Etiology
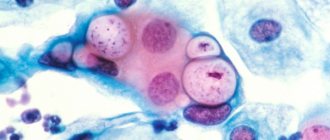
Lactobacillus under a microscope
Lactobacillus are polymorphic, non-motile rods from long and thin to short, cocci-like. They are Gram-stained blue and are located in the smear in short chains or singly. Some strains exhibit bipolar staining and the presence of metachromatin grains.
Lactobacilli are facultative anaerobic bacteria that have the ability to process lactose and other carbohydrates into lactic acid. The most comfortable temperature for their reproduction is 30-40°C.
Lactobacilli, penetrating the gastrointestinal tract, settle on the mucous membrane. As a result of interaction with enterocytes, they trigger the body’s defense mechanisms: accelerate regenerative processes in the mucous membrane, activate the formation of antibodies to pathogens, enhance the production of lysozyme, and maintain the pH in the intestines and vagina at an optimal level.
Reasons for changes in normal indicators
A decrease in the number of beneficial bacteria indicates disturbances in the functioning of the body. What it is and what causes it can be difficult to figure out on your own. You can learn about the causes of the imbalance of beneficial and harmful microflora through a comprehensive examination, the basis of which is the determination of the DNA of lactobacillus and other microorganisms.
The following factors cause a decrease in the number of lactobacillus spp in a woman:
- changes in hormonal levels - in the second phase of the menstrual cycle, during pregnancy, after childbirth, during menopause and puberty;
- failure to maintain personal hygiene - using alkaline soap, wearing sanitary pads for a long time, neglecting to clean underwear;
- independent douching with herbal decoctions or water to cleanse the vagina;
- promiscuity, contacts without barrier contraceptives;
- parasitic infections;
- taking antibiotics, glucocorticosteroids;
- poor nutrition, consumption of large amounts of simple carbohydrates and alcohol abuse.
Research shows that women who regularly drink beer are more likely to suffer from vaginal candidiasis.
To increase the number of lactobacilli in a smear, drug therapy is needed
Approximately 95-98% of all vaginal flora is represented by lactobacilli (Dederlein's rods).
It is lactobacilli (Lactobacillus), which destroy glycogen and produce lactic acid, which provides an acidic environment in the vagina and protects it from infection. The remaining 2-5% of the flora are represented by gram-positive rods, gram-negative cocci, gram-positive cocci, gram-negative obligate anaerobic rods and enterobacteria.
How to restore the vaginal microflora after taking antibiotics
All these representatives of the vaginal flora are in symbiosis with the human body, without causing harm to health, but, on the contrary, protecting it from disease. With the normal functioning of the microflora, the infection entering the vagina is neutralized due to the acidic environment.
The microflora of the genital tract is not the same at different periods of a woman’s life and reflects the influence of a complex of factors from both the external and internal environment.
Even during one menstrual cycle, fluctuations in phases are detected. Thus, in the first days of the cycle, the pH of the vaginal environment rises to 5-6, which is associated with the breakdown of endometrial cells (Endometrium) and blood, while the number of lactobacilli decreases, but the balance is maintained by an increase in facultative and obligate anaerobes.
At the end of menstruation, everything is quickly restored and by the middle of the cycle and the secretion phase it is 3.8-4.5, and is accompanied by the maximum number of lactoflora, glycogen and lactic acid content.
Reasons for increasing the level of leukocytes in a smear
If a vaginal smear shows a level of white blood cells that is atypical for this period, then this may indicate a number of diseases that women may suffer during menopause. Among the causes of leukocytosis we list the following:
- Nonspecific vaginitis - provoked by Escherichia coli, streptococci or staphylococci. With this disease, the level of leukocytes is significantly increased, cells of the surface layer of the epithelium are practically absent, and at the same time a significant amount of desquamated epithelium is determined.
- Bacterial vaginosis - outwardly has all the signs of an inflammatory process, but opportunistic microorganisms are not detected. Today the disease is classified as dysbacteriosis. A vaginal smear reveals many gram-positive cells - desquamated epithelium covered with small bacteria. Typically, such cells are not found in women, but in menopause, 94 percent of smears have this characteristic. The number of lactobacilli is also significantly reduced, due to which the acidity level increases, and anaerobes are present.
- In some cases, an increase in leukocytes indicates sexually transmitted infections - trichomoniasis, gonorrhea, candidiasis. In a vaginal smear, you can notice not only all the signs of the inflammatory process, but also identify the causative agent of the disease.
Main functions
Lactobacillus takes an active part in metabolic processes and corrects microecological disorders. They are used to produce probiotics and food products.
Main functions of lactobacilli:
- The antagonistic or protective function is due to the ability of bacteria to produce lactic acid. Lactobacilli also synthesize antimicrobial and antibiotic-like substances - lysozyme, hydrogen peroxide, bacteriocins, fatty acids. Lactic acid bacilli participate in the process of developing colonization resistance by blocking macroorganism receptors, preventing the adhesion of pathogenic microbes.
- Immunomodulatory function – stimulation of phagocytosis, antibody formation, cytokine biosynthesis. Lactobacillus activates weakened immunity and does not affect the normally functioning immune system.
- The anticarcinogenic effect of lactobacilli is the ability to suppress or block the penetration of carcinogens into the cell, as well as accelerate the processes of inactivation and elimination of them from the cell. This function is associated with the production of glycopeptides and enzymes that stimulate mononuclear phagocytes, which trigger the work of the entire immune system of the macroorganism.
