How does radio wave treatment of the uterus work?
The impact on the affected tissue is carried out by high-frequency radio waves in the range of 3.8-4.0 MHz, which cause the evaporation of intracellular fluid, coagulation of the protein structures of the cell with its subsequent death. Thus, acting on the tissue, the radio knife creates an ultra-thin incision, simultaneously seals the vessels and does not causes deep damage to surrounding tissues, unlike a laser beam or a conventional scalpel.
Under the influence of radio waves, a thermal effect occurs. Don't be surprised if you feel warm in the surgical area during the procedure. During the process, there is no bleeding, nearby tissues remain practically intact, which promotes good healing without the formation of rough scars and deformations of the cervix. In connection with this fact, the method is used in young women before pregnancy and childbirth.
The procedure for radio wave treatment of the cervix is carried out
- without pain
- no blood
- without damage
- without scarring
Ease of use, minimal risk of complications, scars and relapses are the reasons for using radio waves in gynecology.
The flow of radio waves is easy to manipulate, which helps to accurately control the depth and area of the surgical wound. The pathological area of the cervix “cut off” with a radio knife is suitable for histological analysis; this is extremely important for accurate diagnosis of the process in the altered area of the organ. Radio waves eliminate microorganisms at the site of the disease, preventing the development of infections and inflammatory complications.
Indications
The most commonly performed radio wave treatment for cervical erosion is the common term “cauterization of erosion.” The procedure has also proven itself in cases of mild dysplasia, pseudo-erosion (endocervicosis), condylomas, papillomas, polyps, the presence of postpartum deformities and nabothian cysts of the cervix.
What to expect from the procedure?
The procedure is performed on an outpatient basis in a special room. The woman sits on a gynecological chair. The doctor performs preliminary local anesthesia of the cervix and treats the perineum with an antiseptic, and installs a neutral electrode under the gluteal-lumbar region.
Be sure to tell your doctor if you have any allergic reactions to medications!
The gynecologist, using gynecological instruments, spreads the vaginal walls for easier access to the cervix, and after a couple of minutes removes the affected layer of tissue under visual control or using a colposcope.
The procedure takes 5-10 minutes, depending on the size of the pathological changes, is painless, and is easily tolerated by patients.
Acceptable sensations during the operation include a feeling of warmth and mild nagging pain in the perineal area. If you experience severe pain or a deterioration in your general health, immediately inform your doctor.
Preparation
Before performing radio wave treatment of the uterus, the following is required:
- undergo a gynecological consultation;
- be tested for atypical cells, microflora and cellular composition from the vagina and cervix;
- donate blood for markers of syphilis, AIDS and viral hepatitis.
When should I come for the procedure?
The optimal period for performing the procedure is 5-7 days from the first day of cyclic bleeding (the first phase of the female cycle). After such treatment, the woman will not fall out of normal life, she is able to work and feels normal.
Post-procedure recommendations
The healing process on the cervix takes up to 1.5 months. In this period:
- exclude sexual intercourse, going to the pool, swimming;
- Replace baths with showers;
- do not use tampons;
- the pain may persist for up to 2-3 days;
- the appearance of watery or bloody discharge for up to a week;
- spotting on days 4-6 for 1-2 days (time of scab rejection).
If the pain increases, the volume, color and smell of the discharge changes, consult a doctor immediately! Based on the size of the wound surface, the gynecologist can recommend wound-healing and anti-inflammatory ointments and creams.
Contraindications
There are conditions and diseases that are prohibited for radio wave treatment of the uterus. These include:
- any malignant tumors of the genital area;
- local infections and inflammatory changes;
- pregnancy;
- bleeding from the genital tract of any etiology;
- diabetes.
Medical offers radio wave treatment of gynecological problems at an affordable price and in installments. We care about the safety and effectiveness of radio wave therapy for our patients.
