Curettage of the uterine cavity is carried out for endometrial hyperplasia in order to obtain an analysis for research and identify pathology at an early stage of development. In the absence of timely treatment, there is a likely risk of the disease degenerating into oncology.
The most common type of endometrial hyperplasia found in women is glandular cystic hyperplasia. The probability of the disease progressing to cancer with timely treatment is only 1%.
Features of the treatment of endometrial hyperplasia after curettage
Curettage is performed for the purpose of diagnosis and treatment of pathologies in which abnormal thickening of the mucous membranes of the reproductive organ occurs.
In this way, it is possible not only to determine the extent of the lesion and its nature, but also to eliminate pathological tissue. Treatment of endometrial hyperplasia after curettage has a number of features. In many ways, the course of therapy depends on the reasons that led to such changes.
Curettage and pregnancy
Pregnancy after curettage has every chance of occurring. This can happen within a month if you do not take hormonal medications. If a woman follows the doctor’s instructions and undergoes hormonal therapy, then pregnancy can occur 1-2 months after its cessation.
When you can get pregnant after curettage, a doctor can tell you exactly - based on the picture that was seen and described by a specialist who examined the endometrial scraping under a microscope.
It is usually not recommended to plan a pregnancy immediately after the first menstruation: there is still no guarantee that the inner uterine lining has been sufficiently renewed and will be able to allow the fetus to develop until the end of the term. Gynecologists recommend waiting 3-6 months before stopping using contraception.
Indications for the procedure
Curettage is a therapeutic and diagnostic procedure that is prescribed for various gynecological diseases. It is indicated for endometrial hyperplasia. During curettage, the doctor uses a hysteroscope or a simple curette to remove the functional uterine layer, which will be completely restored by the next menstruation. Other tissues are not affected.
Sometimes there is a cure of hyperplasia without curettage, but such cases are extremely rare. Therefore, gynecologists insist on performing this procedure.
For diagnostic purposes, the method is indicated in the following cases:
- failure of the menstrual cycle;
- prolonged and excessively abundant regulations;
- acyclic bleeding;
- pronounced pain syndrome during critical days;
- impossibility of conception;
- suspicion of cancer.
Treatment by curettage is indicated for the following problems:
- uterine fibroids;
- endometritis;
- polyps in the cavity of the reproductive organ and cervix;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- freezing of the fetus in the womb;
- complications after childbirth;
- spontaneous abortion.
If hyperplasia develops during menopause, the procedure is mandatory. This is due to the increased risk of cells degenerating into cancer.
What is curettage?
Curettage for endometrial hyperplasia is both a therapeutic and diagnostic procedure. It involves removing that layer of the endometrium (the inner lining of the uterus) that lies on the border with the uterine cavity. This in itself allows you to get rid of the disease for a while, especially if it was accompanied by bleeding or had a high risk of malignant degeneration.
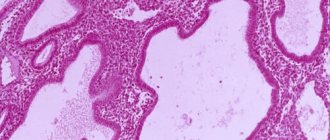
In addition, after examining the removed membrane under a microscope, the doctor will be able to prescribe the necessary treatment that will prevent the endometrium from growing again (and becoming a source of bleeding or cancer).
What exactly will be removed and how will it help?
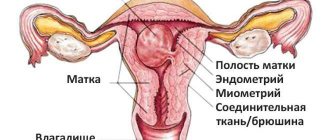
A woman's uterus is an organ that, when a woman is not pregnant, is approximately the size of her fist. And in shape it resembles a clenched fist: its front wall is practically in contact with the back, and it turns out that there is 5-6 cubic centimeters of free cavity left.
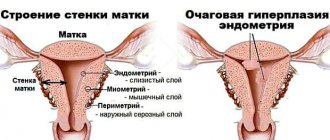
The inner layer of the uterus - the endometrium - consists of two layers. The one that borders the uterine cavity is called functional. It is this that should become a refuge for the developing child, and when fertilization does not occur, it peels off and comes out during menstruation. It is this “waste” layer that a woman sees during menstruation in the form of mucus.
The nature of menstrual blood is the destruction of the vessels that fed the cells of the functional layer and were located between it and the lower layer of the endometrium (basal). The more cells there were, the more intercellular vessels ruptured, the more abundant the release of blood. And endometrial hyperplasia is an increase in the number of cells of its functional layer.
Thus, removing the endometrial layer in which a large number of cells have appeared will temporarily solve the problem of heavy bleeding during menstruation.
