What does a closed cervical canal mean?
Often the cervix is also understood as the cervical canal.
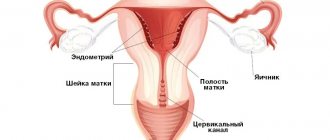
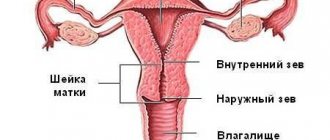
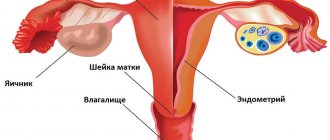
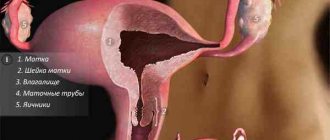
In reality, it is located inside the cervix and is part of it. At an appointment with a gynecologist, patients sometimes hear from the doctor that for some reason the cervical canal is closed. Before answering the question of what a closed cervical canal means, it is necessary to consider its structure and functions. The cervical canal of the cervix connects the uterine cavity to the vagina. It usually has a cylindrical or conical shape. The length is three to four centimeters.
The cervical canal has a lower and an upper part. Its external pharynx opens into the vagina, and its internal pharynx opens directly into the uterus.
This part of the uterine cervix performs several important functions. First of all, the organ cavity is protected from harmful microflora, which can cause inflammatory processes.
The presence of pathogenic microflora in the vagina means that an impressive number of pathogens live on the mucous membrane. It is noteworthy that the uterine cavity normally remains sterile.
The sterility of the uterine cavity is ensured by the cervical canal. It is lined with a special type of epithelium, which contains cylindrical cells of a single layer. The epithelium is characterized by velvety and reddish color. In addition, glands responsible for the production of protective mucus function. This means that the secretion should protect the uterine cavity from infection.
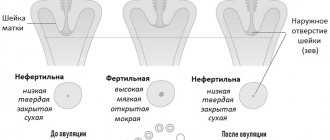
Mucus is heterogeneous on different days of the cycle for certain reasons. At the beginning, as well as at the end of the menstrual cycle, the secretion is quite viscous and has an acidic environment. These conditions cause the death of most microorganisms. Moreover, when sperm penetrate, their motility is lost.
The middle of the cycle is characterized by an increase in the concentration of estrogen in the blood. Thus, the mucus becomes alkaline and somewhat liquid. These conditions contribute to the survival of sperm and further fertilization.
If pregnancy occurs, the level of progesterone in the blood increases. The secretion becomes viscous, eventually forming a plug. This means that this mechanism protects the growing organism from infection.
Useful video about the first symptoms of premature birth
The length of the cervical canal in a pregnant woman: norms, causes and types of pathologies - we reveal secrets about pregnancy on Pitanie4Zdravie.ru
Pregnancy makes a woman truly beautiful. But during pregnancy, many questions arise that need to be answered. Especially for you, in the “Pregnancy from A to Z” section, we publish interesting and useful articles about pregnancy, so that this wonderful time for you will be as “problem-free” and joyful as possible.
You can also find here the main signs of pregnancy, how the baby’s fetus develops at different stages of pregnancy, understand what is possible and what is not possible at different stages of pregnancy. Learn more about the effect of various foods, vitamins (for example, the effect of folic acid) on pregnancy.
Pathological conditions
If we talk about the norm relative to the cervix, this means that it is closed. Dilatation occurs only immediately before birth. However, when patients hear from their treating gynecologist that the cervical canal is closed, they do not always understand that this is a physiological norm.
In gynecological practice, deviations are often encountered, which means that the cervix is not always closed. This occurs due to congenital anomalies.
Congenital anomalies include:
- development of two cervical canals;
- the process of fusion of the cervical canal, that is, when it is closed.
Closing of the canal means that it is closed. This pathology is diagnosed most often. If the canal, called the cervical canal, is closed, this means that for certain reasons adequate communication directly between the uterine cavity and the vagina is disrupted.
When the cervical canal is closed, as a rule, there are no symptoms for a long time. After puberty, the girl notices the absence of menstruation. Bloody discharge accumulates inside the uterine cavity. In such cases, surgical intervention is necessary, since the pathology can cause serious consequences.
