Examination of cervical scrapings
, also known as a smear cytology (Pap test or Papanicolaou smear), is performed to detect precancerous and cancerous conditions of the cervix. The material for cytological examination is cells of the cervical canal (ectocervix and endocervix), which are examined for signs of atypia, dysplasia and malignancy. Smear cytology is a screening method for cervical cancer in most countries around the world.
- Indications and contraindications
- Material collection
- Interpretation of results
- Prices in Moscow
Currently, clinical gynecology around the world pays great attention to identifying precancerous conditions. For this purpose, a Pap smear is taken. In the initial stages of cervical cancer, the reliability of the Pap test reaches 80%.
What is a cytological examination Pap test (Pap test)
Essentially, Papanicolaou cytological examination is one of the staining methods for microscopic examination and is based on the different reaction of cell structures to acidic and basic dyes. But the undoubted merit of George Papanicolaou is that he was the first to use this staining method and substantiate its importance for the diagnosis of precancerous and cancerous diseases of the cervix. The first description of the method appeared in 1928, and in 1943 the method officially began to be used for the cytological diagnosis of cervical cancer practically worldwide. Currently, the Pap test (named after the scientist) is the main diagnostic method for this common fatal disease in women.
Features of preparation
Cytological diagnosis of the cervical mucosa must be accurate. At the initial stage, it is important to carry out preparation, which consists of taking the following measures:
- Before starting the procedure, you should not perform douching and other sanitizing measures;
- At least three days before the examination, you should abstain from sexual intercourse;
- For a certain period, you should stop using tampons, vaginal suppositories, and external agents. They can disrupt the structure of the mucosa;
- There is no need to urinate for 2-3 hours before taking a smear.
In addition, you must take into account some important nuances:
- Examination of material from the cervical canal should not be performed during menstruation. The optimal period would be 10-12 days of the cycle;
- The obtained smear cytology results will not be reliable during the period of exacerbation of the infectious disease. It is advisable to perform the examination after therapeutic therapy;
- It is recommended to stop using intravaginal drugs 5 days before diagnosis. But this should be done only after consulting a doctor.
How is the PAP test performed?
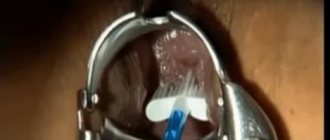
| The collection of material for research is carried out as a regular gynecological examination using vaginal speculum. A smear impression is taken from the exocervix, from the area at the border of the stratified epithelium and columnar epithelium of the cervical canal and from the lower third of the endocervix. The contents are obtained by scraping and applied to a glass slide using special brushes (cervix brush), spatulas, probes. For more convenient and accurate sampling, a special Ayre spatula is used, the long and narrow end of which is inserted into the outer pharynx, and the short and wide to the cervix. |
After collecting the material, it is sent to the laboratory, where it is first stained with basic dyes hemotoxylin or orange, and then with an acidic dye, often eosin. As a result of staining, changes in the nuclei and cytoplasm of cells can be easily determined. First, the nature of the pathological process is determined - inflammatory, reactive, malignant, then, based on the composition and changes (degrees of severity of signs of atypia) of cellular elements, a differential diagnosis of malignant and benign processes is carried out.
| Pap cytology is part of the cervical cancer screening system in all developed countries of the world. The reliability of the cytological method in early forms of cervical cancer reaches 80%. All women over 20 years of age are advised to undergo an annual examination using the Pap test. |
Indications and contraindications
An annual cytological examination of cervical scrapings is indicated for all women over the age of 20 years (or from the beginning of sexual activity). If the smear result is negative twice, you can repeat the test less often - once every 2-3 years, up to 65 years. More frequent (2 times a year) cytology examinations are indicated for women with HPV who often change sexual partners, suffer from menstrual irregularities, obesity, infertility, genital herpes, and take hormonal contraceptives. A cytological examination of cervical scrapings is performed on women before inserting an intrauterine device.
