Mucus in a smear in men
In healthy men, as in women, a smear for microflora almost always reveals a certain amount of mucus.
What if the mucus in the urethral smear significantly exceeds the standard norm?
Most likely, pathogenic microorganisms are present in the genitourinary system in increased quantities, such as:
- candida
- chlamydia
- Trichomonas
- cocci, etc.
They are usually detected during the same study.
But sometimes it is necessary to undergo additional tests to clarify the cause of intense mucus formation.
This will prevent the development of inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system.
And also promptly begin treatment of acute pathological processes or temporarily “hidden” chronic diseases.
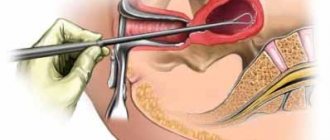
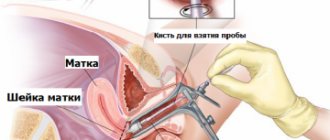
When mucous discharge appears from the man's urethra, a smear is taken.
This is a widespread diagnostic procedure. It is performed to identify pathologies.
A urethral smear will help identify diseases such as:
- inflammation and ulcerative lesions of the urethra
- prostatitis and prostatorrhea
- cystitis
- tumor neoplasms
- STI
When examining a smear, several indicators are assessed.
Slime
A moderate presence of mucus in the material is considered normal.
An increase in its amount can be caused by urethritis, tumor diseases or traumatic injury.
By the detection of spermatozoa in the sample, one can judge about spermatorrhea, and lipoid bodies - about prostatorrhea.
Leukocytes
Up to five white blood cells are allowed.
They are cells of the immune system.
Their increase indicates the course of the inflammatory process.
An increased number of neutrophils and lymphocytes signals an acute inflammatory process in the urethra.
And by the increase in eosinophils, we can talk about an allergic reaction.
Epithelium
Epithelial cells line the walls of the urethra.
The presence of up to ten cells is considered an acceptable norm.
An increase in the amount of epithelium means the course of urethritis in a chronic form.
Red blood cells
In a healthy person, there is no blood in the smear.
Its presence allows us to judge traumatic damage to the urethra.
Red blood cells can also be a manifestation of tumor formation in the urethra.
Microflora
An acceptable indicator is the single presence of cocci.
They belong to opportunistic bacteria.
Such microorganisms can cause diseases only in certain circumstances.
Their increase signals the progression of nonspecific urethritis.
A diagnosis of gonorrhea or trichomoniasis is possible when gonococci or trichomonas are detected.
When examining a smear, it will not be possible to detect ureaplasma, mycoplasma, chlamydia, or herpes virus.
To diagnose and exclude diseases, a PCR test is required.
To avoid false data when examining a smear, you need to prepare:
- one day before taking the sample, avoid intimacy
- do not urinate three hours before the test
- washing the external genitalia
Important!
Only a doctor is able to correctly interpret test results and select the optimal treatment regimen.
An increase in the amount of mucus is characteristic of several diseases.
Let's look at each in more detail.
What are the norms for a smear on the flora?
Based on many years of medical practice and various studies in gynecology, certain standards are identified that the results of laboratory diagnostics must comply with.
The interpretation of the result and norms of indicators are as follows:
- The concentration of lactobacilli varies from 85-95%. Ideally, their number should be close to 95%.
- The presence of mucus in a woman’s smear in moderate quantities inside the vagina is normal. An increase in the indicator indicates inflammation or infection.
- Microscopic examination of leukocytes should show a result of no more than 10 in the cervical canal, in the vagina and urethra - up to 5.
- Normally, there are no red blood cells. If they are found, this indicates internal bleeding or a violation of the integrity of the mucous membrane.
- A sign of healthy flora is the presence of squamous epithelium of up to 15 cells.
- The concentration of bifidobacteria is up to 10 to the 7th power.
- Gram-positive microbes are allowed in the analysis if they are present in small quantities.
- Gram-negative bacteria must be present.
In a normal analysis, there may be fungal spores, but not mycelium; the absence of atypical cells is considered normal; sticks should not be found in the urethra and cervical canal.
Examination of scrapings for flora allows early detection of infectious and inflammatory processes, diagnosis of sexually transmitted diseases, as well as cancer pathologies in women. Visiting a gynecologist and getting tested is the key to women’s health.
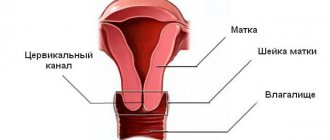
A flora smear is used to monitor the condition of the urinary tract, cervix and vagina. This is a microscopic examination that allows you to identify pathological changes in the reproductive organs and select the necessary therapy.
To determine the condition of the uterus and vagina, a smear is taken for flora
What diseases does a smear reveal?
Even more interesting:
Effective injections for prostatitis
Is duphaston a hormonal drug?