Another danger is hyperplasia. When cells of any organ, including the endometrium, divide, altered structures appear among normal cells. To prevent cancer, the immune system must destroy cells that are atypical for this organ, but the more of them are formed (as with endometrial hyperplasia), the more difficult it is for it to keep track of “order.” This is especially true for women in menopause, whose immunity becomes much weaker.
Thus, curettage as a treatment method immediately eliminates both the source of bleeding and the multicellular layer in which uterine cancer can easily develop.
Curettage technique
Surgery can be performed in several ways: using a hysteroscope or blindly using a curette. Regardless of which option is chosen, the woman will need to be hospitalized for a short period and subsequently undergo a course of treatment. In case of repeated development of pathology or mutation of cells into malignant ones, hysterectomy methods are used and the reproductive organ is completely removed.
Blind scraping
The procedure is carried out according to the following scheme:
- First of all, the woman is given anesthesia.
- When the sensitivity of the genital organs is lost, the operation itself begins.
- The dilator is inserted into the cervix.
- The curette is inserted into the cavity of the reproductive organ.
- The cutting edge of this tool is driven along all the walls, but special attention is paid to the bottom and corners.
- The uterine mucosa is scraped.
- The resulting biomaterial is placed in a special container for subsequent histological examination.
- If necessary, a polyp in the uterus is removed.
- Damaged vessels are cauterized.
- Remove all instruments and the expander.
The operation lasts about half an hour. After its completion, the woman is placed on a gurney and taken to the ward. Once the anesthesia has completely worn off, there is no longer any need to stay in a medical facility.
The disadvantage of this method of surgical intervention is that the operation is performed without spotlighting, and there is a risk of damage to the deeper layers of the uterus.
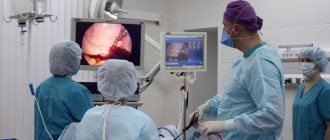
Hysteroscopic
Diagnostic intervention is carried out under visual control, which can be achieved thanks to a special device - a hysteroscope. It is a tube equipped with a light, chamber and channels through which gas or liquid is supplied and a curette is inserted.
At the initial stage, the same actions are performed as with the blind method. First of all, anesthesia is administered and a dilator is inserted. A hysteroscope is placed into the passage that is formed, and gas is injected through its channel, promoting the expansion of the walls of the reproductive organ.
A curette is inserted into the second channel and the condition of the endometrium is assessed. Part of the uterus is viewed on the monitor in an enlarged form. Then cleaning is done. The resulting tissues are placed in a container and sent for histological examination.
At the final stage, the vessels that are bleeding are cauterized and all instruments are removed.
How is curettage performed?
The manipulation is carried out in the operating room. The woman sits on a gynecological chair. The procedure is very painful, so the operation is performed under anesthesia. Curettage after delivery or due to miscarriage does not require intravenous anesthesia; the cervix is already in a dilated state.
In other cases, the cervical canal is opened using a special dilator and the mucous membrane is removed with a surgical spoon. A vacuum aspirator or hysteroscope may also be used. In the latter case, the device is equipped with a camera, which allows you to see all the areas that require cleansing.
When curettage is performed, a biopsy is immediately taken for examination and sent to a histology laboratory.
The woman is carefully prepared for the upcoming operation. Tests before curettage:
- UAC;
- blood for clotting;
- blood for RW, HIV, hepatitis C;
- vaginal smear to detect viruses and infections;
- blood for thyroid hormones.
In addition, it is necessary to limit sexual contact a couple of days before the operation.
Without test results, curettage is allowed if a woman is brought to the hospital with heavy bleeding.
Complications after the procedure
Cleaning the reproductive organ is an operation with an increased risk of damage. Bleeding after it is considered a dangerous symptom. Such discharge may indicate the development of the following complications:
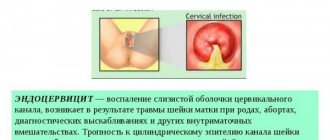
- endometritis;
- cervical tear;
- penetration of infection;
- perforation of the affected walls;
- impossibility of conception.
A repeated recurrence of the pathology is also possible. Therefore, it is extremely important to adhere to all medical recommendations in the postoperative period, restore ovarian activity and normalize hormonal levels.
The occurrence of hyperplasia
Glandular-cystic endometrial hyperplasia often develops after curettage. This is due to the fact that as a result of its implementation, the following changes can occur in the female body, contributing to the occurrence of pathology:
- hormonal imbalance. There is an excessive concentration of estrogen and an insufficient amount of progesterone;
- disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine, cardiovascular and genitourinary systems;
- inflammatory processes in the genital organs;
- fibroids, polyps in the uterus;
- polycystic adnexa and adenomyosis.