- Commensalism is the ability to activate the vital processes of bifidobacteria.
- Vitamin-forming function - participation in the synthesis of vitamins: B2, B9, B7 and others.
- Antioxidant function - the ability to reduce lipid peroxidase.
Lactobacilli are used in the production of medications intended for the prevention and treatment of various inflammatory diseases. To eliminate pathologies of the digestive tract, respiratory organs and genitourinary system, drugs obtained from autolysates, cell-free metabolic products, extracts, dead and live bacteria are used.
Lactobacilli are present in the intestine throughout its entire length. They help digest and absorb proteins, fats, carbohydrates, prevent opportunistic and pathogenic flora from multiplying, and normalize intestinal function. Standards for colonies of beneficial microorganisms are set individually depending on where they are determined. For example, in the stomach there is no more than 10 * 2 CFU per milliliter of biological fluid. In the intestines, this figure increases and reaches 10*6–10*7 CFU, which is the norm for the female genital organs.
The uterus, the main reproductive organ, is regularly attacked by bacteria, viruses and fungi, which can multiply due to poor personal hygiene (Candida) or be transmitted through sexual contact (Chlamydia trachomatis). Lactobacilli suppress the growth of pathogenic microflora and protect the vagina from infection, preventing its penetration through the cervical canal into the uterus. The lack of protective functions leads to the development of inflammation of the external genitalia, which subsequently spreads to the cervix, endometrium and appendages.
Dysbacteriosis of vaginal microflora
When the vaginal microflora is disturbed, the number of lactobacilli decreases. Instead of the normal acidity level of 3.8-4.5, alkalization is observed, in which the pH is 4.5 or higher. This leads to a decrease in local vaginal immunity and the onset of favorable conditions for the development of infectious inflammatory and non-inflammatory diseases.
How to improve vaginal microflora
Epidemiology
Under natural conditions, Lactobacillus lives in the upper layers of soil, especially around plant roots. A child first encounters lactobacilli when he is born. He receives them from his mother while moving through the birth canal. These microorganisms are very beneficial for the newborn.
Lactobacillus dominates among bacteria in the vaginal environment. The following are usually isolated from vaginal discharge: L. fermentum, L. acidophilus, L. plantarum, L. cellobiosis. In the vagina of a healthy woman, their number should not be less than 106 CFU/ml.
It may vary depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle and the amount of hormones in the blood. On critical days, there is a decrease in them, and during pregnancy, an increase. Lactoflora protects the vagina from the penetration of pathogenic biological agents from the external environment, inhibits the growth and reproduction of opportunistic flora.
This happens due to the ability of Lactobacillus spp to maintain the pH of the environment at a certain level. They produce hydrogen peroxide, which kills pathogens from outside, as well as lactic acid, which creates a barrier that inhibits the activity of its own inhabitants.
Their antibiotic activity is associated with the ability to synthesize disinfectants. In older women, as well as in people suffering from chronic diseases of the genital area or severe somatic pathologies, the amount of glycogen in the epithelial cells of the vagina decreases.
Modern medical scientists have proven that lactic acid sticks are safe for humans. But in rare cases, against the background of secondary immunodeficiency, lactobacilli become causative agents of local and generalized infections - endocarditis, bacteremia, inflammation of the lungs and soft meninges, urinary infections.
DETAILS: White discharge in women without odor and itching: causes of thick and curdled leucorrhoea
The norm of lactobacilli in the vagina
Lactobacilli are the dominant species of microorganisms in the vaginal microbiological environment. They play an important role in ensuring the protective functions of the vaginal microflora, therefore their amount in vaginal discharge is of great importance for the health of the female genital area.
The role of lactobacilli in the vaginal microflora
Lactobacilli in the vagina are found in quantities of about 109 CFU/ml (colony-forming units observed in 1 milliliter of vaginal discharge), which is up to 95–98% of the total number of all microflora microorganisms.
The predominant representatives of lactobacilli in the vaginal environment are L. acidophilus, L. plantarum, L. fermentum and L.
casei, which, depending on the individual characteristics of the woman’s reproductive system, can be present in different proportions.
During their life, these microorganisms produce lactic and other organic acids, which provide the necessary pH of the vaginal environment.
Creating the correct level of acidity allows you to suppress the activity of other bacteria and fungi present in the microflora, an increase in the concentration of which can lead to infectious and inflammatory diseases of the female genital area.
In addition, lactobacilli of the vaginal microflora produce antibacterial substances (hydrogen peroxide and bacteriocins) that inhibit the vital activity of pathogenic microorganisms and cause their death.
Thus, it is impossible to overestimate the importance of lactobacilli for a woman’s health - they can rightfully be considered one of the most important factors in the arsenal of the body’s defense mechanisms.
What does the concept of normal mean in relation to microflora?
The vaginal microflora contains many types of microorganisms. Some of them are beneficial to health, others are neutral (that is, they do neither harm nor benefit). Still other microorganisms are opportunistic - harmless under some circumstances and dangerous under others.
They are the ones who can disrupt the delicate balance of intimate microflora - as soon as the acidity of the vaginal environment changes, the activity of such microorganisms increases and they begin to actively multiply.
The most famous opportunistic microorganisms are the yeast-like fungus of the genus Candida and the bacterium Gardnerella vaginalis, which during periods of their activity cause candidiasis (“thrush”) and gardnerellosis.