1-2 days after collecting the biological material, the patient can visit a medical specialist to review the results. By detecting key cells, the following diseases can be identified:
- Polyps are benign growths of the glandular tissue of the uterine mucosa. The reasons are due to hormonal imbalance against the background of various inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system;
- Erosive changes in the mucous membrane imply a transformation of the lining of the genital organ. In other words, it is an open wound, which provides a path for the penetration of various pathogenic microorganisms;
- Chlamydia is a group of infectious processes characterized by acute or chronic course, which are caused by intracellular parasites called chlamydia;
- Gonorrhea is an infectious sexually transmitted disease that is transmitted during unprotected sexual intercourse. Caused by gonococci. In its advanced form, the disease can affect internal organs - liver, kidneys, brain. Lack of treatment increases the likelihood of gonococcal sepsis, which leads to death;
- Cancerous degeneration. An abnormal amount of certain indicators in a flora smear indicates cancer.
If the structure in the smear is not homogeneous (uniform), then timely examination allows us to identify ureaplasmosis, trichomoniasis, mycoplasmosis and other diseases that require adequate conservative treatment.
When to get tested
Indications for a gynecological smear in women are the following conditions:
- aching or paroxysmal pain in the lower abdomen, unpleasant pain or a feeling of heaviness;
- increased mucus secretion that smells bad;
- discomfort in the genitals - itching, burning;
- preventive examinations by a gynecologist at least once every six months;
- in the process of planning a child;
- during pregnancy.
If you have frequent pain in the groin, you need to do a flora smear
What does a smear show on the flora?
In gynecology, analysis of fluid secreted from the vagina shows the composition of the microflora and helps to study important indicators:
- quantity and quality of white and red blood cells (leukocytes and red blood cells);
- identify various cocci, trichomonas or fungal infections;
- number of lactobacilli.
The analysis allows us to determine the cause of a woman’s illness and select the most effective drugs to eliminate pathological changes in the genitourinary system.
Rules for taking a smear
Proper preparation for the procedure and compliance with the requirements for collecting biological material are integral components of reliable results.
Preparing for the study
A woman needs to carefully prepare for an analysis to study the vaginal microflora.
- Avoid sexual intercourse for 48 hours.
- Hygiene procedures should be carried out without special means or douching for 2 days before the test. Do not use vaginal suppositories or ointments.
- Do not visit the toilet 2.5–3 hours before the smear test.
How to take a smear
The procedure for collecting biological material takes place on a gynecological chair. A gynecologist is responsible for the entire process.
- Using a disposable spatula or spatula, the doctor removes part of the discharge from the urethra, cervical canal and vagina.
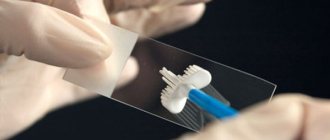
- The material is placed on a sterile glass slide and sent to the laboratory.
Using a special instrument, the doctor removes a small amount of vaginal discharge for analysis.
The process of collecting gynecological material does not bring discomfort to the woman and takes 5–10 minutes. The results are ready the next business day.
Norm
A healthy microflora of the genitourinary system is the presence of several leukocytes and rod flora. The basis is gram-positive rods or Dederlein rods. They must be present in large quantities.
Table “Reference values of smear for flora”
| Indicators | Normal, number of cells in the field of view | |
| Vagina and urethra | Cervical canal | |
| Squamous epithelium (lining the inner walls of the vagina and cervix) | 5–15 | |
| Leukocytes (protective cells responsible for phagocytosis - the elimination of pathogenic bacteria) - | 3–12 (during pregnancy the norm is up to 35) | 3–30 |
| Lactobacilli (Dederlein's bacilli) - provide a healthy acidic environment in which pathogenic microorganisms cannot live | A large number of | No |
| Mucus (the result of the secret glands) | Moderate amount | |
Transcript of research
The presence of pathogenic cells in the smear indicates the development of pathological abnormalities in the genitourinary system.
Depending on what microorganisms are present in the biological material, the disease is determined:
- Blastospores. Immature cells of pseudomycelium show active reproduction of candidiasis pathogens (thrush).
- Increase in key (atypical) cells. The flat epithelium begins to grow, which indicates abnormal disturbances in the microflora and the appearance of bacterial vaginosis.
- Leptothrix or leptotrichia. The cells cause degenerative changes in the epithelium and provoke colpitis (inflammation of the vagina). Pathogenic organisms can accompany the development of chlamydia, candidiasis, and leptotrichiasis.
- Coccal flora. The smear may contain gonococci, which indicates gonorrhea.
- Trichomonas. Pathogenic cells indicate the development of a sexually transmitted infection - trichomoniasis.
- Fibrin threads are evidence of inflammation.
When examining a smear, a lot of attention is paid to detritus - dead cells. The substance is an integral part of healthy microflora in both women and men. It consists mainly of a small number of obsolete epithelial cells. If this indicator increases, we may be talking about inflammation in the cervix or infectious pathologies that provoked massive death of epithelial tissue.
Interpretation of flora smear results
Evidence of pathology can be not only the appearance of pathogenic bacteria, but also changes in the quantity and quality of the permanent composition of the flora.
- A decrease in Dederlein's bacilli and an increase in leukocytes indicates a decrease in local immunity and the development of inflammation in the reproductive organs.
