The inner surface of the uterus is covered with a mucous layer called the endometrium. It changes under the influence of hormones, the level of which fluctuates depending on the day of the menstrual cycle. That is why, when conducting an ultrasound examination on different days of the cycle, the specialist sees different thicknesses and structures of this important functional layer. The mucous membrane can be in several states. Each of them has its own standards. One of them can be called a three-layer endometrium. Let's look at what this means below.
Often, women of reproductive age are concerned about the thickness of the endometrium. It is thanks to regular renewal of the mucous membrane that you can easily become pregnant. To conceive, you definitely need a three-layer endometrium so that the fertilized egg can easily attach to the wall of the uterus and begin to develop.
As you know, today you can conceive a child not only during sexual intercourse, but also through artificial insemination, when an egg is placed in the same test tube with sperm, and then the embryo is implanted into the uterus. In this variant, the three-layered endometrium plays the most important role.
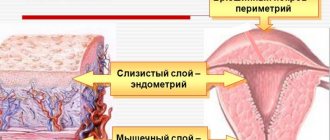
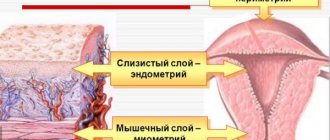
The uterine cavity has two main layers:
- basal - lower;
- functional - top.
- There is also another, uppermost layer - the epithelial layer, which is not always present.
The bottom layer always remains unchanged - the phases of the cycle do not affect it. It is represented by epithelial cells. The structure is quite dense.
The functional layer consists of glandular cells. It's loose. This is what we see during monthly bleeding. Under the influence of hormones, it is rejected if conception does not occur, and is renewed for new attempts.
On top of the functional layer is a very thin layer of epithelium. As with basal, it is not affected by hormone fluctuations.
Now it should become clear what a three-layer endometrium is. On the monitor screen during an ultrasound examination, the specialist should see all three layers, the presence of which is very important after ovulation. If the picture is different, implantation of the fertilized egg is unlikely to take place.
As already mentioned, in order not to miss the presence of three layers of the endometrium, you need to go for an ultrasound. Experts call this state a linear structure. If we talk about echogenicity, the layers absorb ultrasound quite poorly, unlike the space that separates them. In the image you will see four lines where the mucous membrane is clearly divided into three parts of different thicknesses.
After the examination, some women are interested in: the endometrium is three-layered - what does it mean if it does not appear when it is needed? Most likely, we are talking about hormonal imbalance. In this case, after the ultrasound, you need to go to an appointment with a gynecologist, get tested and together with him figure out why this is happening.
Definition
A three-layer endometrium is a necessary condition for natural pregnancy or in vitro fertilization. Even reproductive doctors refuse to carry out the embryo transfer procedure in cases where the three-layer endometrium is absent. What does it mean?
Strictly speaking, this mucosa has two main layers - basal and functional. The basal layer is a fairly dense layer that does not undergo changes during one menstrual cycle. The functional layer is this one, which is rich in blood vessels, has a less dense and looser structure and is located on the basal layer, that is, it directly lines the uterine cavity. It is this layer that is actively rejected, and then grows again during the monthly cycle; it leaves the body along with menstrual flow.
On the functional layer there is a thin epithelial layer, which is almost completely unaffected by hormones. Thus, when these layers are clearly distinguishable and visualized on ultrasound, we can talk about a three-layer endometrium. Thus, we can conclude what it is. This is a situation when all three layers are clearly visualized in the endometrium:
However, this is not always the case, but only at certain stages of the menstrual cycle.
Hypoplasia
In this case, there is no need to say what a three-layer endometrium is. Since we are talking about thinning of the endometrium, the thickness of which does not exceed 6 mm. Normally, it should be about 9-13 mm in the middle of the cycle.
It is impossible to do without the participation of a gynecologist. You should especially seek medical help if the thickness remains unchanged throughout the entire cycle. Perhaps we are talking about chronic endometritis, which is caused by blood supply disorders.