The cervical canal can be expanded not only due to the upcoming birth. During pregnancy, this condition can mean a threat of miscarriage, which requires hospital treatment.
If a dilated, rather than closed, cervical canal is diagnosed in non-pregnant patients, hormonal medications are recommended. Their use means that as a result of correction, the necessary tone of the uterine myometrium increases. Thus, the channel becomes closed.
Causes of enlargement and treatment
If the canal is dilated in the absence of pregnancy, the doctor takes a smear and prescribes additional examinations. Pathology may be a consequence of:
- sexual disease;
- uterine fibroids;
- ovarian cysts;
- endometriosis and adenomyosis;
- chronic form of cervicitis.
Canal enlargement does not always signal a disease. Its diameter changes slightly on certain days of the cycle. During ovulation, an increase in size facilitates the penetration of sperm into the uterine cavity and increases the likelihood of successful fertilization of the egg. It can also expand due to taking hormonal drugs, smoking and slowing metabolic processes.
During pregnancy, dilatation becomes a reason to admit the patient to hospital care in order to prevent premature onset of labor. An examination is carried out to determine the cause of the pathology and treatment aimed at reducing the diameter of the canal.
Treatment of the anomaly is carried out using one of three methods:
- The medication method allows you to adjust a woman’s hormonal levels and reduce the tone of the smooth muscles of the uterus.
- Surgery involves suturing the cervix. Used for developmental defects, the presence of polyps in the canal or injuries. Performed under general anesthesia. During pregnancy, manipulation is performed at 16 or 18 weeks, and the sutures are removed only after 38 weeks.
- Special ring. It is placed on the cervix and tightened. The technique is used during pregnancy to avoid premature dilatation of the cervix. The ring is removed after 37 weeks.
The cervical canal performs important functions in the female body during menstruation, conception and pregnancy. Any pathology is confirmed by a number of studies and requires correct and timely therapy under the supervision of a gynecologist.
Symptoms and prevention
Atresia, which means a closed canal, is a pathology. In this condition, complete infection or obstruction of the uterine pharynx is observed. Pathology sometimes causes anatomical infertility.
A closed canal is manifested by the following symptoms:
- pain during the expected period;
- false absence of menstruation;
- hematometer;
- pyometra;
- pyosalpinx;
- dysfunction of the intestines and bladder;
- loss of consciousness with the development of purulent complications and peritonitis.
Diagnosis is carried out using ultrasound and MRI. The canal can be closed along its entire length or in the area of both the internal and external pharynx.
Provoking factors of the pathological condition include:
- various infections;
- inaccurate curettage of the uterus;
- diathermocoagulation;
- surgical termination of pregnancy;
- malignant tumor;
- endometritis;
- endocervicitis;
- scar tissue.
Treatment of pathology is carried out using the following tactics:
- laser recanalization;
- bougienage.
Laser recanalization means that tissue that is closed is evaporated through a beam. The method has several contraindications:
- blood diseases;
- uterine cervix tumors;
- fusion of the upper sections.
Bougienage means that with the help of a special tool the cross-country ability is expanded. The manipulation is performed under general anesthesia. After the intervention, it is advisable to prescribe antibiotics to prevent inflammation.
Gynecologists pay attention to the prevention of pathology, which means that the canal can become closed.
Experts include methods of prevention:
- timely elimination of inflammatory processes;
- careful and attentive introduction of pregnancy and childbirth;
- careful implementation of interventions.
After surgical operations on the cervix, enzyme agents are usually prescribed to prevent scarring (Longidaza, Wobenzym, Trypsin, Chymotrypsin).
Experts point out the importance of preventive examinations for the purpose of early detection of pathological processes. In order to detect infections that can cause a pathological condition, it is necessary to perform a smear on the flora and a PCR study.
Features of pathologies
Based on the results of smear examination, a diagnosis of cervicitis can be made. This disease is associated with the presence of an inflammatory process. If not treated in a timely manner, it sometimes leads to fusion of the walls. Cervicitis is treated comprehensively with anti-inflammatory drugs and local therapy.
Inflammation of the canal can be caused by various types of bacteria. The cause may also be cervical prolapse, erosion or injury.
Due to inflammation, mechanical damage or changes in hormone levels, benign neoplasms and polyps can form. In these cases, the doctor determines the need for surgical intervention. After a histological examination, the necessary therapy is prescribed.
