Preparing for analysis
No special preparation is required for a smear from the cervical canal, however, there are rules that must be followed in order for the result to be accurate:
- Before the analysis, you should wash yourself, but do not douche;
- The day before the test, you should not use lubricants or gels for the vagina;
- More than a day must pass after the last sexual intercourse;
- It is not advisable to take medications before a smear. If the use cannot be stopped, you should tell your doctor the name of the drug and its dosage;
- Before the analysis, you should not drink alcohol or energy drinks, and you should also stop smoking;
- The day before the analysis, exotic foods, as well as spicy, sour and smoked foods, should be excluded from the diet.
It should be remembered: the optimal time for taking the test is 11-14 days of the cycle, approximately 5-7 days after the end of menstrual flow.
There is no need to be afraid to take a smear from the cervix - taking it is absolutely painless and harmless to the patient.
Standard results for a smear from the cervical canal
| Index | Normal value |
| Leukocytes | 0-30 |
| Flat epithelium | 5-10 |
| Gonococci | None |
| Trichomonas | None |
| Yeast cells | None |
| Key cells | None |
| Microflora | Absent |
| Slime | Moderate amount |
If any of the analysis indicators differs from the normal value, you should definitely contact a gynecologist to prescribe treatment.
Increased mucus content
There are many reasons why a cervical smear may have an increased content of mucus. They are divided into two main groups: physiological and pathological, that is, normal and abnormal.
The first group includes the following changes in the female body:
- Changing hormonal contraceptives;
- Pregnancy and lactation;
- Using new intimate gels or lubricants;
- Change of sexual partner;
- Taking antibiotics and antibacterial drugs;
- Stitches on the cervix, after childbirth or surgery;
- Moving to another region;
- Treatment with mud or turpentine baths, phyto-barrels.
Pathological causes include:
- STDs such as gonorrhea, chlamydia and others. In the case of these diseases, there are usually other changes in the smear;
- Vaginitis, or inflammation of the uterus. A dangerous disease that, if left untreated, can lead to consequences such as infertility and even removal of reproductive organs;
- Urethritis, or inflammation of the urethra. Quite a common occurrence, especially in the cold season. Accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen, pain when urinating. If not properly treated, it also leads to serious illnesses;
- Fibroids, cysts and other neoplasms in the uterus can cause large amounts of mucus, up to 600 ml per day;
- Dysbacteriosis, or imbalance of bacterial balance in the intestines. Rare, but can lead to increased mucus production on the cervix;
- Allergic reaction. The cause of increased mucus content in a smear from the cervical canal may be an allergy to synthetic underwear, lubricant or intimate hygiene products. Rarely, food allergies can also manifest themselves in this way.
An increased content of mucus in a smear is not a disease, but a consequence of the disease. The exact cause of its appearance can only be determined by a doctor after a comprehensive examination.
Slime function
In the female body, mucus performs important functions:
- Protective. Mucus prevents bacteria and foreign substances from entering the uterine cavity;
- Lysing. Mucus can destroy bacteria and foreign substances that enter the vagina;
- Regenerating. Mucus takes part in the restoration of damaged tissue areas, so after childbirth and operations the amount of mucus increases;
- Participates in fertilization. With the help of mucus, sperm enters the uterine cavity for subsequent fertilization of the egg.
Mucus is produced by special cells under the influence of female sex hormones - estrogens. She is alkaline and alkaline, whereas the vagina is acidic. The mucus contains lactobacilli, plasma and some blood cells, and epithelial cells.
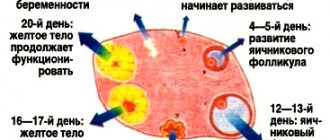
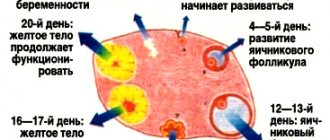
Depending on the day of the menstrual cycle, the composition and amount of mucus changes. From days 1 to 5 it is released in small quantities and has a watery consistency; from days 6 to 10 it becomes thicker and is released in larger quantities. From 10 to 15 days, during the period of ovulation, mucus reaches its maximum quantity and thickness. After the 15th day of the cycle, if fertilization has not occurred, the amount of mucus gradually decreases, and if pregnancy occurs, it increases.
What is cervical mucus like? Let's look at it by day of the cycle
So you've completed the test. Now look carefully at the smear - cervical mucus differs by day of the cycle. Here's what you should focus on:
- Immediately after menstruation, almost no cervical mucus is secreted, and the vagina feels dry. These days the probability of getting pregnant is extremely low;
- after 2-5 days, very thick mucus begins to be produced, resembling glue. It is heterogeneous and consists of individual clots. This substance greatly limits sperm motility, protecting you from conception;
- further, the discharge liquefies, becoming similar to cream or cream. Their color becomes opaque, cloudy white or yellowish. The amount of cervical mucus increases sharply and can leave marks on your underwear. The chances of pregnancy increase, although not to the maximum;
- on days 9-13, watery and extremely copious discharge begins. They are almost transparent, and when you try to touch them, they drip or run off your fingers. This mucus facilitates the passage of sperm, but does not protect them from the acidic environment in the vagina, so that most of the male germ cells die;
- By 14-19 days after the end of menstruation, the time of highest fertility (ability to fertilize) comes - ovulation, which lasts 2-4 days. This period is indicated by viscous cervical mucus, similar to egg white. If you spread your fingers stained with it, a “thread” 2-3 cm long will form from the secretions. This substance is optimal for conception.