It is possible to restrain the growth and activity of opportunistic and pathogenic microbes only with the correct, healthy ratio of all representatives of the vaginal flora.
Thus, the norm of lactobacilli in the vagina is their percentage ratio to other representatives of the microflora, which provides the necessary level of acidity and inhibits the growth of pathogenic and opportunistic bacteria and fungi.
Signs of impaired concentration of lactobacilli
The absence of lactobacilli in the vagina jeopardizes the health of a woman’s entire reproductive system and can lead to disruption of a number of functions, including reproductive function. A change in the balance of microflora quickly manifests itself with unpleasant symptoms, including:
- increased volume of vaginal discharge;
- change in the color of the discharge (milky white, yellow, gray or with a green tint) and its consistency (watery, cheesy or viscous);
- the appearance of an unpleasant odor from the vagina (rotten, distinctly sour, “fishy”);
- itching in the area of the external genitalia and vulvar mucosa;
- signs of irritation of the vulvar mucosa (burning, discomfort, pain during sexual intercourse and hygiene procedures).
If there are no lactobacilli in the vagina for a long time, dysbiosis can provoke atrophic processes, which leads to pathological dryness of the vagina and thinning of its walls.
Moreover, the vaginal mucosa, having lost its microbiological protective mechanism, becomes an entry point for infections that penetrate the urogenital tract during hygienic procedures, swimming in natural and artificial reservoirs, during sexual intercourse, etc.
Restoring the concentration of lactobacilli
Restoring the percentage of lactobacilli to other representatives of the microflora is extremely important for maintaining the health of the genital area and normalizing the functions of the vaginal mucosa. The fastest and easiest way is to artificially populate the mucous membrane with these microorganisms.
To restore microflora, various medications can be used - probiotics, including the new generation drug Lactonorm®, which contains more than 100 million live lactobacilli.
Thanks to the form of release of the drug (vaginal capsules with a soluble gelatin shell), lactobacilli enter directly where they are needed - on the vaginal mucosa. Bacteria in Lactonorm® are kept in a “dormant” state by cold and by maintaining temperature conditions during storage.
The absence of preservatives allows them to quickly activate and begin to normalize the composition of the microflora. In addition, Lactonorm® contains lactose, a natural nutrient medium for lactobacilli.
This helps not only to increase their number in the vagina, but also to provide favorable conditions for the healthy activity of beneficial microflora.
Source: https://lactonorm.ru/stati/norma-laktobakteriy-vo-vlagalishche.php
Reasons for changes in normal indicators
There are a number of factors that influence the likelihood of an imbalance in the vaginal flora. Among them the following can be noted:
- Hormonal surges observed during pregnancy, breastfeeding, abortion, perimenopause, menopause, transition, irregular sex life. For example, many women ask their gynecologists about how to restore the vaginal microflora after childbirth, since due to hormonal changes the mucous membrane becomes excessively dry and irritated.
Expert opinion
As soon as the level of estrogen drops for various reasons, a change in the vaginal biocenosis is observed: the number of Doderlein bacilli is reduced, which creates favorable conditions for the development of opportunistic microflora, as well as for the introduction of pathogenic agents. This is due to the influence of estrogens on the mechanism of glycogen formation and maintaining optimal conditions for the life of lactobacilli.
Obstetrician-gynecologist of the highest category Oksana Anatolyevna Gartleb
- Antibacterial therapy. One of the features of antibiotics is that they destroy not only harmful, but also beneficial microorganisms. Therefore, after taking these medications, it is important to restore the disturbed vaginal microflora. And remember: under no circumstances should you take antibiotics uncontrolled for a long time without consulting a doctor, as this can lead to dire consequences.
- Regular hypothermia. They affect the level of general and local immunity, undermining the body's defenses.
- Insufficient hygiene of the intimate area. If you do not wash yourself regularly, do not change your underwear, used pads or tampons on time, there is a high probability of developing vaginal dysbiosis. Particular attention should be paid to the timely change of tampons during menstruation: this must be done every 2-3 hours, because otherwise ideal conditions are created for disruption of the vaginal microflora. You also need to wash yourself properly, directing the stream of water from the front and not from the back, since in the second case, intestinal bacteria may enter the vagina.
- Using inappropriate intimate hygiene products. For washing, it is necessary to use specialized gels and foams for intimate hygiene. They have a neutral pH level and do not cause symptoms of vaginal microflora disorders. You should also avoid using tampons and pads that contain dyes and fragrances.
- Using an intrauterine device for a long time, taking certain oral contraceptives.
- Staying in an unusual climate. Often, a change in climate zones from cool to warmer becomes one of the reasons for the imbalance of microflora.
- Stressful situations and unbalanced nutrition. Stress undermines the body's defenses, making it more susceptible to infectious processes. An unhealthy diet rich in yeast products, alcohol and simple carbohydrates also leads to a weakening of local vaginal immunity.
An imbalance of the vaginal microflora can be asymptomatic or have certain signs. Symptoms include the following clinical manifestations:
- Atypical vaginal discharge. Most often they have a gray or white color and a characteristic fishy smell. The discharge may also be foamy.
- Itching and burning.
- Painful urination.
- Dry mucous membranes and swelling
- Pain during intercourse.
Symptoms
Lactobacilli are part of an obligate group of microorganisms along with bifidobacteria, bacteroides and Escherichia coli. As a result of the developed imbalance, the functions of lactobacilli are disrupted - antagonistic, immunotraining, vitamin-forming, metabolic.