Taking scrapings for a Pap smear is not performed during menstruation or in the presence of inflammatory diseases of the vagina and cervix, as this may lead to a false result. One day before taking a smear, you should not have sexual intercourse, use tampons or vaginal suppositories.
How is the PAP test assessed?
Since 1954, a classification into five classes has been used, which was developed by D. Papanicolaou. This classification is still used in some laboratories in Russia, but in world practice it is not used and is of only historical interest.
| Classes (1954) | Cytological picture |
| Class 1 | Normal cytological picture |
| Class 2 | Changes in the morphology of cellular elements caused by an inflammatory process in the vagina or cervix |
| Class 3 | Single cells with abnormalities of the cytoplasm and nuclei. The diagnosis is not clear enough; a repeat cytological examination is required or a histological examination of biopsy tissue is necessary to study the condition of the cervix. |
| Class 4 | Individual cells with signs of malignancy: nuclear enlargement, nuclear change, abnormal cytoplasm, chromatic aberrations |
| Class 5 | A large number of malignant cells |
How the material is obtained
To obtain a scraping and diagnose the smear, a special probe is used - endobrush. The use of this tool allows you to obtain the necessary volume of biological material to perform diagnostic measures.
An experienced specialist must take a smear. The procedure is carried out in stages:
- A gynecological examination of the cervix is performed using speculum. The vaginal walls are dilated and scraping is performed;
- At the same time, material is collected to examine the microflora;
- Ready biological samples are applied to glass and fixed.
In the laboratory, the material is combined with reagents. It is then examined under a microscope. During this process the following important criteria are assessed:
- Size and structure of cells;
- The volume of cell localization in a certain area;
- Features of the arrangement of cells to each other;
- Shape of epithelial tissue;
- The presence of pathological changes, deviations from the norm.
What systems are used to evaluate the Pap test?
WHO classification
In 1968, the World Health Organization proposed a new descriptive test scoring system based on morphological criteria. Papanicolaou class 2 was divided into three forms of atypia, class 3 was described in three forms of dysplasia - mild, moderate and severe, class 4 was described as in situ cancer, and 5 as invasive cancer.
| Description (1968) | CIN (1978) | Bethesda 1988 | Classes (1954) |
| Fine | Fine | Negative for intraepithelial lesion or malignancy (NIL) | Class I |
| Inflammatory atypia or tumor | Inflammatory atypia or tumor | ASCUS | Class II |
| HPV | HPV | Low-Grade SIL | Class II |
| Atypia with HPV | Atypia, "condylomatous atypia" and "koilocytic atypia" | Low-Grade SIL | Class II |
| Mild dysplasia | I CIN | Low-Grade SIL | Class III |
| Moderate dysplasia | II CIN | High-Grade SIL | Class III |
| Severe dysplasia | CIN III | High-Grade SIL | Class III |
| Cancer in situ | Cancer in situ | High-Grade SIL | Class IV |
| Invasive Cancer | Invasive Cancer | Invasive Cancer | Class V |
CIN classification
In 1978, Richart proposed a histological classification and introduced the term CIN (cervical intraepithelial neoplasia), the degrees of which corresponded to the degrees of dysplasia of the WHO classification.
Bethesda system classification
In 1988, the US National Cancer Institute proposed a new cytological system for evaluating the Papanicolaou test - the Bethesda system, which is still used in world medicine. All changes were divided into 2 types - ASCUS (atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance) squamous cell atypia of undetermined significance and SIL (Squamous Intraepitelial Lesions) squamous intraepithelial lesions, which in turn were divided into 2 categories - low severity (LSIL - Low-Grade Squamous Intraepitelial Lesions) and high severity (HSIL - High-Grade Squamous Intraepitelial Lesions)
What are benign cell changes?
In some processes, benign changes occur in the epithelial cells of the cervix. These changes are assessed by the Pap test as inflammatory atypia, atypia caused by papillomavirus, or as mixed atypia or as atypia of undetermined significance.