Payment options
Cash payment
Payment by bank card
Installment plan
"Halva" - installment plan for 2 months
“Magnit”, “Smart”, “Purchase Card” and “Fun Card” - installment plan for 2 months
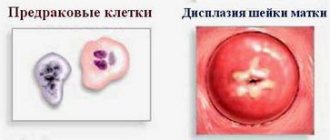
Translated from Greek, the term “dysplasia” means “formation” or “formation”. Accordingly, this pathology is characterized by the appearance of abnormal cells in the cervix. Quite often, dysplasia is also called a precancerous condition, but timely diagnosis and treatment make the process reversible.
Features of the disease
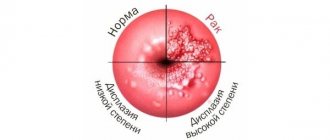
Most pathologies of the cervix are characterized by a violation of the integrity of the mucous membrane, but dysplasia is in most cases a hidden process that cannot always be detected during a routine visual examination. With this disease, profound changes occur that affect the cellular structure. In medical practice, there are 3 degrees of the pathological process:
- mild dysplasia (characterized by damage to the superficial part of the epithelium, up to 1/3 of its layer);
- moderate (cellular changes are found in 2/3 of the thickness of the epithelium);
- severe (all 3 layers are involved in the pathological process, but the growth of cancer cells occurs only within the mucous layer of the cervix).
Reasons for appearance
HPV. The main cause of dysplasia is the entry and prolonged stay in the body of an infection caused by oncogenic types of HPV (human papillomavirus). At the moment, about 100 of its varieties are known. In this case, the following types of virus can cause dysplasia of the 3rd degree: 16th, 18th, 31st, 33rd, 35th, etc. Pathology of the 1st degree occurs due to HPV-6 and HPV- eleven. However, the pathological process may occur several years after infection, and other unfavorable factors may contribute to it: genetic predisposition to malignant processes, smoking, cervical injuries, chronic inflammation of the genital organs, decreased immune defense, long-term use of hormonal drugs, too early or late beginning of sexual activity.
Herpes infection. Herpes virus type 2 can cause grade 3 dysplasia.
Chlamydia. If left untreated, this infection maintains long-term inflammation in the mucous membrane of the cervix, which can lead to impaired epithelial maturation and the subsequent development of dysplasia.
Trichomoniasis. This disease provokes a sluggish inflammatory process in the mucosa, causing a damaging effect on epithelial cells. When conducting a laboratory test of biomaterial for trichomoniasis, atypical cells can already be detected.
Folic acid deficiency. This condition is usually typical for pregnant women. Normally, folic acid ensures the maturation of the cells of the mucous membrane of the cervix, but if it is deficient, the process of functioning of the cytoplasmic structures is disrupted.
Signs and causes of cervical dysplasia of the 1st degree
The cervix has a complex structure and consists of three types of tissue: epithelial, connective and muscle. In turn, the epithelium is divided into two more types - cylindrical and flat multilayer. For example, with erosion, the problem arises in the cylindrical epithelial layer - it moves towards the vagina, but the structure of the cells does not change.
Dysplasia affects squamous stratified epithelium, which becomes prone to proliferation. The protective functions of cells are disrupted. Cells appear that have a multinuclear structure and irregular shape. The multilayered epithelial tissue is disrupted at the genetic level.
Several factors provoke this abnormal development:
- impaired immunity;
- viral infections;
- early sexual life, a large number of sexual partners;
- a large number of pregnancies and births;
- hormonal imbalance or overdose (long-term use of contraceptives);
- bad habits against the background of a monotonous diet.
For first-degree dysplasia to occur, a combination of several factors is necessary. For example, a large number of pregnancies and abortions, which disrupts a woman’s hormonal levels and is a prerequisite for infection. With a weakened immune system and insufficient nutrition, favorable conditions arise for the development of dysplasia.