- Changes in epithelial cells. If squamous epithelium is absent, we are talking about atrophy of the uterus or cervical canal. An increase in such cells indicates inflammatory processes.
- Excessive appearance of columnar epithelium - infectious foci in the uterine tubes, malignant tumors in the cavity of the reproductive organ or cervical canal.
- Mucus in the cervix. Normally, there should be no noticeable discharge from the cervical canal. If there is a large amount of mucus, we are talking about severe inflammation.
Squamous epithelial cells
Squamous epithelial cells are dead cells of the vaginal mucosa that have been desquamated from the surface. On the mucous membranes of various organs, including the vagina, constant renewal of surface cells occurs, during which dead and old structures simply slough off, and new, young elements remain in their place. Therefore, normally 5–10 epithelial cells may be present in a vaginal smear. If there are more epithelial cells in the smear than normal, then this is indirect evidence of the inflammatory process occurring in the vagina. The causes of inflammation are exactly the same as those caused by a large number of leukocytes in the smear.
Degree of purity - what does it mean?
An integral indicator of a smear on the flora is the degree of purity. The marker indicates the level of acidity and the number of pathogenic cells.
There are 4 degrees:
- Poor flora - the biological material is dominated by gram-positive rods (95%), there are some opportunistic bacteria (5%), there are single leukocytes, the environment is acidic. The woman is completely healthy.
- Moderate flora – a large number of lactobacilli, a slight increase in leukocytes (7–10), moderate presence of opportunistic microorganisms. The condition is not painful, but local immunity is slightly weakened, which indicates increased sensitivity to harmful cells.
- Mixed flora - the number of white blood cells is increased (up to 30), the concentration of lactobacilli is reduced, the predominant presence of cocci. The environment is slightly acidic. The woman develops inflammatory processes and has a vaginal infection.
- Abundant bacillary environment - homogeneous mucus contains a large number of leukocytes, there are traces of phagocytosis, and a complete absence of gram-positive rods. High concentration of aerobic or anaerobic bacteria. The amount of fluid released with an unpleasant odor increases. The environment is alkaline. In the genitourinary system there is pronounced inflammation, the presence of a dangerous urogenital infection.
Example of vaginal cleanliness indicators
Treatment
If the results of the flora smear are poor, therapy is prescribed by the doctor based on the specific pathogen and its sensitivity to certain antibiotic drugs.
Table “Treatment of possible abnormalities in the flora smear”
| Analysis result (detected pathologies) | Drug groups |
| Inflammatory processes of various etiologies | Local medications for douching - solution of Chlorhexidine, Miramistin, potassium permanganate |
| Vaginal suppositories – Hexin, Betadine | |
| Urogenital candidiasis | Antifungal suppositories – Pimafucin, Clotrimazole, Livarol |
| Hidden sexual and venereal infections | Antiviral drugs – Cycloferon, Acyclovir, Kagocel, Diflucan, Metronidazole, Ornidazole |
| Penicillin antibiotics – Oxacillin, Ampiox, Ampicillin | |
| Cephalosporins – Ceftibuten, Cefaclor | |
| Macrolides – Sumamed, Clarithromycin, Erythromycin |
Tampons and vaginal suppositories with probiotics can be used to restore flora and strengthen local immunity.
The most effective are:
Adequate treatment is prescribed exclusively by a doctor. The specialist evaluates the results of the smear on the flora and selects the most effective drugs that will eliminate the causative agent of inflammatory or infectious processes in the reproductive organs.
Studying a smear for flora is of great importance in gynecology - the procedure is painless for a woman. Microscopic examination allows you to check the condition of the vagina, uterus and urethra, identify negative abnormalities and identify the causative agent of pathological processes. Proper preparation and compliance with the requirements for collecting biomaterial allows you to obtain reliable results the very next working day.
Rate this article ( 1 ratings, average 5.00 out of 5)
Mucus in a smear is one of the indicators that help assess the condition of the patient’s urogenital tract.
Everyone knows that this indicator is present both normally and with deviations. The characteristics of the discharge, its abundance and other indicators that need to be understood are of significant importance.
Patients often ask what tests are recommended to be taken when abnormalities are detected, and which doctor can help in identifying abnormalities.
What does the appearance of discharge in men mean, and is an infectious process always to blame?
Features of mucus secretion in women
Mucus in a smear in women frightens a significant number of representatives of the fair sex who see this indicator in the results of their research. In fact, as doctors note, there is no reason to be afraid. The presence of mucous discharge is not a reason to make terrible diagnoses or begin active treatment.
It rather acts as an indicative indicator by which the condition of the lower parts of the genitourinary system is judged.
Normally, the indicator can be determined as follows:
- urethral canal;
- in the vagina;
- in the uterine cervix.
Normally, most women do not have mucus in the urethra. In the analysis, this is designated as a minus.
In the vaginal area, the amount of discharge may be scanty, which will be indicated by a single plus.
The area of the cervix may be largely filled with mucus, which is indicated by a pair of pluses or a three. Three pluses are a reason to be wary, but not to make any diagnosis and begin treatment.
