About pathology
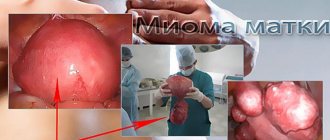
Fibroids are a benign tumor in the uterus in women. May be single or multiple. Most often appears between the ages of 30 and 40 years. In some cases, it forms during menopause.
Myoma nodes can grow to large sizes, causing pressure on other nearby organs. As a result, problems with defecation and urination appear.
At the initial stage of development and small size, the formation does not give any symptoms.
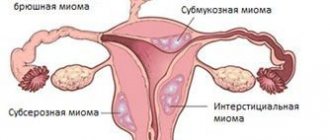
Depending on the location of uterine fibroids, there are:
- subserous or subperitoneal - localized on the surface of the uterus, under the peritoneum;
- intramural - myomatous nodes are formed in the muscle tissue of the organ - the myometrium;
- submucosal – the tumor is located under the endometrium and deforms the uterus;
- cervical - the formation is formed in the neck of the organ or isthmus.
Conflicting opinions
It should be noted that most scientists cannot develop a common point of view on calcifications in the uterus. Some are convinced that this symptom is quite alarming and can indicate a serious hidden pathology inside the body. Others believe that the danger of such deposits is greatly exaggerated; as confirmation of their opinion, they cite statistics indicating numerous cases of successful births with this deviation.
Therefore, you should not be surprised when faced with completely opposite opinions. One gynecologist may advise doing nothing, while another may recommend medications that will stabilize the amount of calcium in the blood. A separate group of scientists suggests that when calcifications are detected in the soft tissues of the body, a special shortage of the corresponding salts should be achieved. After this, the body can “reach out” for replenishment, due to which the tumors will be reabsorbed independently without additional effort.
What does small uterine fibroids mean?
There are different tumor classifications. One of its parameters is size. It is determined by the diameter of the uterus:
- in centimeters and millimeters;
- in weeks - similar to the gestational age.
Depending on the size of fibroids, there are:
- Small – up to 2 cm or up to 4 weeks. It does not manifest itself in any way; the formation is diagnosed during a routine examination.
- Average – from 2 to 6 cm, up to 11 weeks. Causes pain, uterine bleeding, and negatively affects the functioning of neighboring organs.
- Large - more than 6 cm, from 11 to 16 weeks. Surgical treatment is indicated.
Small uterine fibroids – up to 2 cm – do not require therapy. A wait-and-see approach is recommended.
Indications for surgery
In addition to conservative methods, surgical methods are also used to treat fibroids. Although, in general, small benign tumors are not operated on, there are exceptions in some situations. Surgical treatment is indicated in the presence of the following factors:
- submucosal location of the tumor;
- high probability of degeneration into cancer;
- submucous type of fibroids with interstitial and centripetal development;
- the presence of constant heavy bleeding;
- excessive growth of education;
- infertility;
- necrosis of the central node.
Symptoms of pathology
A small formation is characterized by a complete absence of signs. In some cases there are minor manifestations:
- menstrual irregularities;
- pain in the lower abdomen a few days before menstruation;
- heavy and painful periods;
- inability to get pregnant;
- spontaneous termination of pregnancy in the early stages.
The severity of such symptoms depends on the location of the tumor on the body of the uterus. The most painful sensations occur when fibroids are located on the neck.
As myomatous nodes enlarge, the symptoms become more pronounced:
- A noticeable increase in the volume of menstrual flow. Often critical periods last longer, and the discharge is so abundant that anemia develops.
- Intermenstrual discharge. Between periods there is bloody or mucous discharge. The reason is irritation, inflammation and the appearance of microcracks in the tissues where the tumor has formed.
- Pain in the lower abdomen, in the lumbar region. Pulling indicate a large formation, acute appears when the tumor stalk is torsed, cramping is the cause of the development of the tumor process in the mucous tissue of the organ.
- Dizziness, pallor, general weakness. They occur as a result of anemia - a decrease in the level of hemoglobin in the blood.
- Disruption of other organs. Compression of the intestines and bladder disrupts the natural processes of bowel movements and urination.
- Heartache. Large formations affect myocardial tone, significantly reducing it.
- Infertility. The development of nodes in the area of the fallopian tubes prevents the movement of sperm, they do not reach the egg.
Important! The presence of at least one symptom is a reason to consult a gynecologist. Early diagnosis prevents the development of other pathologies and promotes successful treatment.
Indirect factors
The second group of causes of pathology usually includes factors that indirectly determine the beginning of the process of deposit formation. Among them are:
- Alcohol and tobacco abuse. These factors negatively affect the condition of tissues and immunity.
