Uterine fibroids are a benign neoplasm that grows from muscle cells. Among gynecologist patients, it occurs in every fifth woman under 45-50 years of age, and in every third during the menopausal period. The treatment method for interstitial uterine fibroids is chosen based on its size, accompanying symptoms and the woman’s age.
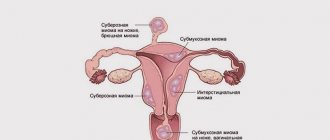
Interstitial fibroids - what is it?
A feature of this pathology is that in this case the tumor grows inside the muscle layers of the cervical tissue. The growth rate of interstitial fibroids is much lower, but inward growth of the node creates difficulties for treatment, and in some cases requires urgent surgical intervention. It is this form that occurs in women more often than others, and also poses the greatest danger.
Complications
Bleeding from fibroids, which is the main complication, is accompanied by anemic syndrome. This condition is characterized by low hemoglobin levels and iron deficiency. Anemia is expressed by symptoms such as:
- Dizziness.
- Frequent fainting.
- Pale and dry skin.
- Deterioration of hair and nails.
- Seizures in the corners of the lips.
- Decreased memory, attention and performance.
- Perverted appetite - the desire to chew chalk, ice, earth.
To treat anemia, it is necessary to eliminate the cause of bleeding, i.e. fibroids, and take iron supplements prescribed by your doctor.
The anterior wall of the uterus is adjacent to the bladder. Therefore, with large myomatous nodes located in this area, compression of the bladder and ureters occurs. Urine from the ureters flows back into the kidneys, leading to hydronephrosis. Stagnation of urine is also complicated by the development of pathogenic microflora, which is accompanied by inflammation of the bladder (cystitis) and kidneys (pyelonephritis). There are also cases when a myomatous node on the anterior wall provokes the occurrence of fistulas between the uterus and the bladder.
Pedunculated fibroids growing in the uterine cavity can break away from the base. The “born” node causes severe cramping pain and severe bleeding from the genital tract.
This condition requires urgent medical attention. Also, emergency surgical intervention is necessary when the pedicle of the subserous node is torsed. In this case, tumor necrosis occurs, which is accompanied by severe pain and signs of inflammation of the peritoneum (peritonitis).
What are the causes of the appearance and growth of interstitial fibroids?
In addition to a woman’s genetic predisposition, doctors identify a number of factors such as:
- Stress, depression, overexertion, nervous conditions;
- Trauma to female organs;
- Excessively long wearing of the intrauterine device (or incorrect installation);
- Hormonal imbalance: due to excess estrogen and progesterone;
- Inflammation in the urinary system, pelvis: infection;
- Physical overexertion;
- Metabolic disease;
- Heredity;
- Too early or late onset of sexual activity;
- Lack of full sexual activity: dissatisfaction;
- Frequent abortions;
- Hypertension;
- Bad habits: alcohol, cigarettes, drugs.
Despite the fact that the causes are varied, specialists often cannot identify a specific cause in their patients. Basically, the causes of pathology are multifactorial in nature.
Important! About half of women aged 30 to 40 experience this disease.
Causes of development of myomatous tumors
Despite the active development of medicine, it has not yet been possible to establish the exact causes of the development of this tumor process. Therefore, scientists are inclined to believe that the growth of myomatous nodes is a consequence of hormonal imbalance. But there are quite a lot of factors that precede such a violation of women’s health. The main ones are:
- genetic predisposition;
- difficult childbirth;
- abortions and other mechanical damage to the uterus;
- a number of concomitant diseases, including diabetes mellitus, thyroid disorders, high blood pressure;
- poor circulation in the pelvic organs due to a sedentary lifestyle.
Symptoms of interstitial uterine fibroids
Undoubtedly, every woman is required to undergo an examination by her gynecologist at least once a year. But if this does not happen, then you should pay attention to the following symptoms:
- Severe pain premenstrually or during menstruation;
- Bleeding between periods;
- Heavy discharge during menstruation (as a rule, blood comes out in clots);
- The pain is localized in the lower abdomen and lower back;
- Abnormal bowel movements, frequent urination, intestinal disorders;
- Disruptions in the menstrual cycle (absence, reduction or increase in menstruation)
- Pain during intercourse, accompanied by bloody discharge.
