This information will help you prepare for your dilation and curettage (D&C) procedure. It will tell you what to expect before, during and after your procedure.
A D&C is a procedure in which the cervix is dilated (slowly opened) and tissue is removed from the uterus. Tissue removal is done with a thin instrument called a curette.
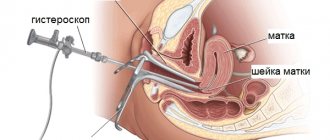
You may have a hysteroscopy at the same time as your D&C procedure. This is a procedure in which a thin endoscope with a light and a camera on the end is inserted into the uterus through the vagina. This gives your doctor a chance to examine the lining of the uterus for any abnormalities.
D&C goal
Typically, a D&C procedure is performed to identify the cause of abnormal uterine bleeding (blood coming from the uterus). Examples of abnormal uterine bleeding:
- bleeding between periods;
- bleeding after vaginal intercourse, including small blood spots;
- heavy, irregular or prolonged periods;
- sudden vaginal bleeding after a year or more of no periods.
The cause of this bleeding may be:
- Endometrial cancer. Endometrial cancer is cancer of the lining of the uterus. The D&C procedure helps diagnose cancer in its early stages.
- Fibroids. Fibroids are growths on the uterus consisting of connective tissue and muscle fibers. In most cases they are benign (not cancerous).
- Polyps. Polyps are growths that form on the inner wall of the uterus and protrude into the uterine cavity (the space inside the uterus). They are generally benign, but some may be cancerous or precancerous (leading to cancer). Polyps can be removed during a D&C procedure.
- Hyperplasia. Hyperplasia is a pathological growth of the inner lining of the uterus. Hyperplasia can be precancerous.
The D&C procedure may also be performed to diagnose or treat other uterine conditions. In addition, it is used to clean the inner lining of the uterus after a miscarriage or induced abortion.
After curettage, endometriosis may grow again
Endometriosis is a benign pathological process that affects the genitals and, in some cases, the abdominal organs.
The main cause of the disease is considered to be impaired regulation of immune and hormonal processes.
Endometriosis is a frequently diagnosed pathology in patients of reproductive age.
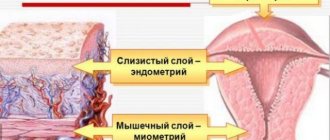
The uterus, as a hollow organ, consists of three layers lining its cavity: endometrium, myometrium and serous membrane.
What is uterine endometriosis
The endometrium consists of a functional layer, which is shed during menstruation, and a germinal basal layer, which forms the upper functional layer. Uterine endometriosis is characterized by growths of glandular tissue in the uterus called heterotopias .
They tend to penetrate healthy tissue and form adhesions.
The growths increase in size, swell and bleed, which explains spotting outside of menstruation.
In addition, abnormal endometrial cells produce a specific fluid that is not excreted, the stagnation of which causes pain. Endometriosis of the uterus can be nodular, diffuse and focal.
According to the depth of penetration into the muscular layers of the uterus, the pathology is divided into four degrees . The lesions vary in size and shape: from a round formation of several millimeters to a shapeless growth of several centimeters in diameter.
Read more about what endometriosis is here.
Symptoms of the disease
In the early stages, endometriosis may occur without significant symptoms.
In the second and third degrees the disease manifests itself:
- Menstrual irregularities - the cycle itself is shortened, the duration of menstruation increases.
- Constant or periodic pain in the lower abdomen, lower back.
- Severe premenstrual syndrome.
- Pain during sexual intercourse.
- Heavy menstrual flow.
- Spontaneous miscarriage, infertility.
With a long course of endometriosis with heavy menstruation, signs of anemia begin to appear: general increasing weakness, dizziness, pale skin.
The first mention of the disease was found in ancient Egyptian manuscripts, which Hippocrates described in his writings.
Popular treatments
To treat uterine endometriosis, complex treatment is used . It is obligatory to take hormonal drugs, which causes a medicated menopause, as a result of which the formation of an egg and the development of the endometrium do not occur.
The treatment course lasts 6 months. During this time, foci of endometriosis shrink and atrophy .