What are the consequences of relapse of endometrial hyperplasia?
If the disease recurs for the first time, it is not scary. It’s worse if this happened for the second or third time. This means that it is impossible to completely cure hyperplasia. In this case, the risk of cancer is very high. Therefore, the only effective treatment will be complete surgical removal of the endometrium or even the uterus. This means that the woman will no longer be able to become a mother.
And hyperplasia itself negatively affects conception, pregnancy and childbirth. The disease can lead to female infertility. This problem is very serious, especially for nulliparous patients. To reduce the risk of infertility, you need to immediately begin treatment for the pathology, immediately after diagnosis. In advanced cases, the disease leads to serious hormonal changes, which leads to disruption of the ovulation process. As a result, fertilization of the released egg becomes more difficult. If the disease has recurred, it can also be treated without surgery.
Treatment options
Treatment of endometrial hyperplasia after curettage is quite long. The course of therapy is selected by the doctor individually, taking into account the woman’s age and the presence of concomitant pathologies. In the first few days after surgery, drugs that normalize hemostasis are used. This is due to the fact that the walls of the reproductive organ are excessively damaged and constantly bleed.
At the next stage, antibiotics are prescribed, with the help of which it is possible to prevent the development of complications. Enzymes act as an additional drug. With their help, it is possible to activate the body's protective functions, speed up the regeneration process and increase the effectiveness of other groups of medications.
Hormonal levels play an important role in the therapy process. For this reason, the treatment regimen must include taking hormones (estrogens and gestagens). The duration of therapy varies from three months to six months. Physiotherapy procedures are prescribed in combination with the use of medications. In addition, a woman needs to adhere to a diet and avoid excessive physical activity.
After finishing taking hormonal medications, it is recommended to conceive as soon as possible. This is due to the fact that during pregnancy the endometrium does not undergo monthly changes, the risk of relapse is significantly reduced.
Menstruation after cleansing appears on the 28th–35th day. If your critical days have not arrived during this period, you should definitely consult a gynecologist. To establish the reason why the restoration of the cycle did not occur, you will need to undergo an ultrasound, during which it will be possible to determine the size of the reproductive organ and the thickness of the uterine layer. If necessary, special medications will be prescribed that provoke the appearance of regulation.
A doctor’s help is also needed if your periods become longer, have an unpleasant aroma or an uncharacteristic consistency. Such symptoms often indicate the development of serious complications that will require additional treatment.
When endometrial hyperplasia is detected, curettage is performed for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. The operation can be performed blindly or using hysteroscopy. In this case, the affected tissue is removed from the uterine cavity and transferred to the laboratory for further histological examination. The course of treatment largely depends on what results are obtained. Only with correctly selected treatment tactics can relapses of the disease be avoided.
After curettage for hyperplasia. What to do
It usually doesn’t end with the procedure itself. After curettage, a recurrence of the polyp or hyperplasia may occur within a month or several months, if actions aimed at correcting the hormonal levels are not taken.
This is because this disease is associated with increased cell division of various layers of the uterus and hyperplasia of the endometrium (inner layer) or the formation of polyps (focal outgrowths of connective tissue covered with epithelium) under the influence of hormone imbalance. And this is a cyclical process for a woman.
The most common method of radical treatment is repeated curettage with mandatory testing of cells for malignant degeneration. But, it is clear that few people want to repeat the operation. Read the most important information about what to do and make your own decision.
What to do to prevent relapse
As usual, there are several ways. How close you are to hormonal treatment or whether you are more of a supporter of a natural approach and influencing the causes is up to you to choose. You can also combine these two options. What you definitely cannot do for reasons of self-preservation is to pretend that this is an accident and continue to eat the same way and treat the processes of cleansing the body of toxins and your nervous system as before.
In this article by the Sokolinsky Center, you will find an unusual approach. Gynecologists do not talk about this very often, preferring to simply prescribe hormones after curettage.
Reasons "why she comes back"
Both processes (endometrial hyperplasia and cervical polyps) are directly related to the increased production of estrogens - female sex hormones (Manukhin I.B., Tumilovich L.G., Gevorkyan M.A. Clinical lectures on gynecological endocrinology. M.: MIA, 2001 ). For many women, it comes as an “unpleasant surprise” that after surgical treatment designed to completely rid them of the disease, doctors prescribe hormones to prevent relapse. Let's figure out why this is needed and what side effects may occur.
