Causes of pathology
As a rule, spotting during pregnancy indicates a change in hormonal levels in a woman’s body. Depending on the period of their appearance, the following reasons can be given:
- aging of tissues inside the uterus, i.e. during the last cycle, the menstrual flow did not pass on time, and, as a result, having aged, the tissue began to come out now, turning brown;
- reaction to taking contraceptives, especially after conception, the body goes through a period of adaptation, which is why discharge appears;
- readiness to fertilize the egg, provided that the daub began after the end of menstruation;
- strong uterine tone;
- various diseases, for example, endometriosis and others.
But perhaps the main reason for the appearance of brown spotting instead of menstruation (or before menstruation) may be a sign of a woman’s pregnancy. Try the table for determining the sex of your unborn child.
Spotting in the early stages of pregnancy can be dark red, light pink, or brownish. This is not a lot of discharge, which rather slightly stains or “smudges” (hence the common name “daub”) the underwear. The reasons may be the following:
- in the very first days after conception, weak discharge appears due to the body adjusting to its new state, this has already been mentioned;
- taking medications to normalize hormone levels, which the doctor sometimes prescribes to prevent pregnancy from continuing, can also trigger the appearance of discharge;
- a short light pink smear in the first days of pregnancy will most likely indicate that the embryo has attached to the wall of the uterus;
- possible deviations from the norm in the body can also cause discharge.
Don't ignore
The appearance of short-term brown spotting during pregnancy, especially in the early stages, is common. Therefore, this should not immediately cause concern on the part of the woman, but this feature should not be ignored either.
The reasons for this pathology are as follows.
- In the very first days, spotting may occur instead of menstruation and be a sign of pregnancy.
- After conception, the hormone Progesterone, which is responsible for the development and preservation of the fetus, increases. This hormone causes periodic spotting at 6-8 weeks of pregnancy. If its level is insufficient, such discharge sometimes indicates a threat of miscarriage.
- In some cases, brown spotting during pregnancy may occur throughout the first trimester on the days of expected menstruation.
- With diseases of the genitourinary system, a woman also experiences discharge.
Possible dangers to the fetus
Any type of spotting during pregnancy indicates a deviation of its development from the norm. In most cases, this feature does not pose a strong threat. But consultation with a specialist is definitely recommended, as this may serve as a signal of possible complications.
- Bloody smear, especially at the beginning of pregnancy, often indicates a threat of miscarriage. For treatment, the gynecologist suggests some hormonal medications.
- The development of an ectopic pregnancy is also accompanied by brown discharge. When the diagnosis is confirmed, cleaning is prescribed (or, if time permits, drug treatment), since fetal development is possible only in the uterus. Refusal of treatment may cause cervical rupture.
- With a diagnosis such as “frozen pregnancy,” when the fetus stops developing and dies, brown mucus is also released. Most often, for this reason, spotting appears in the 5th week of pregnancy, during the highest period of threat of miscarriage. Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) can make an accurate diagnosis. When the diagnosis is confirmed, the woman is hospitalized and curettage is performed to avoid various inflammations in the future.
- Detachment of the fertilized egg, when the body of the expectant mother begins to reject the already attached embryo. In this case, a brown daub appears. Most often, the threat worsens at 7-10 weeks of pregnancy. The woman is admitted to the hospital and prescribed medication.
- Placental abruption. If it is insignificant, then it does not pose a threat to the baby’s development. But with a large detachment there is a risk of fetal death. The doctor prescribes a full examination and further treatment.
- Uterine erosion is also a cause. During pregnancy, it is not treated, just observed. After giving birth, you should definitely consult a doctor about this.
- With the development of genital infections, discharge is observed, which is accompanied by an unpleasant odor and burning sensation, clots or flakes. So, based on the symptoms, a woman should immediately understand the nature of the discharge. The doctor makes a smear to determine. Treatment is prescribed depending on the test results.
What to do?
This depends on the specific symptoms that were described above. If you see and feel that the discharge is normal and does not indicate any abnormalities, you don’t have to do anything - the mucus will come out, and that’s all. But you still need to tell the doctor during one of your regular examinations.
If the symptoms indicate a disorder, as indicated by the color, smell of the discharge, and accompanying pain, you should go to the doctor immediately and begin treatment immediately after diagnosis. It is possible that your life, as well as the life of your unborn child, is under threat.
Norm or pathology
The causes of dark brown discharge that appears instead of menstruation may be natural processes that do not require medical correction. Or maybe pathological disorders that need to be treated. It is impossible to find out on your own what causes this condition.