It is worth noting that this symptomatology is characteristic not only of the centripetal type of fibroids.
Also, depending on the stage of development of the pathology, three types of pain can be distinguished:
- With a small size of fibroids , pain occurs only during menstruation (this is rare for such an early stage, due to the relatively small size of the tumor).
- At the beginning of the growth of fibroid nodes there is a constant cutting pain.
- The decomposition phase of the nodes is a sharp and severe pain, causing nausea and vomiting. The patient's temperature also increases.
How to recognize the disease?
It is no secret that many women in our country ignore preventive examinations by a gynecologist, even if they require a medical examination at work. It is easier for our fair half of humanity to buy a document with seals from unscrupulous medical workers than to think about the question, uterine fibroids - what is it? But the danger of the situation lies in the fact that many diseases of the female genitourinary system are asymptomatic in the early stages, including fibroids. Symptoms appear even when the tumor has grown to a significant size and interferes with the normal functioning of the organs of the reproductive system. At the same time, clinical signs are individual in nature and depend on the location of the tumor, its size, the presence of concomitant diseases, the age of the patient and many other factors.
Complications caused by interstitial fibroids during pregnancy
Basically, the main danger for a woman is complications associated with the pregnancy process. Therefore, it is very important to be checked for the presence of such a tumor before conception.
If the fibroid is already large enough and compresses the tubes, then it blocks the access of sperm to the uterus, and therefore prevents pregnancy.
However, if the size of the fibroid nodes is not large enough, then conception can be successful. But the growth of the tumor will pose a danger to the fetus and the pregnancy process may end in miscarriage.
Drugs for drug therapy of fibroids
- Antigonadotropins. Helps slow down and stop tumor growth. Most often from this group, doctors prescribe the drug Gestrinone to patients. It is indicated for women who have a medium-sized intramural myomatous node.
- Gonadotropic releasing hormone agonists. Drugs in this group have complex pharmacological effects. They are prescribed to women to reduce the level of sex hormones, causing a condition similar to menopause. Systematic use of these medications can significantly reduce the risk of uterine bleeding and partially relieve pain. Most often, drugs from this drug group are prescribed: Triptorelin, Goserelin, Buserelin or Zoladex. After completing the course of therapy, the menstrual cycle quickly returns to normal.
Diagnosis of the disease
If you have the symptoms described above, a visit to a gynecologist is mandatory. With a full examination, the disease can be easily detected. To do this, the doctor will make an initial diagnosis and prescribe a series of tests that the patient needs to undergo.
The first and mandatory step will be taking tests to the laboratory. Among them:
- Complete blood count, blood test for cancer cells;
- Hormone analysis;
- Analysis of the microflora of female genital organs;
- Analysis of urine;
However, laboratory results alone will not be enough. After or before all tests are completed, the patient is referred for ultrasound or x-ray examinations.
Ultrasound diagnostics can determine the growth rate of fibroids, size, location, and type.
Rarely are MRI or CT scans used to clarify the diagnosis.
Treatment
As soon as the presence of tumor-like formations is detected, the patient is admitted to the hospital under medical supervision. This practice is carried out in case the growth of fibroids accelerates and urgent surgical intervention is necessary.
However, despite the severity of interstitial fibroids of the uterine body, depending on the stage of its development, drug treatment can also be used. The stage is considered early if the growth time of the node does not exceed eight weeks.
This treatment is based on taking hormonal drugs:
- Antiprogestogens (Triptorelin, Goserelin, Duphaston);
- Agonists (Mifepristone);
- Androgenic steroids.
- Combined oral contraceptives;
- Gestagens.
Additionally, homeopathic remedies may be prescribed.
These medications control the growth of fibroids, stop them and can help shrink tumor nodes.
Medicines are selected by the doctor individually for each patient. Therefore, independent choice of medications is contraindicated.
