What it is?
The wall of the uterus consists of 3 layers:
- Serous covers the organ from above.
- Dense muscular myometrium is the basis.
- The endometrium is the mucous membrane inside.
The latter, in turn, is also divided into:
- Basal – the one that is closer to the myometrium. Contains glandular, epithelial and connective tissue, feeds on many vessels, is not rejected during menstruation, ensures the growth of a new surface layer after menstruation;
- Functionally similar in composition, but slightly different in structure and differing in hormone dependence. It grows, thickens for pregnancy and is rejected during menstruation.
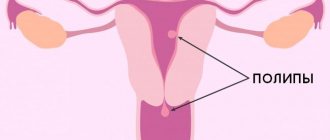
True polyps are formed from the basal layer of the endometrium, false ones from the functional one. They look like a rounded formation on a thin stalk with a bumpy surface or a finger-shaped process. At first, the body appears, like a bulge on the endometrium, then a leg forms and grows. The color is pink, gray, yellowish, with brown spots. Dimensions from nothing to several centimeters. The glandular polyp contains connective fibrous tissue only at the base, and it has a looser structure, therefore the formations are less dense than fibrous or mixed types. A large growth gradually fills the uterus and falls out into the vagina through the cervix. Less common is damage by multiple growths - polyposis.
Sometimes patients are puzzled when they see the diagnosis of a proliferative or hyperplastic polyp. They are actually the same thing and can be applied to any endometrial lesion. Proliferation or hyperplasia is the normal or abnormal process of enlargement due to cell division. In our current case, the glandular tissue of the endometrium of the uterus is susceptible to pathological growth.
Functional or false formations
As a result of incomplete rejection of the upper layer, fragments remain, from which a polyp grows with each cycle. It is dependent on the production of hormones. Therefore, there is a point in drug treatment. Glandular growths of this type are considered a polypoid form of hyperplasia or proliferation of the uterine endometrium. They do not reach large sizes, but can appear in multiple quantities. They are more common in patients of reproductive age.
Secretory variant of the functional type or glandular-cystic polyp - such terms can be seen in the histology transcript. The fact is that the glands of false polyps actively function and produce mucous exudate. However, due to the fact that some do not have access to the outside, the secretion accumulates inside, leading to an increase in cavities. Cysts appear in the polyp. This process is not of particular importance, but the fluid can become infected, which will lead to inflammation of the formation.
Reasons for the appearance of functional growths of the endometrium:
- The main thing is an excess of estrogen or a lack of Progesterone. Moreover, the level analysis may be relatively normal, but their practical interaction is disrupted;
- Endocrine pathologies – diabetes mellitus, hyperthyroidism, and others;
- Hypertonic disease;
- Decreased immunity;
- Excess weight;
- Inflammation, including infectious in the reproductive organs;
- Injuries to the uterus as a result of operations, abortions, diagnostics, pregnancy and childbirth;
- Nervous tension, chronic stress.