Cervical canal of the cervix: its functions and possible pathologies
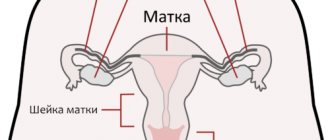
The internal female genital organs are represented by the vagina and uterus, from the corners of which a pair of fallopian tubes extend, connecting it to the ovaries. The cervical canal is the canal of the cervix, which communicates the uterine cavity with the vagina, thus being the border zone between the internal and external environment.
The cervix, like any hollow organ, consists of three layers: internal mucous, middle muscular and external connective tissue. The mucous layer is formed by multilayered squamous and glandular epithelium, the peculiarity of which is the secretion of secretion (mucus), the condition of which depends on hormones. The flat one is located in the distal part of the canal closer to the vagina, and the border between it and the glandular epithelium is a diagnostic sign of diseases of the cervical canal. The condition of the glandular epithelium changes after menopause and childbirth, becoming drier and paler.
Secret functions
- Like any liquid in our body, mucus has a bactericidal effect, preventing infection from entering the uterine cavity.
- At the initial and final stages of the menstrual cycle, the secretion inhibits the movement of sperm by increasing its viscosity and acidity, and in the middle of the cycle it becomes alkaline and liquid. Under such conditions, the survival and motility of sperm increases.
- After pregnancy, it thickens and forms a plug in the cervical canal, blocking the entrance to the uterine cavity. This occurs due to an increase in progesterone in the blood.
- Its condition can serve as a diagnostic sign of many diseases of the reproductive system.
The muscle layer is formed by smooth muscle tissue, which contains a lot of elastic fibers, due to which the cervical canal can stretch greatly. During childbirth, its clearance can reach ten centimeters. Smooth muscles are unique in that their contraction does not depend on our will. They are controlled by a special part of the nervous system, which is called the autonomic one. Thus, the width of the canal lumen is regulated by the nervous system. Depending on the circumstances, the lumen can be open or closed.
Anatomically, it is part of the uterus, which is located in the pelvis. Has a linear or cylindrical shape. The length normally ranges from three to four centimeters, but can shorten during pregnancy. Along its entire length it has two physiological narrowings - the internal and external pharynx. The external one is accessible to visual inspection, and by the opening of the canal one can judge whether the woman has given birth or not. In a young girl, the external opening will be in the shape of a point, but after childbirth it will be in the form of a slit-like opening. The external pharynx is not always accessible to visual inspection; the main thing is that it is visible on ultrasound.
Thus, the cervical canal plays a large role in protecting and communicating the uterus with the external environment, and is also actively involved in childbirth. Its existence ensures the unhindered passage of menstrual blood during menstruation. Any pathology of any of the layers will cause serious disturbances in the homeostasis of the entire reproductive system, therefore the diagnosis of pathologies of the cervical canal plays a very important role.
How does the endocervix change during pregnancy?
This article talks about typical ways to solve your issues, but each case is unique! If you want to find out from me how to solve your particular problem, ask your question. It's fast and free
!
After fertilization and throughout pregnancy, the shade of the cervix structures changes, it becomes bluish. Changes also occur inside the cervix; from the moment of conception, a mucus plug begins to form in it, which is designed to protect the embryo and fetus from the external environment. Mucus production is carried out by the endocervix.
The width of the cervical lumen in women is 7-8 mm, regardless of pregnancy. However, in expectant mothers, the shape of the pharynx may have distinctive features. The shape is also influenced by the number of births, the health of the hormonal system, and diseases of the reproductive organs.
When a woman wants to make sure that pregnancy has occurred, she turns to a gynecologist, who first examines her and then sends her for an ultrasound. This method allows you to see the embryo attached to the wall of the uterus and its size. In addition, using an ultrasound examination, a specialist evaluates the parameters and condition of the cervix to identify possible risks of miscarriage or premature birth.
In the normal position, the ends of the pharynx should close tightly. The length of the cervical canal during pregnancy is in the range of 35-40 mm. The obstetrician can also judge the imminent onset of labor by the condition of the pharynx.