Drug therapy
With early diagnosis of neoplasms, conservative treatment allows women to take control of the pathological process in their body, and even bear the desired child. Such therapy is possible only in cases where the fibroid is localized exclusively in the myometrium, is characterized by a slow rate of development, and is also relatively small in size (up to 12 weeks of pregnancy).
This method of therapy is based on taking hormonal drugs to restore the proper functioning of the female body. In combination with these drugs, doctors prescribe symptomatic medications in each specific case.
Surgery
If treatment with medication is not possible, surgical intervention is performed. This determines a number of indications:
- Excessively large size of tumor-like nodes;
- Infertility;
- Inflammatory process in the body;
- Rapid growth of fibroids (at least 4 weeks per year);
- Heavy bleeding.
- Necrosis of the node;
- Formation of a subcumcosal node.
- Multiple nodes.
As soon as the doctor notices these symptoms, the patient is immediately taken to the surgical bay and begins her preparation for surgery.
The following methods are available for performing the operation:
- Ultrasound or FUS ablation (the least traumatic method, which involves rapid rehabilitation of the patient);
- Laparotomy (surgery in the abdomen);
- Laparoscopy (incision only 0.5 - 1.5 cm);
- Hysteroscopy (intravaginal tumor removal).
In more severe cases, not only the nodes are removed, but also the organ affected by the tumor. As a rule, a woman knows about the need for such an operation.
Doctors can resort to such radical measures only if the life of their patient is threatened.
The least dangerous and gentlest for the patient’s health are laparoscopy and gastroscopy. These operations minimize the risk of losing the uterus and the woman’s reproductive function.
Also, after these operations, the rehabilitation time is significantly reduced, as is the risk of a similar pathology occurring a second time.
Features of the development of the disease
Any fibroid begins to develop in the middle layer of the uterine wall - the myometrium. A myomatous node can develop quite slowly, but only until a hormonal imbalance occurs in the body, due to natural age-related changes or external factors. The further direction of growth directly depends on the location of the pathology. If it is located on the border with the endometrium, then in the absence of timely therapy, the interstitial myomatous node can transform into a submucosal one. And in a location bordering on perimetry - subserous.
Thus, when interstitial fibroids are diagnosed, the choice of a possible method of therapy should be determined immediately. Delaying treatment can lead to further development of the disease and many negative consequences, such as infertility, anemia due to heavy bleeding, etc.
Fuse ablation
This is a completely new method, not yet used in all clinics. However, if the location, size and structure of the myomatous nodes allow a similar procedure to be performed, then this option can be chosen. The mechanism of the operation itself is simple - when biological tissues are exposed to ultrasound, they heat up. This leads to a change in the blood flow of the tissue and complete dehydration of the tumor (its necrosis).
Fuse ablation allows you to reduce small myomatous nodes in 2-3 procedures. However, the larger the tumor, the longer it will take to destroy it. The correct choice of this particular operation should be discussed with a gynecologist.
After operation
After surgery, the patient is under the supervision of specialists for some time, and then discharged.
A preventive measure after discharge is a mandatory visit to the gynecologist’s office, lifestyle control and exclusion of all possible factors leading to the development of pathology.
The rehabilitation period is about six months. At this time, it is important to exclude various physical activities, overexertion, and especially sexual intercourse. After the rehabilitation time has expired, the woman must undergo a re-examination and be monitored again by her attending physician in order to prevent any germs of the disease.
Early diagnosis of interstitial uterine fibroids gives favorable prognosis for treatment. The tumor can be treated with medication without much difficulty.
If you ignore the symptoms and the presence of a tumor, the process of its growth leads to terrifying consequences: infertility, intrauterine bleeding, pathologies in the fetus, miscarriages, diseases of the intestines and genitourinary system.
If the disease is particularly serious, there is a possibility of developing cancer.
An annual visit to the gynecologist is the main prevention of uterine fibroids. The main thing to remember is that you should take care of your health and not neglect visiting doctors.
Video: Uterine fibroids with centripetal growth
Uterine fibroids with centripetal growth.
Video: large uterine fibroids with centripetal growth of the node
Large uterine fibroids with centripetal growth.