Recurrent endometrial polyp
Irina, Moscow
December 2, 2020
Good afternoon. I’m 38 years old, I haven’t given birth, but I’m planning to. On June 15, 2019, hystroscopy with RDV was performed. The ultrasound suspected a polyp, but it was not clearly identified, but the main cause of RDV was the thickened endometrium. Histology conclusion - Microscopic description: 1. c/c Blood, mucus, pieces of the cervical canal mucosa, pieces of proliferative endometrium without atypia. 2. p/m Blood, fibrin, pieces of the functional layer of the endometrium of the proliferation phase, individual polypoid shapes with unevenly compact stroma, indifferent and proliferative glands without atypia, elements of the vascular pedicle. Conclusion: Endometrial (glandular) polyp, fragments of the functional layer of the endometrium in the proliferation phase. + Norkolut was prescribed from 16 to 25 days of pregnancy for 3 months. After the appointment, ultrasound control - everything is fine. In January 2021, spotting appeared before and after menstruation - ultrasound control - the endometrium was thickened. Norkolut was prescribed from 16 to 25 d.m.c., a month later an ultrasound check - everything was fine, changed to duphaston in connection with planning a pregnancy. Two months later there is discharge again - ultrasound suggests a polyp, thickened endometrium. At 6 d.c. thickness 9.8 mm, multi-layered, the line of closure of the endometrial layers is uneven, the outer contour is clear. The structure is heterogeneous due to areas of increased echogenicity. The largest of them in the upper third is 8.6 * 3.8 * 9.9 mm; with CD the vascular pedicle is not clearly defined. 06/15/2020 - hysteroscopy with RDV. In the discharge summary, the doctor who performed the hysteroscopy wrote a conclusion: Conclusion - Polyp of the body of the uterus. Endometrial hyperplasia Histological conclusion: 1. p/m Fragments of the endometrium of a polypoid structure, with fibrosis of the cellular stroma, slight proliferation of non-convoluted glands. Conclusion: glandular polyp of the endometrium of a functional type, proliferative variant. 2. c/k. Fragments of the mucosa with squamous metaplasia, moderate lymphocytic infiltration of the stroma. Conclusion: Chronic inactive endocervicitis. Utrozhestan was prescribed from 16 to 25 d.m.c., as I was planning IVF. While preparing for IVF, already in August 2021, an ultrasound revealed a polyp again. At the moment, the doctor is again sending me for hysteroscopy with RDV, but it’s already scary to do it and expect that everything will happen again. The doctor suggests doing histology and histochemistry and prescribing treatment based on the results, he says the cause is an inflammatory process in the uterus, it needs to be stopped. But if this is not the reason, the polyp can come back again? And what confuses me is the growth of the endometrium on ultrasound and on the results of hysteroscopy, the doctor sees hyperplasia, but on hysteroscopy they don’t diagnose hyperplasia 7, what could it be then? And what is the best course of action now? Maybe before hysterosucopia it is possible to somehow determine whether there is inflammation in the uterine cavity, I heard they do some kind of tube biopsy. I really want to have a baby. Thanks for the answer.
The question is closed
polyp
relapse
True basal polyps
They consist of non-functioning glands, fibers and elements of muscle tissue with a predominance of the former. They do not depend on the menstrual cycle and the concentration of hormones in the body. If functional polyps of the glandular structure arise against the background of other hormone-dependent pathologies, then the basal type can form in a completely healthy woman. However, the cause is considered to be an inflammatory process. True endometrial polyps are localized near the junction of the fallopian tubes and at the bottom of the organ. By cutting such a formation, you can observe a loose spongy structure. This is explained by the structure of gland cavities, which are located in disorder.
The reason for the formation of true polyps on the endometrium:
- Damage to the walls of the uterus;
- Inflammatory processes;
- Infections of the reproductive system;
- Impaired cell regeneration;
- Allergic diseases.
Attention! Basal, as well as functional growths can malignize into a cancerous tumor with a probability of 3%.
Decoding
The results can only be interpreted by the attending physician.
Based on the obtained sample, the following types of endometrial polypous neoplasms are histologically identified::
- Ferrous . At the heart of the polyp are functioning glands. The danger of malignancy remains constant. Women at risk during pregnancy, menopause and active hormonal disorders. Treatment of endometrial glandular polyp is described in detail on our resource.
- Glandular-fibrous . Combined polyp structure with glandular and fibrous cells. Often diagnosed in young women with an adequate menstrual cycle. Read more about the treatment of glandular fibrous polyp here.
- Fibrous . Dense, nonfunctional polyps that rarely become malignant. Cancer risk increases with a woman's age.
- Adenomatous . Such polyps are classified as precancer and are extremely rare in gynecology. Atypical cells of adenomatous polyp are most often activated after childbirth or menopause. Adenomatous polyp of the uterus, find out what it is in this article.
If the analysis is positive, additional examination of the woman is required. Sometimes a positive test may indicate a long-term course of a chronic disease with an asymptomatic course.
