Vaginal secretion is an important indicator of women's health. While carrying a child, women are especially careful about their own well-being. Bloody discharge during pregnancy may indicate a complication and threat to the life of the fetus. However, there are not only pathological, but also natural reasons for this phenomenon. How to distinguish a norm from a violation, and when should you seek help from a gynecologist?
Blood in discharge during pregnancy as a normal variant
Bloody discharge during pregnancy in the first trimester is most often caused by normal processes that do not threaten the development of the fetus:
Embryo implantation
At 2-3 weeks after conception, many women experience minor leucorrhoea with blood. This is caused by damage to the endometrial blood vessels when the fertilized egg implants into the uterine cavity. This phenomenon is sometimes accompanied by slight discomfort, which goes away after a few days.
Sexual intercourse
Hormonal changes provoke a rush of blood to the vessels of the pelvic area. During sexual intercourse, there is a possibility of damaging the small capillaries that are located on the vaginal mucosa. In this case, after sex, slight bleeding or bloody streaks in the mucus discharge may appear.
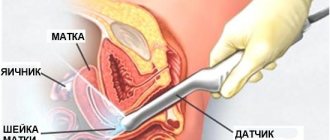
Consequence of gynecological examination
During pregnancy, the structure of the cervix becomes looser and more susceptible to damage. When examined with a gynecological speculum and after taking some tests, girls often observe a small amount of bloody discharge in their underwear.
Menstrual bleeding
Normally, menstruation cannot occur during pregnancy, since its biological mechanism requires the presence of other hormones. However, spotting in the early stages can be similar to menstruation and even occur on days when menstruation would normally begin. This can happen due to hormonal imbalance or if there are two ovulations during one cycle. Thus, one egg is fertilized, and the second reaches the uterus unfertilized, which is why menstruation appears.
Some women do not notice signs of pregnancy because during the first few months they experience bloody discharge similar to their period.
Beginning of labor
Another normal option is the appearance of blood at the end of the third trimester and before the onset of labor. This occurs when the mucus plug is released, when heavy mucous discharge streaked with blood may appear during pregnancy. Naturally, after the mucus plug comes out, the woman will soon begin labor pains.
What happens to the female body during pregnancy?
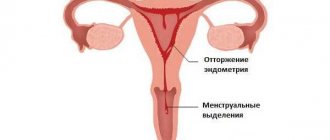
The onset of pregnancy in a woman’s body is directly related to the menstrual cycle – cyclic hormonal and structural changes. The normal duration of each menstrual cycle is 21-35 days, with an average of 28-30 days. The first day of the cycle coincides with the first day of menstrual flow, in other words, menstruation. The duration of bleeding varies between 3-7 days, with heavy discharge noted only in the first days of menstruation.
In the middle of the cycle, ovulation occurs - a period favorable for conception. In the first half of the cycle, the egg matures in one of the ovaries (rarely, in both ovaries). During the period of ovulation, a mature egg leaves the follicle, goes into the abdominal cavity, and then into the fertilized tubes, where it is fertilized by a sperm. A fusion of female and male reproductive cells is formed - the fertilized egg, which descends from the fallopian tubes into the uterus and attaches to its mucous layer (endometrium).
The inner mucous layer of the uterus thickens in the first half of the cycle for successful implantation of the fertilized egg. At the site of the burst follicle, a corpus luteum is formed, which releases the pregnancy hormone progesterone into the blood. This hormone suppresses the effect of estrogen on the uterus and maintains the normal course of pregnancy, until the formation of the placenta.
If fertilization of the egg does not occur, the corpus luteum atrophies, the level of progesterone in the blood decreases, which causes endometrial rejection. Your period and a new menstrual cycle begin. If pregnancy occurs, there is normally no menstrual bleeding, which is a necessary condition for the intrauterine development of the fetus. The occurrence of menstruation during pregnancy is a dangerous sign that requires contacting a gynecologist to diagnose the cause of bleeding and prescribe adequate therapy.
Alarming symptoms
All of the above options exclude the occurrence of pathological bleeding. An anomaly can be identified by the following signs:
- blood in any volume is released for more than 2–3 days;
- accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen, radiating to the pubis, lower back, back or shoulders;
- the nature of the pain can be pulling, cutting or cramping;
- discharge from the genitals has an unusual color and unpleasant odor;
- copious scarlet or pink discharge, as well as brown spotting leucorrhoea.
