Endometritis is a hormonal disease that is characterized by inflammation of the inner uterus (endometrium).
It is into this that the egg is transplanted during pregnancy.
The disease occurs in two forms - acute and chronic, and the symptoms and treatment of each are slightly different.
If you ignore the treatment of the pathological process, this will lead to serious complications, for example, the spread of the infectious process to surrounding organs and infertility.
Very often, the drug Duphaston is used to treat endometritis.
The essence of pathology
The development of endometritis occurs against the background of an increased concentration of estrogen and a lack of progesterone.
In addition, the cause of the disease may be:
- infection;
- weakened immunity;
- inflammation of the genitourinary system;
- hereditary factor.
Symptoms of endometritis are pronounced in the acute form of the disease - but the main signs of the pathological process remain :
- pain during intercourse;
- menstrual irregularities;
- intense pain in the lower abdomen, the intensity of which increases during menstruation;
- discomfort when urinating, defecating;
- fairly heavy periods;
- spotting before and after the end of menstruation;
- intermenstrual bleeding;
- premenstrual syndrome.
NOTE!
The intensity of the clinical picture depends on the location of the lesion.
What is endometritis,
Types of endometrial hyperplasia
Based on the histological characteristics of pathological cells, several types of hyperplastic endometrial pathology are distinguished:
- glandular;
- glandular-cystic;
- focal (uterine polyps);
- atypical (adenomatosis).
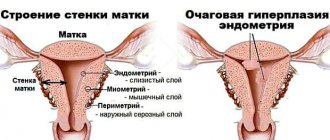
Glandular pathology is characterized by the disappearance of the separation of the basal (base) and functional endometrial layers, an increase in the number of secretory organs and their uneven location, a clear boundary between the muscular layer of the uterus (myometrium) and the abnormal endometrium. All growth energy is directed towards the development of glands, which become tortuous and merge with each other.
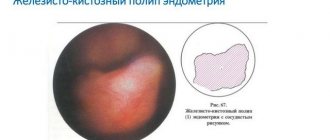
The glandular-cystic form represents a further progression of the disease and is accompanied by cystic degeneration of some of the glands. This is usually associated with blockage of the excretory duct and the accumulation of secretions in the gland capsule, with the formation of a small cystic bladder, the fluid inside of which contains excess estrogen. Cysts are microscopic in size and located inside the functional layer of the endometrium in the form of a cluster. If several cystic cavities merge, they may be detected during ultrasound examination.
Focal or local hyperplasia is the proliferation of the epithelium of the uterus and underlying tissues with the formation of glandular, fibrous or fibroglandular polyps. Atypical hyperplasia (adenomatosis) is characterized by the most intense proliferation and structural restructuring of cells, a decrease in the proportion of connective tissue elements, and polymorphism of cell nuclei. The last two forms (adenomatosis and uterine polyps) have a high oncological potential and are considered in gynecology as a precancerous condition. Adenomatosis degenerates into a malignant formation in approximately 1 case out of 10. In addition, inadequate hormonal treatment and the procedure of curettage of the endometrium in case of hyperplasia pose a threat to oncology.
Some areas of the endometrium are normally thicker than others; this is where the development of hyperplastic processes begins. Endometrial cells in these areas undergo significant changes. This is how focal and mixed forms of the disease develop.
Is drug treatment effective?
It is difficult to cure endometritis with medications.
This can only be done if they are used as part of a comprehensive treatment, and the entire process is supervised by a qualified specialist.
Drug therapy for endometritis has the following goals::
- restoration of reproductive and menstrual function of the uterus;
- normalizing the regenerative ability of the uterine mucosa;
- eliminating existing complications and preventing the formation of new ones;
- elimination of chronic infectious and inflammatory foci.
The following groups of drugs are used to treat the disease:
- antibiotics;
- desensitizing agents;
- sedatives;
- painkillers.
- restoratives.
Prevention of endometrial diseases
Compliance with these conditions is especially important after completing a course of treatment for hyperplasia in order to prevent relapses of the disease:
- timely and complete cure of gynecological and urological diseases, in particular inflammatory processes of infectious etiology;
- regular sufficient physical activity, active lifestyle, mobility, avoidance of blood stagnation in the pelvis;
- a healthy diet with a minimum of fatty, spicy foods, caffeine, etc.;
- regular visits to the gynecologist;
- careful personal and sexual hygiene;
- rational contraception, taking hormonal medications strictly according to the schedule;
- timely treatment of diseases of the endocrine system;
- exclusion of abortion.
A woman should regularly visit a gynecologist and endocrinologist to monitor the condition of the endometrium. Any disease of the female reproductive system requires the woman to contact a gynecologist as soon as possible. Timely, scientifically based treatment promotes a speedy recovery, preserves the possibility of childbearing, and improves a woman’s condition.