If an ultrasound examination reveals a three-layer endometrium in the luteal phase, what does this mean? Along with uniformity in the first half of the cycle, this can be a cause of infertility. They again lie in hormonal imbalance.
The fertilized egg will not be able to attach to the endometrium if it does not meet the required parameters. Therefore, you should definitely consult a doctor to start corrective hormonal therapy. Most often, oral contraception is prescribed, as well as drugs based on progesterone and estrogen.
If you are planning a pregnancy and have difficulty conceiving, you need to undergo a full examination to find the cause.
It is possible that the culprit will be insufficient growth of the functional layer or the absence of its multi-layering. In any case, contact a specialist and together with him go towards your dream - to have a child. Share:
Cycle phase
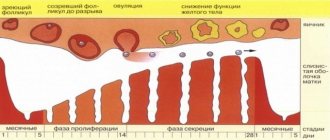
This structure is a normal and physiologically determined phenomenon if it occurs in the first phase of the menstrual cycle, that is, in the proliferation phase. During this period, the endometrium is actively renewed and regenerated, as a result of which it grows and is almost completely restored after menstrual bleeding (at least, it restores most of the thickness and functional layer). This is a natural and normal condition that occurs under the influence of the hormone estrogen, which activates cell division and proliferation.
After this, ovulation occurs. Progesterone begins to influence the body, which, among other things, suppresses the activity of estrogen, and therefore the rate of growth. In the second phase, due to this, the mucous membrane becomes homogeneous; ultrasound examination no longer visualizes clear boundaries between the layers. Thus, a three-layer endometrium is necessary at the first stage of the cycle, as it becomes a condition for normal conception. Even if the endometrium is thin (7-8 mm), but has a three-layer structure, pregnancy is more likely to occur than with a mucous membrane of normal thickness, but not a three-layer structure.
Endometrial thickness
Endometrial thickness and inflammatory damage
In such situations, thickening of the endometrium is just a compensatory reaction in response to one or another stimulus.
Very often this is a chronic infection (STD).
In this case, diffuse thickening of the entire inner layer of the uterus may be observed.
So are focal changes - cystic degeneration, the formation of areas with fibrous (scar) tissue.
Over time, such subacute chronic endometritis has an inhibitory effect on ovarian function and anovulation.
Naturally, such a pathology makes conception and pregnancy impossible.
Viral infections and endometrial thickness
Cytomegaloviruses and other representatives of this type of microorganisms cause quite serious damage to the endometrium.
Often, not only the superficial glandular layer is subjected to such negative effects, but also the deeper one - the basal one.
When a chronic viral infection is combined, the concentration of estrogen receptors in a particular area of the uterus often increases.
The result is the appearance of a glandular polyp.
These formations can be single or multiple.
Often located in the fundus and corners of the uterus, they negatively affect the possibility of implantation and gestation.
What are the most serious situations?
Patients with a heterogeneous structure - areas of normal and thickened endometrium - require special attention.
Physiologically, this can only happen immediately after menstruation or after curettage.
In all other cases, it is necessary to exclude oncological pathology.
The most serious conditions in which endometrial hyperplasia may occur are cancerous processes.
In gynecology in the 50s of the 20th century, it was even believed that such conditions were a direct indication for removal of the uterus.
Now such women are shown screening ultrasound 2 times a year and treatment of the underlying process that caused the pathology.
Endometrial thickness: hypoplasia
The term is slightly relative, since in different phases of the menstrual cycle, the fluctuations are quite significant.
Direct hypoplasia is considered to be a discrepancy between the thickness of the endometrium and the regulatory phases.
Less than 7 mm in the first half (proliferation) and less than 8 mm in the second half (secretion).
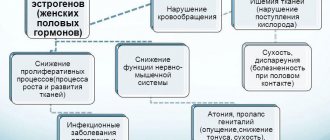
The reasons for this “underdevelopment” may be:
- Chronic endometritis (STIs, nonspecific infections)
- Ovarian hypofunction
- Obesity
- Decreased thyroid activity
- High levels of prolactin (pituitary hormone)
- Polycystic ovary syndrome
- Congenital anomalies of the adrenal glands
With diffuse underdevelopment, incompetence, of the endometrium, the key problem is infertility.