When should you worry?
Normally, mucus does not cause discomfort in a woman. But if:
- There is too much vaginal discharge;
- The discharge is yellowish or greenish in color;
- The discharge has an unpleasant odor;
- Discharge with a cheesy consistency;
- The discharge contains blood clots or brown spots (outside of menstruation);
- Discharge causes discomfort;
- Itching appears in the vagina;
- Redness, spots or acne appear in the perineum;
- Pain appears in the lower abdomen.
You should consult a doctor immediately.
Pay attention to color
The color of the discharge during ovulation and for a couple of days after it is also quite informative
. Be sure to pay attention to it, as it can set off an alarm when seeing a doctor will help a woman maintain her health in the future
For each individual woman, the nature of the discharge is usually stable; it does not change significantly from cycle to cycle. Therefore, the appearance of new characteristics should alert a woman. Normally, discharge during ovulation is transparent. For some, the appearance of pink discharge and small brownish streaks of blood in the discharge 1-2 days after ovulation, without pain or fever, is also considered acceptable.
An admixture of blood appears as a result of injury to the blood vessels, which are also present on the follicle shell. When it ruptures, it is disrupted and a certain amount of blood and fluid from the follicle in which the egg grew and developed enters the abdominal cavity.
Ovulation discharge does not last long, and even for those who normally have it mixed with blood, it should turn white after 2 days. If a woman has always had clear discharge, and suddenly blood appears, she should definitely visit a gynecologist. It is possible that the woman has an inflammatory process of the pelvic organs. This is how endometrial polyps often appear.
Spotting dark bloody discharge during the middle of the cycle (so-called breakthrough bleeding) often occurs with polycystic ovary syndrome. Bloody liquid discharge may be a sign of uterine fibroids - any of these conditions requires mandatory diagnosis and treatment.
Red and brown discharge, as well as pink, orange and others, are all types of blood discharge. It’s just that the color may partially indicate the time of red blood cells entering the mucus - with brown discharge, we can say that the hemorrhage happened a few days ago, the blood has already clotted. The brighter the color of the blood, the more likely it is that the bleeding is fresh and may still be happening.
Yellow and yellowish discharge that appears in the middle of the cycle should not be attributed to the action of progesterone - it is too early for that. They may manifest as bacterial vaginosis, gonorrhea or chlamydia. If the discharge is strong, liquid, not viscous, but watery, possibly with impurities resembling light flakes, you should be examined for sexually transmitted infections
Pay attention to the accompanying symptoms: unpleasant odor, itching and burning in the vagina, discomfort during sexual intercourse, as well as pain in the lower abdomen of any nature
White and thick curdled discharge during ovulation is a sign of thrush. The proliferation of Candida fungi is not directly related to the ovulation process, and we can assume that ovulation simply coincided with this unpleasant genital disease. Creamy, homogeneous discharge of a greenish, grayish or brown color may indicate the presence of a bacterial infection. In this case, the temperature usually rises and the lower abdomen hurts.
Drug treatment of increased mucus content in the smear
It is used depending on the cause of the disease:
- Antibacterial therapy. It is used in case of damage to the body by bacteria or viruses. The antibiotic is selected depending on the sensitivity of the foreign agent. Both general and local drugs are used;
- Antifungal therapy. It is used when the body is infected with fungi (most often the Candida type). Medicines are used both locally and internally;
- Douching. Used for large amounts of mucus. It is carried out with boiled water at room temperature or decoctions of herbs, such as sage and chamomile;
- Hormonal therapy. It is carried out under the supervision of a gynecologist (often in a hospital) in case of hormonal imbalances in the body;
- Treatment of cystitis and urethritis. It is carried out using diuretics and antibacterial drugs;
- Antiallergic therapy. It is carried out with the help of antihistamines (for example, Suprastin, Zodak) and adsorbents (Polysorb, activated carbon).
Surgical treatment
Surgical treatment is carried out in the presence of neoplasms in the uterus or its appendages according to indications.
Treatment with folk remedies
The experience of past generations has accumulated many treatment methods that are still relevant today:
- For infectious diseases, a decoction of elecampane, celandine or fenugreek will help;
- For hormonal imbalances, a decoction of boron uterus, an infusion of rowan in alcohol, and tea from white rose leaves are effective;
- For allergies, a decoction of chamomile and dandelion root will help;
- A decoction of oats and wormwood is effective against dysbiosis;
- To treat urethritis and cystitis, lingonberry leaves and kidney tea will help;
- It will strengthen the immune system and help you cope with any disease more quickly: a decoction of rose hips, echinacea, honey water.
It should be remembered that traditional medicine works individually for each person. You should not use them without consulting your doctor.
Gynecologist's recommendations
To prevent various types of sexual diseases and pathologies, gynecologists recommend:
- Do not wear synthetic underwear made of thick material. It reduces thermoregulation and creates moisture on the surface of the genitals. This promotes the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria.
- At home, wear loose clothing made from natural materials, preferably cotton.
- For preventive purposes, wash the genitals with warm chamomile infusion. It will relieve irritation and soften the skin. Especially necessary after a long day spent in tight and synthetic clothing.
Self-medication if you have periods with mucus is not the best way. If a woman is worried or alarmed by any symptoms, she should contact the clinic. A doctor will help you find out what kind of disease this is.