Women's health and body require careful and careful treatment. However, due to the fact that a modern woman lives in a frantic regime, in which stress and anxiety are constantly present, it is primarily the female genital area that suffers.
Modern medicine has noted an increase in cases of diagnosing inflammation of the uterus. This is due to the fact that when symptoms are detected, a woman is in no hurry to see a gynecologist, citing being busy. This approach is fundamentally wrong and entails irreversible consequences for the female body.
Today we will look at the main symptoms of uterine inflammation, discuss diagnostic, therapeutic and preventive measures.
Female uterus
Before we begin to describe the disease, let us briefly consider the anatomical structure of a woman, more precisely, the uterus.
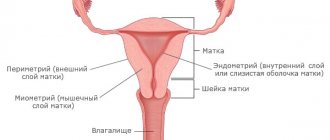
So, the female uterus refers to a muscular, hollow organ that is located between the bladder and the rectum. The uterus acts as a receiving organ that receives all the hormones produced by the ovaries. The surface of the organ is covered with a special layer, which, at the moment of activation of reproductive function, experiences significant changes. These transformations are caused by preparation for the process of fertilization.
Sonography technique
There are three ways to examine the ovaries using ultrasound. The doctor chooses a specific method taking into account the patient’s medical history.
- Transabdominal
- carried out using an external sensor through the abdominal wall. This method is the most comfortable, but the least informative; it can only be used to identify gross organ dysfunction. It is usually used during a general gynecological examination, for virgins and women with vaginal malformations. - Transvaginal
- performed using an intracavitary sensor (transducer), which is inserted into the vagina. The method is the most accurate and informative, since the sensor is located in close proximity to the internal organs. May be accompanied by minor discomfort during insertion of the sensor. This type of ultrasound is contraindicated for virgins and for vaginal malformations. - Transrectal
- carried out using an intracavitary sensor (thinner than for TVU), which is inserted into the rectum. The method is absolutely painless, but very uncomfortable for the woman. It is carried out in individual cases when TAU turned out to be insufficiently informative, and TVU cannot be performed for objective reasons (virginity, atresia (fusion), severe stenosis (narrowing) of the vaginal opening, etc.).
The duration of the procedure is about 15 – 20 minutes.
Routes of infection
Due to the etiological factors described below, the mucous membrane of the organ can become inflammatory in nature. The development of the process may be associated with E. coli, chlamydia, or other pathogens.
In addition, pathogens are represented by viruses and protozoan microorganisms. From the above it follows that endometritis occurs against the background of infection entering the organ. Below we will consider ways of infection penetration.
So, infection occurs in the following ways:
- The first path is upward.
- The second is lymphogenous.
- Hematogenous.
Often the infection enters the organ through the external genitalia. After the infection process starts, the inflammatory process is activated. Due to the fact that the mucous membrane adheres tightly to the muscle layer, the process starts in the muscle tissue. If the inflammation is characterized by a chronic course, the disease is identified as metroendometritis. The process is of a short-term nature, which over time involves the uterine appendages or pelvic peritoneum.
Etiology of the disease
The endometrium includes the following two layers:
- The first layer is functional.
- The second is basal.
The first layer peels off at the end of the menstrual cycle, and the second layer allows the creation of a new functional layer that begins the menstrual cycle again.
The main etiological factor is damage to the uterine mucosa. However, the damage itself is not dangerous; the danger is posed by viruses and virulent microorganisms that have penetrated inside the uterus. Let's figure out what are the main reasons for infection entering the uterus.
So, inflammation develops due to the following reasons:
- Incorrect douching.
- Complicated abortion and childbirth.
- Sexual intercourse during the menstrual cycle.
- Performing instrumental studies, in particular laparoscopy.
Now that we’ve sorted out the etiology, let’s move on to the main symptoms of the pathology.
Why are the ovaries not visible on ultrasound?
In some cases, the doctor cannot recognize the ovary on an ultrasound. This may happen for the following reasons:
- congenital absence of ovaries;
- removal during surgery;
- premature organ depletion;
- severe bloating;
- high density of the abdominal wall with pelvioperitonitis;
- severe adhesive disease of the pelvis;
- dense fatty layer or scars on the anterior abdominal wall.
In this case, a repeat study is usually carried out, in preparation for which an obligatory emphasis is placed on getting rid of flatulence with the help of medications.
Symptoms
As practice shows, the initial stages of the disease are characterized by the absence of symptoms. So that a woman can identify inflammation of the uterus, below is a list of manifestations of the disease. It is worth noting that endometritis can be acute or chronic. The acute course is caused by mechanical damage, while the chronic course is the result of infection from a sexual partner.