Hormonal therapy does not help restore your own hormones and does not always give positive results; it has a number of side effects.
Surgical methods of treatment:
- Laparoscopy is a low-traumatic manipulation that allows you to remove endometrioid lesions and adhesions; laser and electrocoagulation are used. Cauterization stops the growth process and reduces the risk of relapse. Organ-preserving surgery is performed for moderately severe disease. For successful treatment, laparoscopy is combined with medications.
- Curettage or cleaning of the uterine cavity is a radical method, used to stop uterine bleeding in the infiltrative pathological form of the disease.
- In severe cases of the disease, a total hysterectomy is performed - complete removal of the organ and appendages. Preservation of the ovaries will provoke relapses of endometriosis.
Physiotherapy is used as prescribed by a doctor in the absence of contraindications.:
- Electrophoresis of zinc and iodine has an analgesic, sedative effect, and normalizes hormonal levels.
- Magnetic therapy calms the nervous system and improves tissue microcirculation.
- Ultraviolet radiation anesthetizes, relieves inflammation, and has a biostimulating effect on endometriotic lesions.
Balneotherapy includes radon and iodine-bromine baths, vaginal irrigation, microenemas . The procedures have analgesic, anti-inflammatory and sedative effects.
Eliminate hormonal imbalance, normalize thyroid function. A long course of treatment ensures a reduction in pathological endometrium .
Computer reflexology is a method based on the restoration of neuroendocrine connections, immune regulation of the female body, using ultra-weak direct current. The result of therapy is the normalization of uterine functions, restoration of hormonal balance, improvement of immunity and strengthening of the nervous system.
Intrauterine devices are used to treat stage 1 endometriosis . Installed by a specialist after undergoing diagnostic procedures.
Source: https://metmot.ru/simptomy/posle-vyskablivaniya-endometrioz-mozhet-opyat-rasti.html
Before the procedure
Ask questions about your medications
You may need to stop taking some of your medications before the procedure. Talk to your doctor about which medications you can stop taking. Below are some common examples.
- If you are taking a coagulant (blood thinner), ask the doctor who prescribed it when you should stop taking it. These medications include warfarin (Coumadin®), dalteparin (Fragmin®), heparin, tinzaparin (Innohep®), enoxaparin (Lovenox®), clopidogrel (Plavix®), and cilostazol (Pletal®).
- If you take insulin or other medications for diabetes, ask the doctor who prescribed the medication what you should do the morning of your procedure. You may need to change your dose.
Arrange for someone to take you home
You must arrange for someone at least 18 years of age to drive you home after the procedure. If you do not have such a person, call one of the agencies below. You will be provided with an escort to take you home. There is usually a fee for these services and you will need to provide transportation.
| Agencies in New York | Agencies in New Jersey |
| Partners in Care: 888-735-8913 | Caring People: 877-227-4649 |
| Caring People: 877-227-4649 |
Day before the procedure
Write down the time for which the procedure is scheduled
An Admitting Office staff member will call you after 2:00 pm the day before your procedure. If your procedure is scheduled for a Monday, you will be called the prior Friday.
A staff member will tell you what time you should arrive at the hospital for your procedure. He will also tell you where to go. If no one contacts you by 7:00 p.m., call 212-639-5014.
- Do not eat after midnight the night before your procedure. This also applies to hard candies and chewing gum.
- Between midnight and two hours before you are scheduled to arrive at the hospital, you can drink no more than 12 ounces (350 ml) of water (see illustration).
- Avoid eating or drinking two hours before your scheduled arrival time at the hospital. This also applies to water.
Day of the procedure
What you need to remember
Take only the medications your doctor prescribed to take on the morning of your procedure. Wash them down with a few small sips of water.
What to Expect
You will be taken to a locker room and asked to remove all clothing, jewelry, dentures and contact lenses. One of the staff will give you a hospital gown.
After changing into a hospital gown, you will meet with a nurse. A nurse will take you to the procedure room and help you onto the operating table. If you feel cold, ask your nurse for a blanket.
If you feel cold, ask your nurse for a blanket. First, you will be given intravenous fluid, and then anesthesia (medication that will make you sleep) will be given through the same IV. You will also be connected to equipment to monitor your heartbeat, breathing and blood pressure.