What is the danger of glandular formations?
Possible complications:
- Chronic infectious inflammation in the uterus.
- Infertility.
- Pathologies of pregnancy. The growth leads to placental abruption, hypoxia of the child, poor development, death, and abortion for medical reasons.
- Bleeding from polyps is insignificant, but constant, which leads to anemia, and, consequently, a deterioration in overall health.
- Uterine cancer. The likelihood of cancer varies depending on the type of education and individual circumstances, but it is quite significant. Sometimes in polyps that appear calm in appearance, foci of adenomatosis and cancer cells are found during histology.
Symptoms
Glandular formations manifest themselves in the same way as others. Until it reaches a large size or with single growths, there are no signs of pathology. According to the degree of enlargement and reproduction, polyps cause:
- Cycle disturbances in the form of longer periods;
- Increased PMS symptoms;
- Contact discharge of blood as a result of a gynecological examination or sexual intercourse;
- Pain during sex;
- Spotting between menstruation and in menopausal women, after physical exertion;
- Leucorrhoea, profuse mucous or purulent when the polyp is infected;
- Inability to conceive a child.
Attention! Most cases of pathology are discovered by chance during routine examinations.
Symptoms of fibromatous polyps
In most cases, the appearance of polyps in the cervical or cervical canal area is completely asymptomatic; the disease is discovered completely by accident, during a routine examination by a doctor.
A sign of polyposis may be as follows:
- menstrual irregularities, increased duration of menstruation;
- bleeding during sexual intercourse;
- inability to conceive if you refuse to use contraceptives.
A characteristic symptom of gynecological pathology is the appearance of bloody discharge from the vagina, which especially intensifies after sexual intercourse. Quite often, bleeding is accompanied by discomfort and pain in the lower abdomen.
This sign is extremely dangerous for women who have “entered” menopause - if the condyloma begins to bleed, this may indicate that the tumor is becoming malignant.
If treatment of the disease is delayed for any reason, bleeding becomes profuse, this process is accompanied by the development of anemia, weakness, and chronic fatigue. If you suspect an inflammatory process that affects the uterus, a woman must immediately seek medical help.
Diagnostics
On the chair, the doctor will see formations on the cervix or endometrial polyps that have fallen into the area of the cervical canal. For accurate diagnosis, instrumental studies will be required:
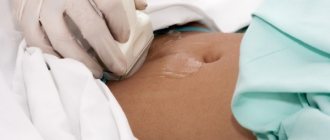
- Ultrasound using a transvaginal sensor in the first days after menstruation will detect polyps, determine their location, size and quantity.
- Diagnostic hysteroscopy is a more accurate method. With its help, the specialist sees the formation through a video camera. It requires preparation through various tests and is performed under anesthesia. Imaging helps to suggest the type of formation and assess the condition of the entire endometrium.
Laboratory research:
- Biochemical and general blood test;
- A smear from the vaginal wall;
- Tests for CSR, hepatitis and HIV;
- PCR diagnostics;
- Blood for hormone levels.
Attention! There are a sufficient number of cases where a polyp detected on ultrasound was not found during hysteroscopy. These are either errors in ultrasound examination, or during camera examination the formation was buried in a loose functional layer. Therefore, to clarify, separate scraping of different areas of the endometrium is done for histological verification.
Treatment for glandular formations in the uterine cavity
Functional polyps may respond to hormonal therapy. For this purpose, oral contraceptives with Progesterone, gestagens and hormone-releasing agonists are used. Some gynecologists completely reject conservative treatment, while others are its supporters. Efficiency in some cases is explained by eliminating the cause in the form of endocrine disorders. However, the only sure way to get rid of it is to remove the polyp.