In order for a fertilized egg to be implanted confidently and firmly after conception, the thickness of the endometrium must be 8 mm or more.
Otherwise, classic female infertility will occur.
Or frequent miscarriages: due to the endometrial layer being too small, the placenta will not be able to fully form.
Modern reproductive technologies help many women increase the thickness of the endometrium to the physiological norm and still become a mother.
But how to achieve this is always decided individually.
Pregnancy and endometrial thickness
After implantation of the fertilized egg, serious hormonal changes begin in the woman’s body.
They also affect the endometrium.
To ensure adequate nutrition of the embryo, it thickens and in the early stages the layer reaches 2 cm and higher.
In the future, during a normal pregnancy, the thickness does not change, but may regress somewhat closer to childbirth.
Endometrial thickness during menopause
With the onset of menopause, the activity of the sex glands - the ovaries - decreases.
This inevitably leads to a drop in estrogen levels and, as a consequence, endometrial involution.
The rate at which the thickness of the inner layer of the uterus decreases is always individual.
But the general trend is the same - physiological hypoplasia up to 1-3 mm during menopause.
(No periods for a year or more).
Proliferative processes and endometrial thickness
This is always a pathology:
- Polyps
- Adenomyosis
- Endometriosis
- Cancer
Single, clearly demarcated areas are usually polyps.
These are benign growths, which, however, can develop into cancer.
It is difficult to detect malignancy based on the thickness of the endometrium.
Doctors rely more on biopsy data.
And if uterine cancer is suspected, a piece of suspicious tissue is taken for cytological analysis.
Adenomyosis and endometrial thickness
This pathology is also called “internal endometriosis.”
Areas of thickening of the endometrium appear due to the fact that it grows into the muscular lining of the uterus.
Manifestations are nonspecific:
- Heavy, prolonged menstruation
- Noticeable enlargement of the uterus; in advanced stages of the process, you can palpate irregularities in the contour of its body
Early forms of adenomyosis practically do not interfere with conception and implantation.
However, during pregnancy and childbirth they can create certain problems.
Endometrial thickness in endometriosis
Against the background of this pathology, the thickness of the endometrium changes slightly.
But it acquires a nodular, heterogeneous structure.
And it is found where it should not be, for example, in the cervical canal, on the ovaries.
Cancer and endometrial thickness
A very dangerous and multifaceted pathology.
The only positive thing.
Malignant tumors almost always grow from foci of endometrial hyperplasia: polyps, myomatous nodes.
The initial stages can only be identified using ultrasound, MRI or hysteroscopy.
Therefore, it is recommended to undergo such examinations at least once a year.
Especially for women with infertility, menstrual pathology and menopause.
If a doctor advises you to get rid of a benign externally nodule, you should listen to the opinion of a professional.
If you have endometrial pathology, contact experienced gynecologists at our medical center.
Danger
A deviation from the norm is a situation when the condition of the mucous membrane does not coincide with the phase of the menstrual cycle. What danger does such endometrium pose in the second phase? If such endometrium is diagnosed at this stage of the cycle, then it is not the endometrium itself that poses the danger, but the reasons that caused it. Often, this is a hormonal imbalance associated with the production of progesterone - if it is not enough - then clear visualization of the layers continues in most cases. But there may be other deviations.
If the endometrium is homogeneous in the first phase, or three-layered in the second, then this could potentially lead to infertility. It primarily develops due to hormonal imbalance. In addition, the inability of the embryo to attach to an unhealthy endometrium plays an important role, so the condition must be treated in a timely manner. Therapy is carried out with hormones - estrogen, progesterone, combined estrogen-progesterone oral contraceptives.
Create an account
Register for an account. It's simple!