To draw any conclusions about the state of women's health, it is necessary to evaluate not just the presence of mucus, but its combination with other indicators. Otherwise, it is impossible to talk about the objectivity of the conclusions.
Mucus in a smear in women of a homogeneous type and the norm of leukocytes
Maternity consultation includes examination by a gynecologist and taking a urogenital smear. If mucus is detected in the smear, this is the starting point for more detailed laboratory diagnostics.
Healthy microflora contains several groups of bacteria, but lactobacilli predominate. A normal test result implies a concentration of lactobacilli of up to 95% and 5% of other microorganisms.
Let's consider a detailed transcript of the smear analysis study.
Key cells
Normally, the vaginal microflora concentrates a small amount of pathogenic microbes. These include fungi of the Candida family, gardnerella, ureaplasma, mycoplasma and other microorganisms. Their content is controlled by lactobacilli, preventing them from multiplying.
It’s worth knowing: key cells are squamous epithelium, which concentrates a variety of microbes on its surface.
When the number of key cells increases, they speak of an imbalance in the body. Against this background, the content of lactobacilli always decreases. The mucous membrane is lined with epithelial tissue; its cells maintain the necessary environment, which has a detrimental effect on pathogenic bacteria.
If the acidic environment is transformed into an alkaline one, then the transformation of squamous epithelial cells occurs. The surface is “covered” with microbes, as a result, key cells are identified in the analysis. In some paintings this signals an imbalance. But sometimes the etiology is due to cancer, erosive changes in the mucous membrane, and other reasons.
Gardnerellas
Gardnerella belongs to the facultative group of anaerobic bacteria, does not contribute to the formation of capsules and spores, and is characterized by good adhesion on the surface of the epithelium. It actively reproduces in the vaginal environment, releasing the products of its vital activity - these are amino acids.
In turn, volatile amines are released from amino acids - compounds that give vaginal discharge an unusual color and an unpleasant odor.
Worth knowing: the dominant sign of gardnerellosis are key cells. The so-called mature epithelial cells - many coccobacilli and gram-variable rods - gardnerella, mobiluncus, etc. - are fixed on their surface.
Leptothrix
This term refers to a gram-negative anaerobic bacterium. In appearance, the microbe resembles a long hair. In 90% of clinical pictures, the bacterium is found in representatives of the fair sex; in men it is almost never diagnosed.
Leptotrichia itself does not pose a danger to women's health. However, they often “settle” with other microorganisms that are sexually transmitted, as a result of which chlamydia or trichomoniasis is diagnosed.
Leptothrix is often detected in women who suffer from diffuse infection, bacterial candidiasis or gardnerellosis. At the same time, the microbe is found in high concentrations not only in scrapings for flora, but also in urine tests.
Preparing for the study
Microflora in a smear for various indicators of the vaginal environment can tell about hidden diseases. To exclude false results, it is recommended to carefully prepare for the study. The scraping is taken no earlier than three days after the critical days, since blood cells can distort the results.
Features of preparation:
- Avoid sexual intercourse for a few days;
- You cannot douche, as douching washes out biological material;
- Three days before the study, stop using suppositories, vaginal tablets, creams, etc.
Scraping should not be done if the patient is taking antibiotics or other strong medications. Their use is excluded in two weeks. If this is not possible, you should inform your doctor about the use of specific medications.
The evening before the examination, you need to carry out hygiene procedures with soap. In the morning, you should not wash the inside of the vagina. It is not recommended to go to the toilet before visiting a gynecologist. If the analysis is taken at a government institution, then the patient must take with her a diaper and a change of shoes. In private clinics this is not necessary; everything is provided there.
Sometimes a re-examination may be required if the first results raise doubts among the doctor. This usually happens in cases where the preparation rules were violated.
Flora smear: how to decipher it?
The results obtained are Latin and Russian letters and numbers. Of course, it is quite difficult for an ordinary person to understand what this or that abbreviation means. The numbers in the smear indicate the amount of epithelium, leukocytes, lactobacilli, etc.
Let's decipher the letters and numbers:
- “V” means that the scraping was carried out from the vaginal walls. The numbers opposite this letter show which microflora was detected.
- “C” is a smear from the cervical canal. The numbers tell the doctor what the laboratory test found. All deviations opposite this letter indicate changes in the cervix.
- "U" - scraping from the urethra. All indicators tell the doctor about changes in this particular area.
- "L" is for white blood cells. The results are always written in abbreviation to save space on the form.
- "Ep" - epithelium. In some cases, laboratory technicians may write “squamous epithelium” or indicate “squamous epithelium.” ep."
- “Abs” is a Latin abbreviation indicating the absence of some parameter. For example, if this abbreviation appears next to the word “Trichomonas,” this means that no infectious agents have been detected.
- "gn" - gonococci, are the causative agents of gonorrhea. The analysis form can be written in different ways. Some write gonococcus in full, others just abbreviate it.
- "trich" - stands for Trichomonas. If “abs” is next to it, then this indicates that everything is in order.
- “Cocci” stands for coccus infection.
It’s worth knowing: gr.+ or gr.- indicate that the microbe belongs to one or another group of pathogenic microorganisms. We are talking about gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, respectively. They have different structures, so identifying their affiliation allows you to select the required medicine.