Impact of metabolic syndrome
First, it is worth telling in more detail why endometrial hyperplasia and polyps most often occur in women of advanced age or who are obese. It's all about the metabolic syndrome - a complex of metabolic disorders that occur with an excess of visceral fat in the body (Gambacciani M., Ciaponi M., Cappagli B et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1997). The “triad of death” in this condition is described:
— Increased insulin concentration and decreased sensitivity of cells to this hormone (resulting in increased blood sugar). Adipose tissue is always well supplied with blood and is practically an “independent organ” of a person. Not only the process of fat deposition constantly occurs in it, but also lipolysis with the rapid entry of fat molecules into the bloodstream. This is the main cause of insulin resistance and high levels of insulin in the blood, which “works” similarly to the luteinizing hormone of the pituitary gland and stimulates the production of estrogen by the ovaries.
Why is it important to detox and support the nervous system?
Because ultimately we want to achieve self-regulation of hormonal levels and antitumor immunity. And they are most influenced in percentage terms by the quality of the liver (participates in the exchange of estrogens and androgens), the level of internal intoxication, and the stability of the nervous system. This is how physiological regulation works.
Therefore, no matter what the best means with a resolving effect (for example, Curcuminum Q10 complex from Europe) or activating antitumor immunity (Meishi, Immunarium) you use, if you do not first carry out a course of detox, they may not have a pronounced effect.
Complicating factors.
It happens that with long-term disturbed microflora, chronic inflammation, excess weight, stagnation of bile, too active influence on the immune system leads to skin rashes. The excretory system is simply not ready! Take your time and start with a detox. There is no natural remedy as fast as hormonal drugs. This is a completely different philosophy, aimed at reasons. Therefore, there is no cure for hyperplasia or polyps - there is a system for restoring women's health.
Don't forget about your nerves.
With constant stress, its negative impact on hormonal levels must be compensated. Read what Biolan is and try it. The complex of amino acids with neuropeptides has helped many people feel better. You will like it, and first of all, because unlike chemistry, it does not cause drowsiness and addiction.
It is imperative to restore normal sleep depth - lasting at least 7 hours a day and no more than 9. Fall asleep no later than 24 hours. It is important. Otherwise, hormonal levels and antitumor immunity are disrupted!
How to take natural remedies. Scheme after scraping
1 month
Immediately after returning home, you can use the Complex for deep cleansing and nutrition with NutriDetox
If the doctor prescribed antibiotics, then we do not take Zosterin Ultra yet (until the end of taking antibiotics), but Unibacter. A special series, on the contrary, we start from the first month with 2 caps. in a day.
You can also immediately add to the course a natural remedy for harmonizing the state of the nervous system - Biolan, 1 cap. REST under the tongue 2 times a day for 20 days.
2-3 month
We use the Complex for fibroids, hyperplasia, endometriosis.
It includes Meishi mushroom polysaccharides (export version) and a natural estrogen form corrector Indogrin and natural tocopherol. Blood purification also continues.
In the autumn and winter, it makes sense to enrich your diet with polyunsaturated omega-3 acids. In the Sokolinsky System it is Megapolynol – 35% omega3 1400 mg per capsule.
There are several studies regarding PUFAs in hyperplasia.
Here's one of them.
From the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, which states that long-chain omega-3 acids, when taken long-term, reduce the risk of uterine cancer.
The study was conducted on approximately 1,000 case histories and surveys of gynecologically healthy women.
When to evaluate the result
The benefit or lack of benefit from natural remedies can be assessed after 2 cycles of curettage. If hormonal levels improve, the cycle is established, the endometrial mucosa is normal, then you are lucky to have found your path and a reasonable gynecologist may agree not to prescribe chemistry.
Is it possible to drink natural remedies along with doctor’s recommendations?
Natural remedies will not interfere with chemistry, but taking indole at the same time as a hormonal drug is pointless. Fine tuning will not work.
How long to take
To be sure that the topic is closed - up to 4 months in a row. Don’t forget to do an ultrasound at the end and possibly take tumor markers if they were violated. Continue to eat wisely and limit foods that provoke hyperplasia. Carry out a detox twice a year, regularly replenish the level of antioxidants, for example NutriDetox, in winter - Megapolynol as a source of omega-3 (from October to March)
Symptoms of pathology
The standard manifestation is repeated uterine bleeding. It happens relatively rarely: no more than once every six months. But most often, in case of unfavorable developments, heavy menstruation occurs once every 3 months. If a woman is faced with the need to curettage the uterus 4 times a year in order to stop profuse bleeding, then this becomes an extremely dangerous situation that threatens the development of oncology. In addition to hormonal disorders, a risk factor is mechanical trauma in the uterine cavity.