You will be given anesthesia (a drug that makes you sleepy) through an IV catheter. Once you fall asleep, the doctor will begin the procedure.
After the procedure
In the hospital
- You will be transferred to the Post Anesthesia Care Unit (PACU). There, a nurse will monitor your body temperature, heartbeat, breathing and blood pressure. You may receive oxygen through a thin tube placed under your nose. You will remain in the recovery room until you are fully awake.
- When you finally wake up, you will be transferred to the recovery area. You will be able to drink tea or juice, have a light snack and see your visitors.
- You may experience aching, spasmodic pain in your lower abdomen (belly). Ask your nurse for medicine to relieve pain. Your doctor or nurse may also give you a prescription for pain medication to take at home.
- Your nurse will give you instructions on how to care for yourself at home. When you are cleared to leave the recovery area (discharged), you must be accompanied by a companion who is at least 18 years of age.
At home
- You may feel drowsy while still under the anesthesia. It is important to have someone with you for the first 24 hours after the procedure.
- For 2 weeks after the procedure, or as directed by your doctor, refrain from: douching;
- using tampons;
- vaginal sexual intercourse.
Call your doctor or nurse if you have:
- temperature 101°F (38.3°C) or higher;
- vaginal bleeding is heavier than normal menstrual bleeding;
- pain that does not go away after taking a medicine recommended by your doctor;
- swelling in the abdominal cavity;
- unpleasant odor of vaginal discharge.
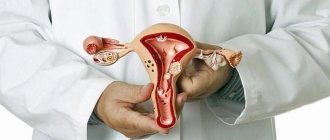
A woman's uterus is a pear-shaped muscular organ. The organ cavity is covered with a mucous membrane called the endometrium. This is where the fertilized egg attaches and the development of pregnancy begins.
Every month, a woman goes through a menstrual cycle, during which the endometrium matures and enlarges in preparation for fertilization. If conception does not occur, it thickens and is rejected from the walls of the uterus in the form of menstruation. If fertilization has occurred and the fertilized egg has attached to the wall of the uterus, the endometrium begins to function, but menstruation does not occur.
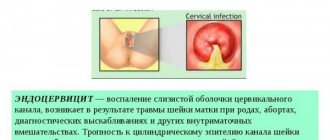
In gynecology, there are cases when, for medical reasons, it is necessary to perform curettage of the endometrium of the uterine cavity. This is a well-known method of cleansing the uterus from various pathological formations.
What is curettage?
Curettage or cleaning is the cleansing of the surface layer of the uterine wall. During the procedure, only the superficial layer of the membrane is removed, so the new layer of the endometrium after curettage will mature in the next menstrual cycle.
Curettage is a surgical intervention that is performed for the purpose of diagnosing and treating various gynecological diseases.
Preparing and performing curettage
Before carrying out the procedure, every woman should prepare for this procedure. At the medical center where this procedure will be performed, the doctor will give directions for the necessary tests. Usually this is a general blood test, a blood clotting test, a biochemical blood test and a vaginal smear test. If necessary, ultrasound diagnostics will be prescribed. Based on these tests, it will be clear whether there are inflammatory processes in the body.
Before cleaning the uterus, a woman should stop taking medications for several weeks, as this can cause bleeding. You should also avoid sexual intercourse and the use of various vaginal creams and sprays.
Immediately before the day of curettage, you must stop eating and drinking.
The procedure is performed under general anesthesia. A woman is on a gynecological chair. The genitals are treated with an antiseptic. A dilator is inserted into the cervix, which allows the doctor to evaluate the structure and condition of the uterus. When performing curettage, the doctor uses a special tool similar to a spoon. The surface layer of the endometrium is carefully removed and placed in a special container.
After examining the walls of the uterus, curettage ends. The doctor removes the dilator and treats the genitals with an antiseptic. A sample of the endometrium is sent for histological analysis. This is a mandatory procedure that will help you make an accurate diagnosis of the disease and select effective treatment, as well as exclude serious cancer of the woman’s uterus.
