Almost every woman in her prime wants to have her own child; this is a great joy that makes up the meaning of life. And for those who are looking forward to the birth of a baby, a frozen pregnancy is a great tragedy.
The cause of fetal death is a whole complex of pathological disorders, and for the most part the cause is a genetic abnormality or chronic endometritis. Infection in the early stages of the fetus leads to damage to the embryo and spontaneous miscarriage.
Interrupt methods
Termination of a frozen pregnancy can be carried out in several ways. Usually the method depends on how far into the pregnancy the pregnancy has stopped.
For example, if the fertilized egg or embryo stops developing before the 7-8th week, then preference is given to medical abortion. If freezing occurs at a later date, experts prefer an interruption method such as curettage.
The medical termination of a frozen pregnancy is usually understood as the evacuation of the embryo using special spasmodic drugs.
What happens when the fetus freezes?
A fertilized egg that is not removed from the uterus in time is a direct threat to the health and life of a woman. Over time, it mummifies, becomes saturated with blood, but the worst thing is the decay products of the dead embryo. They tend to enter the bloodstream, poisoning the body of the failed mother.
Late diagnosis and termination of a frozen pregnancy will lead to fatal consequences. For example, 4 weeks of delay will cost a woman problems with the blood coagulation system. The tissues of the dead fetus that poison the body will provoke the release of tissue thromboplastin into the blood and, as a result, cause bleeding and thrombotic complications.
***
All of the above indicates the need for regular monitoring by a doctor when planning pregnancy and conceiving. The slightest signs indicating fetal freezing should be a signal to prepare for treatment using one of the methods available today.
You cannot ignore the body’s attempts to report a problem, much less wait for an arbitrary resolution of the situation. A dead fetus should not remain in the uterus for a single extra day. A minimum of time should pass from the moment of diagnosis and preparation for an abortion; only then can one count on a successful outcome of treatment and the absence or minor complications.
Medical abortion
Regardless of the type of pregnancy (abnormal, life-threatening, complex), its termination is always stressful for the female body. Medical abortion is considered to be the least traumatic option.
Freezing of the development of the ovum or fetus is determined using ultrasound. The specialist carries out a control study and, if the test results indicate a decrease in the concentration of hCG, prescribes a medical or surgical abortion.
Preparation for the procedure
Before any type of abortion, a woman is prescribed the following examination:
- Laboratory testing of blood samples for blood group, Rh factor, syphilis, hepatitis, HIV.
- Visual gynecological examination. It is necessary to identify pathologies of the reproductive system, if any.
- Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs. Using an ultrasound, the exact duration of pregnancy and the possibility of an abortion are determined.
So, how is a medicinal termination of a frozen pregnancy carried out?
Oksana Igorevna
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT
Abortion and contraception clinic in St. Petersburg - department of the medical gynecological association "Diana"
Make an appointment, tests or ultrasound via the contact form or by calling +8 (812) 62-962-77. We work seven days a week from 09:00 to 21:00.
We are located in the Krasnogvardeisky district, next to the Novocherkasskaya, Ploshchad Alexander Nevsky and Ladozhskaya metro stations.
The minimum cost of a medical abortion in our clinic is 4,500 rubles. The price includes all pills, an examination by a gynecologist and an ultrasound to determine the timing of pregnancy.
Share link:
Manipulation technique
Medical cleansing is usually understood as the process of terminating a pregnancy with the help of medications if the fetus has stopped developing at an early stage. This procedure is mandatory: without an abortion, it is impossible to fully restore the body, and the woman runs the risk of developing infertility.
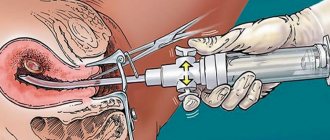
Medication termination of a frozen pregnancy is carried out exclusively in a hospital setting. After a gynecological examination and examination, a woman takes the first pill under the supervision of a specialist. Under its influence, the remaining tissue inside the uterus peels off. After this, the woman takes a second tablet to cause uterine spasm. After some time, tolerable pain of a cramping nature occurs, as a result of which the complete evacuation of the fertilized egg from the uterus occurs.
After spotting occurs, the woman undergoes a second ultrasound examination to monitor the procedure - to assess the condition of the uterine cavity.