If we talk about pregnancy, then brown discharge before menstruation and its subsequent cessation may be a symptom of the attachment of the fertilized egg (so-called implantation bleeding).
But bleeding during the period of expected menstruation may indicate a threat of interruption caused by various factors. Also, the pregnancy may be ectopic or frozen, which requires immediate medical intervention. After all, brown discharge is nothing more than blood in small quantities that has managed to coagulate.
It cannot be reliably stated that spotting before menstruation is a sign of pregnancy. The appearance of such discharge prompts the gynecologist to think about a hormonal imbalance. Also, unusual periods can be the first sign of infectious, inflammatory diseases or pathologies of the cervix.
Brown discharge after conception should alert a woman. If the pregnancy is planned, you should urgently consult a doctor. After diagnosis, it will be possible to talk about normality or pathology, and, if necessary, take some action.
In the 3rd trimester
In the third trimester, for most pregnant women, the discharge intensifies and becomes very varied in consistency. They can be thick, liquid, watery, more or less transparent, and so on.
The main thing is that there is no admixture of blood, pus, or foam in the discharge, so that the discharge is not cheesy and has no odor. As in previous stages of pregnancy, the most dangerous discharge is bloody, which means placental abruption. In this case, there is a high probability that a miscarriage or premature birth will occur, so you should consult a doctor immediately.
This bleeding can be similar to menstrual bleeding and is usually accompanied by pain. Even small clots and streaks of blood are a very alarming sign, and if they appear, you should consult a doctor.
In the last days before giving birth, there may be pink discharge, which is normal.
Could brown discharge be a sign of pregnancy?
You can hear quite often that brown discharge is a sign of pregnancy. However, you cannot rely on this symptom alone. If there is a delay, and the test shows a positive result, then with a high degree of probability we can talk about conception. But even in this case, you cannot be completely sure until the new position is confirmed by a doctor or ultrasound.
If there is no bleeding during menstruation, but instead there is a brown spot, then one can only suspect pregnancy. These signs are not reliable evidence of a new situation. To roughly understand what we are talking about, you should consider all possible situations of the appearance of brown discharge in more detail.
Implantation bleeding
If, after conception, brown discharge appears a week before the expected period, then these may be the first signs of pregnancy before the delay. After the sperm meets the egg, a fertilized egg is formed. Over the course of several days, it makes its way to the final goal - the uterus. By introducing itself into its mucosa, the embryo damages small vessels (embryo implantation occurs). Droplets of blood coagulate, turning brown.
Processes in the uterus cause the appearance of very scanty beige or bloody discharge. A woman discovers that she has spotting a week before her period. Usually this does not bother the fairer sex. Spotting in the middle of the cycle is not perceived as a sign of pregnancy. However, attentive women may be wary. Such discharge during pregnancy goes away on its own within 2-3 days before the delay. Subsequently, menstruation does not begin, and the woman learns about her new position.
What kind of discharge occurs when menstruation is late during pregnancy?
Statistics show that brown discharge instead of menstruation is not perceived by all women as a sign of pregnancy. Most representatives of the fairer sex believe that this is how a new cycle begins. They expect heavy discharge to begin in the coming days, but if conception has taken place, this does not happen.
Spotting due to hormonal imbalance
As already mentioned, brown discharge in early pregnancy occurs around the time of expected menstruation. The fact is that the female body retains information about the cycle and does not yet have time to completely adapt to the new state.
In the midst of hormonal changes, you need to be extremely careful, because this is the most dangerous time for the fetus. Even if there is no brown discharge during pregnancy at any stage, you should follow the following rules:
- Physical activity and heavy lifting are prohibited;
- shows peace and the creation of emotional comfort;
- It is strictly unacceptable to take a bath in water exceeding a temperature of 37;
- It is recommended to refrain from intimacy.
Neglecting these rules can cause heavy spotting in early pregnancy, which can quickly develop into bleeding. And this already threatens the life of both the child and the mother.
Dangerous bleeding in the early stages
If brown or red spotting begins after confirmation of pregnancy (for example, using a test), you should consult a gynecologist. This condition may be a consequence of pathology, and timely medical intervention will prevent the consequences.
Risk of miscarriage
When spotting begins at the expected time of menstruation, it usually occurs when there is a threat of miscarriage. The pathological condition is caused by various factors:
- insufficient production of progesterone;
- endocrine diseases;
- dysfunction of the pituitary gland;
- stress and emotional distress;
- physical exercise;
- bad habits.
Self-administration of medications in the early stages, especially hormones, antibiotics and tranquilizers, is very dangerous. If there is a threat of miscarriage, a woman may experience abdominal pain. Lack of help leads to the cessation of pregnancy progression. As a result, spontaneous miscarriage occurs or gynecological curettage is prescribed.