What diseases does a smear reveal?
1-2 days after collecting the biological material, the patient can visit a medical specialist to review the results. By detecting key cells, the following diseases can be identified:
- Polyps are benign growths of the glandular tissue of the uterine mucosa. The reasons are due to hormonal imbalance against the background of various inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system;
- Erosive changes in the mucous membrane imply a transformation of the lining of the genital organ. In other words, it is an open wound, which provides a path for the penetration of various pathogenic microorganisms;
- Chlamydia is a group of infectious processes characterized by acute or chronic course, which are caused by intracellular parasites called chlamydia;
- Gonorrhea is an infectious sexually transmitted disease that is transmitted during unprotected sexual intercourse. Caused by gonococci. In its advanced form, the disease can affect internal organs - liver, kidneys, brain. Lack of treatment increases the likelihood of gonococcal sepsis, which leads to death;
- Cancerous degeneration. An abnormal amount of certain indicators in a flora smear indicates cancer.
If the structure in the smear is not homogeneous (uniform), then timely examination allows us to identify ureaplasmosis, trichomoniasis, mycoplasmosis and other diseases that require adequate conservative treatment.
Combination of mucus with leukocytes
Often patients, having seen the results of their studies, are interested in what indicators should be used to evaluate the presence of a mucous component in the smear.
After all, if this indicator is not assessed separately, then there is an indicator that gives it greater significance.
First of all, it is recommended to evaluate leukocytes and mucus in the smear. Leukocytes are the first immune cells that respond to infection entering the genital tract.
Moreover, their highest concentration is observed directly in the inflammation zone. As you move away from it, their number gradually decreases.
The presence of leukocytes in excess indicates that there is an inflammatory process in the body. The nature of which is most likely infectious. In some cases, opaque mucus is detected in the smear, which is combined with leukocytes. Such a deviation most often indicates that the patient has developed an infectious process.
It is important to understand that it can be both specific and non-specific. As doctors note, much depends not only on the presence of leukocytes, but also on their number. Normally, women have the most of them in the cervical canal. There you can count up to 30 cells of the immune system. The smallest is in the urethra area, usually no more than 5 pieces.
If the indicators exceed the specified values, this is a reason to be wary. Depending on where exactly the excess of leukocytes is diagnosed, the final diagnosis is made. For example, if the urethra is affected, urethritis may be diagnosed.
With prostatitis, an excess of leukocytes will be detected in the prostate secretion, which is also important for making such a diagnosis.
Leukocytes
White blood cells are cells of the immune system that destroy various pathogenic microorganisms that enter the vagina. Normally, a vaginal smear from a healthy woman can contain up to 10 leukocytes. Pregnant women normally have more leukocytes in a smear - up to 20 - 30 in the field of view. The normal number of leukocytes in a smear from the cervix is no more than 30 cells, and from the urethra - no more than 5. If the number of leukocytes in the smear is higher than normal, this indicates the presence of some kind of inflammatory process occurring in the vagina. Moreover, inflammation can be nonspecific, for example, bacterial vaginosis, colpitis, etc., or specific, that is, caused by a sexually transmitted infection.
An increased number of white blood cells in a smear may indicate that a woman has any of the following diseases:
- Sexually transmitted infections (for example, genital herpes, syphilis, gonorrhea, mycoplasmosis, ureaplasmosis, trichomoniasis, chlamydia, etc.);
- Colpitis (vaginitis) – inflammation of the vaginal mucosa;
- Vulvovaginitis - inflammation of the mucous membrane of the vagina and vestibule of the vagina;
- Cervicitis – inflammation of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal;
- Urethritis – inflammation of the mucous membrane of the urethra;
- Endometritis – inflammation of the mucous membrane of the uterine cavity;
- Adnexitis – inflammation of the ovaries;
- Bacterial vaginosis (gardnerellosis) – vaginal dysbiosis;
- Candidiasis – thrush;
- Malignant tumors of the genital organs.
Reasons why mucus can combine with white blood cells
If there is a lot of mucus in the smear, and this is combined with leukocytosis, then the doctor will diagnose inflammation regardless of the patient’s gender.
The symptom can be detected in both men and women. Moreover, as doctors note, inflammation is just a symptom, and not a full-fledged diagnosis.
When determining it, it is imperative to establish what the specific cause of the pathology is. Most often, the cause of the inflammatory process is microorganisms. They are classified by doctors as pathogenic and opportunistic. The differences between them are quite significant.
Pathogenic microorganisms always lead to the development of some disease. Normally, they are completely absent in the human body, even in minimal concentrations. Examples of such microorganisms are gonococci, chlamydia, and trichomonas.
Opportunistic microorganisms can live in the human body for a long time. However, they do not cause discomfort to the patient until there are only a few of them. If active reproduction begins, unpleasant symptoms of the disease appear, complicating a person’s life. Examples of opportunistic microorganisms are mycoplasma, ureaplasma, and candida.