Double cervical canal
Duplication of the cervical canal is a congenital pathology caused either by heredity or teratogenic factors, which include alcohol intake by a pregnant woman, smoking, exposure to radiation and irradiation, toxic environment, etc. The presence of a double uterus does not cause visible clinical manifestations and is usually diagnosed by ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs during examination. If this pathology is not associated with other disorders, then there is a possibility of a good pregnancy.
Stenosis
Stenosis (narrowing) is classified into congenital and acquired. Congenital stenosis is a disorder inherited from parents through genes. Acquired develops during menopause, cancer of the cervix and the uterus itself, epithelial proliferation, radiation therapy, and surgical operations on the cervix. With stenosis, blood retention in the uterus and its reverse flow may occur. The shed endometrium is also retained, which can lead to endometriosis, a pathological growth. During infectious processes, due to the impossibility of disposal, pus accumulates.
Symptoms differ between premenopausal and postmenopausal women. Thus, before menopause, there is a decrease in the flow of menstruation with incomplete stenosis, but with complete stenosis there will be a complete absence of menstruation. The accumulation of blood or pus in the uterine cavity will stretch the muscle layer, and an enlarged uterus can be seen and palpated through the skin. But after menopause, the course is asymptomatic, and pathology can be detected by chance or in the later stages.
Diagnosis is based on clinical symptoms, ultrasound and CT scanning. For accurate confirmation, probing and cytological analysis of the cervical epithelium are prescribed. In case of pathologies incompatible with normal life, stent placement and dilation of the cervix are prescribed.
The reasons for the expansion of the cervical canal can be both congenital genetic factors and infectious diseases. A special case would be the expansion of the canal during pregnancy, when normally it should be closed. It begins to expand a week before birth to facilitate the passage of the fetus, in all other cases it can threaten miscarriage. If the baby puts too much pressure on the cervix, this will trigger its spontaneous dilation. Other reasons for expansion may include:
- Polyps and cysts. A cyst is a pathological cavity with fluid (blood, tissue fluid, blood). It tends to expand due to the increase in contents and compress the passage. If there is too much fluid, there is a risk of cyst rupture. This can lead to hematometra.
- Malignant and benign formations. If cells begin to divide uncontrollably, tumors form that stretch the walls of the canal, but at the same time can completely or partially close the lumen of the canal. Such formations must be removed immediately.
- Inflammatory processes. The infectious agent negatively affects the structure of the wall of the cervical cavity, weakening and thinning it due to erosion. So, the canal may be wide open and not during ovulation.
Is it possible to prevent uterine access closure?
It is impossible to predict the fusion of the cervical opening. The transition from the reproductive period to the menopausal period is itself a factor suggesting a change in the condition of the pelvic organs.
From this moment on, the woman should regularly visit the gynecologist (at least 2 times a year) and have a smear for cytology.
During manual examination, the doctor may detect narrowing of the cervical foramen and suggest possible atresia in the future.
This condition can be avoided if you follow simple recommendations throughout your life:
- avoid promiscuous sexual intercourse without the use of barrier contraceptives, as they increase the risk of sexually transmitted diseases;
- treat infectious and inflammatory diseases in a timely manner, as they increase the likelihood of the formation of adhesions;
- use contraceptives to prevent abortions leading to cervical canal injuries;
- reduce the frequency of interventions in the uterine cavity that require cervical dilatation;
- avoid stress that aggravates the menopause;
- observe the rules of personal hygiene.
If during menopause there is dryness in the vagina, burning, strange discharge or other complaints, then you should immediately contact a gynecologist.
After the examination, the doctor will prescribe symptomatic treatment that will help stop the fusion in time.
Women all over the world take hormonal replacement medications, which helps them not only prevent uterine occlusion, but also improve their well-being by getting rid of the symptoms of menopause.
How to treat pathologies of the cervical canal of the cervix
Treatment depends on the cause of the disease. Inflammatory processes are stopped with antibiotics, benign formations, cysts and polyps are removed surgically, and malignant ones are removed by radiation therapy. If dilation is diagnosed during pregnancy, immediate hospitalization is required - antispasmodic drugs, vitamins are prescribed, and possible sutures or installation of a ring - pessary.
Complete fusion or absence of the canal is a deep pathology, the origins of which lie in intrauterine development. Such disorders are usually associated with impaired development of the uterus and are incompatible with procreation.