The reasons for changes in the normal number of lactic acid bacteria in the intestines are negative external and internal factors. These include:
- Prematurity,
- Intrauterine infection
- Late latching of the newborn to the breast,
- Artificial feeding
- Diseases of the digestive system,
- Severe chronic pathologies - endocrine, autoimmune,
- Long-term use of antibiotics, hormones, cytostatics,
- Radiation.
There are 4 degrees of severity of intestinal dysbiosis:
- 1 - the number of lactobacilli is not changed, there are no intestinal dysfunctions.
- 2 - a slight decrease in lactobacilli and bifidobacteria, the appearance of abdominal discomfort, bloating, belching, heartburn, bowel disorders - constipation, diarrhea.
- 3 - a significant decrease in the level of lactobacilli to 105 CFU, joining the previous symptoms of stomatitis, tonsillitis, rhinosinusitis with characteristic manifestations.
- 4 - absence of lactobacilli and bifidobacteria, the appearance of inflammatory processes in internal organs: liver, gall bladder, lungs, kidneys, development of anemic, dyspeptic, intoxication syndromes.
Clinical signs of intestinal dysbiosis depend on the depth of the disorder and the state of the body's defenses. If the listed signs are accompanied by symptoms such as fever, chills and acute pain in the lower abdomen, the development of severe complications can be suspected.
The genital organs of the female body are the entry point for any infection. Lactobacilli in optimal quantitative terms help to avoid the development of pathology. Lactobacillus spp. contained in vaginal discharge in an amount of 106–109 CFU/ml.
When Lactobacillus spp levels change and go beyond normal limits, dysbiosis develops with characteristic clinical manifestations. To cope with such an ailment, it is necessary to find out its cause.
The etiological factors of vaginal dysbiosis are: irrational antibiotic therapy, chronic pathologies of the reproductive system, promiscuity, frequent use of lubricants. An insufficient number of lactobacilli in the vagina is a sign of an existing infectious process.
With candidiasis, the number of lactobacilli in the smear decreases. This pathology is popularly called thrush. In patients, pathogenic fungi of the genus Candida are activated. They grow and multiply quickly, exhibiting their pathogenic properties.
there is a persistent feeling of dampness in the perineum, the anogenital zone is constantly irritated, painful and frequent urination occurs, and during sexual intercourse dry mucous membranes appear, burning and discomfort.
With a significant decrease in the number of lactobacilli, pregnant women are susceptible to premature birth or the development of severe diseases of the reproductive system after delivery.
Diagnostics
In women, even minor changes in the number of lactobacilli are reflected in the smear. You can independently suspect an imbalance of microorganisms based on the following symptoms:
- increased mucous secretions;
- changes in the organoleptic properties of vaginal mucus - color and smell;
- the appearance of itching and burning;
- plaque on the external genitalia;
- discomfort in the pelvis;
- pain during intercourse;
- menstrual irregularities.
To determine the number of beneficial bacteria, you need to consult a gynecologist. The doctor will conduct a manual examination and take vaginal secretions for analysis. Diagnostic results can be found out on the same day. The norm for performing analysis is up to two hours after collecting the material.
If laboratory testing shows that the number of Doderlein rods is reduced, an extended analysis is performed. With its help, the types of bacteria in the taken biological material are determined. The polymerase chain reaction allows one to isolate its DNA from a microorganism. Lactobacillus is detected accurately, which ensures high reliability of the analysis.
Normoflora
Diagnosis of intestinal dysbiosis is based on the results of microbiological examination of native feces. Sampling is carried out before the start of antibiotic therapy or 10 days after it. A week before the expected date of analysis, stop taking pre- and probiotics, and 2-3 days - fermented milk products.
Feces are taken with a sterile glass rod from the depth of the material being examined after natural bowel movement into a sterile container. The sample volume must be at least 1 gram. The sample is delivered for analysis within 2 hours from the moment of collection.
In the bacteriological laboratory, it is re-weighed and the study begins directly. A series of tenfold dilutions are prepared from the stool, left to settle large particles, and then inoculated on nutrient media designed to identify a specific microorganism.
To count the number of lactobacilli, inoculation is done in sterile milk. All dishes and test tubes are incubated in a thermostat for 4 days at 37 degrees. Then a small amount containing colonies of microorganisms is taken from the depths of the medium and a Gram smear is prepared.
DETAILS: Treatment of atrophic colpitis in women with drugs
Instrumental diagnostics allows us to identify the causative factor and assess the functional state of the intestine. To do this, a colonoscopy, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, FGDS, and intestinal radiography are performed.
Diagnosis of vaginal dysbiosis includes an examination by a gynecologist and a smear of the discharge for microflora. The material selected with a sterile cotton swab is applied to a special glass and sent to the laboratory, where it is stained and examined under a microscope.
PCR is a modern express method that allows you to quickly and accurately detect the genetic material of bacteria in the test sample. Lactobacillus spp. determined with 100% accuracy.
Lactobacillus spp: normal in women. What is Lactobacillus spp
Bacteria are microscopic living organisms that are found everywhere. They live on all household items, live in water and air, and are also found in the body of humans and animals. Bacteria can be of three types. The former live in the body constantly and do not cause any harm to it.
The latter – conditionally pathogenic bacteria – also live inside us all the time. Their difference is that under various endo- and exogenous factors (for example, decreased immunity, hypothermia, the presence of chronic foci of infection), they begin to multiply intensively and cause harm to the body, causing various diseases.