Ectopic pregnancy
Embryo implantation occurs between 3 and 7 days after ovulation. If the embryo attaches quickly, for example, on the 2nd day after conception, then this occurs outside the uterine cavity. In this case, the pregnancy is considered pathological and is called ectopic. There is no chance of making it out. A woman with such a pathology needs emergency medical care. The sooner it is provided, the greater the chance of maintaining reproductive function.
Symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy include:
- stomach ache;
- weakly positive pregnancy test;
- absence of fertilized egg in the uterine cavity according to ultrasound;
- a slight increase in hCG in the blood;
- vaginal bleeding;
- decreased blood pressure;
- dizziness, fainting (with large blood loss).
Why do I have brown discharge if I'm not pregnant?
Brown spotting before or instead of menstruation can occur in pathological conditions and diseases of the pelvic organs. A comprehensive examination, which includes:
- vaginal smear;
- Ultrasound;
- blood tests;
- colposcopy;
- laparoscopy.
Hormonal changes
Light brown discharge instead of menstrual bleeding occurs in girls during puberty. During the first year from the start of menstruation, the cycle is established. The body adapts to new functions. Periodic failures, disturbances, spotting are normal if not accompanied by additional signs of pathology.
A similar process occurs during menopause. Menstruation becomes irregular and changes in volume. Brown spotting often occurs.
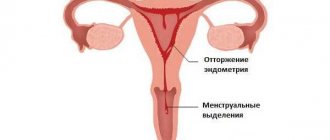
With hormonal imbalance and concomitant diseases (endometriosis, fibroids, hyperplasia, tumor processes), the regularity of bleeding may be disrupted. Pathologies of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands are also accompanied by brown discharge. Hormonal disorders often result in infertility.
Inflammatory processes
Infectious processes and inflammations (STIs, adnexitis, endometritis), which accompany bleeding, pain or itching, must be treated by a gynecologist. Prolonged inflammation of the pelvic organs leads to chronic diseases.
Diseases of the pelvic organs, provoked by hidden infections, can also be accompanied by brown spotting. However, it has nothing to do with pregnancy, so it cannot be a sign of conception.
Polyps are a common cause of discharge. Growths located in the cavity of the reproductive organ or on the mucous membrane of the cervical canal begin to bleed immediately after sexual intercourse. The formation of polyps is associated with the human papillomavirus. It is necessary to undergo tests to determine the type of infection in order to take further action.
Polyps often cause infertility, so a woman tries to see symptoms of pregnancy in the brown spot. Menstrual bleeding with polyposis is usually more profuse and prolonged.
Cervical erosion
An inflamed cervix may bleed. In women with ectopia or erosion, spotting occurs after and before menstruation. Brown discharge begins after sexual intercourse or physical activity.
Spotting associated with changes in the mucous layer of the cervix usually does not suggest pregnancy, as it appears with noticeable frequency. The existing pathology can be determined during a routine gynecological examination.
My period has passed, a smear has begun: what could it be?
The appearance of spotting after menstruation may be associated with pathological processes:
- infectious in nature (for hidden infections or STDs);
- inflammatory pathologies;
- tumors of benign or malignant origin;
- hormonal processes.
Brown spotting in the middle of the cycle may indicate ovulation has taken place (and this is normal).
A common cause of the appearance of dark brown discharge is the growth of the endometrium in a place not intended for this: the ovaries, fallopian tubes or abdominal cavity.
How is discharge pathology diagnosed?
Let us immediately note that pathological discharge occurs not only in the first trimester. A woman may notice pathological secretion both in the middle of pregnancy and at the thirty-eighth week.
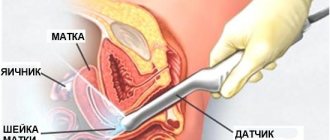
As for diagnosis, in addition to a gynecological examination, ultrasound, it will be necessary to take a smear.
If you have a disease, the smear may contain:
- high white blood cell count;
- increased volume of mucus;
- atypical cells;
- infections and microbes.
Spotting during pregnancy: causes of occurrence
Spotting in early pregnancy is a fairly common occurrence, and in most cases is not a symptom of a threatened miscarriage. It occurs for several reasons. We will consider basic, as well as medical recommendations regarding a particular situation.
