Forms
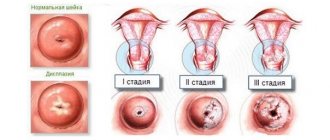
There are two forms of the disease - acute and chronic. The acute form is characterized by myometrial edema, blood vessels overflowing, and bleeding. Due to swelling, menstruation does not occur. Other organs are involved in the process - the bladder and intestines. This form of the disease occurs a few days after an abortion or childbirth. Chronic metritis develops with repeated inflammation, frequent irritation of the uterus due to a full bladder, a sedentary lifestyle, and poor performance of the maternity period. In this case, the organ increases in size, loosens, and becomes highly mobile. Pressure is exerted on neighboring organs - the intestines, the bladder. Over time, the tissue hardens and wrinkles.
What is metritis, how does it happen?
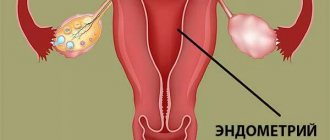
Metritis or myometritis is an inflammatory process affecting the myometrium - the uterine muscle layer. The disease rarely occurs in isolation and is usually accompanied by endometritis, an inflammation localized in the mucous membranes.
There are several forms of metritis:
- Catarrhal is an early stage of the development of inflammation.
- Purulent-catarrhal metritis is a form in which suppuration is present.
- The necrotic form is characterized by trophic disturbances and the onset of tissue necrosis (death).
- Gangrenous metritis is the last stage of the inflammatory process, leading to irreversible consequences.
According to the characteristics of the course, metritis can be acute, subacute and chronic. Acute develops rapidly, but with proper treatment, the symptoms disappear fairly quickly (within one to two weeks). Subacute metritis has pronounced symptoms that persist for 3-4 weeks. The chronic form is a consequence of an untreated acute form. Inflammation persists and occurs with periodic exacerbations (signs are obvious only during periods of relapse).
According to etiology, metritis is classified into infectious, resulting from the activity of various pathogenic microorganisms, and aseptic, developing for other reasons (for example, after rough mechanical influences).
Metritis as a separate disease is extremely rare; quite often it occurs in the form of metroendometritis and other complications that threaten female infertility.
Infectious metritis, in turn, is divided into specific and nonspecific. In the first case, inflammation is provoked by specific pathogens, such as gonococci, trichomonas, and ureaplasma. Nonspecific metritis is caused by the activity of opportunistic flora, which include Escherichia coli and staphylococci.
Why does fluid collect in the uterus during postmenopause?
Common causes are mechanical damage to the vagina, excessive secretion due to inadequate resorption.
An equally common cause of fluid accumulation is:
- fusion of the cervical canal;
- neoplasms, even benign ones;
- cervical canal strictures;
- synechiae of the uterus, etc.
In addition, the cause of the pathology may be excessive secretion of exudate by the endometrium, as well as its penetration from the fallopian tubes.
Serozometra is the accumulation of serous fluid in the uterus. The serous membrane is located between the muscular layer of the uterus and the endometrium, covered with a huge number of vessels. Through the vascular walls, transparent light yellow blood plasma - serous fluid - enters the uterus.
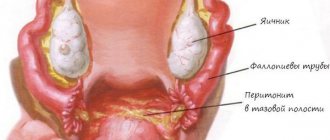
Perimetritis - inflammation of the serous layer of the uterus - develops as a result of the spread of infection from the uterus, its appendages or from neighboring organs (with sigmoiditis, appendicitis). Pathanatomically, two forms of perimetritis are distinguished: adhesive (dry) and exudative (wet). They can transform into one another; the adhesive form is more common, leaving behind a large number of adhesions. In the acute period, both forms are clinically similar. Patients develop fever and ESR increases. Thirst and dry tongue, general malaise, headache, pain in the lower abdomen appear. The pulse quickens. Tension of the abdominal wall muscles is noted.
With exudative perimeteritis, the exudate is located behind the uterus, displacing the uterus in front. On vaginal examination, the walls of the vaults are thickened, the lower boundary of the infiltrate is ovoid, the upper is unclear and difficult to determine. The uterus is painful. The infiltrate has a tightly elastic consistency, is painful, and sometimes fluctuation is observed.
Perimetritis is differentiated from parametritis and from interrupted ectopic pregnancy. With the latter, differential diagnosis is based on a thorough history taking, staging the Mainini, Tsondek, Friedman reactions and diagnostic puncture. Parametritis differs from perimeteritis in the shape, localization and consistency of the infiltrate: with parametritis, the infiltrate spreads fan-shaped to the walls of the pelvis, located lower. The vaginal vaults lose their displacement.