Most often, after cleansing, most women feel pain in the lower abdomen, similar to the pain before menstruation. In this case, you can take painkillers. It is very important to monitor vaginal discharge, and if there is heavy or, on the contrary, very scanty discharge, inform your doctor. Over the course of several days, the discharge should decrease and the woman can return to her previous life.
Surgical manipulation, the essence of which is curettage (or scraping) of the functional layer of the uterine mucosa.
Curettage of the uterine cavity is a surgical procedure, the essence of which is to scrape out (or scrape off) the functional layer of the uterine mucosa. The term RDV (“separate diagnostic curettage”) is also used - it is called separate because it is carried out in stages - first the cervical canal is scraped, and then (a separate manipulation) - the uterus itself; It is called diagnostic because the resulting scraping will be sent for histological examination to establish an accurate diagnosis.
During the curettage process, only the top layer of the endometrium is removed, so the uterine mucosa is subsequently restored.
The scraped material is sent for histological examination. This eliminates the possibility that the disease is malignant. This is the main purpose of curettage performed for diagnostic purposes.
Building up
Many women are interested in how to restore the endometrium after curettage, if this did not happen on their own, or the process was delayed. Initially, it is worth determining what thickness indicates the need for additional measures to increase the thickness of the layer.
So, about a month after the procedure, the woman should undergo an ultrasound examination of her pelvic organs. Thanks to this examination, the specialist will be able to assess the degree of restoration, and if the thickness of the layer is 1-2 mm, then they say that this did not happen.
It may happen that the doctor does not prescribe a control ultrasound for the patient, then the woman should visit the gynecologist after 2-3 months, provided that her menstrual cycle has not stabilized. In this case, it can be assumed that there are problems with the endometrial restoration process.
Thinning of the endometrial layer after curettage. Source: fillword.ru
The mucous membrane of the reproductive organ is a tissue that is dependent on hormones. Normally, changes in endometrial thickness occur in different phases of the menstrual cycle, and this is considered a natural physiological process. The hormone estrogen is responsible for the increase in thickness, so correction of the recovery process is carried out with drugs that contain this substance.
If a woman suffers from severe and unpleasant symptoms, then the therapy will be complex, which almost always includes antispasmodics and antibiotics. Physiotherapy is also very effective. Let us consider in more detail how the endometrium is restored after curettage in various ways.
Hormones
In most clinical cases, with thinned endometrium that does not recover after the curettage procedure, patients are prescribed drug therapy. However, the woman must first donate blood to determine hormone levels.
This is necessary in order to understand which substance is in excess and which is in short supply. So, if estrogen in the body is elevated, it must be lowered with special medications, and vice versa. If the indicators are normal, then doctors will look for another reason why the endometrium is not recovering.
Antispasmodics
If the endometrium does not recover on its own after curettage, then the woman is prescribed drug therapy, which contains drugs with an antispasmodic effect. This is necessary in order to relieve the woman of pain in the lower abdomen. The drugs are discontinued approximately 2-3 days after the procedure. No-shpa helps best for these purposes.
It is better to use No-shpa as an antispasmodic. Source: moy-kroha.info
You should take the medicine 1-2 tablets, which directly depends on the dosage. The drug should be taken no more than twice a day. Thanks to this, it will be possible to relieve the spasm, as well as get rid of pain if it is present. No-spa normalizes the blood circulation process in the uterus, which is disrupted in this condition.
When the required amount of nutrients begins to reach the endometrium, the cells begin to actively divide and the mucous layer gradually increases.
Antibiotics
It is very important that after curettage, the endometrial restoration process occurs without complications. The fact is that after the intervention, the mucous membrane is considered injured and susceptible to the harmful effects of pathogenic microorganisms. Also, during the recovery period, immunity is reduced, so recovery takes longer.
Contraindications and possible complications during the curettage procedure
Absolute contraindications to curettage are acute infectious diseases and inflammatory processes of the genital organs.
With a careful and correct approach by a specialist to this manipulation, complications can be avoided. However, you need to be aware of the possible complications of curettage:
- Perforation of the uterus.
- Cervical tear.