If a woman feels fine and her health does not cause concern to the doctor, she can go home. The maximum period of stay in the gynecological department is 8-12 hours. In some cases, the woman is scheduled for a gynecological examination the next day. It is necessary to monitor the condition of the uterus.
Methodology
The process itself is painless and is carried out in several stages. After the woman has undergone preliminary procedures and the actual date of conception has been determined, the doctor prescribes a medication containing mifepristone in a certain dose.
Its reception is carried out under the supervision of the attending physician, who records the woman’s condition for two hours. After a few days, usually up to two, another drug, prostaglandin, is prescribed, also in a certain dosage, which promotes the release of the fetus that has frozen in its development.
At the same time, the patient experiences sharp pain in the lower abdomen, the appearance of copious bleeding, all this will depend on the individuality of the woman’s body.
A few days later, a second ultrasound is scheduled to detect the absence of pregnancy and completely cleanse the uterus of the embryo. The final stage involves an ultrasound scan after two weeks.
Benefits of medical abortion
It is worth noting that medical termination of a frozen pregnancy in the early stages has a number of advantages:
- Anesthesia and anesthesia are not required.
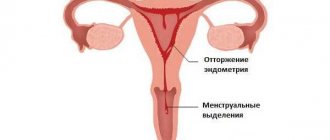
- Abortion with the help of medications is easier for women to tolerate from a psychological point of view, since the process of evacuation of the fetus is more reminiscent of menstruation than abortion.
- There is no contact with uterine tissue, which significantly reduces the likelihood of developing an inflammatory reaction.
- The effectiveness of the procedure reaches 99%.
Advantages
Stopping fetal development in the early stages of pregnancy or failure of the embryo to develop in a fertilized egg is considered a frozen pregnancy. If a woman does not notice it in time, then intoxication may begin in the body, which may be accompanied by:
- Increasing temperature.
- Pain in the lower abdomen.
- General weakness.
- Interrupt methods
As a rule, the choice of terminating a non-developing pregnancy is carried out in several ways, which depend on the timing. If the development of the embryo has stopped for 7-8 weeks, then the most gentle method is used for this - medical termination of pregnancy. It occurs as a spontaneous miscarriage.
Currently, surgical removal of the embryo is not considered a good option, as it leads to damage to the cervix, pain, and recurrent pathology with a non-developing embryo.
The drug method does not have these consequences, and is used until 12 weeks of pregnancy. If drug interruption is not possible, then vacuum aspiration is performed. Since pharmaceutical abortion occurs in the early stages, it avoids great psychological trauma for the woman who is forced to agree to it. It is characterized by ease of execution, which requires taking medications under the supervision of a gynecologist, and is carried out in strict sequence.
Medicines
It is important to find out in advance how medical termination of a frozen pregnancy occurs. Pharmacological preparations for home use are not issued. It can only be taken under the supervision of a specialist in the gynecological department. The two most commonly used medications are:
- Mifepristone (200 mg). Increases the contractility of the myometrium, resulting in the fertilization of the fertilized egg.
- Misoprostol (400 mg). It helps to dilate the cervix and increase its tone, as a result of which the remnants of the fertilized egg, together with the blood, are removed from the organ.
Can also be used:
- "Pencrofton." This drug is of synthetic origin and is prescribed only to nulliparous women.
- Mifeprex is a domestic medicine used in the early stages.
- "Mifolian" is an imported medicine made in China.
- "Mifegin" is a steroid drug that provokes early miscarriage.
The main active component in almost all medications used to terminate a frozen pregnancy is mifepristone. It promotes the rejection of the embryo from the uterine walls. In some cases, if the termination was negative, in order to cleanse the uterine cavity, an additional procedure is used, which involves curettage or removal of the embryo by vacuum aspiration.
In many cases, medical abortion causes menstrual irregularities, the onset of menstruation is delayed, the date of ovulation is shifted, and bleeding is possible. Therefore, experts recommend abstaining from sexual intercourse for several weeks. In addition, planning the next pregnancy is allowed no earlier than 3 months after terminating a frozen pregnancy with medication.
Patients who have seriously experienced the loss of a fetus may develop depressive states and neuroses. To prevent such conditions, it is recommended to consult a psychologist.