Non-infectious causes of mucus in a smear
Mucus in a smear does not always mean the presence of infection. If there are no leukocytes, most likely there are no pathogenic microorganisms. But there are many other reasons for the appearance of mucus in the urethra in men and women. For example, in women, its amount may increase due to physiological reasons, such as:
- pregnancy;
- ovulation;
- frequent or intense sexual intercourse on the eve of taking a smear.
In representatives of both sexes, mechanical irritation of the urethra can lead to mucus secretion. This is possible, for example, when carrying out diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Some of them involve the penetration of an instrument into the urethra. This may be a cystoscopy (examination with an endoscope inserted into the bladder).
Or installation of a urethral catheter (for example, in case of urinary retention). For several days after the procedures, an increased amount of mucus and epithelium is observed. This is considered the norm. In addition, there are pathological causes of mucus hyperproduction without an inflammatory component. Possible diseases include:
- urolithiasis disease;
- the presence of sand in the kidneys (crystalluria);
- oncological pathologies;
- traumatic injuries to the structures of the genitourinary system.
Mucus in a smear: detection of bacteria
Mucus in a smear means that in the fair sex it is not always an infectious process or the norm. It can also be a symptom of dysbiosis. In the event that its excess is detected, but there is no inflammatory process, leukocytosis is not detected.
Normally, the genital tract is not a sterile area. They are inhabited by bacteria, most of which are lactobacilli. Under certain circumstances, the number of these bacilli may fall. This happens when immunity decreases or when antibiotics are used irrationally.
Other microorganisms take the place of lactobacilli. They may not provoke a strong immune reaction and may not accompany their reproduction with an inflammatory process. In this case, mucus will form in large quantities. There will be an unpleasant odor coming from the vagina. It can become a cause of complexes for the fair sex.
This condition is called vaginosis, since there is no inflammation in the organs. Normally, a large number of gram-positive rods will be detected in a vaginal smear. If there are fewer of them than required according to the norms, or they are absent altogether, the doctor concludes that the cleanliness of the vagina is impaired.
If a representative of the fair sex is diagnosed with vaginosis, then treatment is carried out under medical supervision, as is the case with STDs.
The means of therapy are selected individually in each case, and the treatment itself often takes place in two stages.
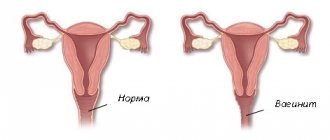
Increased amount of mucus in a smear during colpitis
With this disease, inflammatory processes in the vaginal mucosa can be caused by bacteria.
These include chlamydia, trichomonas, streptococcus, mycoplasma and staphylococcus.
Colpitis, or vaginitis, is widespread among women of reproductive age.
The vaginal microflora consists of lactobacilli (Doderlein bacillus).
They produce lactic acid.
The substance prevents bacteria from entering the vagina.
If the microflora is disrupted, the protective function is reduced.
This can be facilitated by:
- STI
- trauma to the mucous membrane
- endocrine diseases
- uncontrolled use of antimicrobial drugs
- insufficient intimate hygiene
- allergy
- decreased immunity
Manifestations of vaginitis include:
- vaginal discharge with an atypical odor, color, consistency
- burning during urination
- hyperemia and swelling of the external genitalia
- itching
- pain during and after intimacy
- aching pain in the lower back and lower abdomen
The acute form of colpitis occurs for the first time and lasts no more than two weeks.
It can become chronic in the absence of proper therapy.
In this form, the manifestations are less pronounced, and the discharge is very similar to normal.
Symptoms may include itching.
It intensifies after sexual contact or physical activity.
Complications of vaginitis are:
- inflammation of the endometrium
- cervical erosion
- infertility
To make a diagnosis, the gynecologist conducts an examination and prescribes laboratory tests.
These include a vaginal smear, colposcopy, and bacteriological culture.
Attention!
An increased amount of mucus and white blood cells may indicate the presence of vaginitis.
Treatment consists of taking antibiotics and local broad-spectrum drugs.
They will not suppress the normal vaginal flora.
At his discretion, the doctor may prescribe physical therapy, restorative medications and diet.
Mucus in a smear in men
Mucus may also be present in a smear in men. Its presence is normal if biological material for evaluation is taken from the urethral area. In this case, as in the case of women, the amount of discharge plays a role.
If there are more than two pluses on the form, then you should be wary. The presence of excess mucus in a man’s body is assessed only in conjunction with additional indications. Without them, it is impossible to draw conclusions about the presence or absence of any disease.
- the presence of an excess number of leukocytes in the results;
- the presence of epithelial cells in large quantities, which indicates tissue death;
- presence of clearly pathogenic microorganisms;
- an excess of bacteria belonging to the class of opportunistic pathogens (meaning an excess of certain titers, which are determined for each type of bacteria individually).
It is also important to remember that in the stronger sex, excess mucus can be explained not only by infections.
The culprit for the appearance of a symptom in the test results may be prostatitis. With this disease, mucous components are also produced in excess. This leads to an increase in the mucus indicator in the study results. The disease can be combined with urethritis, which only makes the indicator even more pronounced.
Key cells
Key cells are normally absent in the smear. The appearance of key cells is an undoubted and typical sign of bacterial vaginosis.