- Inflammation of the uterus. Occurs when microbes enter the uterus. Currently, to prevent infection of the uterus after curettage, doctors prescribe a course of antibiotic treatment.
- Accumulation of blood in the uterine cavity (hematometra). If, after curettage, a spasm of the cervix occurs, blood, which normally should flow from the uterine cavity for several days, accumulates in it and can become infected and cause pain.
- Damage to the mucous membrane (excessive curettage) – if you scrape very hard and aggressively, you can damage the germinal layer of the mucous membrane, which will lead to the fact that the new mucous membrane will no longer grow.
Why doesn't the endometrium grow?
This layer of fabric performs a very important function. The fertilized egg is attached there. The endometrium creates the right conditions for the development of the embryo. Once conception has occurred, the number of glands and blood vessels increases, which subsequently become part of the placenta. They provide the fetus with oxygen and nutrients. For conception to occur, the endometrium must be of normal quality, thickness, structure, and degree of maturity. However, it may not grow naturally due to the following reasons:
- Congenital pathologies. With such abnormalities, the body does not produce certain hormones in order to grow the endometrium, or their quantity is insufficient.
- Hormonal imbalances. With some of them, the natural growth of the endometrium does not occur on the days of the cycle. Normally, throughout the entire period, the thickness of the mucous membrane layer gradually increases and decreases.
- Poor blood supply to the uterus. This phenomenon may be a consequence of injury, inflammation, diseases of the pelvic organs, or abortion. With the latter, the endometrium is damaged as a result of curettage. This significantly reduces a woman's chances of becoming pregnant in the future.
- Hypoplasia of the uterus. This is the name for the discrepancy between the size of an organ and the age norm. With this pathology, the layer of the mucous membrane needs to be increased.
Preparation for the procedure
- Examination and consultation with a gynecologist.
- General blood analysis.
- Coagulogram (assessment of the blood coagulation system).
- ECG.
- Tests for hepatitis B and C, RW (syphilis) and HIV.
- Vaginal smear (there should be no signs of inflammation).
2 weeks before your curettage: Stop taking any medications or dietary supplements (including herbal supplements) that you have not previously discussed with your doctor who will be performing the curettage. Some medications can change blood clotting and increase the risk of bleeding. If you are taking medications for a serious illness (for example, hypertension, arrhythmia, epilepsy), do not stop treatment, but be sure to tell your doctor about the medications you are taking.
2-3 days before curettage:
- Avoid sexual intercourse.
- Do not douche and refuse to use any intimate hygiene products. To toilet the genitals, use only warm water.
- Stop using any medications in the form of vaginal suppositories, tablets, or sprays unless their use has been discussed with your doctor in advance.
- On the eve of curettage, refrain from eating and drinking 8-12 hours before the procedure. This is necessary for safe anesthesia.
Diagnostic curettage is performed before menstruation, a few days before its onset.
How to enlarge the endometrium when planning pregnancy
If the mucous membrane is thinner than 7-10 mm, then the likelihood of implantation of the fertilized egg is very low. If it is not thick enough, the pregnancy may freeze or a miscarriage may occur. To protect yourself from these troubles, you need to figure out how to grow the endometrium for conception. Various methods are used for this: treatment with hormonal and other medications, physiotherapeutic procedures. In some cases, folk recipes help.
Drugs to help you get pregnant
The process of growth of mucous tissue is directly related to hormones. If you want to find out how to quickly grow the endometrium, then pay attention to hormonal drugs. They will ensure the fastest onset of results. However, self-administration of such medications is strictly prohibited; you must first consult a specialist. For those who do not understand how to grow the endometrium, the following drugs will help:
- medications containing estradiol;
- drugs to increase estrogen levels;
- medications with progesterone.
Proginova for endometrial growth
The drug contains estrogens and estradiol. Taking Proginov helps improve blood circulation in the uterus. The medicine is recommended for girls who have previously had miscarriages for recovery. Taking Proginov is one of the most important stages of preparation for IVF, before which enlargement of the endometrium is necessary. The drug is allowed to be combined with other medications.