Cancer infiltrate is differentiated from parametritis according to anamnesis, examination and palpation of the cervix and vagina.
Perimetritis is differentiated from parametritis and from interrupted ectopic pregnancy. With the latter, differential diagnosis is based on a thorough history taking, staging the Mainini, Tsondek, Friedman reactions and diagnostic puncture. Parametritis differs from perimeteritis in the shape, localization and consistency of the infiltrate: with parametritis, the infiltrate spreads fan-shaped to the walls of the pelvis, located lower. The vaginal vaults lose their displacement.
What causes metritis?
Metritis can develop due to damage to myometrial tissue or due to the activity of pathogenic microorganisms. There are only two development mechanisms. In the first case, injured tissues become inflamed, and in the second case, infectious agents or their waste products penetrate into the muscle layer.
The causes of metritis are the following:
- difficult childbirth or postpartum consequences: rough squeezing of the fetus, manual separation of the placenta (placenta), heavy bleeding;
- operations performed on the uterus: caesarean section, curettage, surgical abortion (the risks of developing metritis increase if sanitary standards and disinfection rules are not observed);
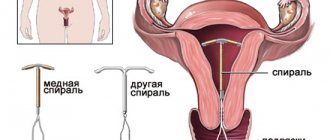
- intrauterine contraceptives - spirals (especially incorrectly installed or untimely removed);
- severe mechanical damage, trauma to the uterus (for example, severe bruises after falls or accidents);
- sexually transmitted infections (trichomoniasis, gonorrhea, chlamydia);
- gynecological diseases of an inflammatory nature (salpingitis, colpitis, salpingo-oophoritis, endometritis, cervicitis, adnexitis);
- general acute infections: typhoid, tuberculosis, diphtheria, cholera (pathogens enter the muscle tissue of the uterus from the primary focus through the bloodstream);
- inflammatory diseases affecting nearby organs, including the intestines, kidneys, bladder (colitis, cystitis, pyelonephritis, appendicitis);
- entry into the uterine cavity of irritating aggressive substances.
Causes of the disease
The uterus of a strong, healthy animal, whose birth went smoothly, independently removes the placenta and closes, returning to the right place in a few days. But if the process was carried out with disturbances, then there is a high probability of metritis. Among the most significant reasons for its occurrence it is worth noting:
- Inaccurate intervention by livestock breeders or veterinarians.
- The use of non-sterile instruments during labor.
- Contamination of the genitals during mating.
- A long period of feeding calves after the previous calving.
- Short dry periods when the cow is not milked.
- Complications arising from intrauterine interventions, abortions, difficult childbirth.
- Premature insemination of young animals.
- Poor nutrition, poorly selected food.
- High levels of stress, poor living conditions for animals.
- Presence of other serious diseases.
Symptoms
The manifestations of metritis depend on the causes of its development, concomitant diseases and form. Thus, acute metritis has pronounced and obvious symptoms, develops rapidly and worsens overall health. The chronic form may be characterized by a sluggish course, the absence of characteristic symptoms and periodic exacerbations provoked by stress, hypothermia, and decreased immunity.
Let's consider all the possible symptoms characteristic of metritis:
- Pathological vaginal discharge. In the catarrhal form, they will be abundant, characterized by a mucous consistency, but odorless. With purulent metritis, pus is discharged and an unpleasant odor appears. In the necrotic form, tissue fragments and clots may be found in the mass separated from the female vagina. In gangrenous form, the discharge is brown or black and smells of rot (rotten meat).
- Soreness. Pain during metritis is localized in the lower zone of the abdominal cavity, often extends to the lower back and sacrum, and sometimes practically spreads throughout the entire abdomen. The character is aching, dull, sharp or cramping (depending on the causes and form of the disease), the intensity varies from weak or moderate to strong and unbearable. Often the pain intensifies with physical activity and movements (bending, turning, lifting the legs), and with mechanical influences (pressure).
- Manifestations of general intoxication of the body: increased body temperature (from 37.5 degrees subfebrile to critical - 39 degrees and above), malaise, feverish state, weakness.
- Bleeding between periods. They can be abundant or moderate, and sometimes scanty in the form of a daub.
- Disruptions of the menstrual cycle: excessively frequent or, on the contrary, rare periods, changes in the duration of breaks between them, painful critical days, heavy or, conversely, scanty discharge.
In chronic metritis, the symptoms are vague and not expressed. Signs occur only during exacerbations and can be very mild. Most often, strange vaginal discharge, menstrual irregularities and mild aching pain appear.