Placental or chorionic abruption
Often, spotting at the beginning of pregnancy (more often in the second half of the first trimester) occurs precisely for this reason. Blood accumulates under these detachments, which women later find on their underwear. Small, non-progressive detachments are not dangerous. Although any woman who has noticed bloody discharge from the genital tract during pregnancy is advised to limit physical activity, not have sex and take medications to avoid miscarriage. Usually "Duphaston" or "Utrozhestan" is prescribed. Moreover, the second drug is considered more effective (recent studies prove this) when used vaginally. In addition, doctors prescribe Magne B6 in abundance, multivitamins for pregnant women, vitamin E can be prescribed separately. This has nothing to do with the treatment of threatened miscarriage, and can (and should) be crossed off from the list of prescriptions. An ultrasound is required to look at how the fertilized egg develops and how large the detachment is. Next, the examination is carried out over time after 7-10 days, or when the discharge intensifies.
Hormonal changes
Quite often, spotting during pregnancy occurs at the time when menstruation should have started, if not for an interesting situation. That is, approximately every 4 weeks (if there was a 28-day menstrual cycle). During these weeks you need to be especially careful, it is advisable to rest more, and not worry.
Frozen pregnancy
Unfortunately, this phenomenon is not uncommon in the first trimester. The most common cause (according to the results of histological studies) is chromosomal abnormalities in the embryo that are incompatible with life. In addition, the cause can be acute infections (for example, if a woman becomes infected with the herpes virus type II while already pregnant) and various teratogenic effects (for example, taking toxic medications, alcohol in large quantities).
A frozen pregnancy is diagnosed by ultrasound (the main sign is the discrepancy between the size of the embryo and the gestational age and the absence of a heartbeat). But the woman herself may notice changes in her condition: in addition to spotting, pain in the lower abdomen may occur, the mammary glands become softer, and toxicosis disappears. If you take a blood test for hCG, the indicator will be significantly underestimated in comparison with what expectant mothers have at the same period, only with a developing embryo.
Abroad, a woman with a frozen pregnancy is not immediately hospitalized, but waits for 2-4 weeks until a spontaneous miscarriage occurs, of course, undergoing an examination every 7-10 days. In Russia and the CIS countries, curettage is usually done immediately after confirmation of the diagnosis, in order to avoid a possible inflammatory process.
Ectopic pregnancy
Spotting in the early stages occurs in cases where the egg begins to develop outside the uterus - in the fallopian tube, ovary or in the abdominal cavity. In its very first weeks, some features may be noted: on ultrasound, the fertilized egg is not visible in the uterus, while hCG is already above 1500 mU/ml. A woman experiences pain in the lower abdomen, often on one side, and again, spotting in the early stages of pregnancy, which is simply perceived as a threat of miscarriage. If measures are not taken in time (this may be laparoscopic surgery, and sometimes medical intervention) to eliminate the fertilized egg, this can lead to organ rupture, since only in the uterus can the fertilized egg develop throughout the entire period.
Cervical erosion and trauma
Ectopia (erosion) of the cervix is a fairly common pathology. But in most cases, it only requires observation (periodic PCP smear and colposcopy). In some cases, ectopia may bleed. This can happen due to mechanical stress on the cervix, be it a gynecological examination with speculum, sexual intercourse or masturbation.
During pregnancy, the vaginal mucosa becomes easily vulnerable. Even a carelessly inserted suppository (medicine) can lead to microtrauma of the mucous membrane and, accordingly, spotting will appear.
No pregnancy
In many antenatal clinics, women who have not undergone an ultrasound of the uterus and have not been tested for hCG are registered for pregnancy. That is, the gynecologist relies only on his own experience. If the uterus is enlarged, the mucous membrane of the vagina and cervix has a bluish tint, the cervix is tilted posteriorly and there are no periods - this means the woman is pregnant. But there are often cases when these conclusions are erroneous. That is, the so-called spotting during pregnancy is nothing more than normal menstruation, which for some reason was delayed.
Sources:
https://sberemennost.ru/planirovanie/methods/maznya-na-rannih-srokah-beremennosti https://myzachatie.ru/zhenskie-zabolevaniya/maznya-vmesto-mesyachnyh-priznak-beremennosti.html https://www. missfit.ru/berem/maznya-na-rannikh-srokakh-beremennosti/
In the 2nd trimester
There is no need to worry if the discharge is clear, white or yellow, has no odor, is not accompanied by pain, is not thick, does not foam, or is not spotting. Otherwise, discharge is a sign of the development of pathology.
The most common causes of pathological discharge in the second trimester are fungal or bacterial infections, erosions of the vagina and uterus.
Discharge with blood is a sign that the placenta has begun to exfoliate, and therefore a miscarriage may soon occur. In this case, you need to go to the hospital immediately.
This may also mean that the placenta is incorrectly positioned, in which it blocks the os of the uterus. This is called placenta previa.