Correct treatment of glandular endometrial hyperplasia Treatment with Duphaston for endometrial polyp. Features and indications for useFeatures of treatment and prevention of endometrial hyperplasiaCauses of endometrial hyperplasia, types of diagnosis and treatment
Duphaston drug
The drug Duphaston is one of the most effective ways to treat endometritis.
It contains a progesterone analogue, which stops the growth of the endometrium and reduces the effectiveness of estrogens, androgens, and corticosteroids.
The effect of the drug does not lead to disruption of ovulation, does not cause the development of male sexual characteristics, and does not affect brain function, metabolic processes and blood clotting.
Taking Duphaston for endometritis helps reduce the contractility of the uterus and its tone, and the risk of miscarriage in the early stages of pregnancy.
The drug relieves pain, reduces menstrual flow, and prevents the degeneration of pathological cells into malignant ones.
Expert opinion
Shustova Olga Leonidovna
Obstetrician-gynecologist of the highest category
“Taking Duphaston for endometritis in practice gives high positive results. With the drug, pregnancy occurs more often, and this is despite the fact that some patients have been diagnosed with infertility. During pregnancy, there are no periods, which means that the endometrium does not grow. After birth, prolonged feeding with breast milk is recommended, because then menstruation is also absent, but Duphaston should not be used due to the penetration of progesterone into mother's milk. Despite this, the drug remains the most gentle method of treating endometritis, since thanks to it it is possible to preserve the usefulness of the genital organs and the reproductive system as a whole.”
Causes of hyperplastic pathologies of the uterine epithelium
The disease can develop in women of any age, but there is a clear dependence on the state of hormonal balance. The likelihood of endometrial hyperplasia is higher in girls going through puberty and women who have reached the age of menopause.
- hormonal imbalances, hyperestrogenism, progesterone deficiency of various etiologies (polycystic degeneration and ovarian tumors, neoplasms, uterine fibroids);
- diseases of the endocrine system: adrenal glands, thyroid gland, hypothalamic-pituitary system;
- metabolic disorders: diabetes mellitus, obesity, arterial hypertension;
- hormonal changes during menopause and adolescence;
- inflammatory diseases of the female reproductive system: endometritis;
- genital surgeries, gynecological procedures, abortions, curettage.
It should be noted that any endometrial pathologies, including glandular hyperplasia, occur much less frequently in women who have given birth. This is due to the fact that during pregnancy the lining of the uterus takes a break from monthly traumatic transformations. Bearing a child, fulfilling a biological female function, thus protects a woman from health problems.
Advantages and disadvantages
Artificial progesterone in the form of tablets promotes numerous useful and necessary changes in the reproductive system, resulting in the restoration of endocrine balance and the creation of adequate conditions for pregnancy.
The following advantages of Duphaston can be highlighted::
- Excellent healing effect. After taking the drug, secretory changes are observed in the uterus, which are so important for preserving the life of the embryo.
- No negative impact on ovarian function. The active components of the drug do not disrupt natural ovulation and do not suppress the production of important female hormones.
- Absence of harmful effects on the female body completely. You don’t have to worry that after taking Duphaston, extra pounds will begin to appear or the functioning of the endocrine organs will be disrupted.
The drug also has disadvantages:
- to obtain a positive therapeutic effect, Duphaston must be taken for a long time - at least 3 months;
- the high price of the drug is 455 rubles.
Composition of tablets
This drug is produced in the form of tablets for internal use. The medicine is based on the active ingredient – dydrogesterone (10 mg).
There are also additional substances:
- lactose monohydrate;
- colloidal silicon dioxide;
- corn starch;
- magnesium stearate;
- titanium dioxide;
- polyethylene glycol.
IMPORTANT!
The tablets are in a blister pack of 20 pieces. Each pack contains instructions for use.
Indications for use
When using Duphaston for the treatment of endometritis, one condition must be met - it is strictly forbidden to independently decide on taking the drug.
The drug is approved for use in the following cases:
- preconception preparation for chronic endometritis;
- artificial termination of pregnancy in the past;
- miscarriage caused by endometrial pathology;
- hormonal deficiency that developed against the background of ovarian diseases;
- any surgical interventions on the uterine appendages;
- infertility.
Changes in the endometrium due to inflammation
In the basal layer of the endometrium, inflammatory changes occur much less frequently than in the functional part of the uterine mucosa.
An important condition for the onset of a desired pregnancy is the secretory transformation of the endometrium (specific changes necessary to create optimal conditions for the embryo). If, due to infection or hormonal disorders, the mucous membrane does not undergo the necessary changes, then conception will become impossible.