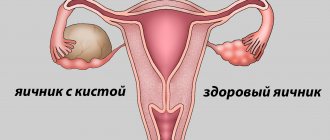
Ovarian pathologies and their signs on ultrasound
Some conditions, such as luteal cyst (corpus luteum cyst) and follicular cyst, are considered “normal” and do not require treatment because they usually heal spontaneously as soon as hormonal levels change. Other cysts and diseases are pathological and require mandatory treatment.
On ultrasound, the cyst looks like a formation of 2.5 cm with liquid inside, having a different structure and degree of staining.
| Ovarian damage | The ovaries have the appearance of oval hypoechoic formations with an uneven intermittent contour; fluid (blood) or echogenic signals of various sizes and shapes (blood clots) may be detected along the lateral uterine wall or in the uterine space |
| Salpingo-oophoritis, oophoritis (acute form) | Increased ovarian size; clear, defined contour; reduced sound conductivity due to swelling; hypoechoic areas can be detected - foci of necrosis (small abscesses) |
| Salpingo-oophoritis, oophoritis (chronic form) | Normal or slightly enlarged ovarian size; fuzzy, blurred outline; increased echogenicity of the organ; heterogeneous tissue structure |
| Dermoid cyst | Visible round neoplasm with thickened walls from 0.7 to 1.5 cm, which contains various hyperechoic inclusions inside |
| Endometrioid cyst | The formation is relatively small in size (up to 7 cm in diameter) with a double contour; unilateral localization - behind or to the side of the uterus; medium and increased echogenicity of non-displaceable fine suspension |
| Polycystic ovary syndrome | Increased size of the ovaries (volume more than 7 cm3); cysts are found in both ovaries (from 10 pieces in each of them) with a diameter of 2 to 8 mm; location of cysts along the periphery of the ovarian structure |
| Malignant tumor | A cyst that has several chambers and spreads to neighboring organs; unclear contents of the cyst; accumulation of fluid in the pelvis or abdominal cavity |
Any pathology detected on ultrasound of the ovaries must be confirmed by other research methods, only after which an accurate final diagnosis can be made.
Signs of acute inflammation of the uterus
Often, after seven days of diagnostic examination, childbirth, or abortion, women note the following symptoms:
- Bad condition.
- Refusal to eat.
- Headache.
- A significant increase in temperature, up to a feverish state.
- Aching and pulling pain in the lower abdomen.
- Atypical vaginal discharge.
- It is extremely rare, but uterine bleeding occurs.
If you notice the above symptoms, you should immediately seek help from a gynecologist. One detail is worth considering. Inflammatory pathologies tend to become ectatic and involve adjacent organs in the process. The longer a woman delays visiting a doctor, the greater the scale of the damage. Late and illiterate treatment is characterized by disastrous consequences.
Symptoms of chronic course
As a rule, a chronic course occurs against the background of late and illiterate treatment of the acute course of the pathology. As noted above, the chronic course is not related to gynecological manipulations. The nature of this form of the disease is associated with sexual activity. Therefore, it is quite natural that chronic endometritis is characterized by those symptoms that indicate the cause of the development of the pathology.
The chronic course is represented by the following symptoms:
- Aching pain symptoms localized in the lower abdomen.
- An increase in body temperature to 38.5 degrees.
- Vaginal discharge. As for the nature of the discharge, it directly depends on the type of inflammatory process. Gonorrhea is accompanied by purulent discharge, trichomoniasis is accompanied by copious and foamy discharge.
- Long menstrual cycle of about one week.
- Infertility and miscarriages.
Diagnosis
Diagnostic measures begin with collecting anamnesis - determining the frequency and regularity of the menstrual cycle. At the same time, the doctor performs an intrauterine intervention. A physical examination allows you to determine such abnormalities as an enlarged uterus, its compaction, and so on.
Laboratory diagnostic methods are represented by blood tests and smears. Acute endometritis is characterized by an increase in erythrocyte sedimentation rate and leukocyte count. In parallel with this, C-reactive protein appears, indicating the presence of an inflammatory process in the body. When diagnosing the disease, microscopy of a vaginal smear plays an important role. Instrumental diagnostic methods are represented by ultrasound, biopsy and hysteroscopy.
Ultrasound for endometrium
Ultrasound examination is associated with some difficulties due to the characteristics of the anatomical structure of the upper female genital organs. Despite some difficulties, this non-invasive research method is often used in diagnosing pathologies not only of the uterus, but also of the appendages.
Ultrasound detects symptoms only in 35 percent of cases. Ultrasound often reveals indirect symptoms of inflammation of the uterus, however, they are all nonspecific and may indicate another disease.
The following changes in the acute course are clearly visible on ultrasound:
- Quenching the endometrium.
- Purulent clots.
The chronic form of the disease is characterized by pathological changes that are difficult to detect on ultrasound. However, this disease is accompanied by changes in the structure of the uterine mucosa, which are detected by ultrasound.