- Poor nutrition, which can lead to decreased immunity.
- Intense loss of calcium ions from bone structures.
- Obesity. Being overweight is an increased risk factor.
- Increased level of calcium salts in the blood. This situation is abnormal; it is fraught with the development of calcification not only in the uterus, but also in other organs and tissues. This factor is often a trigger for the formation of calcifications in the mammary glands, prostate gland, kidneys, lungs, and aorta. In this case, the uterus is damaged less frequently, but in each such case we can talk about multiple lesions of the organ.
- Stressful situations. Against the background of stress, general and local immunity decreases, as there is increased production of cortisol, adrenaline, and norepinephrine by the adrenal glands.
The listed factors are not the only ones that provoke the occurrence of calcifications. This should be taken into account when determining the etiology of the disease.
What calcifications are is now clear. Let's look at the symptoms.
Causes
The main reason that provokes the development of a benign formation in the uterus is a hormonal imbalance.
Other reasons:
- Genetic predisposition. A woman is more likely to develop fibroids if her mother or other close relatives had the disease. The fact is that the hormonal background of genetic relatives has a similar composition.
- Unbalanced diet. Eating large amounts of sweet, fatty foods and a lack of plant foods leads to a lack of fiber and increased estrogen production, which causes hormonal imbalance.
- Diseases of the endocrine system. They affect the synthesis of hormones, disrupting the balance.
- Termination of pregnancy, curettage and other gynecological manipulations. They make uterine tissue less elastic and contribute to the formation of pathological myomatous nodes in the future.
Additional factors that may cause fibroids:
- reduced immune defense of the body;
- lack of vitamins;
- frequent inflammatory and infectious diseases;
- frequent stress;
- irregular sex life or lack thereof;
- regular exposure to the sun.
Description
Calcifications in the uterus are many times more common than in the peritoneal layer or in the myometrium. They are also often found on the uterine cervix. In each of these cases, calcification represents a certain kind of protective reaction of the body. Salts, which have inorganic properties, encapsulate areas where tissue breakdown occurs. This prevents the spread of the necrotic process to other areas. The formation of calcium deposits is secondary in nature and is not a disease in the full sense of the concept.
Calcifications in the uterus are very common. Medical statistics report that calcium deposits form in approximately 30% of all women, and in most cases the process occurs without any external manifestations.
How is it diagnosed?
To make an accurate diagnosis, a comprehensive examination is necessary:
- Examination by a gynecologist using a gynecological speculum.
- Palpation. But small uterine fibroids cannot be detected by palpation.
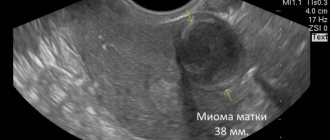
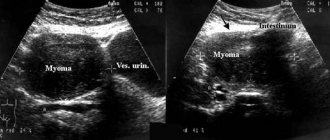
- Ultrasound using transvaginal and transabdominal sensors. Shows the most complete picture - the location of the formation, its size.
- Hysteroscopy. Examination of the organ inside using special equipment - a hysteroscope.
Uterine fibroids on ultrasound
Performance
Diagnostic curettage of the uterine cavity is carried out quickly under general intravenous anesthesia. The procedure takes about twenty minutes, and with a large number of formations, the time may increase.
To gain free access to the uterine cavity, the gynecologist uses special dilators to push apart the walls of the vagina and the cervical canal. Additionally, a gynecological probe may be required.
Only after the cervix is fully dilated is hysteroscopy performed. This is a detailed and thorough examination of the uterine cavity using a special optical device. During a visual examination, the doctor will be able to accurately and correctly count the number of formations, determine their size and location. This simplifies the procedure for taking optimal sections of the endometrium, which are necessary for diagnostic curettage of the uterine cavity.
When the hysteroscopy is completed, the gynecologist will be able to perform a diagnostic curettage. During the procedure, the top layer of the uterine epithelium is removed using a curette. According to the testimony of a specialist, in rare cases, partial curettage of some areas may be performed. The resulting tissue is placed in sterile tubes for further histological examination. The test results will be ready after two weeks, after which the patient will be prescribed the optimal treatment strategy.
How to treat
If small uterine fibroids are diagnosed and there are no characteristic symptoms, then the doctor does not prescribe drugs, but monitors the progression of the tumor.
If the node enlarges, immediate therapy is required. The woman is prescribed hormonal drugs to stop the growth of the tumor.
Surgical intervention for small fibroids is not indicated.
Hormonal drugs
The goal of hormonal therapy for fibroids is to stabilize hormonal levels. It is necessary to force the ovaries to produce less estrogen.