How to properly grow the endometrium with the help of Proginov in order to get pregnant? The method of administration is determined by the doctor. There are these options:
- Cyclical. They take 1 tablet of Proginova for three weeks in a row at the same time, skip 7 days, then repeat the course.
- Continuous. The pills are taken non-stop.
Treatment with Proginova is not recommended for:
- pregnancy for more than two months;
- breastfeeding;
- taking medications with estrogen;
- vaginal bleeding;
- tumors;
- diseases of the liver, gall bladder;
- diabetes mellitus
Divigel with low estradiol
This drug is prescribed to those who are looking for ways to improve the endometrium for conception. It contains estradiol, a synthetic analogue of estrogen. Divigel not only thickens the mucous membrane of the uterus, but also makes the organ itself, the vagina, mammary glands and fallopian tubes, function more actively. The drug is used once a day, strictly at the same time. The gel is applied to clean skin of the shoulders, forearms, lower abdomen, buttocks, and lower back. The dose is determined by the doctor. Divigel should not be applied to inflamed areas, chest, or mucous membranes. It is used only as prescribed by a specialist.
Divigel cannot be used for:
- diabetes mellitus;
- tumors or inflammation of the genital organs and breasts;
- predisposition to the formation of blood clots;
- pituitary tumors;
- uterine bleeding;
- disorders of fat metabolism;
- pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- liver and kidney diseases.
How is separate diagnostic curettage performed?
Curettage of the uterine cavity and cervical canal in our clinic is carried out in our own operating room, equipped in strict accordance with current sanitary and hygienic standards. During the operation, anesthetic equipment with constant monitoring of the patient's condition, disposable materials, surgical equipment and instruments from leading manufacturers of medical equipment are used.
The patient is placed in a gynecological chair and the anesthesiologist performs intravenous anesthesia.
The doctor inserts a speculum into the vagina to expose the cervix. Using special forceps (“bullet pins” there is a tooth at the ends of this instrument) it catches the cervix and fixes it. Using a special probe (iron rod), the doctor enters the cervical canal and penetrates the uterine cavity, measuring the length of the cavity.
Curettage is performed with the smallest curette. A curette is an instrument similar to a spoon with a long handle, one edge of which is sharpened. A sharp edge is used to scrape. The scraping obtained from the cervical canal is placed in a separate jar. If curettage is accompanied by hysteroscopy, then after dilation of the cervical canal, a hysteroscope (a thin tube with a camera at the end) is inserted into the uterine cavity. The uterine cavity and all walls are examined. After this, the lining of the uterus is scraped. If a woman had polyps, they are removed with a curette during curettage. After the curettage is completed, the hysteroscope is reinserted and the result is checked. If something remains, reinsert the curette and scrape it out until the result is achieved.
At the end of the diagnostic curettage procedure, the patient is transferred to a comfortable day hospital ward, where she remains under the supervision of an anesthesiologist and nursing staff until she fully awakens from anesthesia. After the anesthesia wears off, the patient can be discharged from the clinic.
Subsequent recovery after separate diagnostic curettage
Within a few hours after curettage, heavy bleeding and bloody clots from the vagina may appear. This is normal.
After a few hours, the discharge becomes less abundant. Scanty bloody, spotting, brown or yellowish discharge after curettage may persist for another 10 days. The rapid disappearance of discharge after curettage may be a sign of cervical spasm and accumulation of blood clots in the uterus. In this case, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Within 2 weeks after curettage you cannot:
- Have sex;
- Use vaginal tampons (you can use regular pads);
- Do douching;
- Take a bath, visit a sauna or steam bath (you can take a shower);
- Engage in heavy physical labor or intense exercise;
- Take medications containing acetylsalicylic acid (for example, Aspirin).
Traditional therapy
It is immediately worth noting that various methods and recipes of traditional medicine can only be an additional method of influencing the body and should be part of standard complex therapy. Before starting to take any herbs, you should consult your doctor and make sure there are no contraindications.
Borovaya uterus and red brush are used to restore hormonal levels. Source: ginekola.ru
To restore the endometrium, you can take the following herbs in various forms: licorice, clover, lovage, calamus and hops. Most women prefer to take medicinal mixtures in the form of tea (one spoon of herbs is brewed with a glass of boiling water and drunk). Plants contain a large amount of phytoestrogens, so endometrial restoration occurs faster.