Symptoms of chronic inflammation
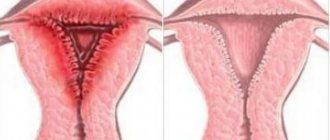
Clinical symptoms depend on the duration of the disease. Pathology manifests itself in the form of menstrual irregularities. A woman notices that after acute inflammation, the duration of bleeding increases and its volume changes.
Sometimes pathological ichorous, mucopurulent discharge may appear. This occurs when inflammation in the uterus worsens. The pain in the lower abdomen becomes aching and dull. If the pathology is protracted, pain may occur during sexual intercourse.
Chronic endometritis leads to the formation of adhesions inside the uterus.
With a pronounced adhesive process, infertility occurs, which cannot be treated. The inability to get pregnant is also associated with changes in the receptive properties of the endometrium. The development of hyperplasia is possible.
Hyperplasia can occur in a diffuse form, then the thickening occurs relatively evenly. With focal hyperplasia, an endometrial polyp is diagnosed.
Therapy
Examination by a doctor for metritis.
How is metritis treated? Therapy is aimed at eliminating the cause that provoked the development of the disease. Treatment can be carried out both at home and in a hospital. It is prescribed after examination by a doctor and may include directions:
- Antibiotics are used when the causative agent of the infection is bacteria. The sensitivity of microorganisms to various drugs is determined. Doses and treatment regimens are prescribed individually.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs relieve pain and inflammation. They are used intramuscularly in the form of injections or orally in the form of tablets and capsules.
- After a bruise, cold is applied to the uterus for some time to eliminate swelling.
- In the postpartum period, agents are sometimes used that enhance the contractile activity of the muscular uterine layer and accelerate the separation of the placenta. If the remains of the placenta are present in the uterus, curettage is performed.
- In case of severe intoxication, saline solution and glucose are administered intravenously.
- In case of menstrual irregularities, hormonal medications are indicated.
- At the recovery stage, physiotherapy is effective: electro- and iontophoresis, UHF therapy, mud therapy, diathermy.
- In severe cases (with gangrenous form of metritis), amputation of the uterus is indicated.
How does acute metritis manifest in women?
The acute form of metritis manifests itself with very obvious, pronounced symptoms, which are accompanied by heavy bleeding and vaginal discharge. Since this is an inflammatory process, the pathology will manifest itself in the form of an increase in temperature to 40-42 degrees, intrauterine sepsis will develop, which poses a threat to the woman and the corresponding vaginal discharge and pain in the lower abdomen.
In addition to obvious signs, doctors also identify a group of rectal symptoms - thickening of the walls of the uterus, its elongation, which is accompanied by the development of edema and attacks of pain in the lower abdomen, radiating to the lumbar region.
Prevention
Prevention will include:
- Avoiding unprotected sexual intercourse.
- Compliance with the rules of intimate hygiene.
- Avoiding injury.
- Refusal of the intrauterine device.
- Timely treatment of all diseases in the early stages of development.
Metritis is a serious and sometimes dangerous disease. But it can be detected and treated in a timely manner by knowing the symptoms and promptly consulting a doctor.
(votes: 2, rating: 5.00 out of 5)
Share the news on social networks
Ask a Question! You have questions? Feel free to ask any questions! And our staff specialist will help you. Go>>
- Recommended Articles
- Gardnerellosis - what is important to know about the disease?
- Hyperpolymenorrhea
- Is it possible to wash yourself with potassium permanganate?
« Previous entry
Folk remedies
How to treat chronic metritis? Traditional medicine produces quite good results. For douching, you can use a tincture of chamomile and cinquefoil flowers. These plants relieve inflammation well and help stop bleeding. To prepare, you will need one tablespoon of a mixture of herbs, pour one liter of boiling water, leave, strain and douche.
Instead of cinquefoil, you can use linden. In this case, chamomile and linden are taken in a ratio of 3:2. Four tablespoons of the mixture are poured into a glass of boiling water, infused and used for irrigation.
A complex decoction is prepared from the following medicinal plants:
- oak bark - 1 part;
- chamomile (flowers) - 3 parts;
- nettle (leaves) - 3 parts;
- bird knotweed grass - 5 parts.
All herbs are mixed. Then 2 tablespoons of the mixture are poured with one liter of boiling water and infused. After this, you can douche with the tincture or make vaginal tampons.