For this, the following groups of drugs are prescribed:
- Oral contraceptives. Recommended for use by young women who are not planning pregnancy in the near future. Once therapy is completed, there is a high probability of further progression of myomatous formation.
- Antiprogestogen drugs. Their action is aimed at blocking progesterone receptors, which stops the growth of fibroids.
- Gonadotropin releasing hormone agonists. Drugs in this group cause a state of artificial menopause when gonadotropin is suppressed. In half of the cases, when treated with such drugs, the tumor stops growing and gradually regresses.
Attention! Hormone therapy is prescribed only by a doctor. You should not take these medications on your own. There is a high risk of not only not affecting the fibroids, but also of worsening the condition, causing its sharp increase.
Vitamin complexes
Vitamins for uterine fibroids must be supplied to the body in the required quantities, which will help it in the fight against formation.
For this, the woman is prescribed vitamin complexes. They do not eliminate the tumor, but strengthen the body, improve blood clotting, metabolic processes, and stabilize hormonal levels.
Without surgery
The following methods are used to treat fibroids without surgery:
- UAE or uterine artery embolization. A minimally invasive procedure that involves stopping the nutrition of the tumor. To do this, they block the blood flow to the fibroids. Pathological cells, not receiving nutrition, gradually die.
- FUS ablation. The method is based on the effect of ultrasound on the tumor, which destroys its tissue structure.
These types of therapy are suitable for small to medium-sized fibroids.
Indications for surgery
Surgery for small fibroids is performed only in one case - when the tumor has formed on a stalk. Its torsion causes acute pain and tissue necrosis.
The indication for surgery is a large tumor. Either only the myomatous node or the entire uterus is removed. Depends on the severity and course of the disease, the woman’s age, and her reproductive plans.
Video about fibroid removal
Symptoms
Calcifications in the uterus practically do not manifest themselves with any symptoms. The presence of weak nagging pain in the lower abdomen may indicate the process of salt deposition.
But, as a rule, in most cases, calcium deposits are discovered incidentally during studies for other pathologies or conditions. Most often, with calcification, symptoms of the underlying pathology are revealed, which became the provocateur of the formation of calcifications.
In this case, the list of possible symptoms is very extensive. Practice shows that the most common causes are endometritis and endometriosis. It is these two diseases that cause the onset of calcification.
An appointment with a gynecologist at the antenatal clinic should be made if there is a suspicion of the development of pathology.
Small fibroids and pregnancy
Myoma can serve as an obstacle to conception. But pregnancy with fibroids is possible.
A single small node does not have a negative effect on the development of the fetus. The risk arises when the embryo attaches to the place where the myomatous node is localized.
Changes in hormonal levels during pregnancy affect the tumor, it begins to grow, which leads to placental abruption or death of the embryo.
Large formations and multiple nodes are dangerous because they deform the uterus, interfere with its normal blood supply, put pressure on the fetus, and as a result it lags behind in development.
We recommend reading the article about nodular uterine fibroids. From it you will learn about the symptoms and causes of their occurrence, dangers during pregnancy and menopause, drug and surgical treatment, and the effectiveness of using folk remedies.
Does a woman's belly grow when she has uterine fibroids? Read here.
Development
Calcification of the node does not occur instantly. Also, fibroids cannot form immediately in this form. The development of the calcium shell often occurs over a long period of time. For this reason, such neoplasms are usually diagnosed as quite large in size. The development of such a tumor occurs as follows:
- As a result of the high content of estrogen in the blood, active cell division of uterine tissue begins;
- A knot is formed from connective, muscle tissue and blood vessels;
- Over time, and as the formation grows, the blood flow in it weakens;
- The tumor begins to actively absorb calcium;
- As a result, a dense calcium shell is formed around it;
- Over time, it thickens both outward and inward, the amount of soft tissue in the node decreases;
What is possible and what is not
When diagnosing fibroids and during its treatment, the following are prohibited:
- lifting weights;
- physical overload;
- massage;
- overheating of the abdominal area - sauna, hot bath, tanning.
For successful treatment, it is important to switch to proper nutrition and avoid overwork and stress.
List of sources:
- Gynecology: textbook / B. I. Baisova et al.; edited by G. M. Savelyeva, V. G. Breusenko. — 4th ed., revised. and additional - M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2012. - 432 p.
- Ishchenko A.I., Botvin M.A., Lanchinsky V.I. Uterine fibroids: etiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, treatment / Moscow: Vidar M Publishing House, 2010 – 244 p.
- Obstetrics and gynecology: lecture notes/A. A. Ilyin/Lecture No. 25. Uterine fibroids.