During ovulation, the canal must be open, since it is at this moment that fertilization must occur. The secretion thins out, the acidity decreases, and the expanded lumen of the canal ensures the movement of sperm to the egg.
Normally, it is open during menstruation to ensure the smooth passage of discharge, so there is no need to be alarmed.
It is also worth taking into account the individual characteristics of the body. All people are different, each has their own specific genetic material, unique environmental conditions, so you should not be surprised that the structure of the cervical canal will vary: large, small, narrow or wide. Even an increase in the width of the lumen to fifteen millimeters in some cases will be the norm, as it will be associated with natural development. Every woman should undergo an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs at least once a year, and if a pathology is detected, its progression should be monitored every six months.
Ultrasound is one of the cheapest and non-invasive methods, that is, the integrity of the organ is not compromised for the study. The picture obtained with this method of research is obtained due to different reflections of sound. The ability to absorb or reflect ultrasound depends on the density of the organ and the fluid content in it. Dense structures, such as bone or a calcified tumor, are unable to receive ultrasound waves and will completely reflect them. The reflected waves are recorded by a receiving sensor and a picture is built in which light areas are visible - hyperechoic areas. But liquids have a high level of absorption, so the image will be dark - anechoic areas. Ultrasound is a completely safe method, although there are unconfirmed hypotheses about harm to pregnant women.
Using CT and MRI, a layer-by-layer image is obtained - sections of the pelvic organs. Prescribed by doctors if a more detailed study is needed to diagnose tumors, for example. If your doctor recommends that you undergo this procedure, then you should not think about the expense; the procedure is mandatory if you suspect a tumor, since ultrasound gives only a subjective assessment.
The easiest way to diagnose many diseases is to regularly visit a gynecologist, since even with a simple examination most pathologies can be identified.
Examination during pregnancy
Already at the first appointment, the gynecologist will take a smear for bacterial culture. Such a study will be repeated several times during pregnancy. If detected early, many infections are not dangerous and can be cured before delivery. If treatment is not possible, vaginal birth is replaced by caesarean section to prevent infection of the baby.
Expectant mothers are concerned about the following questions:
- Does it hurt to take a smear for examination? Gynecologists claim that the procedure is completely painless. Biological material is collected during an examination on a chair using a special brush. If a woman doesn't concentrate on the process, she probably won't notice anything.
- Can the procedure cause an increase in uterine tone? No, the process of collecting material is not at all associated with any mechanical effect on the cervical canal and does not provoke an increase in the tone of the uterus.
- Is taking a smear dangerous for the fetus? Such an examination is absolutely safe for the fetus in the womb. The greatest risk occurs when infectious and inflammatory processes are detected.
Do not worry, the analysis will not harm the pregnant woman and will not affect the development of the fetus in the womb. In some cases, a short-term increase in tone is possible, but more often this is due to the attitude of the woman herself towards the examination procedure.
Norms during pregnancy
With the onset of pregnancy, the cervical canal and cervix close into a tight ring. This condition allows the female body to unimpededly bear the fetus until completion of gestation. During the period of preparation for childbirth, starting from the 36th week of pregnancy, a gradual softening and smoothing of the cervix occurs. This condition is necessary for the normal passage of the baby through the birth canal. If the canal remains narrow, the doctor can open it mechanically using special instruments.
Simultaneously with this process, the cervical canal expands. During the first contractions, its diameter is about 1 cm, and within a few hours the dilation reaches 10 cm. Depending on the internal diameter of the cervical canal, the obstetrician assesses readiness for childbirth. Full readiness is determined when the dilation is 10-12 cm. At this width, the birth canal is ensured, starting from the uterus, passing into the cervix and vagina.
Length and diameter of the cervical canal during pregnancy
Doctors consider the length or extent of the cervical canal as an important marker that allows them to confirm the natural course of gestation. If any deviations from the norm are detected, therapeutic measures are used; they allow the pregnancy to be maintained, especially in the early stages.
| Gestation period (weeks) | Length of the cervical canal in (millimeters) |
| 10-14 | 34-36 |
| 15-19 | 38-39 |
| 20-25 | 40 |
| 25-29 | 40-41 |
| 30-32 | 35-40 |
| 32-36 | 33-36 |
| 36-40 | 29-30 |
Menstruation after bougienage of the cervical canal. What is cervical atresia
The term atresia or stenosis of the cervical canal refers to an anomaly in the structure of the cervix, consisting of narrowing or complete obstruction of the cervical canal. In the medical literature, the term means complete fusion of the walls of a hollow organ. Atresia can be partial or absolute. If the canal is not passable along its entire length, its complete fusion is diagnosed. If pathology is observed in the area of the external or internal pharynx, partial stenosis is diagnosed.