The third group includes pathogenic bacteria; they penetrate from the outside and always bring with them some kind of infection.
What are lactobacilli?
Lactobacilli belong to the natural microflora of the body. They are necessary to ensure normal metabolism, so they are constantly inside us. The habitat of lactobacilli is the entire digestive tract, as well as the external genitalia of women.
These microorganisms can take on different shapes, most often they are found in the form of rods. Lactobacilli are Gram (+) and anaerobic bacteria; they are incapable of forming spores.
These microorganisms belong to the group of lactic acid rods, due to their ability to process lactose and other carbohydrates. During their metabolism, they release lysozyme - a disinfectant, hydrogen peroxide and other metabolic products that have antibiotic activity.
Their main property is the formation of lactic acid, which prevents the development and proliferation of pathogenic bacteria and fungi.
Habitat of Lactobacillus spp
Lactobacilli live in large numbers on the mucous membrane of internal organs. They are distributed throughout the digestive tract, starting in the mouth. Next, Lactobacillus spp spreads to the mucous membrane of the pharynx, esophagus, stomach and intestines.
The place of their greatest accumulation is the final section of the digestive tract.
This is explained by the fact that in the large intestine there are special cells - enterocytes, interaction with which ensures the processes of repair of the mucous membrane, the formation of the body's defenses through the formation of lysozyme and special immunocompetent cells (cytokines).
Another habitat for Lactobacillus spp is the vulva and vagina. The presence of lactobacilli on the external genitalia of women is necessary to protect the mucous membrane from pathogenic factors and prevent infection from entering inside.
Lactobacillus spp: normal in women
In the female body, lactobacilli are found in greater quantities compared to the biocenosis in men. Since the genitals of girls are open gates for various infectious agents, the presence of Lactobacillus spp is necessary there. The norm for women is 106-109 CFU/ml.
If these indicators are found in smears from the vulva, vagina and urethra, then this is not a cause for concern. These bacteria are present in women of all ages, but the greatest number is observed in young girls who have not started sexual activity.
Previously, only the total number of fermented milk microorganisms in a vaginal smear was determined for the degree of purity and they were called Dederlein bacilli. With the development of modern medical technologies, it has become possible to isolate each type of bacteria, and it turned out that a significant number of them are Lactobacillus spp.
The norm for sexually active women is slightly lower than for girls. However, it should not be lower than 106 CFU/ml.
Change in the number of lactobacilli
Lactobacilli, like other microorganisms, have a certain amount that is considered normal. This value is different for each section of the mucous membrane of the digestive tract. For example, the content of lactobacilli in gastric juice is only 102–103 CFU/ml, while the colon contains 106–107 CFU/ml Lactobacillus spp.
The rate of these microorganisms in the vagina is the highest compared to other mucous membranes. Therefore, when lactobacilli are detected in the body, it is necessary to know exactly their quantitative indicators for each department. Normal flora Lactobacillus spp is the norm for a healthy person.
A change in the number of lactobacilli in any part of the body indicates a pathological condition.
Why does the number of lactobacilli change?
If Lactobacillus spp indicators are outside the normal range or do not reach them, then it is necessary to find out the cause of this condition. Typically, an increase in the number of lactic acid bacteria on the vaginal mucosa is associated with dysbacteriosis, which develops with the irrational use of antibiotics.
In addition, it can be observed with constant consumption of kefir, citrus fruits, vinegar, etc. In this case, their quantity will be restored after the acidity of the products decreases. A decrease in lactobacilli in the intestines is also associated with dysbiosis.
If they decrease in the vagina and urethra, you should think about the presence of an infectious process in the genitals.
Methods for diagnosing lactobacilli
If you suspect a change in the number of lactobacilli, you must consult a doctor. Modern diagnostic methods will allow you to quickly establish the qualitative and quantitative composition of microorganisms. In gynecology, the material for research is smears taken from the mucous membrane of the urethra, vulva and vagina.
First, they are subjected to microscopic examination, and when the number of Dederlein rods changes, more accurate diagnostic methods are carried out. A method that allows you to quickly and accurately determine the presence of bacteria is PCR. It is based on the isolation of its DNA from a microorganism.
Lactobacillus spp, like other components of the microbiocenosis of the genital organs, is determined with 100% accuracy.
Use of lactobacilli
Lactobacilli are used in several industries, as well as in medicine and pharmaceuticals. Like bifidobacteria, these microorganisms contain special strains - probiotics - substances used to maintain the normal quantitative composition of bacteria.
They are used for long-term use of antibacterial drugs, and are also added to vitamin complexes to strengthen the immune system.
Lactobacillus spp - what is it? Since lactobacilli are natural microorganisms, they can be safely used for the treatment and prevention of diseases of the digestive tract, as well as inflammatory processes in the female genital organs.
Lactobacilli in the food industry
Due to poor diet and widespread dysbiosis, most people suffer from digestive problems. For this reason, lactobacilli began to be used in the manufacture of fermented milk products, which are not only beneficial for the body, but also help the intestines work faster.
In addition, in the food industry they are used for pickling vegetables, preparing salads, pickled foods, and brines. Some people use lactobacilli in agriculture to make feed. In this case, their benefit lies in the fermentation of silage, which contributes to long storage and the absence of mold formation.
Lactobacilli are necessary in many areas of human life, as they protect our body from pathogenic influences.