Causes of benign changes
- C. trachomatis infection
- Urogenital trichomoniasis
- Human papillomavirus infection
- Genital herpes
- Urogenital candidiasis
- Pregnancy
- Exposure to chemicals (medicines)
- Infection caused by actinomycetes
- Atrophic vaginitis
- Radiation injury (with radiation therapy)
- Intrauterine contraceptive device (spiral)
What are atypical squamous epithelial cells
What is cervical dysplasia
Dysplasia (or cervical intraepithelial neoplasia - CIN) of the cervix is a pathological process that begins in the transitional metaplastic epithelium and is expressed in the appearance of atypical cells against the background of increased proliferation of basal and parabasal cells. Dysplasia can progress to squamous cell carcinoma (cervical cancer ) or spontaneously regress or regress after treatment.
What is ASCUS
| Cellular elements that are difficult to classify are defined as atypical squamous cell of undetermined significance (ASCUS). The most common cause is inflammatory processes of the cervix, however, in some cases, the appearance of cells of undetermined significance may indicate the beginning of neoplastic changes in the epithelium of the cervix. In the vast majority of cases, spontaneous regression of the changes is observed, especially after treatment of the inflammatory process. |
What is Low-Grade SIL
| Low-Grade Squamous Intraepitelial Lesions combine cytologic changes suggestive of mild dysplasia (CIN I) and human papillomavirus-induced morphologic changes (koilocytotic atypia). Low-grade SILs often regress spontaneously, even when induced high-risk papillomaviruses (16,18,31,33), but 25% of women with low-grade SIL progress to high-grade SIL within 4 years |
What is High-Grade SIL
| High-Grade Squamous Intraepitelial Lesions include moderate dysplasia (CIN II), severe dysplasia, and carcinoma in situ (CIN III). High-grade SIL is rare, but as well as Low-Grade SIL (low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions) can spontaneously regress, but most cases progress to carcinoma in situ and squamous cell carcinoma. |
Decoding the results
Please note that only a specialist who has been trained in this type of diagnosis can examine the cervix under magnification and correctly interpret the data obtained. And not every gynecologist is a good diagnostician.
What is the recommended frequency for testing? The frequency of Pap smears depends on age and medical history. Young women are recommended to be tested every two years. Together with your doctor, if there have been 3 consecutive negative tests, you can repeat every 3 years.
Women over 65 who have had 3 negative tests in the past 10 years may stop repeat testing. Risk of developing cervical cancer. A Pap test can detect infection with the papilloma virus, which is the leading cause of cervical cancer. The risk of developing cervical cancer increases to.
Acetowhite epithelium
It is detected through extended colposcopy. The doctor treats the tissue with acetic acid, and if some areas turn white, this may indicate dysplasia or the presence of a human-acquired virus (human papillomavirus - HPV) in the body. To clarify this diagnosis, the woman undergoes a biopsy of the suspicious area. If you find the words “acetowhite (or acetic white) epithelium” in your report without taking a biopsy, do not panic. This can also be a variant of the norm. The epithelium normally turns white when treated with acetic acid. True, not for long. And only in the transformation zone. The acetowhite epithelium rising above the surface is not visible. If the whitish spots are outside the so-called erosion or ectopia, a biopsy needs to be done. And only after receiving the results of a histological examination, do “cauterization” of the cervix. And then if something abnormal is detected, for example, dysplasia (CIN).
Women who become sexually active before age 18 Women who have sex with multiple partners Women who have a partner who has multiple relationships. Women who have or have had a sexually transmitted disease. . Treatment options vary depending on the extent of the cellular changes: minor, moderate, or severe. A Pap test is used to detect abnormal cell changes in the cervix and screen for cervical cancer.