Also, plants such as red brush, hogweed, and their collection are characterized by a high level of effectiveness in the fight against gynecological diseases. The mixture must be combined in a 1:1 ratio and taken in the same way as regular tea.
If after therapeutic or diagnostic curettage there is no restoration of the endometrial layer within one month, then you need to consult a doctor who will advise the most optimal ways to increase thickness.
! See a doctor immediately if...!
- you very quickly stopped bleeding from the vagina and began to experience abdominal pain;
- your temperature has risen above 38°C;
- you have severe abdominal pain that does not go away after taking painkillers;
- you experience heavy vaginal bleeding that quickly fills your sanitary pads and does not stop for several hours;
- you have copious, foul-smelling vaginal discharge;
- your health suddenly deteriorates, you feel dizzy, weak or lost consciousness.
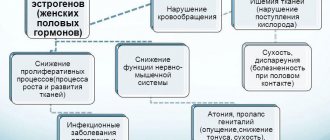
Many women of middle and older reproductive age are faced with the problem of infertility due to changes in the endometrium of the uterus (the cellular layer lining the walls of the uterus from the inside). An endometrium that is less than 8 mm thick is considered thin. This leads to disturbances in the attachment of the embryo and the absence of pregnancy - infertility.
Is it possible to increase thin endometrium? How long will the treatment take? And what exactly will it be? We discuss issues of women's reproductive health together with Lyudmila Tikhonova, a reproductive specialist at the Zhemchuzhina family clinic.
Why has the endometrium become thin?
So, the functional state of the endometrium determines the possibility of pregnancy, its successful course and successful completion. Changes in the structure of the endometrium can cause infertility and miscarriage, and also reduce the success of the IVF procedure.
— There may be several reasons that cause such a condition as hypoplastic or thin endometrium. That is why it is important for a woman to contact a reproductive specialist or gynecologist and undergo a full examination,” emphasizes Lyudmila Tikhonova.
The main reasons for insufficient thickness of the inner lining of the uterus include:
- inflammatory process (it is often sluggish and long-lasting);
- formation of adhesions inside the uterine cavity (formation of films of varying thickness between the walls of the uterine cavity);
- lack of hormones that stimulate endometrial growth, the number of receptors (protein molecules - antennas on the surface of cells that capture hormones) on endometrial cells;
- insufficient amount of transport protein, which transfers the active substance of the estrogen hormone to the receptors;
- disturbance of blood flow and innervation of the pelvic organs.
What to do?
— Each patient is assigned an individual examination plan at a consultation. It necessarily includes ultrasound monitoring of the endometrium, examination to detect infectious agents in a married couple, examination of the uterine cavity using an optical device - hysteroscopy from the sixth to tenth day of the menstrual cycle, says a reproductive doctor at the Zhemchuzhina family clinic. — If gross changes in the uterine cavity are detected (adhesions, septa, polyps, fibroid nodes), a hysteroresectoscopy procedure is performed.
To assess the cellular state of the endometrium, tissue is taken from the uterine cavity (aspirate) from days 7 to 12 and from days 19 to 21 of the cycle. It is this period, from 19 to 21 days of the cycle, that is called the “implantation window,” that is, the most favorable for pregnancy. Using special immunohistochemical tests, it is possible to evaluate the cellular composition of the endometrium, its structure, the number of receptors that interact with hormones, pinopodia (protrusions) on endometrial cells, which recognize the embryo.
Thanks to such studies, it is possible to determine the nature of the changes and carry out treatment.
How to treat?
In medicine, complex gynecological rehabilitation treatment is used.
— As a rule, after identifying the causes of the formation of a thin endometrium and carrying out a course of treatment over three menstrual cycles, in most cases it is possible to restore the functions of the endometrium. During the treatment period, the woman is prescribed anti-inflammatory, cyclic hormonal therapy and supportive medications, comments Lyudmila Tikhonova. — The first includes the use of antibacterial or antiviral drugs, as indicated, and hormonal drugs according to the phases of the cycle. And as part of the preparatory pregravid (before pregnancy) stage, the patient is shown folic acid preparations, drugs that improve blood microcirculation (after consultation with a hemostasiologist) in the vessels feeding the pelvic organs, as well as vitamin D3 and amino acids.