Source: https://FB.ru/article/146708/lactobacillus-spp-norma-u-jenschin-chto-takoe-lactobacillus-spp
How to increase the number of lactobacilli
Carrying out tests of the vaginal microflora
Since the disease is often asymptomatic, many women learn about it only at an appointment with a gynecologist. If the doctor suspects that his patient is not healthy, he takes a urogenital smear to determine the vaginal microflora for laboratory tests.
To obtain results, a smear examination with Gram staining can be used in accordance with European recommendations in accordance with the Hay-Ison scale or with the assessment of Nugent scores and the Russian recommendations of the national guide to gynecology - femoflora analysis (determination of DNA of microorganisms associated with bacterial vaginosis or assessment of microscopic characteristics vaginal biocinosis (Kyra classification).
A smear examination involves the analysis of squamous epithelium, gram-positive rods (including Dederlein's rods), leukocytes, etc.
As a result of the studies, the specialist can determine the composition and ratio of the vaginal microflora, the presence/absence/intensity of inflammation, and also determine the reason for the dysbiosis.
Taking an analysis to identify the ratio of beneficial and pathogenic microflora of the vagina requires certain preparation:
- It is necessary to abstain from sexual intercourse for 24 hours.
- Three days before the smear collection, you should avoid vaginal douching, the use of tampons, suppositories and other local remedies, and do not perform hygiene on the day of the test collection.
- After consulting with your doctor, it is advisable to refrain from taking antibacterial drugs for at least a few days.
Test results can usually be obtained after 1-3 days, after which it is necessary to begin appropriate treatment aimed at restoring, improving and maintaining the vaginal microflora in a normal, healthy state.
If the levels of Eubacterium in the intestines and Lactobacillus in the vagina decrease, measures must be taken to correct this condition. The treatment regimen will depend on what caused the disruption of normal microflora. If the test results show the presence of pathogenic microorganisms, the woman is prescribed a course of antimicrobial and antiprotozoal drugs. Vaginal antiseptics in the form of suppositories, tampons and solutions are also recommended if there are no contraindications for their use. After completing the course, an individual regimen is prescribed to restore the natural microflora.
If the cause of violations is exogenous factors - diet, bad habits, lack of hygiene - measures are taken to eliminate them. Restoring the vaginal microflora involves:
- the use of vaginal suppositories containing live colonies of lactobacilli;
- taking medications to normalize intestinal microflora;
- eating large amounts of fermented milk products;
- nutritious nutrition, including daily consumption of vegetables, fruits, fiber and protein;
- maintaining intimate hygiene, using special products with lactic acid for washing.
Periodic disruption of the microflora of the vagina and intestines in women, accompanied by a decrease in lactobacilli colonies, occurs due to suppressed immunity. To prevent such violations, it is necessary to strengthen the body's protective properties. Regular prevention allows you to constantly maintain the microflora in a normal state.
We also recommend reading: infection with the fungus Candida albicans in women
A form with the test result is given to the doctor or directly to the woman herself. Here is some general information to help you understand the laboratory test.
The table information should not be used for self-medication! Incorrect therapy can aggravate the inflammatory process and lead to an unfavorable outcome!
Table. Place where the smear was taken.
| Letter of the Latin alphabet | Where was the smear taken from (lat) | Translation |
| V | vagina | vagina |
| C | cervix | cervical canal |
| U | urethra | urethra |
For your attention, another table is a transcript of the study results (norm and deviation).
| Indicator (abbreviated) | Indicator (in full) | V (normal) | C (normal) | U (normal) | What may an excess of the indicator indicate? |
| Le | Leukocytes | 0-10 | 0-30 | 0-6 | Inflammation |
| Ep (pl.ep) | Epithelium | 4-10 | 4-10 | 4-10 | Inflammation |
| Slime | Slime | Moderate quantity | Moderate quantity | No | Sign of infection |
| Gn | Gonococci | — | — | — | Infectious disease - gonorrhea |
| Trich | Trichomonas | — | — | — | Infectious disease - trichomoniasis |
| Chlam. tr | Chlamydia | — | — | — | Infectious disease - chlamydia |
| Key. cells | Key cells | — | — | — | Inflammation (bacterial vaginosis) |
| Cand | Candida | — | — | — | Infectious disease - candidiasis |
| Gr.( ) | Gram-positive rods | If not detected, then there may be a violation of the microflora | |||
| Gr.(-) | Gram-negative rods | — | — | — | The appearance is regarded as dysbiosis or possible inflammation |
Degree of purity of a gynecological smear
In medicine, the general condition of the vaginal microflora has a certain formulation. There are four degrees of purity of a gynecological smear, by which the presence of inflammation can be determined.
First degree of purity. Leukocytes – from 0 to 4-5, vaginal pH – acidic. The flora is abundantly populated by lactobacilli. Epithelium and mucus in moderate quantities. The initial degree of purity occurs in girls who are not sexually active and in healthy women in the absence of inflammatory diseases (including chronic ones) of the genital organs.
Second degree of purity. Leukocytes – from 5 to 10, vaginal pH – acidic. The microbiological flora contains coccal infection or yeast fungi (the percentage of normal and pathological microorganisms is approximately the same, or in other words, mixed flora).
Flat epithelium and mucus in moderate quantities. The second degree of purity is not ideal, but there is no need to apply treatment. A woman becomes vulnerable, so she should increase local immunity to prevent the development of inflammation.