An abnormal result on this test is not unusual since the cells of the cervix usually undergo permanent changes. Many abnormal papilloma tests are caused by viral infections, such as human papillomavirus infection, or other types of infections, such as bacteria, fungi, or protozoa.
Leukoplakia
This is a thickening of the uterine epithelium. It is a white or beige-white spot that rises above the surface. If left untreated, leukoplakia can turn into a malignant tumor. It is easy to detect thanks to extended colposcopy, since this procedure makes it possible to clearly examine the condition of the tissue, its size and character. A biopsy must be done to determine the scope and nature of treatment. In uncomplicated cases, anti-inflammatory treatment is prescribed followed by “cauterization.” With advanced pathology, dysplasia, surgery is usually required - conization of the cervix or even amputation.
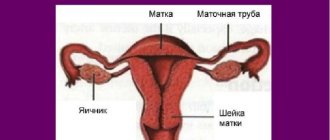
Transformation zone
During examination, great attention is paid to it, since it is most often found to show signs of cancer and symptoms of HPV infection. What is she like? The transformation zone (ZZ) is the area of the uterus where the squamous and cylindrical epithelium meet. But not every woman can see it. The transformation zone of the first type is best visible. Usually occurs in young women. The gynecologist can clearly see the boundaries of the epithelium. It is not so easy to assess the picture well and not miss pathological changes with type 2 transformation zone. This is when it is partially in the cervical canal.
If a woman has the third type of transformation zone, then colposcopy will not bring the desired results, since the desired area is located deep in the cervical canal, where it is impossible to reach with a colposcope. The only way out in this situation is to make a scraping from the cervical canal.
When they talk about an atypical or abnormal transformation zone (AZT), they mean an unfavorable colposcopic picture with atypical vessels, leukoplakia, etc. And if they talk about unsatisfactory colposcopy, then most likely the hidden transformation zone is to blame.
As a result of the Pap test, cytology smear and liquid cytology, you can see the phrase “ cells of the transformation zone are present
" What does it mean? Is this good or bad? More like good. This means that the smear is informative, since cells were taken for analysis from the area where dysplasia and then cancer usually develop.
In order for a smear to be considered adequate, at least 5000 (for liquid cytology) squamous epithelial cells must be present in the smear.
Ectropion
Turning of the cervix outward occurs after childbirth as a result of its injuries. Almost never requires treatment. Only in the case of persistent inflammatory processes, frequent cervicitis. If the woman is not worried about anything, the PAP test is normal and there are no abnormalities in the flora smears; it requires only periodic monitoring - once every 6-12 months. If the doctor believes that treatment is necessary, then one of the types of “cauterization” is used - electric current, liquid nitrogen (cryodestruction), laser, radio waves. Ectropion cannot be cured with medication or herbs.
Ectropion is often combined with scarring on the cervix as a result of difficult childbirth. Then plastic surgery is offered. This is absolutely necessary for women who are planning more children. Otherwise, they will have a risk of premature birth (they will develop isthmic-cervical insufficiency, cervical weakness during pregnancy) or, conversely, the cervix will not want to open during labor, which will necessitate an emergency caesarean section. Scars do not interfere with conception.
Atypical vessels
They are classified as an abnormal colposcopic picture. Every gynecologist knows what normal vessels look like, and only he can understand when they are deformed. Vessels that look unusual, are located chaotically, are tortuous, can have the shape of a hairpin, spiral, or loop; they are called atypical. This happens if the cervix is affected by a malignant tumor. Vascularization (proliferation of blood vessels) that does not fit into the norm is the reason for taking a “pinch” from a suspicious area. Atypical vessels will not react to acetic acid solution.
Mosaic
Upon examination, it looks like polygonal areas separated by thin blood vessels. But if it is just “marbling”, that is, the areas do not rise on the epithelium, it is called tender. The HPV virus may be present in the body, but there is no cancer. If the areas rise above the surrounding tissues, resembling a cobblestone street, this is serious, a rough mosaic, requiring a targeted biopsy.
