.
- Severe burning in the groin area.
Pain during menstruation is a signal from the body that negative processes are occurring in it, which should not be left without due attention. The symptoms themselves, in the form of intense pain in the lumbar region and lower abdomen during and outside of menstruation, may indicate an ectopic pregnancy and inflammation, infertility and other pathologies.
To relieve pain in the lumbar region and lower abdomen during menstruation, it is better for a woman to see a gynecologist, who will identify the cause and prescribe measures to eliminate it. But at home, a woman can take some measures to help cope with the pain syndrome.
- First of all, take a painkiller and to eliminate and relieve pain, you can use moderate heat - for example, a terry towel, a warm belt that you can wrap yourself with or apply a warm heating pad, a mug of aromatic warm tea.
- Try to move in moderation - do not sit or lie on the sofa for days, or, on the contrary, burden yourself with excessive walking. Everything should be in moderation - this will help remove blood stagnation in the pelvic organs and relieve unpleasant symptoms in the form of pain.
- Eliminate all unfavorable factors - never get too cold or sit in the heat for hours, don’t lift weights, and minimize any physical activity or sports. Eat more vegetables and fruits, less unhealthy fast foods, fatty and fried foods, soda, which dehydrates, and so on.
- Give your body proper rest and sleep, learn to relax - this will relieve emotional and mental stress, making it easier to survive menstruation and pain.
- You can massage active points on the body every day, which will help relieve pain. They not only normalize the functioning of the entire body, but also help relieve pain, improve mood and relax. It will take time, and massage should be done regularly, but its effectiveness is greater than that of taking medications.
- You can also practice a set of special exercises - they help relieve pain during menstruation, strengthen the lumbar region and the muscles of the uterus, which will help relieve pain.
- Avoid drinking alcohol - it helps temporarily relieve pain, but for a while and at the same time in the future it provokes heavy bleeding, leading to large loss of blood and fluid, and dehydration.
Discharge
Vaginal discharge during postmenopause does not change its consistency, color or smell - this is the norm. Postmenopause does not affect these indicators. The only exception is the quantity, which is significantly reduced. But if the discharge has changed after menopause, this may be the first symptom of the development of pathologies. The cause may be either an infection or a hormonal imbalance.
During menopause, urogenital disorders may develop. Depending on the rate of progression of hormonal deficiency, complaints of vaginal dryness, itching, burning sensation and extreme discomfort appear. Against the background of such symptoms, a secondary infection may occur. The discharge acquires an unpleasant, specific odor, changes color, and increases in volume.
Against the background of all the changes that characterize postmenopause, discharge is one of the first sources of information for a woman that a malfunction has occurred in the body that requires immediate treatment.
The hormonal imbalance that occurs during this period can also lead to bloody discharge, which should be the reason for an urgent visit to the gynecologist. Problems of this nature can be solved using both medical and surgical methods.
Bloody discharge in women
In the middle of the cycle, minor spotting that does not require the use of feminine hygiene products can periodically occur in any healthy woman. The amount of blood released from the vagina practically does not stain the laundry. A characteristic feature of the discharge is pinkish or brown mucus.
Such unexpected vagaries of the female body can appear on the 14-18th day of the menstrual cycle and are considered completely normal phenomena. Thus, the process of ovulation takes place, during which the egg matures. Based on these signs, you can plan your pregnancy wisely.
In most women of childbearing age, during the process of ovulation, the dominant follicle bursts and the already formed egg is released. Its further development will depend on the meeting with the sperm.
The time of ovulation largely depends on the individual properties of the female body. At the moment the egg is released, the cervix produces cervical mucus in large quantities. Therefore, during this period, transparent, stretchy discharge is observed, the color of which can vary from translucent to bloody. The color of the mucus secreted will depend on the hormone progesterone. The higher its amount in the body #8212; the more saturated the color of the discharge will be.
If during this period the woman does not feel any discomfort #8212; There is no unpleasant odor, itching, pain in the abdomen and lower back, then we can safely say that there are no health problems.
In some cases, when there was unprotected sexual intercourse, it can be assumed that pregnancy has occurred. And barely noticeable bloody marks on underwear in the middle of the menstrual cycle are a sign of fetal implantation - the attachment of a fertilized egg to the wall of the uterus.
However, sometimes such discharge is a reason to consult a doctor.