The third degree of purity causes alarm and concern, since the smear contains an increased number of epithelial cells and pathogenic microflora with an almost complete absence of lactobacilli. Vaginal pH is slightly acidic or alkaline.
The third degree of vaginal cleanliness is considered a bad result, signaling an ongoing inflammatory process. It is important for a woman to undergo serious therapy in order to recover quickly and avoid complications.
Fourth degree of purity. Doderlein bacilli (or lactobacilli) are not detected even in single quantities, so the pH reaction will definitely be alkaline. The flora consists entirely of pathogenic microorganisms; it is impossible to count leukocytes, since they are visualized throughout the entire field.
This is an extreme degree that signals danger. In addition to treatment, a woman needs to undergo a comprehensive examination to exclude dangerous diseases of the genital organs (for example, current oncology of the genital organs often “gives” a bad test result).
Table. Laboratory assessment of smear purity.
| Name of the required indicator | 1st degree | 2nd degree | 3rd degree | 4th degree |
| Lactobacilli | — | |||
| bacteria comma variabile | — | — | ||
| Gr (-) coccal flora and rods | — | — | ||
| Streptococci, trichomonas, gonococci, chlamydia | — | — | -/ | |
| Leukocyte count assessment | — | |||
| Epithelial cells | In single quantity | |||
| Candida | — | -/ |
Examination of a smear for microflora is an important and quick diagnosis that allows for the early detection of serious pathology. Timely and correct treatment will allow you to get rid of the disease, preventing it from becoming chronic.
Young girls and women planning to become mothers should pay great attention to reproductive health so that in the future they do not face the problem of conceiving or successfully carrying a pregnancy to term.
Smear cytology
Under the influence of decreased hormone levels, the ovaries are the first to suffer. Following the fading of their function, the vaginal mucosa begins to undergo changes. Changes in the genital organs do not occur immediately, since some of the functions are transferred to other endocrine glands. In particular, during menopause, the adrenal glands support a function similar to that of the ovaries. This allows a woman to feel menopausal changes less sharply.
That is why smear cytology in menopause at the initial stage shows cells of dead epithelium, still maturing due to the activity of the adrenal glands.
When estrogen levels decrease, cells from the deep layers of epithelial tissue first appear in the smear. The shape of the epithelial cells themselves also changes - their size decreases, they acquire an atypical shape, become more elongated, and sometimes just bizarre.
In a smear, epithelial cells are located either singly or in clusters. Single cells retain their clear boundaries, while cells clustered in groups lose their smooth lines.
The nuclei of epithelial cells become much larger, the membrane becomes clearly visible, and chromatin is noticeable. At the same time, the nucleolus of the epithelial cell cannot be identified. Epithelial cells acquire different colors, despite their uniformity.
In epithelial cells, you can notice an increased content of keratin - it is this protein that gives the cells elasticity. However, with an increase in keratin content, the cells become more coarse and keratinized.
Since insufficient estrogen is produced during menopause, epithelial cells do not mature completely. Thus, they cannot fully perform the function of surface cells, including protective ones.
To protect the vagina from various damages and infections, the body in menopause begins to secrete histiocytes and leukocytes in significant quantities, which take over these functions.
In some cases, when a significant number of leukocytes are detected, doctors diagnose atrophic colpitis. Indeed, leukocytes and histiocytes are markers of inflammation, and such a diagnosis is to some extent justified. However, the nature of atrophic colpitis is somewhat different: if ordinary colpitis is caused by pathogenic microorganisms and requires the prescription of antibacterial drugs, then atrophic colpitis does not need such treatment, because this is a natural reaction of a woman’s body to the aging processes that occur in her. In this case, you should not direct all your efforts to stop the inflammatory process, which is not such.
Treatment
To normalize the number of lactobacilli in the intestines, probiotics are used - “Enterol”, “Acipol”, “Linex”., “Acilact”, “Nerine”. These drugs contain beneficial microorganisms that normalize intestinal function, coping with diarrhea, restoring microflora and protecting the body from toxins.
DETAILS: How to learn how to flirt with a girl correctly: examples of successful flirting || Flirting lessons for women: learning to be attractive
Symptomatic treatment consists of using enzyme preparations - “Creon”, “Mezim”, “Panzinorm”, sorbents “Smecta”, “Polysorb”, “Activated carbon”. Patients are prescribed diet therapy during treatment.
To correct the level of lactobacilli in the vagina, women are also recommended to take probiotics orally. For the same purpose, vaginal suppositories are prescribed - “Gynoflor E”, “Lactacid”, “Lactonorm”, “Lactozhinal”.
They restore the normal microbial composition of the vagina and suppress pathogenic microflora. If vaginal dysbiosis is not treated, inflammation from the vaginal mucosa will spread to the cervical canal. Vaginosis can develop into endometritis and adnexitis.
The composition of the vaginal microflora changes with a decrease in the immunity of the vaginal walls. Women with bacterial vaginosis are prescribed immunomodulators that stimulate local immune defense and control the vaginal microflora.
Lactobacilli are non-pathogenic microorganisms for humans, the deficiency of which develops a special condition - dysbiosis. If the pathology is not corrected, it will lead to serious consequences - diseases of the digestive organs and reproductive system.
How is a smear taken from the cervix?
Biological material can be collected from the cervix in 4 different ways. Diagnosis is performed using a special medical device - the Cusco mirror.