While the woman is undergoing treatment, the gynecologist uses ultrasound to dynamically monitor the thickness of the endometrium during certain periods of the menstrual cycle. If there is a lag from the norm, the patient is adjusted to hormonal therapy and prescribed additional comprehensive treatment, which includes physiotherapy and massage.
You can make an initial appointment with the clinic’s gynecologists regarding the treatment of thin endometrium by calling: (351) 200-34-04 or through the online form on the website. After three cycles of cyclic hormonal and corrective therapy, the thickness of the endometrium is usually restored , and for the next - fourth cycle - the woman is prescribed an ART procedure (assisted reproductive technologies - editor's note).
Free consultations on the causes of infertility and ART programs at the Zhemchuzhina clinic are carried out by appointment by phone or through an online form on the website.
Family clinic “Pearl” in Chelyabinsk:
st. Dovatora, 10A;
Komsomolsky pr-t, 2;
st. Br. Kashirinykh, 138;
Tel., 8-800-222-34-06 (calls within Russia are free);
How to grow the endometrium after curettage
10 MOST EFFECTIVE WAYS TO INCREASE THE ENDOMETRIUM The endometrium is sensitive to the hormonal background of a woman, and it is this feature that affects its size. The endometrium becomes noticeably thicker and is enriched with glands, which provide improved blood supply to the tissue in the last, premenstrual phase of the cycle. This ensures successful implantation of the embryo - that is, it ensures the possibility of conception. Contents of the article: Functions of the endometrium Endometrium and pregnancy Medicines and folk remedies Why is the endometrium needed, what should it be like? The endometrium is the lining of the uterus. This is a system that consists of many components, in particular: Epithelium. Continue reading →
Girls, hello everyone!! Please respond to anyone who has encountered endometrial problems. I had curettage done after the measurement. We take it. three months ago, at the moment the endometrium is only 7 mm with some inclusions. I am planning a new pregnancy. The doctor does not prescribe anything, he just observes for now. HOW TO GROW THE ENDOMETRIUM to the desired size after surgery. Anyone who has encountered this please respond. Continue reading →
Hello everyone! Girls, this is the 3rd time I’ve written about him and I’m hoping for new answers. Further tackle I repeat. The endometrium is small 3.5-5mm. The reason is curettage + repeated curettage in the same B in 2009. Everything was fine with him before. And now I'm suffering. (Who else can advise? How to build it up? I’ve already tried: - pineapples (they work, but they cause stomach problems) - I take duphaston from the 16th-25th day of the cycle (and it doesn’t build up, but helps the endik to ripen and form) - PLEASE NOT RECOMMEND ME SAGE. Sage later put me in the hospital with cysts. Read more →
Girls, help. A year has passed since ST and vacuum aspiration and I have been trying to restore the endometrium for a year now. After curettage there was an adhesive process, then hysteroscopy, then I was in Staraya Russa for almost a month, treated with mud, electrophoresis, gynecological massage and many other different procedures. But the endometrium is not growing, 5 mm and that’s it. My G suggested Leanek and ozone, it passed, but the endometrium does not grow, with a stretch it pulls a little more than 6 mm. At the same time, she also drank tea from raspberry leaves, Viagra and candles, and so on. Continue reading →
10 MOST EFFECTIVE WAYS TO INCREASE THE ENDOMETRIUM The endometrium is sensitive to the hormonal background of a woman, and it is this feature that affects its size. The endometrium becomes noticeably thicker and is enriched with glands, which provide improved blood supply to the tissue in the last, premenstrual phase of the cycle. This ensures successful implantation of the embryo - that is, it ensures the possibility of conception. Contents of the article: Functions of the endometrium Endometrium and pregnancy Medicines and folk remedies Why is the endometrium needed, what should it be like? The endometrium is the lining of the uterus. This is a system that consists of many components, in particular: Epithelium. Continue reading →