- The ovulation process is accompanied by an increase in the hormone progesterone, which stimulates the rejection of the mucous membrane in the uterus. Its level must be controlled and not exceed the norm.
- Taking medicinal and hormonal contraceptives
- Intrauterine device.
- Pathology of the endometrium.
- Diseases of the vagina or cervix.
- Fibroids and uterine polyps.
- Presence of a tumor.
A special signal for a visit to the gynecologist can be the duration of red or brown discharge. If this situation continues for 2-3 days in a row or periodically recurs, the presence of pathology can be assumed. Endometriosis has become a real scourge for women. A characteristic feature of which is the growth of the endometriosis focus and menstruation several days before the onset of full menstruation.
The starting impetus for its development can be complications after an abortion, curettage of the uterine cavity, or cesarean section. To establish an accurate diagnosis, an ultrasound of the uterus and hysteroscopy will be required.
Brown discharge is not the only inconvenience that can accompany this disease. Its symptom is pelvic pain, radiating to the lower back, leg or thigh. Usually, hormonal medications are prescribed for its treatment.
The causes of this pathology are the same as those of endometriosis. The diagnosis is made based on the results of ultrasound, histology, and hysteroscopy. Treatment requires surgery.
Pathology of the cervix
Slight bleeding may occur after an ultrasound examination, gynecological procedures, and also after an examination by a gynecologist. The mucous membrane of the cervix and vagina can become very easily injured during menopause, as well as in women taking oral contraceptives. However, the presence of ectopia, as well as cervical erosion, which causes characteristic discharge, cannot be ignored.
Brown and bloody discharge occurs in women who take hormonal medications for less than three months. Usually they are not numerous and do not cause much discomfort and go away on their own.
Intermenstrual bleeding may occur after taking emergency contraceptives. The presence of a spiral in the uterine cavity also contributes to the appearance of spotting.
In any case, self-medicate as #8212; No matter how trivial the disease may seem at first glance, it is not acceptable. After all, some of them need to be treated without delay and your own experiments. Since the transition to a chronic form will not end well. In addition, by avoiding a visit to the gynecologist, a woman only worsens her health condition.
Postmenopausal pain syndromes
Most women experience pain during menopause. The nature and locations of localization may vary.
Chest pain occurs due to the replacement of glandular tissue with fibrous and fatty tissue. If diseases of the mammary glands are not detected, the cause of such pain may be severe psycho-emotional stress.
Painful sensations in the abdominal area indicate the presence of problems in the genitourinary system or intestines, the cause of which may be a decrease in estrogen levels.
Headaches are constant companions of menopause. They are a normal reaction of the body to stress and depression. Treatment will be to eliminate the causes and take analgesics.
Pain in the back, lower back, and joints should not simply be relieved with painkillers, as they are a manifestation of existing diseases, such as arthritis and arthrosis, osteoporosis. Comprehensive treatment under the supervision of specialists is necessary.
If during menopause your nipples hurt or strange discharge appears from them, this may be a symptom of serious diseases, such as: ductal papilloma, mastopathy, mastitis, galactorrhea, ductal ectasia of the mammary gland, cancer. A consultation and examination by a mammologist is simply necessary.
Chest pain during menopause is often confused with pain in the heart. Cardialgia is one of the companions of the menopause. Manifested by the appearance of chills, increased sweating, and a rush of blood to the head. These symptoms worsen at night. The appearance of such signs should be a reason to visit a cardiologist and rheumatologist.
Causes
The following are medical conditions that may cause low back pain and vaginal discharge at the same time.
Urinary tract infections can cause lower back pain and increased vaginal discharge
An infection that affects the bladder is called cystitis. If a UTI develops in the urethra, it is called urethritis, and if it develops in the kidneys, it is called a kidney infection.
Most cases of urinary tract infections are caused by bacteria, but viruses and fungi may also be responsible.
UTIs can occur in people of any age, including children.
Symptoms of a UTI include the following:
- increased volume of vaginal discharge;
- burning sensation during urination;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- pain in the pelvic area;
- lower back pain;
- weakness and fatigue.
Lower back pain and unusual vaginal discharge may indicate pregnancy. The volume, color, consistency and smell of vaginal discharge may change while a woman is pregnant.
Increased vaginal discharge helps protect the uterus and fetus from infections. During the last few weeks of pregnancy, some women may experience a significant increase in discharge.