A large number of sexual partners and their frequent change without the use of barrier methods of contraception sooner or later leads to infection with dangerous viruses. Infection with a certain type of human papillomavirus can subsequently lead to cervical cancer.
Important! Without visiting a doctor, a woman cannot control the process occurring in the epithelial layer, and there is a risk of advancing the disease to more severe stages.
A large number of births depletes a woman’s body. If the diet is not balanced, the immune system cannot do its job of neutralizing pathogenic microorganisms. After another pregnancy and childbirth, it is necessary to restore body functions with the help of vitamins and especially microelements.
Bad habits - smoking and drinking alcohol - also deplete your defenses. To fight infectious processes, a large amount of nutrients is required, because the cells of the immune system - leukocytes, phagocytes and macrophages - also need nutrition and water regime so that they can fully work and cleanse the body. Moreover, the reproduction of these cells in a toxic environment is unlikely.
The most dangerous thing is the asymptomatic course of the disease process at the first stage of dysplasia. Rarely there is pain or discomfort in the pelvis. Sometimes the disease manifests itself by an increase in the amount of mucous discharge or discharge mixed with blood. After sexual intercourse, there may be pain or bleeding. Minor injuries, such as using tampons or douching, can cause discomfort or bloody discharge. A sign of deteriorating health is general weakness and frequent colds.
Attention! Such symptoms should alert women at risk. In the near future, you need to visit a gynecologist and find out the reasons for the changes in the body.
Human papillomavirus
In most cases, the occurrence of grade 1 dysplasia is associated with penetration of the human papillomavirus (HPV) into the mucous layer of the cervix. This virus has several strains, the most dangerous of which are considered to be 16 and 18. When diagnosing cervical cancer (CC), in the vast majority of cases, HPV is detected in women. There are statistical data - 70% of cases of cervical cancer are caused by exposure to HPV and in 97% it is available based on test results in cancer patients.
But one virus is not enough to cause dysplasia. The body can cope with infection if the immune system is normal. If unfavorable conditions arise - concomitant bacterial infections, diseases, changes in diet - the balance of microelements and vitamins may be disrupted, which will trigger the onset of the pathological process.
The process of virus reproduction can also be affected by pregnancy, in which a woman’s immunity is weakened and does not fully perform its functions. This is a natural mechanism, but if you have HPV, there is a risk of developing dysplasia in the postpartum period.
Diagnostics
To choose the most effective method of treating cervical dysplasia in each specific case, it is necessary to undergo a full examination. It will help identify the cause of the pathology and the extent of tissue damage.
Colposcopy. This method is based on examination of the vagina and the vaginal part of the cervix. If pathological processes are difficult to detect visually, an extended colposcopy is performed. To do this, the epithelium of the mucous membrane is treated with Lugol's solution or acetic acid, after which a repeated examination follows for changes in the shade of the tissue.
Curettage of the cervical canal. This procedure is necessary to collect biomaterial for laboratory research.
Smear microscopy. A smear is taken from the cervical mucosa during colposcopy. Using this type of diagnosis, it is possible to identify a number of changes in the cellular structure characteristic of dysplasia.
Biopsy. Examination of a biopsy allows one to obtain the most reliable data when diagnosing dysplasia. This method involves taking a section of mucous membrane during colposcopy using a special instrument. A biopsy allows not only to study the cell structure, but also the histoarchitecture, which is important when assessing the stage of the disease.
Diagnosis of dysplasia
To make an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct a cytological analysis. This is a quick way to determine the presence of a pathological process. The material is taken in the form of a scraping from the CMM channel. With cervical dysplasia, atypical cells are detected.
Colposcopy is a visual examination of the vagina, walls, and cervix for the presence of external tissue damage. If defects are identified during the procedure, the doctor takes a smear and sends it for cytology. Colposcopy is a traditional method that allows one to suspect the presence of infection in the genital tract and the onset of the disease. In most cases, genital warts are present.