The device is a transparent medical forceps, thanks to which a specialist can push apart the walls of the vagina to get to the cervix. After this, the biomaterial is scraped off.
Gels, creams and sprays to restore vaginal microflora
The selection of means and preparations for restoring and normalizing the vaginal microflora should be carried out exclusively by a specialist, since self-medication can lead to an even more advanced form of dysbiosis.
Below we will look at the main categories of drugs that restore vaginal microflora.
Vaginal suppositories are small, oblong-shaped preparations that look like a ball, oval, cylinder or cone, with a diameter of about 1-1.5 cm and weighing from 1.5 to 6 g. They are inserted intravaginally (into the vagina) - with or without an applicator him.
Vegetable and animal fats, glycerin or gelatin are used as the basis for the manufacture of vaginal suppositories. Under the influence of body temperature, suppositories lose their solid form, due to which the active substance is able to act on the vaginal mucosa.
To restore the vaginal microflora, suppositories are used based on active ingredients such as lactobacilli acidophilus, bifidobacterium bifidum, ascorbic acid, lactic acid, etc.
To normalize microflora, both oral medications (for example, probiotics) and vaginal tablets and capsules are used. They usually consist of a fatty shell, which facilitates easy insertion of the product into the vagina, and a core filled with granular powder.
Restoration of vaginal microflora
Creams, gels and sprays belong to the category of local hydrophilic products. Unlike thicker, viscous and heavy ointments that have a fatty base, these products are much easier to apply, they are quickly absorbed, without leaving a greasy film feeling.
One of the effective products that has a beneficial effect on the vaginal microflora is the Ginocomfort® restoring gel. It not only helps restore normal microflora, but also protects against relapses of the disease in the future.
The product contains natural ingredients such as tea tree oil, which has antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects, and chamomile extract, which has a regenerating effect. Bisabolol and panthenol help cope with irritation and inflammatory processes, and lactic acid helps restore normal vaginal microflora and maintain physiological acidity levels.
How is a urethral swab taken?
Material from the urethral canal can be carried out in 2 different ways.
Smear collection methods:
- Volkmann spoon. The method is prescribed only in the absence of injuries and inflammatory processes in the urethra. The device is inserted into the urethral canal and gently rotated to scrape off epithelial cells.
- Standard method. The material is collected without inserting a spoon. The specialist presses on the anterior wall of the vagina, and then collects the material secreted from the urethra.
The smear is placed in a sterile flask and sent to the laboratory for further microscopic examination.
Vaginal suppositories for restoration, normalization and improvement of vaginal microflora
In a healthy woman, about 95% of lactobacilli are detected in a smear. Lactic acid synthesized by these microorganisms maintains the necessary vaginal environment, thereby providing protection against the predominance of pathogenic flora.
When immunity decreases (for example, during pregnancy, hormonal imbalance, after stress), the number of lactobacilli decreases. This entails a weakening of the female body, which is fraught with increased susceptibility to infectious diseases of the genital area.
Normally, in addition to lactobacilli, the presence of gardnerella and candida in small quantities is allowed in the smear. When immunity decreases, pathogenic microorganisms begin to multiply rapidly, suppressing “milk” bacteria.
For this purpose, special probiotics are used for the vaginal microflora. They are medications that contain strains of lactic acid bacteria or probiotic lactobacilli, the action of which is aimed at normalizing and treating disorders of the vaginal microflora after taking antibiotics. These products can be used both topically (in the form of vaginal capsules) and orally.
- Chamomile. To prepare an infusion of chamomile flowers, pour 1 tbsp into a thermos. l. dry raw materials, pour 1.5 cups of boiling water and leave to brew. Then strain the resulting infusion, strain it and do douching and insert cotton swabs soaked in chamomile infusion into the vagina.
Infusion of chamomile flowers to restore vaginal microflora
- Sea buckthorn oil. Soak a cotton swab in sea buckthorn oil and insert it into the vagina overnight.
If you decide to use any of the traditional medicines, be sure to inform your doctor. And remember: “grandmother’s” recipes can only act as additional therapy.
If you are thinking about how to improve the vaginal microflora, be sure to check out the Ginocomfort product range.
Restoring gel "Ginocomfort" has a balanced composition developed by specialists from the pharmaceutical company VERTEX. The product has undergone clinical studies conducted at the Department of Dermatovenereology with the clinic of St. Petersburg State Medical University under the leadership of Ignatovsky A.V.
and Sokolovsky E.V. As a result of research, the high effectiveness of the restorative gel as part of complex therapy for various dysbiotic disorders has been proven. Regular use of the gel will help you cope with itching, dryness and other unpleasant symptoms of dysbiosis and restore normal microflora.
You can also use Ginocomfort intimate washing gels for daily hygiene: they will ensure effective cleansing of the intimate area without drying it out and without disturbing the microflora.
All Ginocomfort products have the necessary documents and quality certificates.
When studying the microflora of the body, special attention is paid to the condition of the woman’s genital organs. They are inhabited by various bacteria, but lactobacilli are represented in the overwhelming majority. Previously, when conducting analysis, experts called them the general term “Doderlein rods.” Over time, gynecology began to divide beneficial bacteria into types, which made it possible to more accurately determine the causes of disorders and select a correction regimen.
A smear of a healthy woman should contain at least 10 million colonies of Lactobacillus spp in one milliliter of vaginal secretion. In girls who are not sexually active, this figure reaches 10*9 CFU/ml.
Lactobacillus spp in women: normal