The main task of the gynecologist is to distinguish stenosis and atresia of the cervical canal from stricture. With stricture, cervical obstruction occurs due to scar deformities. The disease is detected based on the patient’s complaints and simple diagnostic procedures. The diagnosis of complete stenosis is determined when it is impossible to enter the uterine cavity with a probe with a diameter of 12 mm. The main danger of such a deformation is that it may have an oncological basis. To exclude the possibility of developing cancer, the patient undergoes an endometrial biopsy.
If the woman does not have atypical cells or negative symptoms, surgery is performed. It is worth noting that stenosis detected during menopause cannot be treated; patency of the cervical canal is restored only to women of childbearing age. In some cases, pelvic ultrasound and MRI are performed to diagnose the disease. It should be taken into account that atresia may be accompanied by structural disorders of the genitourinary system. To clarify the diagnosis, urethrocystoscopy is performed.
In medical practice, a distinction is made between acquired and congenital atresia. With congenital pathology, fusion of the cervical canal occurs at the stage of embryonic development. The reasons that provoke such deformation are as follows:
- infection of a pregnant woman with toxoplasmosis, chlamydia or syphilis;
- taking certain medications in the first trimester of pregnancy;
- exposure of a woman to ionizing radiation.
With congenital fusion, the symptoms do not bother the woman until puberty, or more precisely, until the first menstruation. Acquired atresia appears due to age-related changes or due to injuries to the cervical canal. Normally, the menopause period is accompanied by a significant decrease in the size of the uterus and cervix, a change in the structure of all tissues and organs that provide reproductive function. Such changes occur against the background of the cessation of estrogen secretion and cell insensitivity to follicle-stimulating hormone. Against the background of a decrease in the intensity of production, thinning of the epithelium occurs, resulting in a partial narrowing of the lumen of the canal. Over time, the stenosis progresses and complete fusion occurs.
I. Anatomical and functional changes during menopause
First of all, these changes develop in the woman’s genitourinary apparatus and are characterized mainly by atrophy and proliferation of connective tissue.
During menopause, these changes are little noticeable, but with the cessation of menstruation, during menopause, atrophic changes and proliferation of connective tissue begin to progress rapidly, reaching their limit in old age (senium). First of all, the ovaries : the primordial follicles cease to develop and reach the maturity of the Graafian vesicle, lose the ability to secrete full-fledged egg cells and form the corpus luteum. The entire ovary shrinks, decreases in volume and, due to the proliferation of connective tissue, and in places due to lime deposits, becomes dense and lumpy. According to W. Miller, the ovary of a 40-year-old woman weighs on average 9.3 g, and the ovary of a 60-year-old woman weighs only 4 g.
Histological examination of the ovary during menopause reveals a gradual disappearance of follicles and the absence of corpora lutea. However, in some cases, even during a long period of menopause, single follicles are found in the ovaries, the development of which does not reach its peak and does not end with ovulation. This probably partly explains the presence of estrogens in the urine of women who have been in menopause for many years (another source of estrogens can be the adrenal glands during menopause (see below).
In the ovarian parenchyma, connective tissue grows significantly, and hyaline lumps appear in the places of the former corpora lutea. In the vessels (arteries and veins) of the ovary, hyaline transformation and sclerosis are also noted.
Experimental studies in recent years have established that when an ovary from an old animal is transplanted into a young animal, follicles can form and mature in it [R. Stieve]. These studies are consistent with the data of F. S. Otroshkevich, who back in 1896 established that there is no direct connection between the degeneration of ovarian vessels and the cessation of their function; the ovaries cease their function when the number of vessels degenerated in them is insignificant and the nutrition is little changed. The main role in the complex process leading to the cessation of ovarian function, according to F. S. Otroshkevich, is played by the nervous system. Structural changes in the ovary do not always correspond to its function in all respects. N.I. Kushtalov (1918) came to the same conclusions while studying the ovaries of women 65-112 years old. He did not see a strict relationship between ovarian decline and a woman’s age. The importance of the nervous system in the development of age-related changes is currently confirmed by experimental studies by I. A. Eskin and N. V. Mikhailov, which showed that old animals, compared to young animals, respond to unfavorable factors with an altered reaction, and these changes are not associated with a violation formation of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) in the pituitary gland or with a weakening of the adrenal cortex's response to ACTH, and with age-related changes in the central nervous system that regulates the release of ACTH.