The following echo signs are characteristic of chronic endometrium:
- Reduction and increase in the thickness of the uterine mucosa.
- Abnormal position of the uterus.
- Adhesions in the uterus.
Since inflammation can also affect adjacent female genital organs, in particular, the ovaries and fallopian tubes, changes can be noted on ultrasound.
Despite this, ultrasound is an indicative diagnostic method, which, in combination with other methods, makes it possible to establish an accurate diagnosis. Ultrasound examination allows us to exclude a number of diseases that have identical symptoms. A complete and detailed examination includes ultrasound, biopsy, and hysteroscopy.
Due to the fact that the diagnostic process includes an integrated approach, the data obtained during ultrasound gives the right to make a diagnosis such as endometritis.
Interpretation of ultrasound of the ovaries: norms
Normally, the ovaries are located on the sides of the uterus at a short distance from it, often asymmetrically. On the monitor they are visualized as oval, fairly defined, hypoechoic formations, while the ovaries are not identical to each other, the difference in their sizes is minimal. Their surface is considered normal to be lumpy due to the follicles maturing in them. The more time has passed since the beginning of the cycle, the larger these tubercles are.
Normally, the ovaries should be free of cystic, tumor-like and other formations, and the organ itself should not be enlarged. The interpretation of the results contains an indication of the sizes of the ovaries and follicles.
Standard indicators for ovarian size are presented in the table. Values may vary depending on the patient’s age, cycle phase, number of pregnancies, etc.
| Length | 2 – 3.7 cm |
| Width | 1.8 – 3 cm |
| Volume | : 4 - 10 cm 3 |
| Thickness | 1.4 – 2.2 cm |
After the onset of menopause, the ovaries decrease in size and volume by almost 2 times (on average to 2 cm3), their silhouette becomes uneven, wrinkled, and their echogenicity increases.
Normally, the ovaries consist of a capsule and follicles of varying degrees of maturity, the number of which on the left and right may differ. In healthy women, the following follicle indicators are visualized depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle:
| 5 – 7 day | 5 – 10 formations 0.2 – 0.6 cm each |
| 8 – 10 day | 5 – 9 formations up to 1 cm in size, dominant 1.2–1.5 cm |
| 11 – 14 days | dominant follicle size: 1.6–2 cm; Ovulation typically occurs at 1.8 cm |
| 15 – 18 days | corpus luteum (1.5–2 cm) at the site of the burst follicle |
| 19 – 23 days | the size of the corpus luteum is already 2.5–2.7 cm |
| 24 – 27 days | corpus luteum size: 1–1.5 cm |
Therapeutic measures
Treatment of endometritis begins immediately after an accurate diagnosis is made. If the pathology was detected in a timely manner, treatment takes place on an outpatient basis, but under the mandatory supervision of the attending physician. Otherwise, the patient is sent to the hospital. As for the treatment regimen, in most cases it is the same and consists of the following points:
- Antibacterial therapy.
- Mechanical cleaning of the uterine cavity.
- Detoxification.
How to treat acute endometritis?
If the gynecologist detects an acute process in time, then treatment can avoid the development of dangerous complications, including problems with pregnancy. Fortunately for women, this disease is not included in the list of incurable ailments. Treatment takes place in several stages.
At the first stage, the woman is prescribed immunomodulators and a complex of vitamins. At the second stage, the attending physician prescribes a course of antibiotic treatment. Antibiotics are administered both intravenously and intramuscularly. As a rule, the course of treatment is about 5 days. In fact, the duration of treatment depends on the stage of the disease.
To relieve severe pain, patients are prescribed painkillers. Along with antibiotics, therapy also includes the prescription of anti-inflammatory drugs, in particular Aspirin, Ibuprofen. The third stage involves cleaning after abortion, childbirth and cesarean section. The final stage is physiotherapy.
How to prepare for the procedure
Each research method requires special preparation in order to obtain the most accurate and informative result.
Transabdominal ultrasound of the ovaries
This type of study requires careful preparation, including a slag-free diet and cleansing the intestines of gases. 2-3 days before the procedure, you must stop eating foods that cause flatulence (carbonated drinks, beans, fresh fruits and vegetables, yeast and dairy products, etc.). One day before, start taking adsorbent drugs (smecta, espumizan, activated carbon, etc.).
During the procedure, the bladder must be full, so the woman needs to drink 1 liter of liquid (non-carbonated and non-dairy) an hour before the procedure and not urinate.
Transvaginal ultrasound of the ovary
Special preparation for such an ultrasound is not needed, since the only condition for its implementation is an empty bladder. Immediately before the procedure, the woman simply needs to urinate. If there is a tendency to increased gas formation, two days a day, start taking medications that reduce flatulence (smecta, espumizan, activated carbon, etc.).