The appearance of blood in cases of health problems of the mother or fetus is often accompanied by general weakness, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and fever. With excessive blood loss, signs of anemia may appear.
If you start bleeding or there is blood in your discharge for a long time, and there are no accompanying symptoms of illness, you should definitely seek medical help. Some pathologies may appear almost asymptomatic in the early stages.
Factors contributing to the development of complications and the appearance of bleeding during pregnancy:
- Lack of progesterone.
- Infectious inflammations.
- Diseases of the uterus.
- Severe stress.
- The woman's age is over 35–40 years.
- Physical overexertion.
- Abdominal injuries.
- Alcohol, drug use and smoking.
- Blood clotting disorders.
- History of abortion or spontaneous miscarriage.
Bloody discharge before and after childbirth
At 37 weeks of pregnancy, the mucus plug may come out of the cervical canal of the uterus. Its function is a protective barrier between the vagina and the uterine cavity. It prevents the penetration of pathogenic bacteria into the fetal bladder and the inner lining of the uterus. The discharge of the mucus plug usually begins immediately before childbirth, but in some cases it occurs from the 37th week of pregnancy, which is considered a physiological norm. This is manifested by scanty bloody discharge from the genital tract mixed with clear mucus.
After childbirth, bloody discharge – lochia – appears from the woman’s genitals for 4-6 weeks. This is a physiological process that is associated with the cleansing and restoration of the uterine mucosa after the delivery of the placenta and the birth of the child. At first the suckers are bloody with a mixture of clots, then they turn brown. By 5-6 weeks, spotting is normal. Prolonged bleeding from the vagina is a dangerous symptom that indicates pathology of the uterus after childbirth.
Possible complications of pregnancy
The information provided in this article is not a source of self-diagnosis. The main goal is to encourage women not to ignore alarming symptoms and consult a doctor.
Blood during gestation can be a dangerous symptom of complications at different stages.
First half of the gestation period
Brownish-bloody vaginal discharge during pregnancy in the first and second trimester may indicate the following problems:
Hypertonicity
Normally, the muscle tissue of the uterus during pregnancy can only contract during labor. If this happens earlier, gynecologists diagnose increased uterine tone.
Hypertonicity can manifest itself to varying degrees:
- with a mild degree, the woman feels slight cramps and tightness of the abdomen in the uterine area.
- in severe cases, bloody discharge may appear, and uncomfortable pain intensifies.
Hypertonicity most often manifests itself in the 1st-2nd trimester of pregnancy.
In this case, the expectant mother is prescribed bed rest or observation in a hospital. In the last trimester, increased tone can provoke premature birth and dangerous bleeding. In such circumstances, it is necessary to induce artificial labor.
Ectopic pregnancy
When the fetus is attached outside the uterine cavity. During the implantation period, the fertilized egg may mistakenly attach to the fallopian tubes, ovaries, abdominal organs, or cervical canal. Since these organs are not designed to bear a child, ectopic implantation is detrimental to the fetus.
An ectopic pregnancy often results in rupture of the internal organs to which the embryo is attached.
In the early stages, such a pregnancy is no different from a uterine pregnancy. A sign of an anomaly can be a brown spot that appears during the implantation period.
If the pathology is not detected earlier, closer to the middle stages the woman will begin to experience heavy bleeding and acute pain in the abdominal area.
During tubal pregnancy, a distinctive feature is pain radiating to the shoulder, which indicates a rupture of the fallopian tube. The abdominal variety is dangerous due to internal bleeding and the development of sepsis. This condition requires immediate hospitalization.
Risk of miscarriage
We are talking about spontaneous termination of pregnancy before 22 weeks. Thanks to the achievements of modern medicine, the threat of abortion does not guarantee the death of the fetus.
You can prevent a miscarriage if you notice in time such symptoms as: pain in the lower abdomen and lower back, blood in the discharge, the onset of bleeding.
If you contact an obstetrician-gynecologist or emergency medical services in a timely manner, the complication can be treated in a hospital.
Hydatidiform mole
Hydatidiform mole is a pregnancy without an embryo. An anomaly in which a woman feels signs of conception, and a hCG test shows a strong excess of hormone levels in the blood.