When a preliminary diagnosis is confirmed based on the results of colposcopy and cytology, a biopsy is performed - tissue samples are taken for more detailed examination in the laboratory. A biopsy allows you to determine the degree of malignancy of the process that develops in the mucous membrane of the cervix.
Analyzes
In addition to examining the genital tract, the woman is prescribed tests to detect the human papillomavirus. An enzyme immunoassay is an addition and shows the extent of the immune system's response to HPV.
The degree of oncogenicity - the strain of the virus - is checked by the Digene test. The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method allows you to determine which virus causes the pathology.
Diagnosis is considered successful if the pathogen is identified, the degree of oncogenicity and stage of the disease are determined, as well as the state of the immune system.
Treatment
The choice of treatment method for dysplasia depends on several factors: the degree of the pathological process, the size of the lesion, the age of the patient
Conservative. If mild or moderate dysplasia is detected in a young girl (especially a nulliparous girl), then she is indicated for dispensary observation. In some cases, spontaneous regression of the disease occurs. But, if cervical dysplasia was caused by HPV or other dangerous infections, the doctor prescribes etiotropic antiviral therapy, interferon preparations, cauterization of the pathological area with mild substances, and the use of agents to normalize the microflora. It should be noted that conservative treatment does not always give a positive result and is practically ineffective when it comes to grade 3 dysplasia.
Surgical. The following methods can be included in this group:
- diathermocoagulation. When cauterizing cervical dysplasia, the pathological focus is destroyed by high-frequency electric current. After the procedure, necrosis of atypical epithelial cells occurs. But scars form at the cauterization site. This method has recently lost popularity due to its traumatic nature, high risk of complications and relapses;
- cryodestruction. The method is based on treating the pathological focus in the cervix with liquid nitrogen. After the procedure, atypical cells are destroyed and rejected. This method is considered more gentle than conventional cauterization, so it can also be prescribed to nulliparous women;
- laser vaporization. The method involves exposing the affected area of the cervix to a laser beam. In this case, the liquid evaporates from the atypical cells and they are destroyed. This method is considered highly effective, but quite expensive;
- radio wave treatment. The modern Surgitron device is used to carry out the procedure. With its help, the pathological focus is destroyed by radio waves.
Treatment of cervical dysplasia at Medline-Service
If you want to undergo diagnostics and treatment from experienced specialists, contact the Medline-Service network of clinics. We treat intimate problems with understanding, we try to create a comfortable atmosphere for our patients and provide services at a high level. Our specialists are always ready to listen to you, prescribe the necessary examination methods and select the appropriate therapy. If you want to make an appointment at the Medline-Service clinic or check the prices for treatment of cervical dysplasia, call us at the specified contact number.
Radio wave treatment of the cervix is one of the most
popular procedures for the treatment of this pathology. It is actively used in the Doctor Nearby clinic. This technique is considered more effective compared to laser coagulation, diathermocoagulation or cryodestruction.
The main advantage of this procedure is considered to be maximum safety, therefore, it can be used in women who have not given birth. After the procedure, no scars appear on the uterine cervix, despite the complete removal of erosion.
Treatment of 1st degree dysplasia
If you contact a gynecologist in a timely manner, the woman is interested in eliminating the infection and wants to be healthy, the prognosis of the disease is favorable. Treating the disease with the support of the patient is much easier and more effective.
Treatment of grade 1 cervical dysplasia requires following a diet, eating foods rich in “female” vitamins – E, A, and folic acid in large quantities. B vitamins must also be present, which affect the production of blood cells - red blood cells.
Quitting smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages will be a big plus for drug therapy for grade 1 hyperplasia.
Treatment of dysplasia is aimed at eliminating inflammation in the vagina and cervix, stabilizing the functioning of the immune system, and removing the infectious agent from the body.
Antibacterial and antiviral therapy
For the successful treatment of dysplasia at stage 1, antiviral drugs and, if necessary, antibacterial therapy are used primarily.