The fallopian tubes also undergo regression: the muscular layer of the tube becomes thinner, gradually being replaced by connective tissue; folds of the mucous membrane atrophy, lose their cilia; the lumen of the tube narrows - partial atresia or complete obliteration of the lumen of the tube appears.
the uterus is somewhat enlarged, juicy, softened, then it begins to decrease in volume, its muscle fibers atrophy and are replaced by connective tissue, and the vessels become sclerotic. The average weight of the uterus in women aged 21-30 years is 46.43 g, and in women aged 61-70 years - 39.51 g. The uterine cavity narrows and shortens. The endometrium changes especially dramatically: first its functional and then its basal layer gradually atrophies. During menopause, when the follicles finally disappear, the lining of the uterus gradually disappears. turns into atrophic senile mucosa, in which differentiation into functional and basal layers is completely absent.
During menopause, true glandular-cystic hyperplasia (occurs no earlier than a year after menopause) and simple cystic enlargement of the glands (with prolonged menopause) are often observed in the uterine mucosa. These forms of mucosa are not functionally active, since the cause of their occurrence and development are mechanical factors, a kind of ovula Nabothii of the endometrium [E. I. Quater, Alcohol (N. Speert), McBride (J. M. McBride)]. During menopause, the endometrium becomes increasingly atrophic. With low estrogenic activity, endometrial polyps are often observed. The spiral tortuosity of the arterioles disappears. The venous network appears to be located close to the surface of the mucous membrane. Ruptures of these veins can cause uterine bleeding during menopause. The glands shrink and their secretion decreases. The cervix and its vaginal part decrease significantly in size, sometimes the partio vaginalis completely disappear. The cervical canal narrows; In old age, stenosis and synechiae form in it, causing its complete obstruction. In such cases, secretions may accumulate in the uterine cavity, which, if infected, can cause pyometra (accumulation of pus). Due to the developing atrophy of the ligamentous apparatus and wrinkling of the pelvic connective tissue, the pelvic floor and the position of the uterus change: anteflexio turns into retroflexio, atrophy of the pelvic floor muscles often leads to prolapse of the uterus.
The vagina at the beginning of menopause is hyperemic, later it becomes dry, smooth, low-elastic, the mucous membrane loses its folds, in places it loses its epithelium (on this basis, adhesions of the vaginal walls sometimes develop), in general the vagina is smoothed out and shortened. A decrease in glycogen and lactic acid reduces the pH of the vaginal contents, which leads to disruption of the normal vaginal flora and a weakening of the “protective” properties of the vagina. Senile colpitis, trophic disorders and stenotic processes (Craurosis fornicis vaginae) begin.
Age-related changes occurring in the vagina are reflected in the cytological picture of vaginal smears and indicators of the functional state of the ovaries.
Changes that occur in the vagina during menopause and at all periods of a woman’s life are presented in Table 5 (Davis and Pearl).
Table 5 Age-related changes occurring in the vagina (according to Davis and Pearl). A diagram showing the role of estrogen hormone in the biological state of the vagina, the structure of its mucosa and the nature of its secretion.
Bougienage of the cervical canal: the need for the procedure
By not agreeing to surgical intervention, representatives of the fairer sex expose themselves to serious risks. Firstly, when planning children, this very problem may become the only reason for the failure of a long-awaited pregnancy. For women who have not yet reached menopause, it is important to understand that a barrier to the elimination of the endometrium can lead to constant inflammatory processes, the formation of polyps, the formation of endometrial hyperplasia and even cancer.
During the postmenopausal period, in the absence of pain, the operation “bougienage of the cervix” is not prescribed; regular examination by a gynecologist is required. Unfortunately, it will not be possible to take material for cytology to detect or refute oncology with a sealed passage. In this case, surgical intervention is indicated.