The “microflora” column usually indicates the predominant type of bacteria, for example, rods, cocci, yeasts, etc. If approximately the same amount of several types of bacteria is determined in the smear, then all types are indicated in the “microflora” column, for example, “rods + cocci”.
Normally, the vaginal microflora should be represented by Doderlein bacilli, which are usually indicated simply as “bacillus” or “bacillus” on the analysis results form. If rods or bacilli are indicated in the “microflora” column, then the woman has a normal vaginal flora.
Mucus is one of the indicators that are determined in a smear on the flora. Let's talk about how much of it should be normal and what deviations from normal indicators indicate.
- »
- What kind of mucus should be in a smear in women?
- Leukocytes and mucus in a smear
- Leukocytosis and mucus in a smear: causes
- Bacteria and mucus in the smear
- Mucus in a smear in men
- Mucus in the urethra with cystitis
- Non-infectious causes of mucus in a smear
- What to do if mucus appears?
Mucus in the smear and cystitis
Patients often forget that the urethra is in close connection not only with the genitals.
Moreover, many patients tend to believe that only the genitals can be a source of mucus. Although in fact this opinion is incorrect.
The main job of the urethra is to remove fluid from the body in the form of urine. This means that the urethral tract is connected not only with the genitals, but also with the organs of the urinary system, such as the bladder and kidneys. In this regard, mucus in a urethral smear can indicate not only damage to the genital tract. Often it indicates involvement of the bladder, kidneys, and ureters in the pathological process.
The most common inflammation of the bladder in practice is cystitis. Most often, cystitis occurs in the fair sex. This is due to the structural features of their genitourinary system. Pathology can be caused by E. coli and other pathogens.
For men, cystitis is an uncharacteristic disease, but it should not be ruled out.
Yes, it is less common in the practice of urologists, but the likelihood of encountering it remains.
Leukocytosis and mucus in a smear: causes
If increased mucus production plus leukocytosis was detected in a man or woman, this indicates an inflammatory process. But inflammation is not a diagnosis. For quality treatment, it is necessary to establish the cause of the pathology. That is, it is necessary to identify the origin of the inflammatory process. It is usually caused by pathogenic or opportunistic microorganisms.
What is the difference? Pathogenic microorganisms always cause disease. Normally, they should not be in the urogenital tract at all.
Opportunistic pathogens may be present, but in small quantities. If their population increases, inflammation develops, and mucus and leukocytes appear in the smear.
How to find the cause of inflammation? Some pathogens can be detected already during bacterioscopic examination.
Mucus and leukocytes are indicators of smear microscopy. During the same microscopy, the doctor can detect candida, gonococci or trichomonas.
Candida are opportunistic fungi. If they are detected in a smear, this indicates that their concentration is at least 1000 cells in 1 ml of clinical material. Because with a smaller number of fungi, they are not detected by microscopy.
Gonococci and Trichomonas are causative agents of sexually transmitted infections. Identification of at least one of the listed pathogens is a reason for prescribing treatment. But microscopy usually fails to identify the pathogen. In addition, the presence of gonococci or trichomonas in a smear does not exclude the presence of other pathogenic microbes. Therefore, all patients who have more mucus and leukocytes in their smear than normal are subject to examination for sexually transmitted infections using the PCR method. All common diseases are diagnosed. These are primarily chlamydia, trichomoniasis, gonorrhea, mycoplasmosis, ureaplasmosis, and candidiasis.
If certain symptoms are present, tests may be conducted for other microorganisms. In addition, patients may be prescribed bacteriological culture for flora. During the study, opportunistic bacteria are determined and their quantity is indicated in colony-forming units. They can also cause increased mucus production and the appearance of an excessively high number of white blood cells in the smear.
Are infections always to blame when there is mucus in a smear?
Mucus in a smear is not always a sign of an inflammatory process of infectious origin.
Many patients forget about this, causing panic when receiving test results. In fact, the indicator can be observed in other conditions of the body.
For example, this happens if:
- the woman is pregnant;
- a representative of the fair sex was tested on the eve of ovulation or during it;
- on the eve of the study there was an episode of active sexual contact (because of this, it is also recommended to limit sexual activity during preparation).
A number of therapeutic and diagnostic interventions can provoke pronounced deviations from normal indicators. In this case, its appearance is explained quite simply: the urethra is irritated, which triggers the mechanisms of excretion production.
Cystoscopy, or taking a smear from the urethra in men, is a common cause of increased rates. We must not forget about non-inflammatory diseases that provoke changes in tests.
With urolithiasis or sand in the kidneys, the indicator may increase.
It often changes with oncological pathologies of the urinary system.
Mucus in a flora smear always requires careful assessment in combination with other indicators.
In no case should a patient be diagnosed solely on the basis that the examination results show an increased amount of this element! Naturally, the patient himself should not engage in self-diagnosis. He should seek help from a doctor.
Increased mucus with urethritis
The inflammatory process in the urethra is called urethritis.
This disease is common among people of both sexes.
It is characterized by painful emptying of the bladder, and sometimes even pain.