Hydatidiform mole develops due to the fertilization of a defective egg that does not contain chromosomes for the development of an embryo. As a result, the chorion grows in the uterus in the form of bubbles filled with liquid.
The pathology can only be accurately determined by ultrasound, but you should pay attention to such symptoms as: vaginal bleeding, pain in the lower abdomen, severe nausea and vomiting, and too rapid growth of the abdomen.
Hydatidiform mole is a benign disease that can transform into malignant metastases.
Cervical erosion
This ulcerative damage to the lining of the uterus is not a dangerous complication for pregnancy. However, it can cause discomfort due to pain in the lower abdomen, copious mucous and purulent discharge with an unpleasant odor, and discomfort during sexual intercourse.
Also, expectant mothers often notice that erosion bleeds at different stages of pregnancy. Since treatment methods for erosion can negatively affect the child’s health, complex therapy is usually carried out after the end of the lactation period.
Second half of the gestation period
Although the first trimester and the beginning of the second are considered the most dangerous for the development of complications, problems can also arise in the second half of pregnancy.
In midterm and the third trimester, there is a likelihood of developing the following pathologies:
Placental abruption
We are talking about the rejection of a healthy placenta from the uterine wall before 37 weeks.
The severity of symptoms depends on the area of placental separation. In acute abruption, the pathology causes large blood loss in the mother, painful cramping pain and fetal death. The separation of the placenta is characterized by scarlet and light pink spotting in late pregnancy. Acute and chronic conditions usually require hospitalization.
A small abruption requires bed rest and hospital observation, while a severe separation of the placenta may require an emergency delivery.
This condition can disrupt the blood supply and development of the fetus, and in severe cases, lead to a missed abortion.
Placenta previa
An anomaly in which the placenta covers part of the internal os, located in the lower parts of the uterus, is called placenta previa. It can be complete or partial. The risk of pathology is high in women with endometrial diseases, curettage, uterine fibroids and a history of pregnancy complications.
Bleeding can begin at various stages of the gestation period. With complete presentation, bleeding may develop suddenly and not be accompanied by pain. Abnormal discharge may stop and reappear at the very end of pregnancy. In case of partial bleeding, bleeding develops at the beginning of labor.
Premature birth
Delivery before 37 weeks of pregnancy is considered premature. They can be caused by a wide range of reasons, from previous infections and hormonal disorders to stress and bad habits.
Symptoms are manifested by intermittent pain in the lower abdomen, radiating to the lower back and hypertonicity of the uterus. The onset of premature labor is accompanied by cramping pain. Due to early placental abruption, bleeding may begin during early labor.
If symptoms appear, you should seek medical attention immediately, as a premature baby will need medical attention immediately after birth.
What to do if a pregnant woman experiences bleeding
If bloody discharge from the genital tract occurs, you should seek medical help. Even if there is a high probability of physiological bleeding, it would not be superfluous to consult a gynecologist. Only a specialist can make the correct diagnosis after examining the pregnant woman and prescribing additional examination methods. Any bleeding from the vagina during pregnancy should be treated as an alarming symptom.
If you have spotting, you should visit a doctor at the antenatal clinic, accompanied by a loved one or relative. In case of bleeding, you should immediately call an ambulance. Before the doctors arrive, it is important to calm down and not be nervous - the release of adrenaline into the blood during stress increases the contractility of the uterus and increases the risk of spontaneous abortion. It is necessary to lie down on the bed and reduce physical activity as much as possible.
If there is a threat of miscarriage, premature birth, or placental abruption, the woman is usually offered to go to the hospital. You should not refuse hospitalization - in a hospital environment it is easier to maintain bed rest, and constant monitoring by medical personnel will allow you to promptly notice the deterioration of the pregnant woman’s condition and take the necessary measures.
If an ectopic pregnancy is diagnosed, the woman will undergo surgery. Depending on the timing of detection of ectopic pregnancy, the tube is cleared of the fertilized egg or removed. The remaining tube allows the woman to conceive a child in the future. Modern medicine performs laparoscopic operations to eliminate ectopic pregnancy - a less traumatic surgical intervention compared to the classical method.
To prevent complications during pregnancy, it is necessary to undergo a diagnostic examination at the planning stage of conception. Timely treatment of sexually transmitted infections, inflammatory diseases of the genital and other organs, strengthening the immune system will reduce the risk of miscarriage or disruption of intrauterine development of the fetus.