The mucous layer located on the inner surface of the uterus, which changes greatly under the influence of the hormonal cycle, is called the endometrium. Therefore, the ultrasound picture of this area in different menstrual phases is very different. Based on this, doctors identify several conditions of the mucous membrane associated with the stages of the female body’s cycle. One of them is a three-layer endometrium. Next, we will consider what it is, whether this phenomenon has signs of pathology, whether it is dangerous, or whether it is a variant of the norm.
Definition
The presence of a three-layer endometrium is required for conception, occurring naturally or extracorporeally. Reproduction specialists do not transfer an embryo if the uterine lining is in a different condition.
There are two main layers. The basal one, consisting of epithelial cells, is dense, it does not change with the phases of the cycle. The functional one, from glandular cells, is loose, it is quickly rejected and comes out along with menstrual blood, and then forms again after a certain time. There is a very thin epithelial layer on it, which is practically not affected by hormonal changes. As a result, when all three parts of the mucosa are clearly visible on an ultrasound examination, we can conclude that the endometrium is three-layered. That's what it means.
But this condition is not observed all the time, but only at a specific stage of the cycle.
Hyperplasia
With the growth of the endometrium, the inner mucous membrane of the uterus grows excessively and does not correspond to the indicators that a healthy woman should have. This disease is often accompanied by intermenstrual bleeding.
If the thickness of the lining does not change throughout the month, this may be a manifestation of a chronic form of inflammation of the uterine mucosa or endometritis.
Any of these pathologies can be treated, and the sooner it is identified, the less effort will have to be spent on fighting the disease.
How to identify
It was previously noted that the main diagnostic method in this case is ultrasound. Experts called this state a linear structure. The fact is that the space between the three layers has good echogenicity, unlike these areas themselves (basal, functional and epithelial), so that in the resulting image they take the form of clear lines. The picture clearly shows the mucosa divided into three parts.
If the three-layer endometrium does not appear on time, then there is a hormonal imbalance. Then an ultrasound is not enough; you need to be tested for infections in order to understand the nature of the deviation.
Cycle phase
This condition is considered normal when it appears in the first phase of the hormonal cycle, called the proliferation stage. At this time, the endometrium grows rapidly, recovering from menstruation. Its previous thickness returns and the functional layer is regenerated. This is a common phenomenon in the female body, which is stimulated by the hormone estrogen, which causes cell division.
This is followed by ovulation. It is stimulated by progesterone, which suppresses estrogen and slows down growth. Only within a few days after ovulation does the endometrium in women have its maximum thickness. During this period, he is ready to receive a fertilized egg.
Thus, at the second stage, the mucous membrane looks homogeneous, the boundaries between its layers on ultrasound are erased.
So, a three-layer endometrium should be present precisely at the beginning of the cycle, as a condition for possible pregnancy. Even with a thin (7-8 mm) but three-layer endometrium, conception is likely to occur. But if the mucous membrane is of acceptable thickness, but homogeneous, this is unlikely.
Three-layer endometrium
The inner surface of the uterus is covered with a mucous layer called the endometrium. It changes under the influence of hormones, the level of which fluctuates depending on the day of the menstrual cycle.
That is why, when conducting an ultrasound examination on different days of the cycle, the specialist sees different thicknesses and structures of this important functional layer. The mucous membrane can be in several states. Each of them has its own standards.
One of them can be called a three-layer endometrium. Let's look at what this means below.
Often, women of reproductive age are concerned about the thickness of the endometrium. It is thanks to regular renewal of the mucous membrane that you can easily become pregnant. To conceive, you definitely need a three-layer endometrium so that the fertilized egg can easily attach to the wall of the uterus and begin to develop.
- Definition
- Menstrual cycle
- Hyperplasia
- Hypoplasia
Menstrual cycle
The menstrual cycle is divided into two parts - the follicular and luteal phases. In the first half, endometrial proliferation occurs - cells divide and it grows.
The process is quite fast, since as we know, the cycle itself lasts from 21 to 35 days. As soon as the next menstruation ends, a new functional layer is already being prepared, and so on ad infinitum, until menopause occurs.
The growth of the endometrium occurs due to the action of estrogens. These hormones promote cell division.