Transrectal ultrasound
Preparation for such an ultrasound is similar to preparation for a transvaginal examination. Additionally, 9–10 hours before, it is necessary to clear the intestines of feces using a cleansing enema (1–1.5 l), microenemas, glycerin suppository or laxative.
The timing of the study depends on its purpose. If the ultrasound is planned, then it is performed on the 5th – 6th day of the menstrual cycle and no later than a week after the end of menstruation. In severe situations, an ultrasound is performed on the day symptoms are detected. If it is necessary to evaluate the functioning of the ovaries, the procedure is prescribed three times (on days 8-9, on days 14-15 and on days 22-23 of the menstrual cycle).
Chronic course: therapy
As noted above, the chronic stage is characterized by a different nature of occurrence, so the goal of therapy is to eliminate the specific causative agent of the disease. To find a suitable and effective treatment regimen, specialists resort to taking a smear for culture. This allows you to accurately determine the sensitivity of the pathogen to various medications. Based on the results of such a study, a list of effective drugs is formed. Therapeutic measures for chronic pathology are based on antibacterial and antiviral treatment.
Important! One of the most effective methods of treatment is the introduction of a medicinal substance into the uterine mucosa. This approach allows you to influence the source of inflammation.
So, therapy is based on the following manipulations:
- On hormonal treatment. Women are prescribed oral contraceptives.
- On the splitting of adhesions through surgery.
- At physical therapy. Physiotherapy plays an important role in the treatment of endometritis. It allows not only to increase the outflow of mucus and pus from the uterine cavity, but also to normalize the functioning of the ovaries.
As for the purulent form of the disease, therapy is based on mechanical cleaning of dead tissue. Of course, such a procedure is unpleasant, so the woman is given general anesthesia.
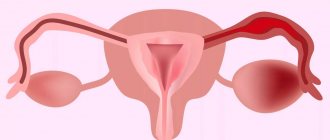
Inflammation of the appendages
Inflammation of the appendages in the acute phase is treated in a hospital setting with the patient observing bed rest, physical and mental rest, a diet based on easily digestible food, adequate drinking regimen with an assessment of excretory function. The main treatment for adnexitis is antibacterial etiotropic therapy depending on the diagnosed causative agent of the disease: penicillins, tetracyclines, macrolides, aminoglycosides, fluoroquinolones. If there is a risk of anaerobic infection, a combination of different groups of antibiotics is prescribed, for example, metronidazole is added to the above drugs (intravenously, orally).
Conservative therapy also includes painkillers, drugs that relieve the effects and consequences of intoxication (infusion therapy). For purulent complications of inflammation of the appendages, surgical treatment is used. First of all, preference is given to low-traumatic gynecological surgery - laparoscopic manipulations, evacuation of the purulent contents of the saccular formation through puncture of the posterior vaginal fornix with the possible subsequent administration of medications. In case of advanced inflammation, when there is a risk of purulent melting, surgical removal of the appendages is indicated.
After eliminating the acute signs of inflammation of the appendages, a course of physiotherapeutic procedures is prescribed: ultrasound, electrophoresis using Mg, K, Zn preparations, vibration massage. These same methods, along with etiotropic antibacterial therapy, are indicated in the treatment of chronic inflammation of the appendages. Sanatorium rehabilitation treatment is prescribed to promote the resorption of the adhesive process and prevent the formation of adhesions. Resorts that use mud therapy, paraffin treatment, medicinal baths and irrigation with sulfide and sodium chloride mineral waters are preferred.
Forecast and prevention of inflammation of the appendages
With timely initial treatment of symptoms of acute inflammation of the appendages and adequate therapy, complete clinical recovery occurs in approximately 10 days. Adnexitis in the chronic stage requires regular examinations and supportive therapy, sanatorium and rehabilitation measures, and systematic monitoring of the patient’s condition.
In order to prevent relapses of inflammation of the appendages, especially for patients at risk (using IUDs, having unsuccessful pregnancies and abortions in history), it is necessary to exclude factors that provoke the disease - hypothermia, stress, sexually transmitted infections. It is recommended to use rational methods of contraception and promptly carry out comprehensive adequate therapy for diseases of the pelvic organs, taking into account the causative agents of the pathology. A visit to the antenatal clinic at least once a year for a preventive examination by a gynecologist should become the norm for every woman who cares about her health.
Complications
Inflammatory processes occurring in the female body worsen the standard of living. A woman’s sex life suffers due to severe pain that increases in intensity during sexual intercourse. In parallel with this, the infection through the lymphatic and circulatory system can spread throughout the body.
One of the most dangerous complications of the disease is sepsis. As is known, the advanced form is accompanied by the formation of adhesions in the pelvis. Adhesions in the body lead to a long absence of conceiving a child or to problems with bearing a fetus. The disrupted uterine process is accompanied by menstrual irregularities. Therefore, to prevent the complications described above, it is recommended to adhere to simple preventive rules.