Lower back pain is another common symptom of pregnancy. It usually occurs when the child grows and becomes heavier or moves around, putting pressure on the nerves that affect the back.
An ectopic pregnancy is a condition that occurs when a fertilized egg implants and begins to develop outside the uterus. This usually occurs in the fallopian tubes.
In an ectopic pregnancy, the doctor must remove the fertilized egg before it becomes too large and begins to cause damage to internal organs.
An ectopic pregnancy can cause the following:
- sharp pain in the abdomen;
- pain in the rectum;
- severe pain in one of the sides, which radiates to the back;
- nausea.
This condition causes inflammation of the joints. Infections, including those that are sexually transmitted, can cause symptoms.
Reactive arthritis can cause unusual vaginal discharge and lower back pain, but the condition is not a serious health threat.
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection (STI). Its symptoms usually do not appear immediately after sexual intercourse, but after some time.
Because it takes a period of time for symptoms to appear, gonorrhea is often not treated promptly. This can cause serious complications, including infertility.
Most women with gonorrhea experience no symptoms at all. When symptoms present, they may include vaginal discharge and pelvic pain that sometimes radiates to the lower back.
PID results from infections of the upper reproductive organs. This condition affects the uterus, fallopian tubes, or ovaries.
PID most often develops in women under 25 years of age, but can affect women of all ages.
PID can be caused by the following:
- vaginal discharge yellow and green;
- pain in the pelvic area;
- pain during urination;
- nausea;
- fever.
In rare cases, cervical cancer can cause lower back pain and unusual discharge. In such cases, the discharge may be pink and have an unpleasant odor. Pelvic pain is another symptom of this form of cancer.
Cervical cancer often does not show symptoms in the early stages of development. That is why doctors recommend that every woman undergo a Pap test regularly.
Herbal medicine for postmenopause
Herbal medicine for the treatment of postmenopausal symptoms has a very effective effect on the general condition of the patient. However, it cannot be a substitute for hormonal therapy prescribed by the attending physician.
In nature, there are plants that are organic substitutes for estrogen. These include:
- St. John's wort. Used to treat climatic neuroses, reduces the frequency and severity of hot flashes.
- Ginseng. Reduces fatigue and reduces stress levels.
- Licorice. Causes estrogenic activity in the body, improves the condition of bone tissue.
- Angelica Sinensis. Improves sleep quality, relieves anxiety and irritability
- Sage. Significantly reduces sweating and is also used for insomnia, nervous exhaustion, and rapid heartbeat. Jujube and astragalus have the same properties.
Lifestyle during postmenopause
The well-known “three pillars” of a healthy life will help to significantly alleviate the symptoms of postmenopause.
- Change your diet to be healthier. It is absolutely necessary to switch to proper nutrition, taking into account the age-related needs of the body for vitamins and microelements.
- Playing sports and physical activity does not harm anyone, and during the postmenopausal period it will also help reduce the risk of joint diseases and also give you energy.
- Stressful and depressive conditions can be overcome by proper, healthy sleep and consultations with a psychologist.
- You definitely need to give up bad habits such as smoking and overeating. Excess weight leads to a decrease in the production of estrogen, which is already insufficient at this time. Therefore, getting rid of these habits will help the body feel better.
Ovarian inflammation: how does it manifest?
One of the causes of pain in gynecological pathologies is inflammation of the ovaries (often with the fallopian tubes). The process can be not only acute, but also chronic with periods of remissions and exacerbations. Against the background of acute inflammation of the ovaries, sharp pain develops in the lower abdomen, radiating to the groin or tailbone area, and sometimes to the lower back. Fever, sometimes reaching 38-39℃ with chills and severe sweating, lower abdominal tension with general malaise and weakness, muscle pain and headaches will also be typical. In some cases, urinary disorders may also be added. If inflammation of the ovaries is not treated, it can become a chronic process, which can remind itself both during periods of exacerbation and almost constantly. Chronic inflammation of the ovaries is typically characterized by the presence of dull or aching pain in the lower abdomen or groin, in the vaginal area. Sometimes the pain is reflected. Against their background, the menstrual cycle is upset, it becomes irregular, with delays and painful periods. The discharge can be either copious with clots and prolonged, or in the form of a scanty smear. Also, against the background of the inflammatory process, libido decreases and discomfort occurs during intimacy.