Plantain can be used for medicinal purposes. Since ancient times, people have known about the high hemostatic properties of this plant. To prepare a tincture that is consumed orally, you will need 200 milliliters of boiling water and one tablespoon of herbs. It is necessary to infuse for 15 minutes, then strain. In addition to taking plantain tincture, it is recommended to douche or use tampons.
You can buy calendula tincture (alcohol) at the pharmacy and take 10 drops 4 times throughout the day. Calendula has bactericidal properties and has a positive effect on the restoration of the structure of the uterus.
Classification of the disease
Acute metritis
With this pathology, pronounced symptoms are noted, and the main reason for the development of this form of metritis is abortions and problems during labor.
Acute metritis is accompanied by the appearance of copious discharge, as well as a sharp rise in body temperature.
If purulent-necrotic metritis progresses in a woman’s body, an increase in body temperature to 41 degrees is observed, which can lead to death due to the rapid spread of sepsis.
Upon careful examination of the woman, a change in the size of the uterus and its increased pain are observed. If certain treatment is not carried out, the progression of the pathology occurs with increased force, and signs of severe sepsis appear. In addition, there is a transition from acute metritis to a chronic form of the course, which requires much more effort and time to completely cure it.
Chronic metritis
The reason for the development of this form of the disease is untimely or ineffective treatment of acute metritis. Among the variety of reasons that led to the development of pathology, the following can be distinguished:
The symptoms of the disease in the chronic form are not very pronounced, and there are no acute complications.
Treatment of pyometra
After examination and diagnostic tests, the specialist will choose the optimal treatment option. Modern veterinary medicine offers two main methods of ridding an animal of pyometra:
Conservative. In this case, we are talking about the use of medications that are designed to fight inflammation of the uterus and intoxication of the body. The advantage of the technique is the preservation of the reproductive system and the possibility of subsequent use of the dog for breeding.
Operational. Involves removal of the uterus and ovaries. Consequently, the bitch can no longer take part in breeding. The advantages of the technique include high efficiency. This surgical intervention is not considered a complex manipulation and is performed under general anesthesia.
We recommend reading the following articles:
Sterilization of dogs: good or bad for your pet
Castration of dogs: pros and cons of the operation
After 2-3 days, a significant improvement in the dog’s condition is noted, and after 2.5-3 weeks the animal is completely restored and returns to its usual way of life.
The decision regarding the choice of treatment should be left to your veterinarian. Based on the results of the examination and assessment of the animal’s condition, he will choose the optimal technique that will give the most effective result in each specific case. Attempting to choose medications on your own will lead to aggravation of the situation or death of the animal.
Let's look at both treatment methods in more detail.
Drug treatment
The specialist chooses conservative treatment in several cases:
- We are talking about a breeding bitch;
- An extremely serious condition of the animal or an old dog that may not tolerate anesthesia;
- The owner’s desire to get a healthy pet at minimal financial cost;
- Therapeutic measures before surgery, designed to improve the animal’s condition and facilitate the recovery period.
It is important! Clinical studies have shown that 20% of bitches experience a recurrence of purulent endometritis after drug treatment.
Experts choose prostaglandins as the most effective and affordable medicine. The choice of dosage and frequency of application directly depends on the body weight, age and condition of the animal.
If, 7 days after the start of drug treatment, the diameter of the uterine horns in a bitch exceeds 1-1.5 cm, then surgical intervention is necessary.
Surgery
The reason for surgical treatment of pyometra is the threat to the life of the pet, a high degree of intra-abdominal pressure, as well as an increased risk of uterine rupture as a result of the accumulation of purulent discharge with a closed cervical canal.
At the same time that the uterus is removed, the veterinarian also removes the ovaries. The animal can no longer take part in breeding, but after a short time it is completely restored and is ready to return to its normal life. After surgery, the specialist prescribes a course of antibiotics, as well as drugs designed to eliminate intoxication of the body.
Preventive actions
To avoid the appearance of chronic metritis, you should eliminate any factors that could lead to the development of the disease. Firstly, it is necessary to abandon abortions and all kinds of curettage that can disrupt the integrity of the uterus. Infectious diseases of the pelvic organs, casual sexual intercourse, and also avoid hypothermia should be avoided.
If it already happens that a woman is sick, then gynecologists recommend regular preventive examinations. You should never forget about the rules of personal hygiene; you also need to maintain your immunity and try to prevent colds.
Life forecast
How long do people live with metritis? The disease is not fatal, but can lead to sepsis, which can lead to death, or to impaired reproductive ability, which will worsen not the prognosis, but the quality of life of a woman. To avoid this, you need to carry out prevention:
Source: https://vospalenia.ru/metrit.html