When everything is ready, the ovulatory period begins. It is short, only 2-3 days. Progesterone is already needed here. Without a sufficient level of this hormone, you may not know what a three-layer endometrium is.
Under the influence of progesterone, the production of estrogen slows down and the endometrium stops growing as actively. The thickest layer of the endometrium is observed after ovulation. He will be like this for a couple of days. The created conditions are favorable for the implantation of the fertilized egg.
Therefore, unprotected sex these days can lead to a long-awaited pregnancy if ovulation has taken place.
The second phase of the cycle is characterized by blurred boundaries between the layers, which the specialist will see on an ultrasound. The endometrium becomes homogeneous.
The beginning of the cycle and the endometrium is three-layered - what does this mean? That's right, optimal conditions for conception. And here the thickness is not as important as the presence of the top layer. Even with a total size of 7-8 mm, implantation is possible. If the endometrium is homogeneous, then the probability tends to zero. Below we will talk about why in the second phase of the cycle the norm is a homogeneous structure without division into layers.
The endometrium can be in two pathological states called hyperplasia and hypoplasia.
Hyperplasia
Endometrial hyperplasia is the thickening and excessive growth of the uterine lining—endometrial tissue. The process is benign. It occurs against the background of proliferation.
In early gestation, if the endometrium begins to grow excessively, a miscarriage may occur. With hyperplasia, intermenstrual bleeding usually occurs.
Hypoplasia
In this case, there is no need to say what a three-layer endometrium is. Since we are talking about thinning of the endometrium, the thickness of which does not exceed 6 mm. Normally, it should be about 9-13 mm in the middle of the cycle.
It is impossible to do without the participation of a gynecologist. You should especially seek medical help if the thickness remains unchanged throughout the entire cycle. Perhaps we are talking about chronic endometritis, which is caused by blood supply disorders.
If an ultrasound examination reveals a three-layer endometrium in the luteal phase, what does this mean? Along with uniformity in the first half of the cycle, this can be a cause of infertility. They again lie in hormonal imbalance.
The fertilized egg will not be able to attach to the endometrium if it does not meet the required parameters. Therefore, you should definitely consult a doctor to start corrective hormonal therapy. Most often, oral contraception is prescribed, as well as drugs based on progesterone and estrogen.
If you are planning a pregnancy and have difficulty conceiving, you need to undergo a full examination to find the cause. It is possible that the fault will be an insufficient growth of the functional layer or the absence of its multi-layering. In any case, contact a specialist and together with him go towards your dream - to have a child.
Source: https://Pro-MD.ru/ivf/infertility/female-factor/endometrij-trehslojnyj-chto-eto-znachit/
Three-layer endometrium
Lenok
three-layer endometrium 13.4 mm before menstruation 3 days? ultrasound error or all good
Hello everyone and have a nice day! Girls, tell me I had an ultrasound at 10dpo, the endometrium was 13.4mm, three-layered? corpus luteum 18mm in the right testicle.
uterus 595153 for me these are the largest indicators of the uterus for this year, the sizes of the ovaries are also large 3721 and 3724, I tested progesterone at 7 dpo 44.
7 nmol look, is everything okay? I’m just reading and it says that three-layer endometrium occurs at the beginning of the cycle? Thank you very much to everyone who answers!
Read more…Mummy
Three-layer endometrium
Hello girls. Today I saw the doctor. Today I have 16 dc, in support of proginova, 1 tablet 3 times a day. But! For the first time in my life, my gynecologist told me that she was satisfied with the thickness of the endometrium, but was not satisfied with the fact that it was not three-layered...
She said to come see the dynamics in 5 days. Tell me, should I panic? or in different cycles it somehow grows differently....she told me that we can do a transfer, but then there will be a roulette, but we can transfer it another...
Read more...Dashutka
Girls, who implanted embryos on the thin but three-layer endometrium, did everything work out?