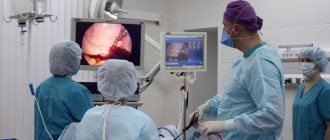
Hysteroresectoscopy
Therapeutic hysteroscopy is performed on an outpatient basis and in a hospital setting, it all depends on the severity of the pathology. For a simple operation, short-term intravenous anesthesia or a medical sleep mask are used. The method allows you to act with precision and see everything that is happening on the monitor screen. The formation is removed by stripping the basal layer, the wound is treated with a laser, electrode or liquid nitrogen. The procedure can be completed with separate diagnostic curettage, when endometrial fragments are collected from suspicious areas.
After a standard hysteroscopy, a woman can leave the clinic after a few hours. Modern drugs for anesthesia do not cause consequences in the form of a serious deterioration in well-being.
Laser equipment is considered the most effective because the percentage of relapses is low and scars that can interfere with childbearing are not formed. But in Russia only one clinic owns the equipment. In other cases, the polyp is cut off, cauterized or twisted. The surgeon’s task is to remove the growth tissue as much as possible so that there is no relapse.
Interesting fact! In provincial government medical institutions, glandular formations are removed by curettage or vacuum aspiration. The remaining fragments of the base provoke the reappearance of the growth after 2-3 months.
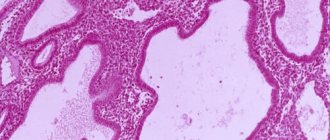
Histology
After removal, a polyp of a basal or functional type is sent for complex microscopic examination. The results will be ready in 10-14 days. Only this analysis can reliably establish the diagnosis, the exact type of formation, the presence of atypical cells and foci of adenomatosis. The conclusion is written in Latin and requires a doctor to decipher it.
Rehabilitation and prevention
During the recovery period after hysteroscopy, treatment continues. A course of antibiotics is prescribed for the first week to avoid infection. Once the histology results are received, the issue of hormonal therapy is decided to prevent relapse. After removal of a basal or functional glandular polyp, in most cases, 3-6 months of taking hormonal drugs are prescribed with constant monitoring of the state of the endocrine system.
In addition, a woman can use antispasmodics for pain after hysteroscopy and for uterine contractions. Taking vitamin complexes is mandatory.
In the first month it is prohibited:
- Swim or wash with complete immersion in water;
- Bask in the sauna or in the sun;
- Have sex;
- Place foreign objects in the vagina - tampons, suppositories, douching;
- Lift anything weighing over 3-5 kg;
- Engage in sports and heavy physical work.
The endometrium is restored by the next menstruation, so the woman is already able to become pregnant. But taking hormones requires postponing planning for conception by several months.
What should the patient do to avoid recurrence of the glandular polyp in the uterus:
- Follow all treatment instructions during the postoperative period;
- Undergo preventive examinations within the time limits specified by the gynecologist;
- Treat any diseases of the reproductive system in a timely manner;
- Normalize weight;
- Do not take hormones without a doctor's prescription;
- Take protection from unwanted pregnancies and STDs seriously;
- Lead a healthy lifestyle.
Causes
The main cause of glandular hyperplasia is considered to be a hormone imbalance. With excessive production of some hormones (estrogens) and a lack of others (progesterone), the risk of polyp formation in the uterus increases. The development of the disease is provoked by the following factors:
- Ovarian dysfunction due to inflammation or the formation of tumors, cysts of various origins. Growths in the endometrium are often detected in patients with polycystic disease.
- Surgical interventions on the ovaries.
- Malfunction of the pituitary gland.
- Pathologies of the endocrine system and liver, which take part in the formation of hormonal levels.
- Long-term use of steroids.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Psychological or physical overload.
No less common reasons for the appearance of growths in the endometrium: fasting, bad habits (alcohol abuse, smoking), and a decrease in the body’s defenses.
The disease is caused by a violation of the structure of the endometrium, namely:
- damage to the basal layer during curettage and other traumatic procedures;
- tissue scarring;
- circulatory disorders.
Women with metabolic disorders, diabetes, hypertension, and those who have used an intrauterine device for a long time are more likely to develop endometrial polyps.