What to do for different types of frozen pregnancies
The course of the process depends on the classification of the failed miscarriage and the type of frozen pregnancy, which happens:
- With anembryonia type 1.
In this case, the embryo located in the fertilized egg is not visualized on ultrasound. The size of the uterus corresponds to the 6th week of development. With this pathology, both the fertilized egg and the embryo stop developing. For up to 6 weeks, the patient is prescribed drugs that stimulate uterine contractility - causing a miscarriage. After 1-2 days, the contents of the uterus come out on their own. - With anembryonia type 2
. The fertilized egg continues to develop, it corresponds to the required development period, but the embryo has already died and is not growing. The woman undergoes a cleaning to remove any remaining fertilized egg. - All types of fetal death after 7 weeks.
After 7 weeks of pregnancy, the patient is prescribed a cleaning for any type of pregnancy loss. A course of antibiotics is also prescribed to prevent the development of endometritis - inflammation of the endometrial layer in the uterus.
Contraindications to medical abortion
Does everyone undergo a medical termination if there is a missed miscarriage? Despite the fact that it is generally considered a gentle method, this procedure has certain contraindications, which are associated with ectopic pregnancy, impaired blood clotting, pathologies of the reproductive organs, and diseases of the digestive tract.
If the body does not independently get rid of an abnormal pregnancy in the early stages (an arbitrary miscarriage did not occur), then the gynecologist decides on the need for medical termination.
Diagnosis of pathology
A woman’s health and ability to conceive and bear a healthy child after miscarriage will depend on the timeliness of treatment. In turn, medical abortion in the early stages of a missed pregnancy or surgical intervention is prescribed after determining the diagnosis, which is indicated by the following signs:
- symptoms of early toxicosis disappear sharply;
- the breasts lose their shape and become soft;
- cutting or nagging pain appears in the lower abdomen;
- discharge with blood is formed;
- The pregnancy will have to be terminated at 15 weeks if there are no fetal movements or heartbeats.
In extremely rare cases, a frozen pregnancy occurs with almost no symptoms and is detected completely by chance during the next routine examination by the supervising doctor. Pathology is indicated by a uterus that does not correspond in size to the gestational age, or by the results of an ultrasound examination.
According to doctors, the last option for determining pathologies is the most correct. The problem can be identified already a few weeks after conception. Additionally, to confirm the diagnosis, a blood test is performed to measure the level of the hCG hormone. During a frozen pregnancy, hormone levels are an order of magnitude lower than normal.
In addition, a sign of pathology will be a heartbeat that cannot be heard after the 7th week when a fertilized egg or a mature embryo is detected.
Miscarriage during a stopped pregnancy
Statistics show that almost every woman who has regular sex life has experienced a spontaneous miscarriage at least once. Fertilization of an abnormally developed egg occurs. The body reacts to this feature immediately, provoking uterine contractions, as during menstruation. Together with the blood, the defective zygote is evacuated. The woman herself may believe that there is simply a delay of 7-10 days.
Incidence of spontaneous miscarriage
The freezing of an egg or embryo at certain stages can be caused by many factors:
- Infectious lesions, viruses leading to mutations or arrest of development of the fertilized egg.
- Thick blood. In this case, a blood clot forms, as a result of which the fetus dies from exhaustion.
- Rejection (autoimmune reaction of the maternal body).
- Abnormal formation of the placenta due to insufficient nutrition.
- Genetic mutations.
The female body is genetically programmed to produce healthy and full-fledged offspring, and therefore all conditionally rejected embryos are brought out - development freezes or an arbitrary miscarriage occurs. According to statistics, such situations occur in 10-12% of pregnancies.
Consequences of medical termination of a frozen pregnancy
In some cases, negative consequences are likely to develop after the drug interruption procedure:
- Allergic reactions.
- Temperature increase.
- Pressure changes.
- Headache.
- Vomit.
- Attacks of nausea.
- Pain in the lower abdomen.
- Uterine bleeding.
In this case, the gynecologist prescribes medications to the patient to promote rapid recovery.
Complete rehabilitation, during which a woman fully recovers from hormonal shock and stress, can last for different periods of time. Its duration depends on the individual characteristics of the woman’s body.