Drug treatment of hyperplasia and polyps
Stimulation of excessive proliferation of endometrial cells occurs under the influence of increased levels of estrogen, which normally “prepare” the uterus for embryo implantation and restoration of the endometrium after cyclic bleeding. Therefore, if after curettage you do not resort to hormonal anti-estrogenic therapy, the doctor believes that the process will resume in 100% of cases. For treatment, progestins, androgens, and analogues of gonadotropic releasing hormone are used (Chernukha G.E. Adenomatous and glandular hyperplasia of the endometrium in reproductive age (pathogenesis, clinic, treatment, 1999).
To convince the doctor that changing your diet, detox, and using natural hormonal balance correctors can replace hormonal therapy, many more tests are needed. So far, there are dissertations confirming the effectiveness of plant indoles and antioxidants, as well as omega-3 acids.
In each case, health belongs to the woman herself and she has the right to decide how to be treated after curettage. Natural remedies are not medicine. Their goal is harmonization and influence on the causes of failures.
Progestins (medicines)
Analogs of own progesterone. They inhibit the production of follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones of the pituitary gland, which results in a decrease in the release of estrogen by glandular cells of the ovaries. But at the same time, progestins cause the replacement of ovarian tissue with connective tissue (fibrosis), the endometrium of the uterus becomes thinner and loses its ability to recover (Serov V.N., Prilepskaya V.N., Pshenichnikova T.Ya. Gynecological endocrinology. M.: Medicine, 1993 ). Endometrial atrophy leads to undesirable effects such as spotting or even uterine bleeding.
Hormones have androgenic and residual glucocorticosteroid activity. Therefore, women often experience a decrease in libido, weight gain and engorgement of the mammary glands, nausea, and vomiting. Mood may change, even to the point of depression.
GnRH (gonadotropin releasing hormone agonists)
Estrogens are the end product of the “work” of the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian system. If the pituitary gland receptors are “stimulated” for a long enough time (several hours continuously), their sensitivity decreases and ultimately blockade occurs (Emons G., Schroder B, Ortmann O. et al. High affinity binding and direct antiproliferative effects of luteinizing hormone releasing hormone analogs in human endometrial cancer cell lines // J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metabol. 1993). This is how GnRH works, but unlike progestins, it does not interfere with metabolism: lipid metabolism and cell sensitivity to insulin.
On the other hand, when a woman uses these hormones, an artificial menopause occurs with all the unpleasant symptoms in the form of “hot flashes” and other vegetative reactions. The most dangerous thing is the premature formation of osteoporosis, which greatly limits the permissible duration of treatment (O.A. Slyusareva // Proven or not? Modern ideas about the treatment of endometrial hyperplasia // 2013).
The described side effects require careful use of hormones in patients with obesity and other manifestations of metabolic syndrome. In parallel with their use, a special diet aimed at reducing body weight must be prescribed. Considering the increased risk of developing atherosclerosis due to the accumulation of low-density lipoproteins in blood vessels, it is important to monitor the lipid spectrum of the blood and, if necessary, prescribe statins (drugs to lower cholesterol levels).
This is the biggest problem in the treatment of endometrial hyperplasia and cervical polyps: on the one hand, obesity is an important provocateur of this pathology, on the other hand, it is with obesity that the positive effect of hormonal drugs can be completely “neutralized” by their side effects, which increase with increased body weight.
Symptoms
Clinical symptoms of recurrent endometrial hyperplasia have its own characteristic features for each period of a woman’s life. Most often, women of reproductive age experience the following symptoms:
- Long and heavy menstruation;
- Meno - and metrorrhagia;
- Irregularity in the menstrual cycle;
- The appearance of painful periods (dysmenorrhea);
- Infertility or miscarriage.
But we cannot exclude the possibility of a completely asymptomatic course of the disease, which a doctor can detect only during a preventive examination, a visit to which is the key to early detection of pathology and effective timely treatment.
Symptoms of hyperplasia in women during menopause:
- Prolonged and heavy bleeding;
- Bloody, spotting discharge;
- No symptoms.
Symptoms during postmenopause:
- Bloody discharge (profuse, scanty);
- Pain syndrome with localized pain in the lower abdomen, cramping in nature.