Girls, I’m being stimulated now, a puncture is coming soon. The endometrium has long been thin, but three-layered. I’ve been treating for a long time, doing everything I haven’t done. I have HE. It was decided to try it anyway. We also have MF. As the doctor says, we only help, but the soul GOD is already giving. My endometrium is a maximum of 6.5. Please tell me your stories. Thank you
Read more…Lily
three-layered endometrium
Girls, I’m already in despair. Is the three-layered endometrium very important? Almost always was. It’s been 4 months since she disappeared... has anyone done a transfer to a non-three-layer heterogeneous endometrium or is it not worth it? Has anyone gotten pregnant like this? The last snowflake remains. I won’t do eco anymore. This is the 5th attempt. thank you all in advance for your answers...
Read completely…
Conception
Discuss your topic in the community, find out the opinions of active Babyblog users
Go to community
Julia
Girls, help me understand foliculometry
At 9 days there are 15 follicles, 3.5 endometrium. At 12 dc there are 21 follicles, the endometrium is 6.8 three-layered. Isn't this a small endometrium? A focal form of endometritis was diagnosed along the posterior wall of the uterus. I’m generally at a loss as to what to do with this enlometritis, and we’ll probably take it.....
Read more…Konfetochka
Girls, is three-layer endometrium good? Can endik grow dramatically in a couple of days?
It’s just that it was always two-layer in the first phase, but now it’s three-layer... And what is your dynamics of endometrial growth, for example, after 3 days? I was at 15 dc and was only 6.6 mm, can he grow to at least 8 by 19? Ovulation 18-19 days. Today is 18 d.c. Sorry for bombarding you with questions)))
Read completely…
question
Hello girls!!! Please tell me, what does three-layer endometrium mean? I went for folliculometry, yesterday I had it Oh, today the endometrium is 9 mm and also three-layered?
Read more…Maria
The endometrium does not enter the second phase of the cycle
This is already the second cycle, the endometrium does not change after ovulation, it shrinks and thickens and does not change its structure, it remains three-layered as in the first phase, why can this be?
Read more...Yulichkaaa
Duphaston in the second phase. Three-layer endometrium corresponds to phase 1
Girls, who drank duphaston, until what day of the cycle did they take it? I am 2dpo, I did an ultrasound, ovulation has passed, but the endometrium is 10 mm corresponding to the first phase, it has not become loose, the doctor is afraid that the embryo will not attach, she prescribed duphaston 1 tablet. Repeat ultrasound in a week to see how the endometrium is. What do you say, who has any thoughts.....
Read more...Ekaterina
Question about the endometrium at 5-7 DPO, 18 DC
Girls, tell me, what is the endometrium with a three-layer structure with a thickened basal layer? Is this normal endometrium after ovulation? 7-8mm thickness
Read more...Olenka
Not three-layered endomeerium (before transfer!
Girls, tomorrow I will have a replantation, but my endometrium is not three-layered ((. Please respond to someone who had a replantation with a non-three-layered one and was successful? Please support. 15 dts - 10 mm. Thickness is normal.
Read more…Anastasia
And again yay
Dkvochka question: if conception has occurred, how do I understand the endometrium is rising from a three-layer to a single-layer structure? Or not... I’m reading the information and I’m confused......
Read more...Nadezhda (replaced ava)
Folliculometry
And so the 8th day of the cycle: Three-layer endometrium 4 mm, Right ovary 8 mm, left 9 mm. Day 11 of the cycle: Three-layer endometrium 8 mm, right ovary 7 mm, left 16 mm.
Read more…Yana
NOW I'M DEFINITELY IN A STUNNER
Either I’m an idiot, or every doctor sees things differently. About a week ago I was checked and they said my uterus was enlarged, a cyst in the left ovary was 23 mm, pregnancy was in question. endometrium 13mm three-layer.
Today I went for a bridle test. The uterus is of normal size, there are no cysts and most importantly the endometrium is 9.4 mm. Is it possible for the endometrium to shrink? Follicles from 0.5-0.7. Pregnancy is not visible.
Source: https://congress-ott.ru/bolezni/chto-takoe-trehslojnyj-endometrij.html