Iodine negative zone
The doctor performs an extended colposcopy using the Schiller test and treats the tissue with an aqueous solution of iodine, or rather Lugol’s. When it gets on healthy tissue cells, as a result of a reaction to iodine they turn brown, and cells with pathological changes do not change color at all, so they are very easy to detect in this way. Tissue samples are taken from the identified iodine-negative area for analysis. Some specialists perform a Schiller test during a routine gynecological examination, and only if some areas are unpainted do they perform a full-fledged colposcopy. A positive Schiller test is indicated if the entire epithelium is uniformly stained. This is good. About negative - if there is iodine-negative epithelium.
Ectopia, open glands and Nabothian cysts
Or “congenital” erosion. Variant of the norm. The boundary between two types of epithelium. If it does not have concomitant pathology, then it is treated when it is located over a large area. Ectopia is not a disease and does not need to be treated, but once a year it is necessary to take a smear for cytology and, if atypical cells are found in it, conduct a colposcopic examination to make sure that no negative changes have occurred.
There is also true erosion, but it is diagnosed very rarely, since the mucous membranes of the human body are very quickly restored and healed. But while the wound is there, it may bleed during or after sexual intercourse. So-called contact bleeding occurs.
Open glands (OG) and Nabothian cysts are simply medical terms. These words in the conclusion do not have any fundamental meaning. Both of them arise in the transformation zone. Nabothian gland cysts sometimes become a “repository” for infection. You can read about this.
Puncture (pinpointing) - vascular anomaly
The doctor sees it as individual capillaries, numerous red dots. Apparently, this is why the erroneous name for this colposcopic sign - punctuation - has become widespread. She can be gentle and rough. Gentle occurs in young women with insufficient ovarian function, during a short period of time after and during taking hormonal contraceptives, with inflammation and viral infection. Perhaps it’s a flat candyloma, there’s nothing wrong with that either.
Coarse punctation (these are raised dots) is one of the signs of developing cervical carcinoma, that is, cancer. Indication for mandatory biopsy. Moreover, even if the results of a smear for oncocytology did not reveal dysplasia.
In addition, a histological examination is necessary if the puncture partially goes into the cervical canal, that is, the doctor cannot visually exclude atypia. Then it is recommended to undergo a cervical biopsy or endocervical curettage - curettage of the cervix.
What are atypical glandular cells
Using the Pap test, atypical glandular epithelial cells can be identified.
| ACG - atypical glandular cells (atypical glandular cells) Endocervical (from the cervical canal) cells Endometrial cells. These cells may be present in a menstruating woman, but should not be present in postmenopausal women. Atypical glandular cells with neoplastic changes Endocervical Glandular Endocervical adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) Endocervical Endometrial Ectopic |
What to do if there is an abnormal Pap test
IARC Recommendations (France and USA)
For cytological features of the LSIL type (low-grade cervical intraepithelial lesions or features of HPV and CIN I), the International Agency for Research on Cancer recommends:
| Options | Events |
| Option 1 | Carry out a repeat cytological examination after 3 months. Then, if the smear is normal (negative), repeat again after 6 months, after 1 year and after 2 years. If LSIL (positive) results are repeated, refer the woman for colposcopy |
| Option 2 | Perform a colposcopy. In the absence of abnormal colposcopic signs (normal), the cytological examination should be repeated after 6 or 12 months (depending on whether an oncogenic type of HPV is present or not). When indicated, a biopsy and diagnostic curettage of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal is performed. If the results of colposcopy are unsatisfactory (when an adequate conclusion cannot be made), therapy for the concomitant pathology should be prescribed (anti-inflammatory or estrogen therapy is possible) and colposcopy should be repeated |
| Option 3 | HPV test using the hybrid capture method (HPV Digene test) or PCR. If oncogenic types of HPV are present, colposcopy is indicated; if not, repeat cytological analysis is indicated after 6 months. |