Doctors have the following medications at their disposal:
- Isoprinosine and its analogues;
- Panavir;
- Galavit;
- Promisan (dietary supplement);
- Indole;
- Indinol;
- Laferobion.
You should know! Despite the fact that some of these drugs are dietary supplements, they are often used by doctors to boost immunity, as they contain all the necessary components to stimulate the defenses: zinc, selenium, calcium, iodine and iron.
Antibacterial therapy allows you to quickly relieve inflammation from the area of the vagina that borders the cervix. Antibiotics are most often used. Some patients prefer to be treated with folk remedies.
In addition to the use of drugs, normalization of hormonal levels, giving up bad habits and regular monitoring by a doctor are required.
Normalization of nutrition
The dependence of immunity on nutrition and water regime has been confirmed by scientific research. Therefore, diet correction is an integral part of therapy. It is recommended to include fruits, raw vegetables, nuts, and pumpkin seeds in your daily menu. Increase your consumption of clean still water.
Surgery for grade 1 dysplasia
Surgical intervention for first-degree dysplasia is rarely practiced. Monitoring patients for a year after diagnosis, correcting nutrition, and using medications allows the disease to be cured without the use of radical methods. Conization or amputation of the organ is indicated in subsequent stages of dysplasia, when the process is so advanced that it cannot be cured with conservative methods.
If the doctor, with the consent of the patient, decides to perform surgery at stage 1, then he must take into account the patient’s age and her desire to have children in the future.
For nulliparous patients, soft surgical methods are used:
- laser;
- radio wave destruction.
Even if these methods are safe, surgery is not recommended, since within two years there is a chance to recover from dysplasia on your own.
Method of radio wave therapy
The radio wave method of treating cervical dysplasia is carried out in the first half of menstruation. This is due to the fact that during this period the risk of bleeding decreases and tissue regeneration improves. Treatment of the cervix using the radio wave method is carried out on an outpatient basis, without requiring hospitalization of the patient. The duration of the procedure is at least 20 minutes.
During the procedure, the woman sits on a gynecological chair. Next, disinfection and anesthesia of the cervix are carried out. Radio waves ensure tissue dissection in the required location without directly affecting the mucous membrane. The steam formed as a result of evaporation of cells promotes coagulation of blood vessels. This is a very gentle technique that promotes rapid tissue healing by the next menstrual cycle.
During the procedure, a woman may feel slight discomfort and pain in the lower abdomen. Therefore, in case of excessive sensitivity, local anesthesia is possible. The discharge may continue for 10 days after the procedure, but then disappear on its own.
Radio wave treatment usually requires only one session. For a month after radio wave therapy, it is not recommended to have sexual intercourse, visit baths, saunas, or run intensely.
conclusions
To prevent cervical dysplasia, it is enough to visit a gynecologist once a year. A balanced diet and taking vitamins support the body in case of infection. If you have symptoms of dysplasia, you should begin treatment immediately to increase the chances of a favorable outcome of the disease.
Video: Treatment of cervical dysplasia
Cervical dysplasia - treatment
Video: Radio wave conization of the cervix
Radio wave conization of the cervix
Contraindications to radio wave treatment
Radio wave treatment of cervical leukoplakia or erosion is contraindicated in the following situations:
- Menstrual bleeding or any bloody discharge from the genital tract;
- Exacerbation of inflammatory diseases of the external and internal genital organs;
- Acute infectious diseases of other organs and systems, against the background of which immunity may decrease.
- Pregnancy at any stage;
- Pathology of the blood coagulation system;
- Diabetes mellitus in the stage of decompensation;
- Mental disorders;
- The presence of an artificial pacemaker or device in the uterus.
At the Doctor Nearby clinic, radio wave treatment is performed using modern equipment. We employ experienced specialists, which guarantees high efficiency and safety of the procedure.