Indications for bougienage:
- inability to get pregnant within 6 months;
- disruption of blood flow in the uterus;
- narrowing of the cervical canal before menopause;
- the appearance of hypertrophic scars;
- inflammatory processes (endometritis or endocervicitis);
- abortion, curettage or electrocoagulation.
It should be noted that bougienage does not make sense in the event of the development of a malignant process. When cancer cells form, specialists take drastic measures to eliminate the tumor.
Also, with false amenorrhea, which has been observed for 6 months, unsealing of the cervical canal by using a bougie is not done. They resort to recanalization of the cervix using a plastic method.
If the lumen is not completely closed, drug treatment may be prescribed, including hormonal therapy, intravaginal creams, douching with an anti-edema solution and suppositories. But in most cases, bougienage of the cervical canal in Moscow is still prescribed, since the initial stage of narrowing is detected extremely rarely.
The cervical canal is overgrown. What is the cervical canal
The cervical canal is the canal of the cervix, connecting the vagina and the cavity of this organ. It has two small holes - the internal and external pharynx, the normal diameter of which is 2-3 millimeters. The external pharynx is visible during a standard examination, has a dotted shape if the woman has not given birth, and after childbirth or abortion it becomes slit-like. The layer of mucous membrane covering the cervix is called the endocervix.
Atresia of the cervical canal
A disorder that results in fusion or obstruction of the cervix is called cervical atresia. The disease can be a congenital pathology or acquired as a result of illness or injury. Congenital disorders are cases of abnormal formation and development of internal organs. Acquired atresia in most cases is caused by abortion, cervical cancer, inflammation in the inner and outer layers of the canal tissue.
The cervical canal is closed, what does this mean?
Whether the sperm will pass through to the egg largely depends on the condition of the cervix. When the cervix is completely or partially closed, doctors diagnose stenosis. It can be distinguished by the following symptoms: absence or painful menstruation, infertility, pain during sexual intercourse. A narrow cervical canal and conception are poorly compatible; first you need to eliminate the cause, then carry out bougienage. If you still manage to get pregnant with this disease, there is a high probability of incoordination of labor and subsequent cesarean section.
The cervical canal is dilated, what does this mean?
At any stage of pregnancy, the doctor can report the news that the cervical canal is dilated - what does this mean? This means that the cervix cannot perform its functions of holding the fetus. Enlargement of the cervical canal can be caused by an increased amount of male hormones that soften the cervix, multiple pregnancies, developmental abnormalities and injuries. The following steps can be taken to prevent a possible miscarriage:
- medications are prescribed that strengthen the cervix;
- installation of a special ring, which will be removed only at 37 weeks;
- stitches were placed around the cervix.
Causes of enlargement and treatment
If the canal is dilated in the absence of pregnancy, the doctor takes a smear and prescribes additional examinations. Pathology may be a consequence of:
- sexual disease;
- uterine fibroids;
- ovarian cysts;
- endometriosis and adenomyosis;
- chronic form of cervicitis.
Canal enlargement does not always signal a disease. Its diameter changes slightly on certain days of the cycle. During ovulation, an increase in size facilitates the penetration of sperm into the uterine cavity and increases the likelihood of successful fertilization of the egg. It can also expand due to taking hormonal drugs, smoking and slowing metabolic processes.
During pregnancy, dilatation becomes a reason to admit the patient to hospital care in order to prevent premature onset of labor. An examination is carried out to determine the cause of the pathology and treatment aimed at reducing the diameter of the canal.
Treatment of the anomaly is carried out using one of three methods:
- The medication method allows you to adjust a woman’s hormonal levels and reduce the tone of the smooth muscles of the uterus.
- Surgery involves suturing the cervix. Used for developmental defects, the presence of polyps in the canal or injuries. Performed under general anesthesia. During pregnancy, manipulation is performed at 16 or 18 weeks, and the sutures are removed only after 38 weeks.
- Special ring. It is placed on the cervix and tightened. The technique is used during pregnancy to avoid premature dilatation of the cervix. The ring is removed after 37 weeks.
The cervical canal performs important functions in the female body during menstruation, conception and pregnancy. Any pathology is confirmed by a number of studies and requires correct and timely therapy under the supervision of a gynecologist.