Women notice leakage from the vagina, and men notice leakage from the urethra.
Representatives of the stronger sex may complain of hyperemia and swelling of the head of the penis.
Inflammation of the urethra can be of a bacterial or non-bacterial nature.
Bacterial urethritis is caused by specific and nonspecific bacteria.
Causative agents of specific urethritis:
- gonococci
- streptococci
- staphylococci
Non-specific:
- trichomonas
- chlamydia
- mycoplasma
- ureaplasma
- herpes virus
Non-bacterial inflammation of the urethra is often provoked by trauma to the urethra.
This happens, among other things, from the impact of a urinary catheter or calculi.
Allergic reactions are a common factor in the occurrence of urethritis.
The addition of an infection can transform the non-infectious form of urethritis into an infectious one.
Characteristic symptoms for urethritis:
- pain and pain during urination
- discharge from the urethra or vagina, including mucous
- pain in the groin area
Nonspecific infectious urethritis is characterized by discharge with mucus and pus.
They have a gray-green color and an unpleasant odor.
Inflammation of the urethra caused by gonococcus is manifested by the separation of whitish pus from the urethra.
Anatomically, the male urethra is structured differently than that of women.
Their urethra is somewhat longer and at the same time narrower.
Therefore, men feel the symptoms of the disease much earlier and more clearly.
Symptoms of urethritis are less intense in the fair half.
They may not cause much discomfort, so they often go unnoticed.
Inflammation rises up the urethra.
The prostate and testicles are involved in the process.
Complications of urethritis include inflammation of the testicles, epididymis and prostatitis.
In the future, they can lead to infertility.
Complications of urethritis in women are vaginal dysbiosis and cystitis.
The structure of the urethra often develops - a narrowing of the urethra.
This disease is characterized by a violation of the outflow of urine due to a weakening of the pressure.
The pathology develops against the background of ignoring the symptoms of urethritis.
Important!
If you detect at least one of the symptoms, do not delay your visit to a specialist!
The diagnosis is made by a urologist or venereologist based on the collected medical history and research results.
To clarify the diagnosis, you must pass:
- general urine analysis
- bacteriological culture of urine
- general blood analysis
- urethral swab for men or vaginal swab
- PCR of biological material
Therapy is based on the use of antimicrobial agents.
Mucus in a smear: which doctor to go to for help and what to do
Patients often ask which doctor corrects deviations identified in tests.
You should contact a urologist, gynecologist or dermatovenerologist. One of these specialists will be able to provide the right help.
He will give recommendations regarding additional examinations and decide how to treat deviations from the norm.
First of all, the patient is recommended to undergo a series of tests.
They are aimed at excluding STIs and nonspecific infectious processes and making an accurate diagnosis. Depending on the final diagnosis, therapy is selected for the patient. Treatment will help significantly reduce the severity of symptoms or eliminate them altogether. Naturally, if the treatment is successful, the amount of mucus in the smears will also become less.
Mucus is a normal secretion from the human genitourinary tract.
Another thing is that its quantity does not always correspond to the norm.
To talk about pathology, it is necessary to evaluate this indicator in conjunction with other analysis results. Otherwise, the results will be far from reliable.
It is best to entrust the treatment of the deviation to a doctor who can determine its cause and choose a method of correction!
If mucus appears in a smear, contact the author of this article, a venereologist in Moscow with many years of experience.
“>
Mucus in a smear with inflammation of the prostate
Inflammatory lesions of the prostate gland are called prostatitis.
The disease affects men of different ages and professions.
Prostatitis is most often recorded in middle-aged and older men.
Remember!
If prostatitis is suspected, consultation with a urologist is necessary.
Acute prostatitis is characterized by a course with severe symptoms.
The patient is concerned about pain in the perineum.
More than five urges to stool per night.
The acts of urination and defecation cause pain.
The urine stream is weak, there is no feeling of relief from urination.
There may be blood in the urine.
Attention!
This condition requires immediate specialist intervention.
Complications include acute urinary retention and abscess formation.
The chronic inflammatory process in the prostate gland has a broader picture of clinical manifestations:
- groin pain, pain during ejaculation
- Polakiuria – urination in very small amounts
- predominance of nighttime urination
- burning in the urethra
- erectile disfunction
- ejaculation disorders
The causes of the disease are infections, decreased immunity, hypothermia, and a sedentary lifestyle.
These include the lack of regular intimate life and alcohol abuse.
Important!
To carry out an adequate diagnosis, you need to contact a urologist.
After collecting anamnesis, the doctor will prescribe the necessary diagnostic tests.
Based on them, the doctor will be able to choose the optimal treatment.
One of the research methods is a smear from the urethra.
An increased amount of mucus can indicate the presence of an inflammatory process.
This also applies to inflammation of the prostate gland.
Other diagnostic procedures are also carried out:
- general clinical urine test
- bacteriological culture
- prostate juice test
- urofluometry
- Ultrasound
Treatment of the disease is very labor-intensive.
It is based on antimicrobial therapy.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used to relieve pain.
Additionally, symptomatic treatment is prescribed.