One of the causes of infertility due to inflammation is secretory insufficiency of the endometrium, therefore the treatment regimen at the stage of preparation for pregnancy always includes special hormonal drugs that ensure transformation of the endometrium.
Instructions for use
An effective method of treating endometritis involves taking Duphaston tablets for 3-6 menstrual cycles in one of the following regimens:
- from 11 to 25 days of the cycle - 1 tablet every day;
- from 14 to 25 days, 1 tablet 2 per day;
- from days 16 to 25, 2 tablets every day.
For each patient, the doctor chooses cyclic therapy individually. Over the course of 3 cycles, it is necessary to evaluate the result, which is noticeable by changes in menstruation and according to ultrasound data.
Positive effects include:
- normalization of cycle regularity;
- decreased frequency of menstruation;
- thickening of the endometrium;
- the onset of ovulation with the obligatory formation of the corpus luteum in the ovary.
The medication promotes the growth of the endometrium, so it is not recommended to stop taking it even after pregnancy.
How to treat glandular hyperplastic pathology of the endometrium?
Therapy for glandular endometrial hyperplasia must be comprehensive and consist of several successive stages.
- First of all, it is necessary to stop non-functional uterine bleeding. To do this, the patient undergoes a separate diagnostic and treatment procedure for curettage of the walls of the uterus and endocervix. Unlike abortion curettage, the purpose of which is targeted hormonal destruction, LDV is designed to eliminate the source of bleeding. A mandatory histological analysis of the scraping is carried out, and its results determine the further direction of treatment. If cancer cells are found in tissue samples, removal of the uterus is indicated.
- When the source of bleeding is eliminated, recovery from significant blood loss is necessary.
- Further therapy is aimed at restoring the monthly cycle. To do this, functional, anatomical and medicinal causes of disruption of ovulation mechanisms are established and eliminated.
Hormonal therapy for the disease:
- Combined oral contraceptives (Regulon, Yanina, Zhanin), containing gestagen and estrogen in different ratios.
- Gestagens (Duphaston, Utrozhestan) compensate for the deficiency of hormones responsible for the maturation of endometrial cells. The Mirena intrauterine system, containing a gestagen and locally affecting the endothelium, has been successfully used.
- Progesterone and its analogues promote the reverse development of hyperplasia foci.
- Gonadotropin releasing hormone antagonists normalize the functioning of the endocrine and nervous systems.
Hormonal medications are prescribed to the patient for a period of several months (about six months).
Duphaston in the treatment of endometrial hyperplasia
The drug Duphaston is an effective medicine in the treatment of hyperplastic endometrial diseases. Its action is to increase the amount of the hormone progesterone in the patient’s body. The drug is also successfully used in the treatment of endometriosis, dysmenorrhea, various cycle disorders and uterine bleeding. Treatment with Duphaston is effective as hormone replacement therapy.
The active ingredient of Duphaston is dydrogesterone, which is not a derivative of testosterone, but is structurally similar to it. The drug does not have androgenic, estrogenic, anabolic, corticoid or thermogenic effects on the woman’s body. Once in the body, Duphaston is quickly absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract, ends up in the uterus and selectively affects the pathological endometrium, preventing hyperplastic and carcinogenic processes.
The patient should take the drug every day from days 5 to 25 of the menstrual cycle. Dosage - 10 mg 3 times a day. It should be remembered that Duphaston is not a contraceptive, so conceiving a child and a successful pregnancy during treatment are possible. Sometimes adverse reactions to the drug substances occur, including migraines, headaches, general weakness, and increased sensitivity of the mammary glands. An allergic reaction may occur. Occasionally, patient intolerance to the components of the drug occurs. Duphaston is dispensed from pharmacies only with a doctor's prescription.
Treatment of endometrial hyperplasia
In parallel with taking hormonal medications, supportive rehabilitation treatment is carried out: vitamin therapy, physiotherapy, etc.
In addition, it is necessary to treat diseases that accompany and provoke anovulation:
- stress and mental overexcitation;
- pituitary tumors;
- autoimmune pathologies, including rheumatism;
- metabolic disorders;
- polycystic ovarian changes.
If it is not possible to achieve ovulation, the woman undergoes surgery on the appendages to surgically disrupt the thickened ovarian wall, which prevents the release of the egg from the follicle. The intervention is performed using classical resection or laparoscopic drilling. Ablation or resection of pathological endometrium is relevant if the disease recurs and the patient is interested in preserving reproductive function.
After 3 and 6 months, the patient undergoes a control ultrasound examination, and at the end of the treatment course, a repeat biopsy of endometrial tissue. For further use, medicinal ovulation stimulants are prescribed.